Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in Chicago (2017 Report)
Bulgarian Church of God in Chicago
2254 North Narragansett Ave, Chicago
GraceInternational.TV
Active since 1995
New Life Bulgarian Evangelical Church
1480 Oakton St – Des Plaines, IL 60018
Active since 1997
Word of Faith and Life
916 E Central Rd
Arlington Heights, IL 60005
http://www.bulgarianfamily.org/
Active since 1998
Bulgarian Baptist Church
6334 W Diversey Ave.
Chicago, IL 60639
Active since 2005
READ MORE:
- First Bulgarian Church in Chicago Opened in 1907
- Gateway Cities for Bulgarian Evangelical Churches
- How to Start a Bulgarian Church in America from A-to-Z
- Unrealized Spiritual Harvest as a Paradigm for Cross-Cultural Ministries among Migrant and Disfranchised Ethnic Groups in America Today
110 Years Ago the First Bulgarian Mission in Chicago was Started
 In May 1907, sponsored by the Chicago Tract Society, Petko Vasilev opened the Bulgarian Christian House in Chicago. The facilities had beds and a kitchen and served as a hotel and a shelter for new immigrants. In 1908, the name was changed to Bulgarian Christian Society and later was relocated several times.
In May 1907, sponsored by the Chicago Tract Society, Petko Vasilev opened the Bulgarian Christian House in Chicago. The facilities had beds and a kitchen and served as a hotel and a shelter for new immigrants. In 1908, the name was changed to Bulgarian Christian Society and later was relocated several times.
A second similar work was started at the same time by Daniel Protoff called the Russian Christian Mission. Located in Chicago, it supported church services and a Bible school. In 1909, the City Missionary Society called Basil Keusseff to lead the mission. Keusseff was a Bulgarian born minister who was converted in Romania and was a graduate of the school in Samokov and Cliff College in Sheffield, England. In the 1890s, Keusseff pastored the Baptist church in Lom and then moved to Pittsburgh where he worked with Robert Bamber, pastor of the Turtle Creek Christian Church. The mission ministered to Russian, Bulgarian, Serbian, Croatian, Macedonian and Turkish minorities.
Around 1910, the ministry of the Bulgarian Christian Society was aided by Reverend Paul Mishkoff, a student at Moody Bible Institute. Coming from a poor but strong Protestant family, Mishkoff was called to preach at a very early age. He studied in the school at Samokov and was often sent to preach in the nearby villages. After finishing the school, Mishkoff decided to come and study at the Moody Bible Institute. He was helped by a Methodist missionary who gave him four dollars – the price of a third-class ticket from Sofia to New York where he was put on the immigrant’s train to Chicago. He was denied admission to Moody with the explanation that there was neither room nor funds for him. With no job and no money, the young preacher had to find food at the saloons where it was offered free for ones who drank. During his struggles, Mishkoff had lost all his possessions except a pocket size New Testament. In his personal story, he recalled, “But I had the copy of the Bulgarian Testament in my pocket not only to keep it, but to read it when I was sitting on the benches of the Union Station and other public places night after night. My soul was wakened anew. An ambition was roused in me: I must prepare myself for a preacher any way.” Through a financial miracle, Mishkoff was eventually able to graduate from the Moody Bible Institute. During the course of his studies, he was supported by Chicago Tract Society and he was able to minister to the 5,000 Bulgarians living in Chicago.
Also in 1910, the Bulgarian Christian Society established a library which served the Bulgarian community for over twenty years. The congregation of the mission numbered about fifty. The ministry included English classes and immigration law seminars. Several changes in the leadership of the mission began in 1921. In 1924, the mission was headed by Zaprian Vidoloff and the mission was renamed the Bulgarian Christian Mission. Vidoloff was a graduate of the Samokov School in 1910, a student of philosophy at the University of Sofia and a graduate of Union Theological College in Chicago. He entered pastoral ministry in 1915 and later served as the secretary of the Baptist Union. At the same time, he was secretary of the Bulgarian legation in Washington, D.C. from 1921 to 1923.
All Bulgarian religious organizations initiated by evangelicals before 1930 existed as missions. In February 1932, the First Bulgarian Church pastored by Joseph Hristov was started in Chicago.
