Pentecostal Theology of Freedom for the Postcommunist Era
“Stand fast therefore in the liberty wherewith
Christ hath made us free” for “if the Son therefore
shall make you free, ye shall be free indeed”
This paper is intended as a part of larger research entitled Theology of the Persecuted Church. It focuses on they way freedom is understood by the underground church and its successor, the postcommunist church after the fall of the Communist regime. In this sense, the research presents the theological view of freedom from the time of postmodern transition in Eastern Europe in retrospect with the times of underground worship and in dialogue with the major modern theologians. The main purpose is to construct an authentic view of freedom in the major areas of the life and ministry of the postcommunist Pentecostal church.
Postcommunist Europe
On his first official visit to West Germany in May 1989, Mikhail Gorbachev informed Chancellor Kohl that the Brezhnev doctrine had been abandoned and Moscow was no longer willing to use force to prevent democratic transformation of its satellite states. At 6:53 p.m. on November 9, 1989, a member of the new East German government gave a press conference to inform that the new East German travel law would be implemented immediately. At the East Berlin Bornholmer Strasse, the people demanded to open the border. At 10:30 p.m. the border was opened.[1] That meant the fall of the Berlin Wall and the end of the Cold War.
The unification of one Germany brought the clash of two political extremes within one nation. It brought together two Europes kept apart for half-a-century, a dynamic which introduced the continent to a new set of opportunities among which was the vision for a unified Europe and its realization.
A new set of dilemmas was introduced as well. Among all economical, political, social, cultural and simply human points of diversity, religion remained central for the process through which the European Union was emerging. The official “United in Diversity” (reminding of the American E Pluribus Unum) claimed unification, without mentioning God. The new European constitution announced that Europe draws “inspiration from the cultural, religious and humanist inheritance of Europe.”[2]
For us who lived in the last days of Communist Bulgarian, the fall of the wall was a miracle which the world witnessed. Coming out from the severe Communist persecution and surrounded by the Balkan religious wars, suddenly the country of Bulgaria experienced a time of liberation which gave the start of spiritual revival mobilizing Bulgarian Protestants. In the midst of extreme poverty, due to prolonged economical crisis, this revival became an answer for many. It also provided a sense of liberation, but not in the Western political understanding of democracy and freedom, but rather liberation toward the realization of the Kingdom, a world much higher, much better and in way more realistic than any human ideality. The liberation from sin then turns not only into a social movement, but as a theological conception it provides an alternative to the existing culture thus becoming a reaction against the surrounding context and proposing a new theological model and a new paradigm for life itself based on substantive faith and belief.
Freedom of Will
Even when approached theologically, in the Eastern European postcommunist context today, the term freedom of will carries a strong political nuance. For many Eastern European Protestants, freedom characterizes the struggle against the communism regime and the divine motivation to endure it as a calling of faith for the individual and the community.
The years before communist era were characterized with opposition against the historical monopoly of the Eastern Orthodox Church. In this context, the protestant movement in Bulgaria also struggled against spiritual dominion defending the cause of religious freedom and the right of each individual and community to believe and express beliefs.
The hundred years of Bulgarian Protestantism have been accompanied with constant struggle against oppression of conscience and will thus creating a general acceptance of free human will. This has coincided with the theology of the largest and fastest growing Evangelical movements in Bulgaria. In this context, even evangelical churches, like the Baptists, have grown to accept and practice the doctrine of free will.
Based on the political, socioeconomic and purely ecclesial factors, in postcommunist Eastern Europe, the Calvinistic paradigm of predestination and election as practiced in a Western sense are not successful. This is based partially on their new doctrinal presence within the Bulgarian reality and their untested effectiveness through under persecution. It is also natural that they are often qualified in parallel with political and religious oppression, and therefore rejected as divine attributes or actions. If human regimes are oppressive through limiting freedom and consciences, how is God to identify with such regimes and practice the same type of “horrible decree?” On the contrary, in Eastern European Protestant theology, God is seen as a Liberator of human consciences and a desire for freedom.
By no means, is this tension to be confused with a denial of the total authority of God. God remains the electing God in Jesus Christ, but how?[3] Is it through a “horrible decree” or through a personal life-changing experience defined by the Bible? Is it through an oppressive act of lawful but unconditional predetermination which God by His nature is omnipotent to implement, or through an act of supernatural transformation of humanity through divine self-sacrifice? And does this election barricade every possible human choice? No, as it is obvious in the denial of Peter; but also as seen in his restoration, that every choice of human will is answered by God through unconditional divine love.
