March 4, 1906: William Seymour is expelled from the Santa Fe Mission
March 5, 2026 by Cup&Cross
Filed under Featured, Missions, News, Publication
On March 4, 1906, Seymour preached during the morning service at the Santa Fe Mission that speaking in tongues is the biblical evidence of baptism in the Holy Spirit. When he returned for the evening service, he found the church doors locked by Julia Hutchins. After consulting the leadership of the Southern California Holiness Association, to which the Santa Fe Mission belonged, Hutchins informed Seymour that she did not accept speaking in tongues (glossolalia) as part of the doctrine of holiness. One of the elders’ arguments was that Seymour himself had not been baptized in the Holy Spirit and had not experienced what he preached.
However, Seymour was not the first to make the connection between speaking in tongues and baptism in the Holy Spirit. Even his teacher, Charles Parham, who systematized the theological link between biblical sanctification and Spirit baptism, was an heir to a rich tradition of preachers and churches that accepted speaking in tongues as the sign of the baptism in the Holy Spirit within the holiness doctrine.
1905 – Lucy Farrow, who introduced Seymour to Parham and later helped him receive the invitation to pastor the Santa Fe Mission in Los Angeles, was baptized in the Holy Spirit and spoke in tongues. She was the niece of Frederick Douglass and pastor of a Holiness church in Houston. Lucy Farrow received the baptism in the Holy Spirit while working in the home of Charles Parham. At a prayer meeting in Houston in early 1906, she prayed for 25 people, all of whom were baptized in the Holy Spirit and spoke in tongues simultaneously. Shortly afterward, she traveled to Los Angeles, and when Seymour was expelled, it was Lucy Farrow who prayed for the first believers to receive Spirit baptism during the home prayer meetings that began on Bonnie Brae Street in April 1906.
1896 – During the revival meetings known as the “Shearer Schoolhouse Revival,” more than 100 men, women, and children were baptized in the Holy Spirit. They were part of a mountain community in North Carolina called the “Christian Union,” from which the Church of God (Cleveland, Tennessee) would later emerge.
1887 – In the revival meetings of Maria Etter, under the power of the Holy Spirit, believers (mainly Quakers and Methodists) fell into trances and spoke in unknown tongues, leading the secular press to call her a “voodoo priestess.”
1880 – The “Pentecostal Holiness Church Movement” documented Holy Spirit baptisms among its members.
1889 – Jethro Walthall of Arkansas was baptized in the Holy Spirit along with many others during a prayer meeting.
1875 – E. B. Swan testified that the so-called “Gift People” in Rhode Island practiced speaking in tongues.
1874 – Similar testimonies came from healing meetings in New York State, where many were baptized in the Spirit and spoke in tongues.
1855 – William Dowie spoke in unknown tongues during meetings of Frank W. Sandford in Shiloh, Maine. Later, Dowie founded the “Gift People” movement, and Sandford started a Bible school called “The Holy Spirit and Us” as part of his church. Ambrose J. Tomlinson, who in 1907 would organize the Church of God, also visited Shiloh in October 1901. Even Charles Parham stayed at the school for six weeks during the summer of 1900 to listen to Sandford’s lectures. It was there that Parham first heard speaking in tongues among the students in the school’s old prayer towers.
In 1906, the participants in the Azusa Street Revival sought the same experience of speaking in tongues that had occurred in the early hours of January 1, 1901, at Charles Parham’s school in Topeka, Kansas. Interestingly, a publication from January 6, 1900, reported that at Sandford’s school in Shiloh, many had been baptized in the Holy Spirit and spoke in unknown tongues following a prayer meeting that began on New Year’s Eve and lasted about ten days.
1854 – W. P. Simons and Robert Boyd separately testified about speaking in unknown tongues during evangelistic meetings led by D. L. Moody, attended by followers of the Scottish preacher Edward Irving.