How to Start a Bulgarian Church in America from A-to-Z

The Unrealized Spiritual Harvest of Bulgarian Churches in North America
 ….A closer examination of the ministry and structure of the network of Bulgarian churches in North America will give answers to essential issues of cross-cultural evangelism and ministry for the Church of God. Unfortunately, until now very little has proven effective in exploring, pursuing and implementing cross-cultural paradigms within the ministry opportunities in communities formed by immigrants from post-Communist countries. As a result, these communities have remained untouched by the eldership and resources available within the Church of God denomination. There are presently no leaders trained by the Church of God for the needs of these migrant communities. Thus, a great urban harvest in large metropolises, where the Church of God has not been historically present in a strong way, remains ungathered. Although, through these communities, the Church of God has the unique opportunity to experience the post-Communist revival from Eastern Europe in a local Western setting… (p.84, Chapter III: Contextual Assessment, Historical Background, Structural Analyses and Demographics of Immigration in a Paradigm for Cross-Cultural Ministries among Migrant and Disfranchised Ethnic Groups in America Today) Read complete paper (PDF)
….A closer examination of the ministry and structure of the network of Bulgarian churches in North America will give answers to essential issues of cross-cultural evangelism and ministry for the Church of God. Unfortunately, until now very little has proven effective in exploring, pursuing and implementing cross-cultural paradigms within the ministry opportunities in communities formed by immigrants from post-Communist countries. As a result, these communities have remained untouched by the eldership and resources available within the Church of God denomination. There are presently no leaders trained by the Church of God for the needs of these migrant communities. Thus, a great urban harvest in large metropolises, where the Church of God has not been historically present in a strong way, remains ungathered. Although, through these communities, the Church of God has the unique opportunity to experience the post-Communist revival from Eastern Europe in a local Western setting… (p.84, Chapter III: Contextual Assessment, Historical Background, Structural Analyses and Demographics of Immigration in a Paradigm for Cross-Cultural Ministries among Migrant and Disfranchised Ethnic Groups in America Today) Read complete paper (PDF)
How to Start a Bulgarian Church in America from A-to-Z
Sanctuary Gateway Cities for Eastern European Slavic and Bulgarian Immigrant Churches in North America
 Since 1994 Cup & Cross Ministries International has assisted churches across the United States and has strategically planned and developed a process which incorporates Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in North America. The first success of this endeavor was the establishment of the Bulgarian Evangelical Church of God in Chicago in 1995.
Since 1994 Cup & Cross Ministries International has assisted churches across the United States and has strategically planned and developed a process which incorporates Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in North America. The first success of this endeavor was the establishment of the Bulgarian Evangelical Church of God in Chicago in 1995.
The Bulgarian Church of God in Chicago followed a rich century-long tradition, which began with the establishing of Bulgarian churches and missions in 1907. (read the history) Consecutively, our 1995 Church Starting Paradigm was successfully used in various studies and models in 2003. The program was continuously improved in the following decade, proposing an effective model for leading and managing growing Bulgarian churches.
Based on the Gateway cities in North America and their relations to the Bulgarian communities across the continent, it proposed a prognosis toward establishing Bulgarian churches (see it here) and outlined the perimeters of their processes and dynamics in the near future (read in detail). Since 1995 twelve more Bulgarian churches have been started in strategic immigration gateways across the United States and Canada. For the past four years our team have been involved in the process of establishing Bulgarian congregations in Atlanta, Phoenix and San Francisco. Read complete paper (PDF)
Toward Context of Ministry Applications
In the beginning of the 21st century the Protestant Church in Bulgaria is entering a new constitutional era in the history of the country. Since the fall of the Berlin Wall, the political and economic challenges in Eastern Europe have strongly affected the Evangelical Churches. More than ever before, they are in need of reformation in doctrines and praxes in order to adjust to a style of worship liberated from the dictatorship of the communist regime. In order to guarantee the religious freedom for our young, democratic society, the Protestant Movement in Bulgaria needs a more dynamic representation. Such can be provided only by people who will create a balance between the old atheistic structures and the new contemporary, nontraditional style of ministry.
Similar is the case among Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in North America which also share analogue dynamics with congregations of Latin American immigrants. Several facts are obvious from such comparison. It is apparent that Bulgarian immigrants come to North America in ways similar as other immigrant groups. Large cities which are gateways for immigrants are probable to become a settlement for Bulgarian immigrants due to the availability of jobs, affordable lodging and other immigrants from the same ethnic group.
The emerging Bulgarian immigrant communities share religious similarities and belongingness which are factors helping to form the communities. As a result of this formation process, the Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in North America emerge. It also seems natural to suggest that as this process continues, Bulgarian Evangelical Churches will be formed in other gateway cities and other large cities which meet the requirements to become a gateway city. Such has been the case with Latin American churches. If this is true, it should be proposed that the Bulgarian Churches in North America follow a strategy for church planting and growth which targets these types of cities.
It is encouraging, at the same time, to observer that one of the positive estimates provided by our doctoral project is also coming to reality. In 2002-2004, based on analyses provided by the New Religious Immigrants Project, our research suggested that the next Bulgarian Evangelical Church will be established in the last of the Seven American Gateway Cities which was still without a Bulgarian Church, namely the city of San Francisco. Our resent visit in the area of the Bay Area showed that this prediction is already progressing into a reality as the Bulgarian Diaspora there is already producing a Bible study group out of uniting Bulgarian college students from Barkley and young computer professionals in the area.
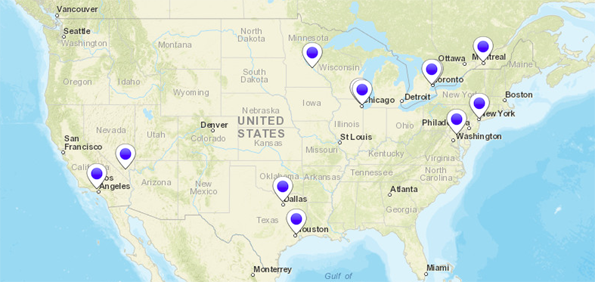
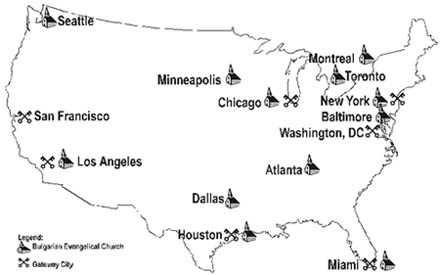
Geographical Location of Bulgarian American Churches and Gateway Cities.
