BibleTech or BUST: 15 Years Later
3 Decades Later: Evangelical Education in Bulgaria at Halt
With the new Bill on Religion in Bulgaria, the Muslim community has been given amnesty on some $4,500,000 of public debt, while granted another $3 million in annual government subsidies. As a result, the monthly salary of Muslim clergy (imams) has already increased with 20% and a new Islamic school is being opened in one of the historically oldest Christian places in Bulgaria, the city of Sliven. All while, the evangelical protestant communities are not receiving financial support under the new law and their schools remain without proper government legalization via the Bulgarian Ministry of Education.
Though this legal precedent follows the Russian Law on Religion that has already effectively closed the evangelical seminaries in Moscow, it is manifesting a political agenda undergoing in Bulgaria for over a decade. What remains unsaid with the recent changes in the Law of Religion in Bulgaria is the ultimate halt of evangelical education in the country. The Bulgarian Evangelical Theological Institute has been functioning at its operational minimum for years now. Students are trained mainly online or via small local groups spread in various cities. They are called to the school departments only for graduation or occasionally lectures by visiting scholars. Even after years of waiting, the Institute was never granted official accreditation through Bulgaria’s Ministry of Education and most of the students preferred getting their degrees from other accredited and licensed institutions. Less than 1% of the students who were not in ministry at the time of their enrollment entered the ministry post graduation. And even fewer of them remain in ministry today; which ultimately ensures the lack of adequately trained ministers for placement in the evangelical churches of Bulgaria.
The last Bulgarian to graduate from the Church of God Theological Seminary did so over a decade ago, and 2009 was the last class of the Bulgarian Theological College (seminary). One of the greatest mistakes made was closing the college in 2009, thus leaving the movement with virtually no higher ministry training for the last decade.
We were present at the national meeting of elders on September 10, 2009 in Sofia when the final decision to close the Church of God Theological College was voted. Only a few others along with us disagreed with the vote and pleaded with the assembly to make everything possible and keep the school open. At the final vote, it came down to a few thousand dollars due in annual membership fees and the school was closed.
Five years prior to these events in 2004, we published an article on evangelical education in Bulgaria with some warnings. The article proposed a change of the evangelical educational paradigm in anticipation of new legal changes and the prolonged waiting for a governmental accreditation. In fact, the same issues addressed in our proposal repeated themselves in 2016 upon Russia changing its own legislation on religion and religious education thus effectively illegalizing evangelical seminaries and overall missionary work. Today, similar legal measures are put in place by the Bulgarian government as well.
The final of our 10-point proposed plan in 2004 included the following observation:
- Naturally, the well-educated graduates have chosen not to occupy themselves with denominational politics both to avoid confrontation and to express their disagreement. This dynamic has been partially ignored by leadership remaining from the period of the underground church when religious education was virtually nonexistent and lacking a complete realization of the power of education. This unnoticed trend, however, endangers Bulgarian Evangelism creating a lack of continuity within the leadership and preparing the context for the emerging leadership crises.
With the new Bill on Religion in Bulgaria closely following the effective closure of evangelical seminaries in Moscow, the opportunity for a government recognized ministerial training in Bulgaria may be legally impossible to regain. In the light of those resent changes, our 2004 proposal for a legal ministry training alternative was successfully implemented and used for our Master of Chaplaincy Ministry graduates since 2009 providing a single valid alternative for evangelical education in Bulgaria.
Missions for the Third Millennium 15 Years Later
The time of changes in the world of missions is at hand. The search for a new paradigm for doing missions in the beginning of the 21st century has begun. Much like in the world of the internet, it cannot be a closed-circuit reinstallation of the same old software, which changes the interface, but not the structure; or a copyrighted etalon designed to be used by a tender legal minority. It must be an open-source, people oriented, social networking, body-like organism of believers that practice the Bible providing the diakonia of missions to peoples and nations in a need of salvation.
This necessity for a fresh evaluation of the way we do missions in the Spirit is based on issues which older missional paradigms were unable to adequately address. Rethinking of world missions today, includes rethinking the global problems of economic crises, world terrorism, immigration and open border markets. Problems that point not to new frontiers in some unknown cosmic future, but back to the old countries upon which modern day civilization was built.
Churches and missionaries, then, cannot afford to simply follow any secular, political, social or economical wave, but must propose Biblical solutions, which surpass both the understanding and history of the natural world to the realm of the Kingdom of God – the sole solver, provider and proprietor of the restoration of God created humanity, social justice and every relationship within the universum for eternity.