THE PASTORAL TRIALS ELIMINATE THE AVANTGUARD OF BULGARIAN EVANGELICALS FOR AN ENTIRE GENERATION (PART 3)
THE PASTORAL TRIALS ELIMINATE THE AVANT-GARDE OF BULGARIAN EVANGELICALS, BEHEADING IT FOR AN ENTIRE GENERATION (Part 3)
[Editorial note: The following text is translated from the Bulgarian original. The documents contain memorandums, archival records, State Security (Darzhavna Sigurnost / DS) interrogation files, survivor testimonies, and secondary scholarly sources. Bracketed insertions in the original are the author’s. Handwritten portions of the source document are noted where applicable. Archival reference: pp. 155–177.]
Yanko Nikolov Ivanov
Completed his studies in Frankfurt (1925). He had earlier withdrawn from the Faculty of Law at Sofia University and redirected his path towards commerce. He successfully completed the Commercial and Industrial Chamber in Ruse. His father, Nikola Ivanov, financed his studies and sent him to study theology at the Methodist Church seminary in Frankfurt. Immediately upon returning from Frankfurt, he was appointed to Gorna Mitropolia at the 28th Annual Conference in Sofia (1925). The following year Yanko Ivanov was elected assistant secretary of the Conference and appointed to the Evangelical Methodist Church (EMC) in Vidin for a period of four years. During this period he was elected secretary of the Annual Conference and treasurer of the Church Charitable Society. In 1930 he was sent to Lom for three years, where he subsequently served as pastor. During his stay in Lom the newly constructed Methodist church building was sold. From 1933 to 1940 he served in Pleven, and was then, with the approval of Alphonse Prache, transferred to the EPC Sofia as secretary of the Annual Methodist Conference. From 1944 he held the position of supreme superintendent of the EMC and deputy religious representative of the Evangelicals within the United Evangelical Churches (OETs), until the commencement of the Pastoral Trials.
From the State Security interrogation file: ‘His arrest for anti-people and espionage activities was met by him with arrogance. At the outset of the investigation he maintained an arrogant manner and with marked irony attempted to answer the questions. He relied on foreign intervention and on his high ecclesiastical rank. He denied everything without reservation… By this stance he greatly impeded the investigation. He displayed a strong will, a firm character, and steadfastness. He possesses a sound logical faculty.’
Despite being subjected to torture both ‘behind the curtain’ and in the ‘devil’s cell’ during pre-trial detention, he endeavoured to protect his colleagues from dangerous deviations in the political sphere. He attempted to warn the others that two of the accused pastors were assisting the investigation with their testimony, but his effort was thwarted. According to his testimony, at the OETs assembly of 1944, a hostile line towards the Fatherland Front was discussed, at which ‘Zyapkov reported that he had made contact with the American and British Legations in Sofia and received assurances of protection should the authorities take measures against them as a result of their conduct (according to the testimony of N. Mikhailov, Georgi Chernev, Yanko Ivanov, and others, in part)… That in 1945 Yanko Ivanov, in his capacity as deputy religious representative, met with a certain Tobias — who had entered the country under cover as a delegate of the British youth delegation and was an American intelligence operative — who came to Ivanov in strict secrecy and presented himself as an emissary of Methodist Bishop Garber, to whom Ivanov provided written information on the situation in the country and on the conditions under which the sects operated; which information he had gathered from all four sects in written form; and that he received directives for agitation and slander against the people’s authority from Tobias, which directives Ivanov subsequently transmitted at one of the sessions of the Supreme Council of the OETs (according to the testimonies of Ya. Ivanov, G. Chernev, and N. Mikhailov).’
In his own defence he stated: ‘I am proud to declare that the honourable Ministry of Foreign Affairs has never experienced any difficulties owing to violations committed by members or employees of the Methodist Church. In all circumstances, the Methodist Church as a community and I as its representative have acted straightforwardly, honestly, and loyally towards the authorities, as any good Bulgarian would. Never and under no circumstance have I sought the intervention of foreigners, not even that of our bishop Dr. Garber, in order to achieve a proper resolution of disputed matters with the authorities. In such cases I have always sought the assistance of the authorities and the laws of the country, but not the interference of any foreigners whatsoever.’