Currently, Bulgarian Evangelical Churches are located in cities which have a high concentration of foreign-born immigrants. Such cities are called gateway cities, a large immigrant point-of-entry city to the United States. Immigrants typically enter the United States through one of these cities and settle there. Such cities contain over half of the foreign-born population in the United States. There are Bulgarian Evangelical Churches active in six of the seven gateway cities as follows:
Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in Gateway Cities
| Gateway City | Foreign Born | Percent of Foreign Born | Bulgarian Church |
| 1. New York, NY | 3,657,269 | 18.7% | Yes |
| 2. Los Angeles, CA | 3,944,828 | 27.1% | Yes |
| 3. Houston, TX | 460,380 | 12.3% | Yes |
| 4. Washington, DC | 578,786 | 8.6% | No |
| 5. Miami, FL | 1,072,843 | 33.6% | Yes |
| 6. Chicago, IL | 914,58 | 11.1% | Yes |
| 7. San Francisco, CA | 1,250,693 | 20.0% | No |
Several facts are obvious from the above comparison. It is apparent that Bulgarian immigrants come to North America in ways similar to other immigrant groups, channeled through the listed gateway cities. Large cities which are gateways are more probable to become a settlement for Bulgarian immigrants due to the availability of jobs, lodging and other immigrants from the same ethnic group. The emerging Bulgarian immigrant communities share religious similarities and belongingness which are factors helping to form the communities. As a result of this process of formation of Bulgarian immigrant communities, the Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in North America emerge. It also seems natural to suggest that as this process continues, Bulgarian Evangelical Churches will be formed in the remaining two gateway cities (Washington, D.C. and San Francisco) and other large cities which meet the requirements to become a gateway city (for example, the city Atlanta). If this is true, it should be proposed that the Bulgarian Churches in North America follow a strategy for church planting and growth which targets this type of cities. With all this in mind, the Unrealized Spiritual Harvest of Bulgarian Churches in North America remains unforgiving in history…
Resources for Further Study:
- Seven Churches of Revelation
- How to Start a Bulgarian Church in America from A-to-Z
- Bulgarian Churches in North America: Contextual Assessment
- Bulgarian Churches in North America: Statement of Problem
A Decade Ago Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association Gained Legal Status
 The Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association has finally received official legal status with the Bulgarian government, after battling courts throughout the country for the last four months. Global religious freedom watchdog FORUM 18 closely followed the case of chaplaincy ministry in Bulgaria recognizing its “underground” status and releasing an informative article about the current situation of chaplaincy in Bulgaria which can be found at: http://www.forum18.org/Archive.php?article_id=919
The Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association has finally received official legal status with the Bulgarian government, after battling courts throughout the country for the last four months. Global religious freedom watchdog FORUM 18 closely followed the case of chaplaincy ministry in Bulgaria recognizing its “underground” status and releasing an informative article about the current situation of chaplaincy in Bulgaria which can be found at: http://www.forum18.org/Archive.php?article_id=919
After a decade of ministry, the Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association held a national founding meeting in August, 2006 and submitted a petition for registration with the Bulgarian court. The purpose of the establishment was the legal representation of Bulgarian evangelicals who minister in various fields of chaplaincy despite legal limitations and open government restrictions. Their campaign for legalizing chaplaincy in the Bulgarian armed forces has formed “The Case of Underground Chaplaincy in Bulgaria.”
After months of legal battle, the Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association was officially registered through the Sofia Municipal Court on February 23, 2007. The result was made possible by a joint initiative of the Association’s establishing members, the representing legal team led by former Bulgarian presidential nominee, Ivan Gruikin with the assistance of legal council Latchezar Popov of the Rule of Law Institute and the Balkan Center for Law and Freedom.
Bulgarian Cookbooks Available Worldwide in Germany, Japan, France, United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Spain, Mexico on AMAZON.com
Amazon has marketplaces worldwide and offers all Bulgarian Cooking Cookbooks for purchase with the simple click of a button.
To purchase in Germany (Jetzt Kaufen): https://www.amazon.de
To purchase in UK: https://www.amazon.co.uk
To purchase in Spain (Comprar Ahora): https://www.amazon.es
To purchase in Japan: https://www.amazon.co.jp
To purchase in France (Achetez-le Maintenant): https://www.amazon.fr
To purchase in Canada: https://www.amazon.ca
To purchase in Mexico (Comprar Ahora): https://www.amazon.com.mx
Temp Bulgarian Government Assigned before Early Elections in March 2017
During their first cabinet meeting, the caretaker ministers of Bulgaria have agreed on a new structure of the government and have been assigned several tasks. There will be four Deputy Prime Ministers in the interim government, the same number as in the previous cabinet, according to the list of decisions sent by the government’s press office. Their portfolios, however, will be slightly different as the elected cabinet had a Deputy PM for “coalition policy”, while the caretaker government does not include such a post and has a deputy to oversee the preparation of Bulgaria’s Council of the EU presidency instead.
- Interim Health Minister Ilko Semerdzhiev will also be Deputy Prime Minister in charge of social policies.
- Stefan Yanev, the caretaker Defense Minister, for his part will have a Deputy Prime Minister office overseeing internal order and security.