It is there, in the very Kingdom identity, or the lacking of such thereof, that the problem of ministry in missions is found. And this problem is deep, penetrating the very soul and make of the church, changing it from a community of mission minded believers willing to dedicate their lives to missions, to an agency that sends half-prepared, half-sponsored, half-aware missionaries to a mission filed where cultural, leadership and financial dilemmas hit them as a hurricane and never seize to oppose their call to minister in a foreign land.
Several characteristics are apparent immediately. The ministry of missions in the 21st century must be:
1. More mission minded than agency structured
2. More missionary focused than leadership centralized
3. More operational than organizational
4. More result oriented than self and strategy containable
5. More praying than thinking while more feeling, than cognitive
6. More giving than fundraising oriented
7. More focused on the Dominion of the Kingdom, than the denomination.
A proposal of such caliber must begin simultaneously at three starting points. First, perhaps not by importance, but by legal requirement, a professional counsel is a must. Many mission agencies follow the secular practice of debriefing missionaries, who have been on the field for a long time as part of their reentry. It is expected that post-missional experiences are often defined as problems requiring a professional counselors. But there are so many more cultural, financial, leadership, church and purely structure related problems. For example, how can one ever imagine doing missions in the 21st century without assertive financial planning in difficult times and rapidly changing international currencies, or political and security advisory in times of ever-present global terrorism? If addressed properly by in-house professionals beforehand, most of them can and should be easily prevented in the ministry of the missionaries. Thus, released from the burden of solving problems they are not qualified to deal with, missionaries will be allowed to fully focus on their main goal: namely, the salvation of eternal human souls.
Second, but equally important, are some very practical implications concerning the church recognition of the ministry of the missionary. Unfortunately, even in the beginning of the 21st century, some of the leading Pentecostal denominations in the world do not have the ministry of missions present on their ministerial report forms, as if it simply does not fit there. Others are yet to include missions as a ministry occupation on their voting registrations for business meetings at assemblies.
And finally, a word about the Prophetic Utterance of Pentecostal Missions. Historically, we, the missionaries baptized with the Holy Ghost, seldom followed models and paradigms. Our guidance has been that prophetic Word, that utterance of the Spirit, that divine guidance and Heavenly call that are never wrong. We went without knowing. We prayed without ceasing. We prophesied without seeing in the physical or even purposefully refusing to reckon with it. We preached without a season, for preaching was the vibe of our ministry and the life of our churches. And this made us Pentecostal. Even more important, this made us powerfully Pentecostal and Pentecostally powerful.
And if indeed, it is true that this very power is being lost today, it means that the very identity of our movement has changed from power giving to power needing – from powerful to powerless. The main questions that must be raised then are these: “What is the prophetic word for Pentecostal missions in 21st century?” and “What does the Spirit wants us to do?” And their answers could be found in the restoration of Pentecostal preaching, prophecy and prayer, as the foundation of any paradigm or model on which we continue to build the Ministry of World Missions.
Our 1999 Thanksgiving Letter 25 Years Later
Greetings in the wonderful name of our Lord and Savior Jesus Christ.

During this Thanksgiving season my gratitude is extended to the Almighty and Eternal God for giving me the opportunity to minister His Word and encourage His people. I also want to thank you for your tremendous support and caring guidance. My heart joins with yours, in a prayer for blessing, success and prosperity of your family and church in the upcoming Millennium. We all need to use the little time that remains as an opportunity for spiritual renewal and personal preparation for the 21st Century.
After finishing this semester at the Theological Seminary, I will have a few weeks free during the last part of December. During this time, I would love to join with you in the effort to win the lost for the Kingdom of God. If I can be of any help in this quest for truth and spirituality, please do not hesitate to let me know.
Sincerely,
Rev. Dony K. Donev
3 Decades Later: Evangelical Education in Bulgaria at Halt
With the new Bill on Religion in Bulgaria, the Muslim community has been given amnesty on some $4,500,000 of public debt, while granted another $3 million in annual government subsidies. As a result, the monthly salary of Muslim clergy (imams) has already increased with 20% and a new Islamic school is being opened in one of the historically oldest Christian places in Bulgaria, the city of Sliven. All while, the evangelical protestant communities are not receiving financial support under the new law and their schools remain without proper government legalization via the Bulgarian Ministry of Education.