He was found guilty of participating in ‘a reconnaissance network in favour of a foreign intelligence service’ and transmitting ‘numerous items of information of a military, economic, and political character constituting state secrets’; receiving ‘remuneration from a foreign state and representatives of a foreign intelligence service’; disseminating ‘abroad false and grossly distorted accounts, substantially damaging the dignity of the Bulgarian people and state,’ as well as ‘false rumours, reports, and assertions,’ and ‘verbally within the country, offensive, defamatory, and false assertions’ with the aim of harming ‘our good relations with a friendly state or its authorities,’ diminishing ‘the prestige of such a state or its authorities,’ all of this serving ‘another state in a hostile act against the Bulgarian state.’ He was sentenced to life imprisonment with hard labour, a fine of one million leva in favour of the state, deprivation of pastoral rights, and confiscation of all his property. He was released after thirteen and a half years of imprisonment — only a few months before his death, which came on Christmas Day, 1962.
Note on his son: Nikolai Yankov Ivanov, residing at 86 ‘Rakovski’ Street, served as secretary of the Methodist Church youth section. He was expelled from the Shumen Aviation School on charges of fascist activity. He had made attempts to leave the country with no intention of returning. He had also escorted and arranged meetings with persons suspected of espionage for one Lord Shier, who arrived in Bulgaria in 1948.
Vasil Marinov Popov
Completed his studies in Brussels and theology in Cremona, Switzerland (1920). Detained and sent to a labour camp without sentence together with the Methodists Kiril Yotov, Marin Gluharov, and Nikola Pulev. The Pastoral Trials found him serving as pastor of the EMC in Varna. The investigation unearthed his earlier case from Lovech, where he had served as pastor (1940–1945) and had been acquitted. He maintained close ties with the American household at the boarding house in the city of Lovech, and demonstrated Germanophile tendencies, being a member of the Bulgarian-German Society in the city. He attended the OETs assembly held at the end of September and beginning of October 1945 in Burgas, at a special gathering of pastors convened at Zyapkov’s request; and also the conference of 1938 in Pleven, attended by Dr. John L. Newlson, Dr. Ralph Diffendorfer, and Alphonse Prache (according to the testimony of Yanko Ivanov and Mitko Mateyev).
Simeon Dimitrov Popov — Age 43
Completed his studies in Frankfurt; married to a Swiss national (Elza Walter Gisler). After completing secondary school in 1922, he was sent on a pastoral internship in Popovo, and the following year became assistant to Pastor Iv. Todorov in Veliko Tarnovo. At the Annual Conference in the autumn of 1924 he was sent to study theology at the seminary in Frankfurt am Main, Germany (1924–1927). After his return he served five years in Svishtov, and in 1932 was appointed senior pastor of the EMC in Lovech for a further five years. In 1937 he succeeded Vasil as pastor in the Czech village of Voyvodovo, remaining there until the moment of his arrest in 1949, when he was charged with espionage. He was sentenced to seven years and six months’ imprisonment, of which he served five years and four months in the prisons of Sofia, Varna, and Belene. He was released in 1955, and in 1958 assumed the pastorate of the EMC ‘Dr. Long’ in Sofia. His success was such that the authorities compelled him to relocate to Svoge, from where he commuted to services, until he was ultimately banned even from entering Sofia. In 1960 he assumed leadership of the EMC in Shumen, where he devoted himself to the meticulous collection and preservation of the Methodist archive.
In a letter from Zyapkov to the Methodist Church historian Samuil Vasilev, dated 25 March 1971, we read: ‘Is the bishop not interested in your work? Could Simeon Popov not help you in gathering materials? In my view he is the best worker in the Methodist Church today!’