- Deputy Prime Ministers on EU funding (Malina Krumova) and the rotating EU presidency(Denitsa Zlateva) will have no portfolios.
The Prime Minister will have as many as 16 staff, including advisers, experts and assistants in his political cabinet. Each deputy Prime Minister with a portfolio will have three experts and the same number of advisers and assistants on his or her team. Deputy PMs without portfolios will count on 10-strong cabinets. In a separate move, Health Minister Semerdzhiev and Labour Minister Galab Donev have been tasked to be the government’s representatives to the National Council on Tripartite Cooperation – meetings of state authorities with businesses and trade unions.
As Deputy PM on internal order, Stefan Yanev has been tasked with the overall coordination of the early parliamentary election scheduled for March 26.
Bulgarian vs Russian New Problematic Laws on Religion
As Bulgaria prepares to assume the Chairmanship of the 55-nation Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE), its Law on Religions is a concern, as several provisions are out of step with Bulgaria’s religious freedom commitments as an OSCE participating State. Reports of problems with the new law are already arising. The Sofia City Court, which is mandated to handle all registration applications, has reportedly stalled on the re-registration of some groups, as the new registration scheme includes additional elements not previously required. For instance, since visas are contingent on re-registration, the Missionary Sisters of Charity and the Salesians have reportedly been denied visas. Unfortunately, in the rush to approve the legislation in December 2002, some religious communities were reportedly not consulted during the drafting process, and the government’s promise to have the draft critiqued again by the Council of Europe went unfulfilled. Also, on July 15, 2003, the law was reviewed by the Bulgarian Constitutional Court, in response to a complaint brought by 50 Parliamentary deputies. The Court upheld the legislation, despite six judges ruling against and five in favor. Under Bulgarian law, seven of the court’s twelve judges must rule together for a law to be found unconstitutional. Notwithstanding this decision on the constitutionality of the law, the following report highlights areas in need of further evaluation and legislative refinement in light of Bulgaria’s OSCE commitments on religious freedom. Concerns exist with how the Bulgarian Orthodox Church is favored over the alternative Orthodox synod and other religious groups. In addition, the new registration scheme appears open to manipulation and arbitrary decisions, thereby jeopardizing property holdings and the ability to manifest religious beliefs, as both depend on official registration. The sanctions available under the Law on Religions are also ambiguous yet far-reaching, potentially restricting a variety of religious freedom rights. It is therefore hoped the Government of Bulgaria will demonstrate a good faith effort to ensure the religion law is in conformity with its OSCE commitments. This report outlines a number of suggested changes. The government could also submit the Law on Religions for technical review to the OSCE Panel of Experts on Freedom of Religion or the Council of Europe. Either of these bodies could highlight deficiencies addressable through amendments.
 GOVERNMENT RECOGNITION OF A “TRADITIONAL” CHURCH
GOVERNMENT RECOGNITION OF A “TRADITIONAL” CHURCH
Article 11 was crafted to force a resolution to the longstanding church dispute between the Bulgarian Orthodox Church and an alternative Orthodox synod, which split after the fall of communism. Article 11 enumerated detailed characteristics of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church, thereby establishing the synod of Patriarch Maxim above the other Orthodox synod and all other religious communities. In short, Article 11(1) attempted to settle the church dispute through legislative fiat by establishing the Bulgarian Orthodox Church as the “traditional religion,” a politically expedient decision which is inconsistent with Bulgaria’s OSCE commitments.
While Article 11(2) automatically registers the Bulgarian Orthodox Church, the other Orthodox synod is faced with going through the complete registration process. Registration is critical, as the law ties property ownership rights to legal personality. However, the process is open to manipulation where the government could deny registration to select religious groups. Considering the animosity between the Orthodox synods over property, this appears to place the unrecognized Orthodox synod at a great disadvantage. Article 11(3) does state: “Paragraph 1 and 2 cannot be the basis to grant privileges or any advantages [to the Bulgarian Orthodox Church] over other denominations by a law or sub-law.” However, while this claims no special benefits accrue, Article 11(2) is contradictory as it automatically gives the Bulgarian Orthodox Church legal personality, an “advantage” no other church or religious group receives through the law. Favoritism of this kind also creates internal conflicts within the religion law, as Article 3(1) prohibits limitations or privileges based on “affiliation or rejection of affiliation to a religion,” and Article 4(4) states “no religiously based discrimination shall be allowed.”
Considering the problematic nature of these provisions, removing Article 11(1) through amendment would allow these two religious Orthodox communities to reconcile their differences independently without government involvement. The appropriate venue for the handling of these types of disputes is the court system, not the Parliament . In addition, amending Article 11(2) either to allow automatic registration of all previously registered churches or omit entirely this provision would lessen the discriminatory effect of the law.
REGISTRATION
It is positive that the law does not require registration, nor does it establish temporal or numerical thresholds for religious communities to meet. Yet, the proper administration of the registration process has increased in importance, since many rights and powers of organizations and their communities appear tied to registration status and other avenues for legal personality have been closed. For example, Article 29(2) provides that nonprofit organizations do not have “the right to accomplish activities which represent practice of religion in public.” As a result, if a group does not obtain official registration as a “religious community,” no other options exist to provide some type of legal personality. The Law on Religions does provide guidelines for the registration process. Article 16 requires that all religious groups wishing to register must do so before the Sofia City Court. This is problematic, as it adds an unnecessary burden for groups existing outside the capital. Improvements to the law should allow the submission of national registration requests in every provincial capital court or other designated government office.