Though this legal precedent follows the Russian Law on Religion that has already effectively closed the evangelical seminaries in Moscow, it is manifesting a political agenda undergoing in Bulgaria for over a decade. What remains unsaid with the recent changes in the Law of Religion in Bulgaria is the ultimate halt of evangelical education in the country. The Bulgarian Evangelical Theological Institute has been functioning at its operational minimum for years now. Students are trained mainly online or via small local groups spread in various cities. They are called to the school departments only for graduation or occasionally lectures by visiting scholars. Even after years of waiting, the Institute was never granted official accreditation through Bulgaria’s Ministry of Education and most of the students preferred getting their degrees from other accredited and licensed institutions. Less than 1% of the students who were not in ministry at the time of their enrollment entered the ministry post graduation. And even fewer of them remain in ministry today; which ultimately ensures the lack of adequately trained ministers for placement in the evangelical churches of Bulgaria.
The last Bulgarian to graduate from the Church of God Theological Seminary did so over a decade ago, and 2009 was the last class of the Bulgarian Theological College (seminary). One of the greatest mistakes made was closing the college in 2009, thus leaving the movement with virtually no higher ministry training for the last decade.
We were present at the national meeting of elders on September 10, 2009 in Sofia when the final decision to close the Church of God Theological College was voted. Only a few others along with us disagreed with the vote and pleaded with the assembly to make everything possible and keep the school open. At the final vote, it came down to a few thousand dollars due in annual membership fees and the school was closed.
Five years prior to these events in 2004, we published an article on evangelical education in Bulgaria with some warnings. The article proposed a change of the evangelical educational paradigm in anticipation of new legal changes and the prolonged waiting for a governmental accreditation. In fact, the same issues addressed in our proposal repeated themselves in 2016 upon Russia changing its own legislation on religion and religious education thus effectively illegalizing evangelical seminaries and overall missionary work. Today, similar legal measures are put in place by the Bulgarian government as well.
The final of our 10-point proposed plan in 2004 included the following observation:
- Naturally, the well-educated graduates have chosen not to occupy themselves with denominational politics both to avoid confrontation and to express their disagreement. This dynamic has been partially ignored by leadership remaining from the period of the underground church when religious education was virtually nonexistent and lacking a complete realization of the power of education. This unnoticed trend, however, endangers Bulgarian Evangelism creating a lack of continuity within the leadership and preparing the context for the emerging leadership crises.
With the new Bill on Religion in Bulgaria closely following the effective closure of evangelical seminaries in Moscow, the opportunity for a government recognized ministerial training in Bulgaria may be legally impossible to regain. In the light of those resent changes, our 2004 proposal for a legal ministry training alternative was successfully implemented and used for our Master of Chaplaincy Ministry graduates since 2009 providing a single valid alternative for evangelical education in Bulgaria.
InJOY Church of God Leadership Study 20 Years Later
Source: COG Leadership Development: The Consultant’s View
Dated: 7/12/2002
For the past two years, the Church of God has benefited from an association with INJOY denominational consultants Dr. Conrad Lowe and Dr. Ron McManus. Recently they presented a comprehensive report with the Church of God Executive Council, which is shared here with COG News readers. John Maxwell Denominational Partnerships wishes to thank God and the leaders of the Church of God for the privilege of working closely together in the leadership development initiative. This endeavor has been a highlight of our ministry.
During Phase I, we witnessed this great vision cast across the entire Church of God in North America. Visionary leadership was modeled by the Executive Committee and the Executive Council. State overseers have invested in extensive training. Approximately 2,000 pastors and lay leaders have been trained in various ministry skills. Mentoring groups have begun in most states. Many growing churches have begun to grow, and many declining churches have accelerated, many plateaud churches have begun to grow, and many declining churches have stabilized. Finances, conversions and membership have increased. Church health and “excellence” have also improved for many churches.
The future goal is that additional pastors and churches will be added as we move to more intensive leadership training. In addition, the leadership development initiative will add leadership “coaching” to the mentoring strategy.
One of our tasks as consultants is to bring awareness of potential barriers to the vision of the Church of God. At this juncture in the process, we suggest there are five areas that should be addressed by the Church of God.
Church of God DNA
From our observation, the Church of God has at least three prominent formative influences—holiness, Pentecostal experience and a predominant rural culture.
· The holiness lifestyle defines your character.