Despite his advanced age, in Shumen Pastor Popov participated in a network for the clandestine distribution of Bibles. During one of the searches of his home, the State Security Service confiscated 4,000 Bibles, and he himself was arrested. During Johnnie Noer’s visit in 1989, Shumen was placed under blockade, and Pastor Simeon Popov — despite his advanced years — spent the day at the local militia headquarters in order to prevent the expulsion of the foreign visitors to Romania. Pastor Popov was known among the faithful of that era for his letter ministry, dispatching messages to over 1,200 believers throughout the country. Initially these were typed on a typewriter and later reproduced on a Roneograph. The Ministry of the Interior confiscated all the machines, but workers at the BCP party bookshop in Svoge secretly printed the messages at night. His book Why I Believe in God, begun in 1940, was printed in the Netherlands in 1982. In 1992 it received official approval and a recommendation from the Ministry of Education and Culture as a teaching aid for the optional study of religious instruction.
Gavril Tsvetanov Tsvetanov — Age 47
Completed his studies in Constantinople and at the episcopal seminary in Rome; residing in Sofia, 28 ‘Skobelev’ Street. His father, Pastor Tsvetan Tsvetanov, officiated at the wedding of Georgi Dimitrov and Lyuba Ivoshevich in Pleven on 20 October 1906. Gavril was born the same year in Sevlievo. He served as an associate professor at the Faculty of Economic and Social Sciences, and as secretary of the Supreme Council of the OETs and personal English-language correspondent of Yanko Ivanov. In 1920 he was sent on a scholarship to a theological school in Manchester. In 1923 he was sent to Italy to study theology, and contributed to the fascist newspaper Popolo d’Italia. In 1925 he was transferred again to study in Manchester. He attended the Methodist conference of 1938 in Pleven, together with Dr. John L. Newlson, chief secretary of the Board in America, Dr. Ralph Diffendorfer, and Alphonse Prache.
Before 9 September 1944, he was head of the ‘Cultural Section’ of the Bulgarian Workers’ Union (BRS). From August 1943 until 9 September 1944 he was mobilised at the Army Staff ‘Reconnaissance Company’ under Captain Armyanov. He organised a clandestine radio transmitter which, at Tsvetanov’s insistence, broadcast fascist content for a year and several months. He was a contributor to the newspaper Vecher, with records indicating that he served British intelligence. Detained for his fascist activities and sent to a corrective labour camp from 20 March to 20 October 1945. After 9 September he accompanied Yanko Ivanov to the American Mission, where Captain Andrénond received them, and served as interpreter for the conversation between the two. They also visited Strong, Reiminkel, and Cyril Black. During the visits of Bishop Dr. Paul Garber, Tsvetanov served as interpreter and transmitted informational data about Bulgaria, which were subsequently published in the foreign press, thereby exposing Bulgaria to the outside world. At the end of 1947 the chairman of the World Council of Churches, Cockburn, organised a conference with the pastors at the Hotel Bulgaria, with Gavril Tsvetanov serving as interpreter. For maintaining contacts with legionaries after 9 September, Tsvetanov was detained at the beginning of 1948 but released on 29 March 1948 owing to insufficient evidence. The foregoing is attested to by the testimonies of Yanko Ivanov and Haralan Popov, as well as by the data contained in file No. 155382.
Tsvetan Alexandrov Litov
Completed his studies in Frankfurt; currently specialising in America. He served as pastor of the ‘Dr. Long’ church in Sofia, which during his tenure numbered over 280 members. In 1934 he was one of only thirteen pastors in Bulgaria to receive a written certificate from the Ministry. As secretary of the OETs he participated in the Union of Youth Evangelical Organisations in Bulgaria. According to the confessions from the Pastoral Trials, he was among the first to whom Cyril Black’s petition was transmitted. He was then compelled to gather detailed information about the Sofia garrison and the Pernik–Voluyak railway line. The information was transmitted in 1945 in two tranches — to Black and to Melony Turner. He was the only one to escape conviction, being in the United States at the time and not returning to Bulgaria. Upon his departure he was replaced by Pastor Zdravko Bezlov.