For local branches to form officially, Article 21 requires the organization to first register at the national level and then re-register at the local level through a mayor’s office. While the drafters intended this to be a perfunctory requirement, it is problematic, as it creates yet another unneeded bureaucratic hurdle to overcome. Additionally, the involvement of mayors in the registration of religious groups should be avoided, as in the past registration through mayoral offices were plagued by arbitrary and non-transparent decisions. Revisions should remove registration requirements obligating groups already registered to re-register at the local level. If local re-registration must occur, amendments should permit re-registration at a local court or other designated government office. The Article 19(2) requirement that a “short statement of religious beliefs” be included in an application, which can be reviewed by the Directorate of Religions for an “expert opinion” (Article 18), is highly problematic. This places the government in the subjective position of evaluating the beliefs of a religious community to determine if they “qualify” as a religion. Therefore, the removal of the Article 19(2) requirement is recommended, so that the Directorate of Religion cannot base recommendation for registration eligibility on the religious beliefs of an applicant group.
There are at least two instances in the Law on Religions that demonstrate the critical nature of registration. Article 5(3) appears to allow only registered religious organizations to engage in the public manifestation of religion. “The religious belief is expressed in private when it is accomplished from a specified member of the religious community or in the presence of persons belonging to the community, and in public, when its expression can as well become accessible for people not belonging to the respective religious community.” How the government will apply this article is unclear, as it attempts to distinguish the public versus the private practice of religion. If only registered religious organizations can publicly manifest their beliefs, this is inconsistent with OSCE commitments that protect the right to practice religion with or without legal entity status. It should consequently be made explicit through refining amendments that unregistered religious groups and their members have the right to engage in the public manifestation of their religious beliefs.
Furthermore, it is unclear if individual members of a religious community can own property in their personal capacity for use by the corporate body, as only registered communities can hold property under Article 24(1). The article states: “Religions and their branches, which have acquired status of a legal person, according to the procedures of this law shall have right to their own property.” This reenforces the importance of ensuring the registration process is timely and transparent. Amendments should make explicit that individual members of a religious community may own private property for use by the corporate body.
LIMITATION CLAUSE
Article 7(1) of the religion law provides: “Freedom of religions shall not be directed against national security, public order, people’s health and the morals or the rights and freedoms of persons under the jurisdiction of the republic of Bulgaria or other states.” This language is similar to other limitation clauses, but its structure is problematic, as it enunciates standards not found under Article 17 of the Vienna Concluding Document of the OSCE or Article 18 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights. For example, the Vienna Concluding Document in Article 17 declared, “The participating States recognize that the exercise of the above-mentioned rights relating to the freedom of religion or belief may be subject only to such limitations as are provided by law and consistent with their obligations under international law and with their international commitments.” The next sentence is also an important qualifier, declaring States “will ensure in their laws and regulations and in their application the full and effective exercise of the freedom of thought, conscience, religion or belief.” Article 18(3) of the ICCPR stated: “Freedom to manifest one’s religion or beliefs may be subject only to such limitations as are prescribed by law and are necessary to protect public safety, order, health, or morals or the fundamental rights and freedoms of others.”
It is well settled that restrictions on manifestations of belief must be consistent with the rule of law and must be necessary in a democratic society— directly related and proportionate to the specific need on which the limitation is predicated. For example, it is not enough to justify burdensome limitations by merely arguing they are key to maintaining public order. Only when limitations further a legitimate government objective and are genuinely “necessary” can negating a religious freedom be justified. To be sure, this test is not easily met. In addition, international custom has not established “national security” as a legitimate reason for limiting religious rights, so amendments to the law should correct Article 7 to reflect the abovementioned international standards.
SANCTIONS
Article 9 of the Law on Religions allows courts to impose sanctions against groups if they determine
that an Article 7 violation has occurred. The six available sanctions available under Article 9 include:
(1) Prohibiting dissemination of certain printed publications;
(2) Prohibiting publishing activity;
(3) Restricting public manifestations;
(4) Depriving registration of educational, health or social enterprises;
(5) Cancelling activities for a period of up to six months;
(6) Nullifying registration of the legal entity of the religion.
The Article 9 restrictions are vague yet extensive in their scope, potentially curtailing a variety of fundamental freedoms. Accordingly, the use of the Article 9 sanctions list must be predicated on a finding of abuse under the Article 7 limitations clause. However, the situations enumerated in Article 7 are for exceptional situations. As these sanctions touch upon fundamental rights, use of Article 9 and the denial of these rights should not occur for mere infractions of administrative regulations. As previously discussed, international commitments make clear that limitations on the manifestation of religion are permissible only in narrowly defined situations.
A distinction must also be made between the actions of individuals and punitive sanctions on the entire religious community. It is individuals, not whole religious groups, who may be involved in criminal activities, so penalties should not punish the entire community for the actions of individuals. However, provision (3) empowers courts to restrict the public manifestation of religious views for an entire religious community, in effect restricting an individual member’s right to practice his or her faith. Provision (6) is also a concern; if a court can remove a religious group’s registration status, it is unclear who would hold their property, potentially exposing their holdings to seizure.