Therefore, we experience “the secret of predestination to blessedness,” not in a cause and effect paradigm as Augustine and the Reformers, but rather through preserving its significance by experiencing the love of God.[4] Thus, the human will is freed by the love of God to receive salvation for eternity. The human freedom then is not ignored or oppressed, but on the contrary it is “placed in the context of cosmic drama” where the real bondage is not the one by God, but the one by sin which oppresses the human will and distances it to death. The Gospel, however, proclaims the victory of Christ over these oppressors thus liberating human will to its initial creation state as a gift from God.[5] This theology comes from a concrete experience of God in real life, and the quest to serve and follow God. As theology shows that the truth about God and the truth about ourselves always go together, the experience of God is a constant tension and a dynamic process, rather than blind servanthood to rigid principles that can never fully encompass the divine will. And through this experience of liberation of the human will in order that one may be free to choose salvation through Christ, God establishes His “testament of freedom.”[6]
Freedom from Oppression
As God liberates humanity from sin, He liberates it from sin’s moral and social consequences. Thus, forgiveness of sin presupposes not only the quest for sanctification and perfection after the image of God, but also the struggle against oppression and establishment of social balance. As the above shows, the postcommunist revival in Eastern Europe cannot be explored apart from the contextual political and socioeconomic dynamics. The reason for this is that the Spirit with value before God is a social spirit that makes the expression of the divine liberation the very purpose of the existence of the church.[7] The practice of this expression challenges the relationship between theology and practice as it questions theology’s epistemological and praxis relationship to the oppressed with whom Christ is crucified.[8]
As in such context, theology is challenged to identify with action, the church must choose between contextualizing and enforcing theology. To choose contextualization is to attempt to relate it to the existing culture thus creating a state of relativism. Such approach is observed in some Asian and Black theology. The danger is to go beyond the boundary pass which theology ceases being theology in action and becomes simply a nominal religious culture. In Eastern Europe, such approach has been long-practiced by the Eastern Orthodox and has unquestionably resulted in nominal religion. The nominality of its expression has been a factor preventing the experience of God, thus denouncing the very reason for the church’s existence. Attempts to restore the Eastern Orthodox “symphony” between church and state have altered the existence of the independent synods which claim the succession of the same historical religious institution.
The second direction, to move toward enforcement of theology after the paradigm proposed by Liberation theology, is quiet a dangerous approach often resulting in armed conflicts. Keeping in mind the historical tension on the Balkans and Bulgaria’s success in undergoing the postcommunist transition without an armed civil conflict, this approach is virtually inapplicable. Therefore, an alternative must be proposed before history itself become oppression.
In this context, a move toward a theology of freedom seems most reasonable. It must purpose to prevent political and socioeconomic oppressions which are already present in various legal and illegal forms in Bulgaria. Such paradigm must also be concerned with intrachurch oppressive tensions which are present both among and within religious denominations, striving especially against such oppressive modes that come from the desire of an oppressed mentality to oppress others.
Such working model of social transformation is presented in Paul’s Epistle to Philemon. An older interpretation of the book explains that Onesimus, a runaway slave, meets Paul in prison, becomes a Christian and is sent by Paul back to his master. A more cotemporary interpretation claims that Onesimus is a slave sent by Philemon to help care for Paul in prison where he converts to Christianity and desires to stay with Paul as a missionary associate.
Regardless of the interpretation of the story plot, the epistle carefully presents a more in-depth set of problems that deal with persecution, imperialism, slavery, mastership, classes, ownership, imprisonment and above all justice. It further makes a more aggressive mood and places the church, represented in the text not merely by masses, but by the very divine appointment of apostolic authority.
The theme of imprisonment as a direct result of persecution is clearly present through the epistle’s plot and more specifically verses 1, 9, 13 where Paul uses the expression “prisoner of Christ” to describe his present status. The expression “prisoner of Christ” carries a sense of belongingness making the phrase different than the sometimes rendered “prisoner for Christ.” While the latter wrong rendering moves the focus toward the purpose of Paul’s imprisonment, the Greek genitive in the phrase “prisoner of Christ” denotes ownership. Although imprisoned in a Roman prison and kept by a Roman guard, Paul denies the Roman Empire ownership of himself, thus claming that he is owned by Christ alone. This is also a denial of the Roman citizenship that has led to this oppressive state of persecution and the recognition of a citizenship in the divine reality of liberation.
Paul’s negation goes a step further, proposing that while the Roman Empire may be authoritative in the temporal context, by no means it is authoritative in the spiritual eternal reality. Having established the temporality of Rome and the eternity of God, Paul denies to the Roman Empire the right to pronounce judgment over social injustice and to establish social status or world order, proposing that no one but the Christian church is the agent divinely designed and supernaturally equipped for these functions. The social injustice of persecution and wrongful imprisonment, the social tensions between classes, the problems within the church and every dilemma presented in the epistle are to be judged by no one but God through his elect. The reality of the situation is that the church is experiencing severe persecuting because the Roman Empire is denying the church social space. Paul, however, denies the reality of such oppressive human system and claims that the church is the one that must deny social space for oppressive structures as the Roman Empire.
The text calls for revolution; not merely, a revolution in the physical violent sense, but a revolution of the mind where human existence and mentality are liberated through Biblical paradigm combined with divine supernatural power to participate in a new spiritual social reality where justice is set by the standard of God. Such a move calls for a new paradigm and for a theology of freedom which creates an anti-culture and an alternative culture to the existing oppressive system. Such idea challenges the church with the claim that Christianity is and should be a scandal and an offence to the world, and not merely a religion but the belief that “Jesus is the most hazardous of all hazards.”[9]
Feast of Freedom or the Bulgarian Easter
Amidst political and socioeconomic crises since the fall of the Berlin Wall, Bulgaria has experienced a rebirth of Bulgarian spirituality. Many observers have referred to this restoration process as the rebirth of the Bulgarian Easter, and even which historically has been connected with the unity and power of the Bulgarian nation.
Bulgaria accepted a Christian country in 864 AD under the reign of Kniaz Boris I. A millennium later, in the middle of the 19th century, Bulgaria found itself occupied by the Ottoman Empire and religiously restricted by the Greek Orthodox Patriarchy which dictated the religious expression of the Bulgarian church.