· The Pentecostal experience empowers you through the Holy Spirit.
· The rural culture gives you your mental model of ministry.
The dangers we envision are as follows: (1) the importance of holiness may not be passed to the next generation; (2) the Pentecostal experience may lead you to focus on the gifts and neglect the disciplines of ministry; (3) a rural model of ministry is not readily transferable to other cultures, including ethnically diverse, suburban and urban cultures.
RECOMMENDATIONS
1. A plan of education in your heritage holiness must heavily influence your next generation. It may take place in institutions, distance learning, books, tapes, seminars, and so forth. At this point, we observe many Church of God pastors receiving their theology from external sources rather than their denomination.
2. Focus on you Pentecostal experience as your distinctive relationship with God, but add the disciplines of ministry to your gifts. For example, the training offered by the International Executive Committee during the spring and fall events focused primarily on ministry disciplines such as evangelism, assimilation and change management, along with others. Eventually, Church of God leaders will excel in the exercise of the gifts and the disciplines of ministry.
3. Learn how to plan and grow churches in diverse cultures.
Leadership Rotation
It appears that you believe you can “lead by taking turns.” The theory is based on the belief that every leader who is voted into offices next is as productive and skilled as the one being replaced. This organizational model works only if all leaders are equally capable. That theory is never true. This system always produces a roller-coaster effect of good and bad leadership. There is never time for the accomplishment of a vision; instead, each new leader is determined to leave his personal mark. The new leaders then feel free to change everything every time there is an election. If any group is lead by a great leader, they should do everything possible to keep the same leadership in place for sustained success. If not, the quality of leadership in the Church of God will always be “peaks and valleys” depending on whose “turn it is this year.”
Imagine any local Church of God. If they get a great leader and the church is prospering, they would do anything to keep that leader because they know one thing from experience—we have fine leader, but if he leaves, the next one may not be as good. We encourage the Church of God to rethink this underlying assumption about how your denomination is led. Major ministries are led by (1) great leaders and (2) those leaders stay long enough to build something that lasts. For great leaders, the longer they lead, the better the organization will become.
RECOMMENDATION
Focus on productivity instead of “taking turns leading.” As John Maxwell says, “Everything rises and falls on leadership.” The local Church of God churches will “rise and fall” on the quality of the leadership in your pulpits, your state and regional offices, and the international offices. The future of your movement depends on your ability to attract and keep our most gifted and productive leaders in your positions of influence.
Leadership Skills
The present system of choosing leadership in the Church of God encourages “political skills” instead of “leadership skill.” The regular votes for leaders (state, national and international levels) express the will of the minority. This is true because the majority do not vote in most political systems.
RECOMMENDATION
Hold the elected leaders accountable for the improved ministry of the churches they serve instead of “popularity votes.” Choose the best leaders among you. Then give them the resources to do the job. Support them with prayer and cooperation. Finally, hold each leader accountable for the results of their leadership and measure how well the churches are doing under their leadership.
We encourage the Church of God to continue its dependence upon the leadership of the Holy Spirit in making decisions which improve the church. As consultants, we find few people who are purely political, but we raise a major warning that the present system encourages “patronage.”
Structure
The Church of God is historically structured as a “hierarchy.” It can be visualized as a pyramid with pastors and churches at the bottom, state overseers in the middle, and international executive leaders at the top. As one moves upward in the pyramid, renown, finances and power increase. Under the leadership of Dr. Lamar Vest, the pyramid is being inverted. The principle is Biblical “servant leadership.” The international executive leaders serve as a resource for the state overseers, while the state overseers serve as a resource for the local pastors and churches.
We encourage the Church of God to “stay the course” moving in the direction of servant leadership. Jesus said, “He who would be greatest among you, let him become the least among you.” In the body of Christ, we must focus attention and resources on those who labor in the fields of the Lord’s vineyard.
RECOMMENDATIONS
1. Focus on the right group. Every successful structure must align the members to achieve the ultimate goal. The goal of the Church of God is to reach the lost and to train fully devoted followers of Jesus Christ. In most organizations, the structure evolves to benefit the people who make the policies. Improvement occurs when they focus on the right people, the lost and those being involved in ministry.