Concerns exist that the Article 9 sanctions list will be employed in situations not meeting international standards, thereby allowing the restriction of the freedom of speech, the freedom to the religious education of children in conformity with the parent’s convictions, and the freedom to profess and practice, alone or in community with others, religion or belief. Therefore, removal through amendment of the Article 9 sanctions list would be positive, as it potentially allows overly burdensome restrictions on basic human rights. Further concerns over potential sanctions exist in other areas of the religion law. Later in Article 37(8), the law also gives the Directorate of Religion the unchecked and potentially arbitrary powers to take complaints from citizens concerning violations of Article 7, and when deemed appropriate, forward the complaints to the public prosecutor. Allowing the Directorate to function in this manner opens the opportunity for the politicization of religious freedom issues, potentially exposing the Directorate to pressures to act arbitrarily against certain minority religious communities. Consequently, legislators are encouraged to eliminate the ability of the Directorate of Religion to forward complaints to the public prosecutor, as this role is better left with law enforcement agencies.
Article 38 has established monetary penalties for “any person carrying out religious activity in the name of a religion without representational authority.” The provision appears crafted to penalize the unrecognized Orthodox synod for using what it considers to be its name, and could easily be misused against religious communities deemed by authorities as unpopular or out of favor.
property.” This reenforces the importance of ensuring the registration process is timely and transparent. Amendments should make explicit that individual members of a religious community may own private property for use by the corporate body.
LIMITATION CLAUSE
Article 7(1) of the religion law provides: “Freedom of religions shall not be directed against national security, public order, people’s health and the morals or the rights and freedoms of persons under the jurisdiction of the republic of Bulgaria or other states.” This language is similar to other limitation clauses, but its structure is problematic, as it enunciates standards not found under Article 17 of the Vienna Concluding Document of the OSCE or Article 18 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights. For example, the Vienna Concluding Document in Article 17 declared, “The participating States recognize that the exercise of the above-mentioned rights relating to the freedom of religion or belief may be subject only to such limitations as are provided by law and consistent with their obligations under international law and with their international commitments.” The next sentence is also an important qualifier, declaring States “will ensure in their laws and regulations and in their application the full and effective exercise of the freedom of thought, conscience, religion or belief.” Article 18(3) of the ICCPR stated: “Freedom to manifest one’s religion or beliefs may be subject only to such limitations as are prescribed by law and are necessary to protect public safety, order, health, or morals or the fundamental rights and freedoms of others.”
It is well settled that restrictions on manifestations of belief must be consistent with the rule of law and must be necessary in a democratic society— directly related and proportionate to the specific need on which the limitation is predicated. For example, it is not enough to justify burdensome limitations by merely arguing they are key to maintaining public order. Only when limitations further a legitimate government objective and are genuinely “necessary” can negating a religious freedom be justified. To be sure, this test is not easily met. In addition, international custom has not established “national security” as a legitimate reason for limiting religious rights, so amendments to the law should correct Article 7 to reflect the abovementioned international standards.
SANCTIONS
Article 9 of the Law on Religions allows courts to impose sanctions against groups if they determine
that an Article 7 violation has occurred. The six available sanctions available under Article 9 include:
(1) Prohibiting dissemination of certain printed publications;
(2) Prohibiting publishing activity;
(3) Restricting public manifestations;
(4) Depriving registration of educational, health or social enterprises;
(5) Cancelling activities for a period of up to six months;
(6) Nullifying registration of the legal entity of the religion.
The Article 9 restrictions are vague yet extensive in their scope, potentially curtailing a variety of fundamental freedoms. Accordingly, the use of the Article 9 sanctions list must be predicated on a finding of abuse under the Article 7 limitations clause. However, the situations enumerated in Article 7 are for exceptional situations. As these sanctions touch upon fundamental rights, use of Article 9 and the denial of these rights should not occur for mere infractions of administrative regulations. As previously discussed, international commitments make clear that limitations on the manifestation of religion are permissible only in narrowly defined situations.
A distinction must also be made between the actions of individuals and punitive sanctions on the entire religious community. It is individuals, not whole religious groups, who may be involved in criminal activities, so penalties should not punish the entire community for the actions of individuals. However, provision (3) empowers courts to restrict the public manifestation of religious views for an entire religious community, in effect restricting an individual member’s right to practice his or her faith. Provision (6) is also a concern; if a court can remove a religious group’s registration status, it is unclear who would hold their property, potentially exposing their holdings to seizure.
Concerns exist that the Article 9 sanctions list will be employed in situations not meeting international standards, thereby allowing the restriction of the freedom of speech, the freedom to the religious education of children in conformity with the parent’s convictions, and the freedom to profess and practice, alone or in community with others, religion or belief. Therefore, removal through amendment of the Article 9 sanctions list would be positive, as it potentially allows overly burdensome restrictions on basic human rights. Further concerns over potential sanctions exist in other areas of the religion law. Later in Article 37(8), the law also gives the Directorate of Religion the unchecked and potentially arbitrary powers to take complaints from citizens concerning violations of Article 7, and when deemed appropriate, forward the complaints to the public prosecutor. Allowing the Directorate to function in this manner opens the opportunity for the politicization of religious freedom issues, potentially exposing the Directorate to pressures to act arbitrarily against certain minority religious communities. Consequently, legislators are encouraged to eliminate the ability of the Directorate of Religion to forward complaints to the public prosecutor, as this role is better left with law enforcement agencies.