Iliya Yakov Iliev — Age 38
Born in 1907 in Kalugerovo (near Pravets, above the Borovets fortress). He attended the ecclesiastical school of the Cherepish Monastery but could not sing. He completed secondary school in Botevgrad and established contact with the pastor of the EMC in Botevgrad, Spas Miloshev. He was appointed as a trainee pastor in 1929 under Pastor Alexander Georgiev in Pleven. The following year, at the Annual Conference of 1930, he was sent to the seminary in Frankfurt, where he studied alongside Popov, Iliev, Yotov, Litov, Kishishyan, Yanko Ivanov, and Georgi Sivriev. The rector, Dr. Mele, personally covered half of the tuition fee. He served with the Missionary Tent throughout Germany. At the 37th Annual Conference of the EMEC in Varna he was appointed by Bishop Nilsen to Hotantsa, where he worked for eleven years until the end of the Second World War.
His wife, Marta Müller — a German national — was to have been sent together with other Germans to a camp in the USSR, but the entire village interceded on her behalf, and the family relocated to the EMC in Lovech. At the end of August 1948 the American Girls’ School in Lovech was closed, and Pastor Iliev was charged and convicted at the second closed Pastoral Trial to three years’ imprisonment. He served his sentence in the Sofia Central Prison, while during the same period his son developed pulmonary complications. In August 1951 Pastor Iliev was released, but the church hall had been taken over as a warehouse by the Pharmaceutical Directorate — Lovech. From 1953 he conducted Sunday services simultaneously in the Methodist and Baptist churches in Ruse. Two years later the entire family settled in that riverside city, where he remained until his death in 1997.
Marin Dobrev Gluharov
Completed his studies at the theological seminary in Frankfurt. Born in Yablanitsa (1909). He graduated from the Theological Seminary in Sofia, and subsequently continued his studies in ‘Finance and Accounting’ at the Free University. In 1932 he received a scholarship for theological education in Germany. Upon his graduation in 1935 he assumed leadership of the Evangelical Methodist Church (EMC) in Vidin, and the following year was transferred to Sevlievo, where he served for four years. During the Second World War he fulfilled his pastoral duties in Ihtiman. During the Pastoral Trials he was sentenced to six years’ imprisonment, which he served in the labour camps at Belene and Bobov Dol. Because of his refusal to give testimony he could not be definitively convicted, but as a result of the inquisitions during interrogation and the brutal beatings inflicted upon him, he sustained severe physical injuries, including a fractured spine.
Stefan Bochev describes the condition of Pastor Gluharov, whom he encountered in the camp, in the following terms: ‘He could not stand upright. He dragged himself on his stomach, having fitted his palms with hand-clogs so as not to injure them. He would raise himself slightly on his hands in order to move forward. Yes, they had succeeded in reducing him to the condition of a reptile… crawling with his hand-clogs through the mud of Persin, yet with the gaze of a human being and a spirit worthy of the heights.’
Zdravko Stefanov Bezlov
At the age of twenty-eight, he graduated with distinction from Frankfurt (1943) and was awarded a scholarship for doctoral studies in the United States. Nevertheless, he returned to Bulgaria during the war and, after several months of work in Ruse, assumed leadership of the ‘Dr. Long’ church in Sofia. With the advent of the Communist regime, Pastor Bezlov was removed from the pulpit and began his path of martyrdom — passing through the cells of the State Security Service, labour camps, coal mines, and stone quarries. He was sentenced to fifteen years’ hard imprisonment, a fine of 250,000 leva, and deprivation of civil rights for fifteen years.