2. Make decisions at the level closest to the work. The correct consulting term for this is empowerment. The Church of God must organize the denomination to develop the potential in every church. Ephesians 4 clearly describes the congregation of the church as “ministers,” not “spectators.” The Bible then says those lay ministers should choose laypeople to lead their ministry. The task of the pastor and staff is to equip the people in the congregation to build a great ministry. Structure the future to develop strong lay ministries with everyone else serving as a resource for that local ministry.
3. Make the structure flexible enough to meet current challenges. The foundation of the Church of God is its holiness, Pentecostal experience and Biblical authority. They are the bedrock principles that should remain the same. Structure, however, is temporary and changes as the organization grows and faces new challenges. A denomination plateaus or declines when it treats structure as if it were a foundational principle. You cannot confuse structures with foundational principles. You improve the Church of God when the structures serve the people instead of the people being saddled with an outdated structure.
4. Form Follows Function in Structure. The Church of God must find what God is blessing and then structure itself to join Him. Most denominations begin to decline and decay when they retain their present forms even if they can no longer be successful within those forms. It is time to simplify structure, increase flexibility to encourage innovation, and form your structures to fit your functions.
State/Regional Overseer Productivity
After consulting with the Church of God for almost two years, it is our conclusion that the key to transformation for the future rests primarily in the leadership of the state/regional overseers. They are the denomination’s primary influence on the field of ministry. If the state/regional overseer provides resources; models visionary leadership; and implements the strategies of “mentoring, coaching, consulting, modeling and teaching churches,” that state or region will experience health and growth.
RECOMMENDATIONS
1. Choose only your best leaders in the Church of God as state/regional overseers. They should have sterling character, be holy in their reputation, and have a “track record” of successful leadership; and train them to move from “doing” to “coaching”
2. Evaluate state/regional overseers solely on their ability to move their churches to new levels of quality and quantity.
3. Increase the training for state/regional overseers with one goal: our most productive leaders are overseers.
4. Leave them in place long enough to make a major, positive difference in their state or region. Instead of inheriting a stronger state or region, require the state/regional overseer to build a better state or region.
Leadership Trust
It appears that some Church of God policies have been established as a reaction to leadership failures in the past. Large organizations are notoriously slow to personally address misbehavior. When they do, they often make a general policy that punishes everyone rather than addressing the specific leader involved. The result is “leadership suspicion.” Those within the organization begin to mistrust all leaders and make broad defensive policies. The result is tragic—leadership for the organization is diminished.
RECOMMENDATION
Elect and appoint leaders who meet Biblical standards and who are recognized as people of Christian integrity. Then take the risk to trust and honor them as Scripture requires.
CONCLUSION
We believe the Church of God must address these issues in order to move boldly into the leadership role God has offered you. We do not offer detailed solutions at this point. It is simply our duty to help you recognize some of the issues that will determine the future.
We believe that you must minister as if your dreams are bigger than your memories. Your past has been glorious, but it is no place to live now. Your leaders are being endowed with vision fro God for your denomination, every state or region, and every local church. We encourage you to grow into those visions and resist being defined by the past.
Most important, we believe the church is poised for an unprecedented time of spiritual harvest. The great news is the issues you must address are all issues of growth, not of decline. The difficult news is, you must give serious consideration to some strategies changes. We believe every denomination in America needs to see one leadership group experience miraculous reformation. The rest will gladly follow. We are praying that you—the Church of God—are the group willing to learn enough, work enough, receive enough and pray enough to respond to God’s great promise—that your ministry will multiply “like the sands of the sea and the stars of the sky.”
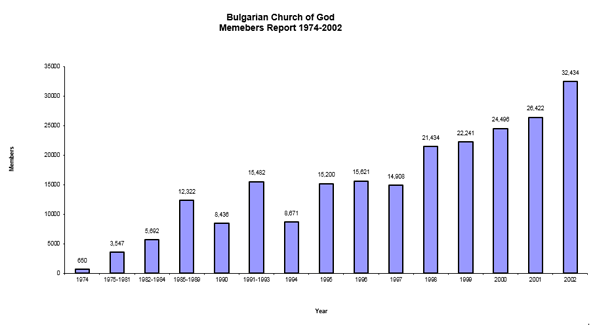
Bulgarian Church of God Membership 20 Years Later
Pentecostal Education in Bulgaria Two Decades Later
This article was originally authored in 2008 and now addresses issue that have been ongoing for over 20 years
The missionary strategy of Protestant denominations toward Bulgaria within the 19th century effectively included evangelistic, publishing and educational outreaches. The educational paradigms, which the western missionaries introduced, were soon adopted by the Bulgarian people, quickly realized as progressive and successfully implemented in both religious and secular Bulgarian schools. These trends continued in the next several decades, educating Bulgarian youth and producing the first generation of Bulgarian leaders who took their rightful place in political, economical, social and religious structures in the Bulgarian lands.