On April 3, 1860, during Easter Sunday service in Constantinople, the Bulgarian bishop Illarion of Makriopol expressed the will of the Bulgarian people by solemnly proclaiming the separation of the Bulgarian church from the patriarchal in Constantinople. The day commemorating the Resurrection of Jesus Christ coincided with the resuscitation of the Bulgarian people. Although, the struggle continued for another decade, under the influence of Russia, Turkey was forced to legally recognize the independence of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church. In 1870 a firman of the sultan decreed the establishment of an autonomous Bulgarian church institution.
The connection between the historical Bulgarian Easter and the contemporary rebirth of Bulgarian spirituality has been used in many aspects of the Bulgarian politics and culture at the beginning of the 21st century. As part of the Eastern Church, Bulgarian orthodox theology pays much more attention to the resurrection rather than to the birth of Christ thus placing its eschatological hope in a future experience rather then a past one. Such dynamic is natural, as the acceptance of Christianity in Bulgaria purposes to bring hope in national politics and communal life. Thus, in an almost historical tradition, the Bulgarian Easter represents the Bulgarian eschatological hope for a supernatural national revival. It also communicates with the sense of liberation from political, economical and religious oppression and a longing for the freedom to live life.
The Bulgarian Easter then provides an alternative to the present moment of tension and straggle in the crucifixion. Similar to Moltmann’s view of the resurrection of Christ, the Bulgarian hope foresees the resurrection of the Bulgarian nation as a divine act of protest against oppression and injustice and as recognition of God’s passion for life.[10] Thus, the resurrection is an alternative not only to the present world, but also to the reality of eternal death.
Death is therefore seen not only as an agent of eternity, but also as an agent of fear, suffering and oppression in the present reality which affects life in all its economical, political, social and even religious aspects. As death diminishes the value of life, the liberating power from Easter often remains ignored. But in order for the church to continue being a church, it must speak as a witness of the resurrection which is impossible without participating in God’s divine liberation which recreates the word to its original state of creation. Thus, the hope of Easter means rebirth of the living hope.
The resurrection hope is an influential factor which directs the life dynamics of the church beyond its walls. Being liberated from sin, the believer desires the liberation of others and claims the right to serve. But true Biblical servanthood cannot exist and therefore does not tolerate oppression, thus becoming a social transformation factor in the midst of oppressive cultures. The resurrected church rebels against the destruction of life and the denial of the right of very human to live. But different than other human systems, the church does not feed off its resistance against oppression. Its source of power is the eschatological hope for the full restoration of life and its eternal continuation in eternity.
A final question must be raised about the pessimistic character of such hope, as traditional evangelical eschatology in Bulgaria has been premillennial and due to its Pentecostal majority clearly pretribulation. Such eschatological views, at large, have been considered to be pessimistic and escapist in nature due to their strong focus on the future. Yet, such determinative presupposition seems inaccurate and much limited in its observation when applied within the postcommunist context where Protestant churches have been greatly involved in the struggle against oppressive regimes and constraining politics even to the point of martyrdom.
It is then natural, that in the underground context of persecution it is unthinkable for the church to identify with the regime in anyway. Actually, such identification is vied by the believers as spiritual treason and cooperation with authority is viewed as backsliding. By no means, however, is such a premillennial eschatological view in this context pessimistic for the church. Neither does the church remain unconcerned with the present reality. On the contrary, through its very act of negation of the right of an oppressive system to dictate reality, the church establishes an alternative culture which is the Kingdom of God. Thus in the midst of persecution and oppression, the church remains in its Biblical boundaries as an agent of the Kingdom of God by providing eschatological hope.
Yes, this eschatological view is escapist, as it promotes eternal separation from the oppressive reality. What other alternative can a persecuted and underground church find to survive and relate to the Biblical image of the ecclesia and at the same time it is clearly concerned with the transformation of the present world as shown above? For while its pessimism concerns the oppressive system of the world, its optimism declares the church as an already-reality in which freedom of sin, death and oppression and eternity with God is celebrated. Therefore, the church itself remains an optimistic reality and optimistic eschatological hope. For, without this hope the tension of life toward future and even life it self will vanish.[11] Without hope for the beyond, we remain in the now for eternity.
Epilogue
Due to its relational and reactional role to historical process, Eastern European postcommunist theology is a new historical and theological event. Yet, as theology of freedom, it relates to other theological approaches internationally. This similarity is enforced by the approaching postmodern era which the Bulgarian nation seems unprepared to understand. In such context, the church and its theology become the agents providing answers to social tensions.
Postcommunist theology provides a point of departure from the oppressive system of the communist regime toward a new social and ecclesial alternative. Such dynamic is by no means new to the Protestant movement in Bulgaria, which has dealt successfully with these same issues even in more severe context of underground existence and persecution. Therefore, the church has proved its commitment to identify with the oppressed through addressing and engaging its experience through the experience of God and its adequate and substantive theological interpretation. Such approach provides an alternative to oppressive system and structures, unquestionably critiques their tools and methods, and rebukes the agents who represent and practice them, thus denying them place in history.
A further concern for developing strategies for social transformation is also strongly present including education, law, politics and economics. These dynamics employ Christians in a common task and motivate the church for further development and implementation in order to connect theology with practice and thus to fulfill the divine calling for church’s role in the processes of restoration of justice and social transformation, both now and eschatologically.