Despite all of this, he remained one of the few who refused to plead guilty — alongside Ivan Angelov, Hristo Neychev, Dimitar Hristov, and Zdravko Bezlov himself. He once confided: ‘I am in the camp, and do you know — when you fail to meet the quota, apart from being beaten with a cudgel, what it feels like to sleep in a pit full of mud.’ After thirteen and a half years Pastor Bezlov was released, but the authorities continued to persecute him as a former political prisoner. After 1989, already half-paralysed, he organised the restoration of the Methodist Church in Bulgaria and the ‘Dr. Long’ church. In 1992 the World Methodist Council awarded him its Peace Prize. The entire sum of the award he donated to the Organ Fund of the ‘Dr. Long’ church.
Nikola Mikhailov Naumov
Completed his studies in Hamburg, Germany. From 1922 a member of the editorial committee of the quarterly publication of the Evangelical Baptist Churches of Bulgaria (SEBC), together with Vidolov and Zashev. According to the confessions: ‘Mikhailov [i.e., the defendant Pastor Nikola M. Naumov — ed.] was also interested in the course of the war. I would communicate all information to him. Mikhailov would pass it on to the Americans… Mikhailov travelled throughout the provinces on church business.’
According to the indictment: ‘In 1938, the Baptist pastor Carl Filbrand — a long-standing major agent of American and German intelligence with several years’ experience in subversive work in the USSR, of German origin from Russia, residing in Vienna — convened a conference with Baptist pastors in Bulgaria at which he assigned them the very concrete task of propagating German influence in the country and gathering information of a political, economic, and military character. He organised an extensive agent network from all Baptist pastors, appointing as residents the pastors: Ivan Angelov, Georgi Vasov, and Nikola Mikhailov. This apparatus began to function immediately, with information being transmitted to Filbrand and Mikhailov (according to the testimony of N. Mikhailov, G. Chernev, and G. Vasov).’
Ivan Petrov Igov
Completed his studies in Hamburg, Germany. Born in Berkovitsa (1905); Baptist pastor residing in Sofia, 17 ’20 April’ Street. Sentenced and sent to Belene on account of his faith, where he spent six long years. His family was interned in Golintsi, without the right to return to Sofia. After his release, Igov served as pastor in Lom, and later in Varna and Plovdiv.
According to the indictment: ‘In 1925 he was recruited by Filbrand. He completed his studies at a theological seminary in Hamburg, Germany, a classmate of Georgi Vasov. In 1938 he participated in the re-recruitment of all Baptist pastors by Loishner, at which point he was designated as one of four individuals to establish the intelligence apparatus among pastors of the Baptist denomination. Until the war he received his support directly from America. In 1938 he returned to Sofia with Pavlov Schmidt, who was in Bulgaria at that time together with Filbrand. After 9 September, he attended all gatherings of the pastors, congresses, and so forth. He also attended the unofficial gatherings of the pastors, at which decisions were taken against the Fatherland Front authority. At the Baptist church congress of September 1947, Igov stood as a candidate for chairman of the Baptist Union. Mikhailov opposed him. Igov then rose and declared before everyone that he was leaving the Baptist Union congress and going to report Mikhailov to the authorities and reveal who Mikhailov was and what he was doing. Engineer Milan Kostov intervened and compelled them to reconcile. He received money from the illegally exchanged dollars. Igov was a collaborator of Georgi Vasov, to whom he transmitted his information. He was a travelling pastor among the Baptist churches. From 1931 to 1939 he visited Hungary, twice Germany, four times Switzerland, and Sweden (according to the testimony of Mikhailov, Zahari Raychev, Dimitar Mateyev, and G. Vasov).’
Vasil Georgiev Angelov
Completed his studies in America. Born in Stob (1909). On the recommendation of Pastor Pavel Mishkov, he completed his studies at Wheaton College in Chicago and the Theological Seminary in Dallas. He did not return to Bulgaria until 1938, where for a brief period he served as pastor in Yambol, Haskovo, and Samokov. From 1946 to 1948 he published the magazine Good News (Dobri Vesti).