Article 38 has established monetary penalties for “any person carrying out religious activity in the name of a religion without representational authority.” The provision appears crafted to penalize the unrecognized Orthodox synod for using what it considers to be its name, and could easily be misused against religious communities deemed by authorities as unpopular or out of favor.
Christmas Book Sale: The CASE of a NATO CHAPLAINCY MODEL within the BULGARIAN ARMY
In the past five years since 2011, we have authored over two dozen books related to our ministry and mission work in Eastern Europe. As several of the prints are now almost exhausted and second/third editions and several new titles are under way, we are releasing all currently available editions in a Christmas sale through the month of December. All titles are available at up to 30% off and Amazon offers free shipping and extra savings for bundle purchases.
Our book available on sale today is:
THE CASE OF A NATO CHAPLAINCY MODEL WITHIN THE BULGARIAN ARMY (Submitted to the Manfred Wörner Foundation)
 In April 2004, Bulgaria was officially accepted into the global structure of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). The event followed a long series of historic developments that were accomplished despite the existence of highly antagonistic forces that opposed the very idea of Bulgaria’s membership in any Western alliance. Among these were internal and external political, economical and social factors that historically have forced the country to remain under the influence of the forces opposing the West.
In April 2004, Bulgaria was officially accepted into the global structure of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). The event followed a long series of historic developments that were accomplished despite the existence of highly antagonistic forces that opposed the very idea of Bulgaria’s membership in any Western alliance. Among these were internal and external political, economical and social factors that historically have forced the country to remain under the influence of the forces opposing the West.
As the country of Bulgaria is now a member of NATO and awaits acceptance into the European Union in 2007, international experts are working with various government institutions and consultant agencies to create an atmosphere in which the Bulgarian mindset can experience a new national revival in the 21st century. NATO’s involvement in this process serves as a catalyst both for reinforcing Bulgaria’s infrastructure and attracting international interest in the country’s affairs. Issues concerning national security, military involvement, international relations, economical development and ethnic diversity are continuously and carefully taken into consideration. However, one issue still remains untouched neither by NATO’s official position in Bulgaria, nor by the Bulgarian government. This is the issue of faith.
Three reasons make such topic of relevant importance. First, Bulgaria claims traditional and historical religious belongingness to the Eastern Orthodox Church. Furthermore, the centuries of religious wars on the Balkans have formed a complete dependency on ethnic religiosity, making faith the prime factor for animosity, hatred and genocide. Finally, the issue of morale and morality in the armed forces remains open for any military unit and will need to be addressed sooner or later in the context of NATO’s presence in Bulgaria.
This research will show how the above issues could be resolved by the presence of a NATO paradigm for chaplaincy within the Bulgarian Armed Forces. The paper will explore the current developments of chaplaincy in Bulgaria on three levels: church, society and government. It will then present the case of “underground chaplaincy” in Bulgaria and provide an appropriate solution to be implemented through the newly established Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association. The conclusion will outline the benefits that can be achieved by a partnership between local NATO representatives and the Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association who combine efforts to restore the spirituality within the Bulgarian Army through the legalization of chaplaincy ministry within its structures.
Also important [click to read]:
- U.S. Department of State recognizes our chaplaincy efforts in Bulgaria
- Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association: Integration Proposal with Local NATO Programs
- Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association: Vision and Resolution
- Chronology of our role and involvement in developing Church of God chaplaincy in Bulgaria since 2001
- Master’s of Chaplaincy Ministry Program in Bulgaria Reflections
- The Past Decade of Chaplaincy in Bulgaria (2006-2016)
- Related Publications and Presentations by Cup & Cross Ministries International
Chronology of our role and involvement in developing Church of God chaplaincy in Bulgaria since 2001
History of Events
05/12 Anticipated Date for Graduation of the First Cohort of Master’s Program of Chaplaincy Ministry in Bulgaria
2011
09/11 – Master’s of Chaplaincy Ministry Program Module 3: Counceling Completed
07/11 – Master’s of Chaplaincy Ministry Program Module 2: Theology Completed
03/11 – Master’s of Chaplaincy Ministry Program approved by the Educational Committee of the Bulgarian Evangelical Theological Institute
01/11 – Master’s of Chaplaincy Ministry Program Continues
2010
10/10 – Master’s of Chaplaincy Ministry Program Module 1: Chaplaincy Completed
09/10 Master’s of Chaplaincy Ministry Program begins in Sofia, Bulgaria
06/10 Chaplaincy Conference and Master’s of Chaplaincy for Bulgaria
01/10 Proposal masters program finalized and submitted for approval to the Educational Committee of the Bulgarian Evangelical Theological Institute
2009
10/09 Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association holds an introductory chaplaincy course in Yambol, Bulgaria
2008
12/08 Family Seminar for Military Men and Women held in Yambol
11/08 Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association Annual Meeting
09/08 – Bulgarian Chaplaincy Associations noted in Church of God publications
06/08 – The Case of a NATO Chaplaincy Model within the Bulgarian Army released