Bibliography
Anderson, David E. “European Union Debate on Religion in Constitution Continues”
May 26, 2004.
Barth, Karl (tr. E.C. Hoskyns), The Epistle to the Romans (Oxford: Oxford University
Press: n/a).
Ford, David F. ed., The Modern Theologians (Malden: Blackwell Publishers, 1997).
Geffrey B. Kelly & F. Burton Nelson, A Testament to Freedom: The Essential Writings
of Dietrich Bonhoeffer (San Francisco: Harper Publishing House, 1995).
Green, Clifford. Karl Barth: Theologian of Freedom (Minneapolis: Fortress Press, 1989).
Grentz, Stanley J. Theology for the Community of God (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans
Publishing Company, 1994).
Johnson, Ed. Associated Press, June 19, 2004.
Moltmann, Jürgen. The Power of the Powerless, (Norwich: SCM Press Ltd., 1983).
Taylor, Mark K. Paul Tillich: Theologian of the Boundaries (London: Collins, 1987).
[1] The Fall of the Berlin Wall, http://www.dailysoft.com/berlinwall/history/fall-of-berlinwall.htm June 29, 2004; also Jeremy Isaacs and Taylor Downing, The Cold War, Thomas Fleming, The Berlin Wall and Wolfgang Schneider, Leipziger Demotagebuch.
[2] Ed Johnson, Associated Press, June 19, 2004 and David E. Anderson, “European Union Debate on Religion in Constitution Continues” May 26, 2004.
[3] Clifford Green, Karl Barth: Theologian of Freedom (Minneapolis: Fortress Press, 1989), 184.
[4] Karl Barth, (tr. E.C. Hoskyns), The Epistle to the Romans (Oxford: Oxford University Press: n/a), 324.
[5] Stanley J. Grentz, Theology for the Community of God (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans Publishing Company, 1994), 437.
[6] Geffrey B. Kelly & F. Burton Nelson, A Testament to Freedom: The Essential Writings of Dietrich Bonhoeffer (San Francisco: Harper Publishing House, 1995).
[7] Green, 106.
[8] David F. Ford, ed., The Modern Theologians (Malden: Blackwell Publishers, 1997), 369.
[9] Barth, 99.
[10] Jürgen Moltmann, The Power of the Powerless, (Norwich: SCM Press Ltd., 1983).
[11] Mark K. Taylor, Paul Tillich: Theologian of the Boundaries (London: Collins, 1987), 325.
God as to Water: The Musing Continues
June 1, 2023 by Cup&Cross
Filed under News, Publication, Research
by Kathryn Donev, LPC-MHSP, NCC

and His voice was like a noise of many waters: and the earth shined with his glory – Ezek 43:1-7
In the beginning of 2011, thoughts began flooding my awareness about “God as to Water”. Scripture after the next along with revelation came in one instant supported by many questions from loved ones during this period while on the territory of Eastern Europe. Overwhelmed by the ruminations, on July 5, 2011 the topic was dismissed along with written works. In 2022 on July 5, while in North America, the ponderings proceeded. I begin looking for the article which I convinced myself was written over a decade ago, but to no avail. Only disjointed insights were jotted down on paper. The following attempts to expand on something that is far beyond comprehension.
If in the beginning was the Word and the Word was with God and the Word was God, then God or the Word was always in existence and all things came from this. Everything was made from Him. He, God, giving of Himself, created the Heavens and the Earth. But this “Earth” was formless, but deep, empty and dark. All while God’s Spirit hovered over the waters, plural. One could imagine this as an omnipresent being floating ever connectedly to the essence of wholeness. Then, division came, but it came only from that which was in the beginning – the Word, God.
Separation of entities occurred; light from darkness for us to see the vault that separated water from water? Splitting water from itself? Electrolysis that happen with an energy input so great that perhaps came with a sound of a mighty rushing wind or sonic boom? With this endothermic reaction, hydrogen stands alone.
Everything in the Universe is made up of matter and energy. Einstein said that “Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be changed from one form to another.” The world depends on energy to provide for all humankind activities. Hydrogen is the base element of our physical universe. All elements and matter can be created from or broken down to hydrogen. That which came from water. The atom in water that is surrounded by hydrogen is oxygen; the element of breath needed to support all flesh on the earth just as God supports all life by His Spirit. The water on our Earth today is the same water that it has always been. No new water has been created. Water is the only element that exists on our planet in a solid, liquid and gaseous aggregate state reminding of the Trinity. The molecules of water are self-attractive. They are drawn to each other to support things. This characteristic of water assists in capillary action.
If it was only God in the beginning then could God perhaps be energetic water; formless, but with infinite depth. Being ever presents in everything. There are over 700 references to water in the Bible and many of these refer to God, in some way as that water. At times He is even referred to a cloud or mist attempting to label His Glory.
and the house was filled with the cloud, and the court was full of the brightness of the LORD’S glory. – Ezek 10:4
In Genesis chapter six, God chose to use water as the means of destroying a sin-cursed world. Thus water became a “dividing line” between the cleansed and the uncleansed. When God delivered the children of Israel from Egyptian bondage, he led them to the Red Sea. They were immersed in cloud and sea and there was freedom (1 Cor. 10:1-f). When Jesus healed the man born blind (John:1-f) he used water in the form of saliva as the “dividing line” between blindness and sight. Water is a universal solvent having the ability to cleanse. It can dissolve even gas and can recycle chemicals. There is life in water, without is death. It is mention in every chapter of the 4th Gospel.