Unfortunately, when the Communist Revolution took place in Bulgaria, all religious schools, with the exception of the Eastern Orthodox Seminary in Sofia, were closed down and religious education was outlawed. For the next half century, Bulgarian evangelical ministers were destined to do ministry without any former religious education.
When the Berlin Wall fell in 1989, the tension for religious education reached its culmination and a number of religious schools were quickly established across Bulgaria. The instruction methods used ranged from Bible study home groups to Bible colleges all to fulfill the niche for religious education. Two important milestones must be mentioned here, and they are the opening of the Logos Bible Academy in the Danube town of Russe and the starting of a long distance program by ORA International.
Naturally, the general trend of Bulgaria’s post communist governments to control these educational institutions resulted in the registration of a religious institute under the Directorate of Religious Affairs, a government agency formed to register, manage and supervise the activity of religious formation on the territory of Bulgaria. It was in this context that the Bulgarian Evangelical Theological Institute (BETI) was formed and registered in the capital Sofia. It included five departments (often called faculties), representing Bulgarian evangelical denominations with a predominant focus on the Pentecostal wing.
The Theological College in Stara Zagora, often mistakenly called a Theological Seminary, was established in 1998 as one of these departments to represent the Bulgarian Church of God. Because of current developments within the Bulgarian Church of God, the department was started in the city of Stara Zagora, located some four hours east of the capital and became the only of the faculties not located in Sofia. Naturally, its location, staff, affiliation and purpose created a sense of independence, both in its theology and structure.
With the acceptance of the new Act of Confessions in 2002, the Bulgarian government employed a more drastic approach toward all religious institutions not fitting the standard denominational profile. Since BETI was among them, the government initiated the process of the Institute’s accreditation with the Ministry of Education. Five years later, the government is yet to grant the accreditation. It was not until the publication of this article in March, 2008 that the Bulgarian Government moved toward finalizing the long-awaited accreditation of BETI.
Meanwhile the Institute’s management is facing a tri-dimensional dilemma which includes economic, cultural and leadership tensions. Some of them have not been resolved due to the lack of recourses; others have not been resolved due to the lack of essential prerequisites in the long-term educational strategy of the school. The following is a list of the challenges, which must be resolved immediately in order for the Institute to continue to operate under the said government accreditation:
1. The school’s baccalaureate program, structured primarily after 20th century American Bible college model, is practically incompatible with the requirements of the Bulgarian Ministry of Education. The dilemma of changing the program to meet the accreditation requirements or to retain the school’s evangelical identity is yet to be resolved on part of BETI as a whole, as well as its theological departments individually.
2. Three masters programs that were to focus on the subjects of Christian counseling, chaplaincy ministry and missions were secured from the Bulgarian government several years ago. However, because of the lack of students and experts on the said topics, only one of them, the master’s program in counseling, has been partially developed. Today, it remains in its initial phase as a distance-learning program, while the other two programs are virtually untouched.
3. It has taken BETI over a decade to comply with the country’s requirements for higher education. In this process, the school has not facilitated the opportunity for religious master’s programs thus missing its mission to become a higher education authority in religious studies.
4. The resistance toward the evangelical movement and more specifically its presence within the educational process of Bulgarian adolescents has resulted in continuous protests on part of the Bulgarian community. They have been followed by restrictions from the government, which has forced the Institute at the periphery of the educational process. Two waves of attacks against Bulgarian evangelicals in 1990-1993, 2002-2004 and the current trend of the government to establish mandatory religious classes for children ages seven to twelve has contributed to this alienation and has forced the inability of evangelical education to find and establish its place within the Bulgaria community. Much of this has to do with the lack of an adequate placement strategy for graduates upon the completion of the college’s program.
5. Furthermore, scholarships for individual students and sponsorship for the colleges of the Institute has weekend since 9/11 creating an economical dilemma with which the Institute is still struggling. The financial crisis has brought about the rethinking of the economic strategy of the Institute, its dependency on religious support sources and its financial self-sufficiency.