06/08 – Celebrating 10 Years of Military Ministry in Bulgaria
2007
10/07 – Bulgarian Chaplaincy Associations Recognized by U.S. Department of State
07/07 – National Chaplaincy Conference in Yambol, Bulgaria
03/07 – Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association was officially registered
02/07 – Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association gains legal status
01/07 – Bulgarian Chaplaincy Assassination noted by international religious freedom watch dog Forum 18
2006
12/06 – Registration Rejected Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association by Bulgarian court
11/06 – A master program in chaplaincy ministry has been proposed for the Bulgarian Evangelical Theological Institute in Sofia
10/06 – Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association Founder’s Meeting in Sofia, Bulgaria
10/06 – A contextualized course for chaplaincy ministry is offered at the Bulgarian Evangelical Theological Institute in Sofia
08/06 – Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association’s Resolution No. 1 sets course toward chaplaincy in churches, education and government institutions
07/06 – National Chaplaincy Meeting in Yambol, Bulgaria
06/06 – Meeting with NATO Chaplains
05/06 – Cup & Cross Ministries submitted a research paper to NATO’s Manfred Wörner Foundation dealing with the case of underground chaplaincy within the Bulgarian Armed Forces
03/06 – A contextualized course for chaplaincy ministry was offered in Veliko Turnovo
02/06 – www.kapelanstvo.com was released to serve as the official website of the chaplaincy movement in Bulgaria
2005
10/05 – A national training seminar held in Veliko Turnovo
10/05 – The Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association was presented before the Bulgarian Evangelical Alliance
09/05 – Regional meeting in Nova Zagora which addressed the current issues
08/05 – A regional chaplaincy meeting in Sliven
07/05 – Publication of camouflage New Testaments and Bibles, some of which we distributed to Bulgarian army personal including the divisions currently serving in Iraq
2004-2001
- Chaplaincy Conference and Master’s of Chaplaincy
- Chaplaincy Course in Yambol, BULGARIA
- Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association Annual Meeting
- Family Seminar for Military Men and Women
- Cup & Cross Ministries in Church of God Publications
- The Case of a NATO Chaplaincy Model within the Bulgarian Army
- 10 Years of Military Ministry in Bulgaria
- Bulgarian Chaplaincy Associations Recognized by U.S. Department of State
- National Chaplaincy Conference
- Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association Gains Legal Status
- Chaplain Dees Visits Bulgaria
- Chaplaincy Course at the Bulgarian Evangelical Theological Institute
- Bulgarian Chaplaincy Association
- Meeting the NATO Chaplain
- National Chaplaincy Meeting
- Chaplaincy Developments in Bulgaria
- U.S. Bases in Bulgaria
- National Chaplaincy Meeting
- Chaplaincy in Bulgaria
- HEALTHCARE CHAPLAINCY IN BULGARIA
- Chaplaincy in Bulgaria
- Mission Bulgaria
Christmas Book Sale: Bulgarian Congregations in North America
In the past five years since 2011, we have authored over two dozen books related to our ministry and mission work in Eastern Europe. As several of the prints are now almost exhausted and second/third editions and several new titles are under way, we are releasing all currently available editions in a Christmas sale through the month of December. All titles are available at up to 30% off and Amazon offers free shipping and extra savings for bundle purchases.
Our book available on sale today is:
Bulgarian Churches in North America: The Unrealized Spiritual Harvest as a Paradigm for Cross-Cultural Ministries among Migrant and Disfranchised Ethnic Groups in America Today
 ….A closer examination of the ministry and structure of the network of Bulgarian churches in North America will give answers to essential issues of cross-cultural evangelism and ministry for the Church of God. Unfortunately, until now very little has proven effective in exploring, pursuing and implementing cross-cultural paradigms within the ministry opportunities in communities formed by immigrants from post-Communist countries. As a result, these communities have remained untouched by the eldership and resources available within the Church of God denomination. There are presently no leaders trained by the Church of God for the needs of these migrant communities. Thus, a great urban harvest in large metropolises, where the Church of God has not been historically present in a strong way, remains ungathered. Although, through these communities, the Church of God has the unique opportunity to experience the post-Communist revival from Eastern Europe in a local Western setting… (p.84, Chapter III: Contextual Assessment, Historical Background, Structural Analyses and Demographics of Immigration in a Paradigm for Cross-Cultural Ministries among Migrant and Disfranchised Ethnic Groups in America Today) Read complete paper (PDF)
….A closer examination of the ministry and structure of the network of Bulgarian churches in North America will give answers to essential issues of cross-cultural evangelism and ministry for the Church of God. Unfortunately, until now very little has proven effective in exploring, pursuing and implementing cross-cultural paradigms within the ministry opportunities in communities formed by immigrants from post-Communist countries. As a result, these communities have remained untouched by the eldership and resources available within the Church of God denomination. There are presently no leaders trained by the Church of God for the needs of these migrant communities. Thus, a great urban harvest in large metropolises, where the Church of God has not been historically present in a strong way, remains ungathered. Although, through these communities, the Church of God has the unique opportunity to experience the post-Communist revival from Eastern Europe in a local Western setting… (p.84, Chapter III: Contextual Assessment, Historical Background, Structural Analyses and Demographics of Immigration in a Paradigm for Cross-Cultural Ministries among Migrant and Disfranchised Ethnic Groups in America Today) Read complete paper (PDF)