“Everyone who drinks this water will be thirsty again, but whoever drinks the water I give them will never thirst. Indeed, the water I give them will become in them a spring of water welling up to eternal life.”
-John 4:13-14
And the musings continue….
Full Gospel Pentecost Sunday
I keep on repeating this through the years, but the need for the constant repetition comes from the simple fact that among new doctrinal teachings and Hillsong style of worship the True Message of Pentecost remains long forgotten
- Salvation – That a man must be saved while the hour of grace is still upon us has been that teaching of every protestant evangelical since the Reformation. Why people attend church all their lives without getting saved is beyond me. But I do know that the commitment of the CHURCH to REVIVAL brings people to SALVATION.
- Sanctification – The Wesleyan teaching of sanctification resolves that the sanctification of the believer is definite. This means that though it may progress and evolve through time, as the believer gets closer to God in his/her daily walk, sanctification must become ENTIRE i.e. allowing NO sin to abide in the believer’s body, soul or spirit. Without ENTIRE sanctification resulting in holiness, no one will ever see God (Heb. 12:14).
- Holy Ghost Baptism – The doctrine of the Baptism with the Holy Ghost means that when baptized we speak in one tongue with God because we are ONE with His Spirit. Not just in us or upon us, but that we are IN the Spirit as John was on the day of Revelation.
- Healing in the Atonement of Christ belongs to every believer. This means you, your family and your church members. The healing provided in the Atonement is for ALL believers – no exception. It is also for ALL sickness, disease, viruses, infections, tumors and cancers. But that it belongs to does not yet mean that it has been received by the believer. For this reason, God does not stop healing neither in this age nor through eternity, as the leaves of the Tree of Life in the New Jerusalem are still and forever for the healing (Rev. 22:2)
- The Second Coming of Christ for Pentecostals is not simply pre-millennial, but also pre-Tribulation. There have been MANY teachings on the End Times until today. Post-millennials claim we live in the Millennium even now anticipating the return of the Lord; a-millennials that there will be no Millennium at all. Post-tribulationists expect his return at the end of the Tribulation, mid-post-tribulationists in the middle. But in Pentecost, we expect Christ to return before the Tribulation that we may be saved from the hour of trial (Rev. 3:10) and before the Millennium so we may reign with Him 1,000 years. Any other message is no message of hope for the Church of the Living God.
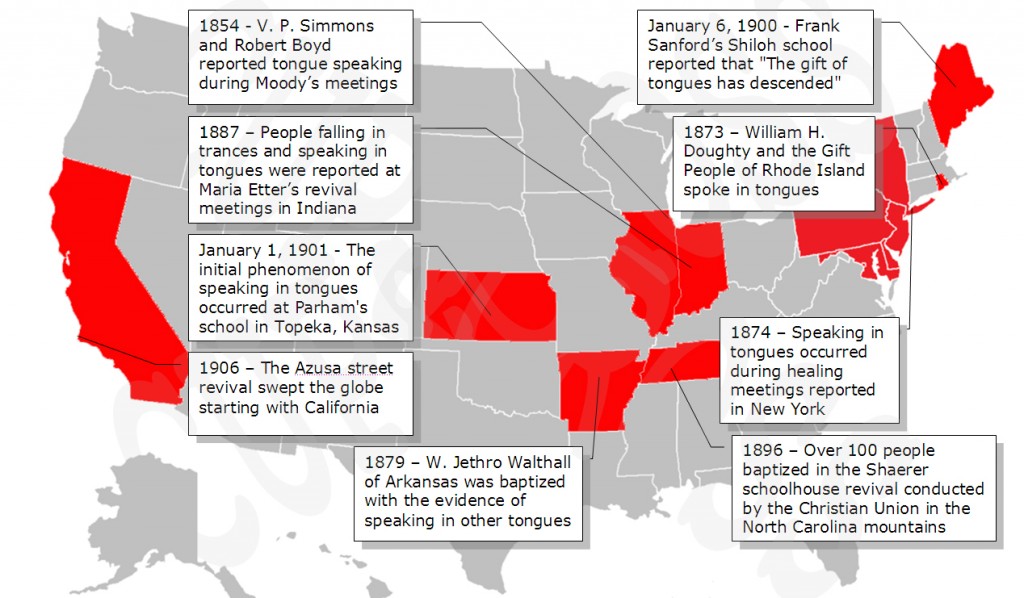
Speaking in Tongues in America Prior to the Azusa Street Revival of 1906
April, 1906 – The Azusa street revival swept the globe starting with California
January 1, 1901– The initial phenomenon of speaking in tongues occurred at Parham’s school in Topeka, Kansas
January 6, 1900 – Frank Sanford’s Shiloh school reported that “The gift of tongues has descended”
1896 – Over 100 people baptized in the Shaerer schoolhouse revival conducted by the Christian Union in the North Carolina mountains
1887 – People falling in trances and speaking in tongues were reported at Maria Etter’s revival meetings in Indiana
1874 – Speaking in tongues occurred during healing meetings reported in New York
1873 – William H. Doughty and the Gift People of Rhode Island spoke in tongues
1854 – V. P. Simmons and Robert Boyd reported tongue speaking during Moody’s meetings

FURTHER READING:
Church of God (Cleveland, TN)
- Alive, alive! (A personal testimony)
- Church of God Primitivism
- Bulgarian Church of God
- J.W. Buckalew
- Why revival came? by Dr. Charles Conn
Azusa Street Revival of 1906
- Lucy F. Farrow: The Forgotten Apostle of Azusa
- The FORGOTTEN ROOTS OF THE AZUSA STREET REVIVAL
- Azusa Street’s Apostolic Faith Renewed
- Azusa Street Sermons
- Pentecostal Primitivism Preserved
Prior to Azusa Street Revival of 1906
- First person to speak in tongues in the Assemblies of God was William Jethro Walthall of the Holiness Baptist Churches of Southwestern Arkansas