6. Additionally, a number of Roma/Gipsy communities have received substantial educational grants from the European Union upon Bulgaria’s official membership. This has taken a great number of the Roma/Gipsy students within the Institute in a different direction.
7. Immigration has also taken its toll on the Institute’s graduates, as many of them have seized the opportunity to continue their training in religious educational institutions abroad, while other have simple forgone their higher religious education in the struggle for personal survival, both groups never to return and practice in Bulgaria.
8. It is also unfortunate, that most of the professionally trained Bulgarians who have graduated with a higher degree in religious studies from foreign colleges and universities, have been unable to find their place within the structure of the BETI and have been employed in educational institutions, religious centers, ministries and missions which often have to do very little with Bulgaria.
9. The denominational affiliation of each of the departments, has contributed to the dilemma of structural incompatibility with the leadership and vision differences between the denominations that are affiliated with the Institute. The recent crises in several of the member dominations have added to the escalation of the above dilemmas and the incapability for the resolution from a denominational standpoint.
10. Naturally, the well-educated graduates have chosen not to occupy themselves with denominational politics both to avoid confrontation and to express their disagreement. This dynamic has been partially ignored by leadership remaining from the period of the underground church when religious education was virtually nonexistent and lacking a complete realization of the power of education. This unnoticed trend, however, endangers Bulgarian Evangelism creating a lack of continuity within the leadership and preparing the context for the emerging leadership crises.
As an educational institution of the Bulgarian Church of God and a member of the Bulgarian Evangelical Theological Institute, the Theological College in Stara Zagora has experienced all of the above dilemmas and more. Its physical distance from the capital Sofia has jeopardized its accreditation with Bulgaria’s Ministry of Education, the latest guidelines of which have constituted that a school department cannot be more than 25 miles away from its main office. Since Stara Zagora is almost 200 miles away, the Church of God Bible College has been forced to find a suitable alternative. One logical solution may be to move the school or parts of the school to a Sofia location.
However, the Stara Zagora Theological College has had very little if any representation in the capital for its decade of existence. A move to Sofia would propose a number of new problems such as the relocation of teachers and a forced split of focus between two campuses. Another immediate challenge would be the development of a long-term financial strategy to meet a budget, which in the capital would be three-four times the cost of the same operation in the city Stara Zagora. And finally, a successful strategy for establishing a new level of cooperation with the rest of the Institute’s departments, which have operated in the capital Sofia for over a decade is a must, before a successful educational program can be initiated by the Bulgarian Theological College at the new location.
Arizona State Quarter: A Decade Later
 We used the time in the San Francisco Bay Area to meet up with old friends from our youth group in Bulgaria. While having coffee at the El Cerrito Starbuck’s early Sunday morning, we reminisced about friends and stories from the past. Leaving the coffee shop, we came across an Arizona state quarter lying on the pavement. After picking it up, my friend shared how his brother just recently moved to Phoenix with his family.
We used the time in the San Francisco Bay Area to meet up with old friends from our youth group in Bulgaria. While having coffee at the El Cerrito Starbuck’s early Sunday morning, we reminisced about friends and stories from the past. Leaving the coffee shop, we came across an Arizona state quarter lying on the pavement. After picking it up, my friend shared how his brother just recently moved to Phoenix with his family.
At this time we had no intentions of going to the southern part of Arizona, as we had planned to travel straight across through New Mexico to reach Houston for our Easter service there. Yet, the Lord had other plans and we ended up having a last minute cancellation in our schedule which allowed for us to travel to Phoenix and spend time with our friends there.
This occasion was one of the most blessed of times of fellowship on our trip. We were able to establish divine connections as we prayed for a new Bulgarian Church in the Phoenix area. We were also able to work out the details of being able to broadcast live feed from Bulgarian churches in the US and abroad – a vision which we have held closely to our hearts for the past decade while being involved with the Bulgarian Christian Television and ministry on the internet. Together, we called this broadcast Divine Connections. As a result, Cup & Cross Ministries has been able to broadcast LIVE services from all around Bulgaria in the past month and our team is planning to broadcast live the 2009 annual conference of Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in North America, which will be held May 22-25 in Los Angelis, California.
2020 UPDATE:
- We’ve hosted over one million LIVE broadcast on Bibliata.TV since 2009
- The Bulgarian church in Phoenix has been operational for several years now
- We will be broadcasting the 2020 Bulgarian church conference LIVE via Zoom from Las Vegas, Nevada