- The Work of the Spirit in Rhode Island (1874-75)
- Speaking in Tongues in America Prior to the Azusa Street Revival
- WAR ON THE SAINTS: Revival Dawn and the Baptism of the Spirit
- How Jezebel Killed One of the Greatest Revivals Ever
The Unforgotten: Historical and Theological Roots of Pentecostalism in Bulgaria
SEE MORE at Amazon.com by clicking this link
13 Titles and Resources at Flower Pentecostal Heritage Center
April 30, 2023 by Cup&Cross
Filed under Featured, News, Publication, Research

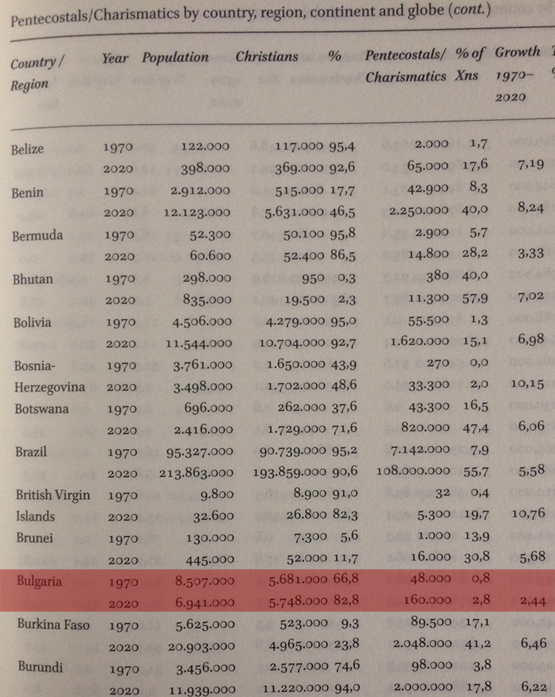
160,000 Pentecostals in Bulgaria Reported by the NEW Encyclopedia of Global Pentecostalism
Toward a Pentecostal Strategy for the City
Toward a Pentecostal Strategy for the City
One of the questions that seems to come up in this course discussion is how to change the world around us with a more positive and effective approach toward using the Gospel of Salvation. In this particular module, the difficulty addressed is ethnocentricity. The particularity of our search then arrives at the more detailed question, how can we change the culture (respectively subcultures) of our church congregations? This is a drastic move from a closed circle toward an outreach community that many congregations are unable to accomplish. How do we then empower such congregations to be transformed into cultural reach-outs to a single ethnos or multiple ethnic groups?
Problem
The problem in the first quarter of the 21st century has been incongruity of our church strategy with the times we live in and the mindset they occupy. We’ve been preparing the church for the multicultural battle, all and while we should have been equipping the saints how to rebuild the walls since the battle has been lost.
We’ve been equipping leaders for the ministry while the church ship has been sinking only to end up with well trained captains of a sunken fleet. And in a doomed attempt to reconcile the reality of the ministry with their training, they have turned to wave walkers who briefly surface for breaths of fresh air during Sunday worship only to return to the deep blue walk of their daily ministry never finding their lost piece of eight.
For the battle was lost long ago before the present generation of ministers ever came to existence. They know not the battle. They’ve only seen the ruins that were left within the broken walls of the church. And they have been struggling to reconcile the incomputable of what church eldership has been teaching them to battle against with the Nehemiah calling for restoration, which God has placed upon them. For the answer has never been in building a New Jerusalem for a fresh start, but restoring the old Jerusalem and its former glory to a new state that reclaims our history and heritage.
Context
Recent analysis of migrant churches in the United States reveals that the predominant majority of them are located in cities which have a high influxation and concentration of immigrants. Such localities are called “gateway cities”. Immigrants typically enter the United States through one of these cities and settle there. These areas contain over half of the foreign-born population in the United States as follows:
- New York, NY – Foreign born population 18.7%
- Los Angeles, CA – Foreign born population 27.1%
- Houston, TX – Foreign born population 12.3%
- Washington, DC – Foreign born population 8.6%
- Miami, FL – Foreign born population 33.6%
- Chicago, IL – Foreign born population 11.1%
- San Francisco, CA – Foreign born population 20.0%
Strategy
Asking the right questions is important, but the answers cannot be generic for all ethnic groups or cultural settings. There is a strong need to be flexible and observe changes in culture, but not to change the message of the Gospel or compromise our witness. Several common things are noted in any cultural setting where our ministry is involved:
First and foremost, people of all cultures prefer to be personal with a purpose, rather than being project driven. No one longs to be part of someone else’s project. Yet, our very existence demands personal purpose, which could serve as a great cultural catalyst in a church ministry.
Secondly, cross cultural ministry is not done merely on relationships, but on being real in the relationships. The greatest halt of ministry work is when people realize the relationship with the church has not been a real one, but merely a part of a program or a paradigm.
Finally, our cross cultural model for ministry should not be just salvation oriented, but soul oriented. There is a great difference between writing down the number of saved every Sunday and actually caring for the eternal well-being of the saved souls. In fact, this is so fundamentally determinative that it should be the goal in mind of every new church plant.
Spiritual Fullness (Fullness in the Spirit) among Early Bulgarian Pentecostals and Today

Bulgaria’s early Pentecostals insisted on a spiritual fullness that included: (1) salvation, (2) water baptism and (3) baptism with the Spirit.[1] As a formula of spiritual experience, it satisfied the witness of blood, water and Spirit (1 Jn. 5:8) on earth; but also corresponded with the triune God in heaven (1 Jn. 5:7), from whom the believer’s spiritual experience originated. Many conservative Pentecostals in Bulgaria today still uphold “the fullness” teaching and would not use Bibles that exclude Johannine Comma (1 John 5:7) for these three “bear record in heaven.”[2]
However, even with the already present Trinitarian experience of the believer and the enormous theological Methodist influence, it is astounding that the doctrine of sanctification was not taught as a separate work of grace among Bulgarian Protestants. Even when after Pentecostalism spread in Bulgaria, it was not included in the tri-fold formula for “spiritual fullness” of the believer. During the persecution of the Communist Regime, speaking in tongues during Communion was done as a spiritual confirmation that the person has “fullness in the Spirit” or is not a government agent sent by the police to spy on the rest of the church. Interpretation often followed to confirm the spiritual stand of the believer. Early Bulgarian Pentecostals did not distinguish between the initial evidence and the gift of speaking in tongues. Even communist propaganda author Boncho Assenov, who categorized Pentecostals as a sectarian cult, defined this fullness as fundamental for the sacramental theology of the early charismatic communities in Bulgaria.[3]
[1] Mollov, 209.
[2] Zarev, 28.
[3] Boncho Asenov, Religiite i sektite v Bŭlgariia (Sofia: Partizdat, 1968), 167, 367.
See also:
The Practice of Corporate Holiness within the Communion Service of Bulgarian Pentecostals
Sanctification and Personal Holiness among Early Bulgarian Pentecostals
Water Baptism among early Bulgarian Pentecostals
First Pentecostal Missionaries to Bulgaria (1920)
The message of PENTECOST is still the same…
February 10, 2023 by Cup&Cross
Filed under Featured, News, Publication
Since the beginning of the 21st century, only 6-10% of new born believers in America receive the Baptism with the Holy Spirit, which by 2018 has resulted in:
- Over 60% within Global Pentecostalism do not speak in tongues
- A major doctrinal shift within Pentecostal Theology today claims speaking in tongues is not the only evidence of Holy Spirit Baptism
- Some theologians even claim there is no initial evidence in the Bible
- Others today go further to believe that no outward sign of the Holy Spirit baptism is necessary.
For this reason, WE are re-committing ourselves and ministry to revival and restoration of the Pentecostal Message through praying, fasting and preaching:
- Salvation of the sinner’s soul and entire sanctification through the Blood of Jesus
- Baptism with the Holy Spirit and fire with initial evidence of speaking in tongues
- Supernatural gifts and ministries of the Holy Spirit
- Healing, deliverance and signs following
- Pre-Millennial return of Christ and pre-Tribulation Rapture of His Church to glory
Please consider the URGENCY of this generation!
Let us reason together what can we do to prevent this rapid decline in Biblical spirituality.
Revival will not come without preaching!
Revival of Pentecost will not come without preaching the Message of Pentecost.
Speaking in Tongues in America Prior to the Azusa Street Revival of 1906
April, 1906 – The Azusa street revival swept the globe starting with California
January 1, 1901– The initial phenomenon of speaking in tongues occurred at Parham’s school in Topeka, Kansas
January 6, 1900 – Frank Sanford’s Shiloh school reported that “The gift of tongues has descended”
1896 – Over 100 people baptized in the Shaerer schoolhouse revival conducted by the Christian Union in the North Carolina mountains
1887 – People falling in trances and speaking in tongues were reported at Maria Etter’s revival meetings in Indiana
1874 – Speaking in tongues occurred during healing meetings reported in New York
1873 – William H. Doughty and the Gift People of Rhode Island spoke in tongues
1854 – V. P. Simmons and Robert Boyd reported tongue speaking during Moody’s meetings

FURTHER READING:
Church of God (Cleveland, TN)
- Alive, alive! (A personal testimony)
- Church of God Primitivism
- Bulgarian Church of God
- J.W. Buckalew
- Why revival came? by Dr. Charles Conn
Azusa Street Revival of 1906
- Lucy F. Farrow: The Forgotten Apostle of Azusa
- The FORGOTTEN ROOTS OF THE AZUSA STREET REVIVAL
- Azusa Street’s Apostolic Faith Renewed
- Azusa Street Sermons
- Pentecostal Primitivism Preserved
Prior to Azusa Street Revival of 1906
- First person to speak in tongues in the Assemblies of God was William Jethro Walthall of the Holiness Baptist Churches of Southwestern Arkansas
- The Work of the Spirit in Rhode Island (1874-75)
- Speaking in Tongues in America Prior to the Azusa Street Revival
- WAR ON THE SAINTS: Revival Dawn and the Baptism of the Spirit
- How Jezebel Killed One of the Greatest Revivals Ever
13 Years of Chaplaincy on the High Seas
 We began our literal journey of ministry on the high seas in 2009. After exploring the opportunity for several years’ prior and submitting applications to various chaplaincy organizations which dealt with such ministry, the doors finally opened for Cup and Cross.
We began our literal journey of ministry on the high seas in 2009. After exploring the opportunity for several years’ prior and submitting applications to various chaplaincy organizations which dealt with such ministry, the doors finally opened for Cup and Cross.
This search for a ministerial identity and its proper application in the real world coincided with the start of the Master’s in Chaplaincy Ministry Program which we designed for the Bulgarian Evangelical Theological Institute in Sofia around 2008-2009. The long standing relationships with professors, active military chaplains from various fields and countries, and the wisdom of several Generals in the field helped us calibrate our ministry focus with what is needed by real people in the real world.
The new fad “to be real” is not enough in a realistic ministry setting. When 25ft. high storm waves beat the aft and the ship is thrown towards the dark wall of ocean waters ahead, one cannot help but “to be real” and depend on a very real and skilled crew. A captain alone cannot run the boat through a storm even if all systems are reported working. It is the crew deep down in the engine room and making its way on the slippery deck that makes it all happen.
The Crew. Some of them have not seen their families for months or even a year at times. They struggle with the same fears and anxieties as the rest of us. Except, while the rest of us can hold on to something for dear life, the crew is obligated by duty to continue to serve and move the boat ahead. The little chapel on the top deck becomes a passage to a lagoon past the riffs of stormy life where stories are shared, prayers are lifted up together and human lives are reclaimed anew for Heaven.
We have found these nontraditional paths of travel and ministry yielding the most unique encounters and connections for Kingdom growth. Our family is thankful for these 10 years and looking forward to even more means of ministry outside of the four church walls. If you would like for us to come to your church as share our journey feel free to reach out to us.
God as to Water: The Musing Continues
October 15, 2022 by Cup&Cross
Filed under News, Publication, Research
by Kathryn Donev, LPC-MHSP, NCC

and His voice was like a noise of many waters: and the earth shined with his glory – Ezek 43:1-7
In the beginning of 2011, thoughts began flooding my awareness about “God as to Water”. Scripture after the next along with revelation came in one instant supported by many questions from loved ones during this period while on the territory of Eastern Europe. Overwhelmed by the ruminations, on July 5, 2011 the topic was dismissed along with written works. In 2022 on July 5, while in North America, the ponderings proceeded. I begin looking for the article which I convinced myself was written over a decade ago, but to no avail. Only disjointed insights were jotted down on paper. The following attempts to expand on something that is far beyond comprehension.
If in the beginning was the Word and the Word was with God and the Word was God, then God or the Word was always in existence and all things came from this. Everything was made from Him. He, God, giving of Himself, created the Heavens and the Earth. But this “Earth” was formless, but deep, empty and dark. All while God’s Spirit hovered over the waters, plural. One could imagine this as an omnipresent being floating ever connectedly to the essence of wholeness. Then, division came, but it came only from that which was in the beginning – the Word, God.
Separation of entities occurred; light from darkness for us to see the vault that separated water from water? Splitting water from itself? Electrolysis that happen with an energy input so great that perhaps came with a sound of a mighty rushing wind or sonic boom? With this endothermic reaction, hydrogen stands alone.
Everything in the Universe is made up of matter and energy. Einstein said that “Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be changed from one form to another.” The world depends on energy to provide for all humankind activities. Hydrogen is the base element of our physical universe. All elements and matter can be created from or broken down to hydrogen. That which came from water. The atom in water that is surrounded by hydrogen is oxygen; the element of breath needed to support all flesh on the earth just as God supports all life by His Spirit. The water on our Earth today is the same water that it has always been. No new water has been created. Water is the only element that exists on our planet in a solid, liquid and gaseous aggregate state reminding of the Trinity. The molecules of water are self-attractive. They are drawn to each other to support things. This characteristic of water assists in capillary action.
If it was only God in the beginning then could God perhaps be energetic water; formless, but with infinite depth. Being ever presents in everything. There are over 700 references to water in the Bible and many of these refer to God, in some way as that water. At times He is even referred to a cloud or mist attempting to label His Glory.
and the house was filled with the cloud, and the court was full of the brightness of the LORD’S glory. – Ezek 10:4
In Genesis chapter six, God chose to use water as the means of destroying a sin-cursed world. Thus water became a “dividing line” between the cleansed and the uncleansed. When God delivered the children of Israel from Egyptian bondage, he led them to the Red Sea. They were immersed in cloud and sea and there was freedom (1 Cor. 10:1-f). When Jesus healed the man born blind (John:1-f) he used water in the form of saliva as the “dividing line” between blindness and sight. Water is a universal solvent having the ability to cleanse. It can dissolve even gas and can recycle chemicals. There is life in water, without is death. It is mention in every chapter of the 4th Gospel.
“Everyone who drinks this water will be thirsty again, but whoever drinks the water I give them will never thirst. Indeed, the water I give them will become in them a spring of water welling up to eternal life.”
-John 4:13-14
And the musings continue….