According to the indictment: ‘[The pastors] gathered and transmitted to their foreign missions numerous items of information of a military, political, and economic character — such as the production of the military factories in Kazanlak and the aircraft factory and their output; the production of Koralovag; the production of the Mülhaupt factory in Ruse; the production of the Pirin mines; the mobilisation of conscripts; the movement of military units; traffic on the Danube and at Danubian ports; the mood of the popular masses; etc. (according to the testimony of N. Mikhailov, Georgi Vasov, Dimitar Mateyev, Zahari Raychev, Georgi Chernev, and Haralan Popov).’
Atanas Andonov Georgiev — Age 52
Completed his studies in Hamburg. Born in Sumitsa (1897); residing in Ruse, 35 ‘G. Dimitrov’ Street. Baptist pastor, recruited in 1925.
According to the indictment: ‘In 1937 re-recruited by Filbrand, and in 1938 recruited by Loishner. He supplied information of an economic, political, and military character to N. Mikhailov. After 9 September he continued his intelligence activities, again transmitting information to Mikhailov. According to the old and new construction of the intelligence apparatus, he was required to transmit his information to Nikola Mikhailov. From the information sent to us from Ruse regarding him, it is evident that he was hostile in his disposition towards the Fatherland Front authority. This is most clearly apparent from the sermons he delivered. He received from abroad for the year 1947 six parcels — 42 kg; for 1948 — one parcel of 8.5 kg; and for the period 1947–48 received from Mikhailov from the illegally exchanged dollars the sum of 324,000 leva.’
Mitko Mateyev Dimitrov — Age 39
Completed his studies in Germany.
According to the indictment: ‘Every Evangelical pastor who receives his support from abroad (and all of them do) was obliged to send reports to his foreign mission on his work and the conditions under which he operated — reports in which he was required to provide as extensive information as possible on the mood of the people among whom he worked, on economic life, on the political mood of the masses, etc. — reports constituting in essence intelligence despatches on the political and economic life of the country (according to the testimony of N. Mikhailov, Yanko Ivanov, Georgi Chernev, Georgi Vasov, Dimitar Mateyev, Haralan Popov, and others).’
Exiled to Varna, Persin, and Belene. After Belene he worked at Elhima. He was denounced by someone close to him for planning to emigrate. He was sentenced to a further seven years of hard imprisonment. He subsequently emigrated to Canada, where he published a book about the years spent in prison, entitled Upon Thy Word I Have Placed My Trust.
Translated from the list with pastors from the document above:
LIST OF BULGARIAN EVANGELICAL PASTORS WHO COMPLETED THEIR EDUCATION ABROAD
State Security Service Memorandum, 1948
Archival Reference: 155/3/177
Editorial note: The following is a complete transcription and translation of the archival document photographed at pastir.org. Text underlined in the original manuscript is rendered with underline formatting below. A handwritten annotation reading ‘до тук’ (‘to here’) appears at the foot of the original page, indicating the end of the handwritten portion of the document. Checkmarks (✓) visible in the original against certain entries are noted in brackets. The preamble and closing summary are translated verbatim from the Bulgarian.
Preamble (verbatim translation): ‘In order not to speak in generalities and to substantiate the foregoing, I find it necessary to append a list of the names of the pastors who completed their education in America or in some other foreign country, who, in addition to their religious fanaticism, have unquestionably acquired the character and mentality of the “secular” Western democracies. For example:’
THE LIST
- Vasil Georgiev Zyapkov — age 47. Completed advanced theological studies in Manchester and New York.
- Lambri Marinov Mishkov — age 40. Completed his studies at the theological seminary in Princeton, USA.
- Simeon Petrov Iliev — age 37. Completed his studies at a theological seminary in Switzerland.
- Konstantin Stoyanov Marvakov — age 55. Completed his studies at a seminary in Austria.
- Kiril Yotov Vladov — age 43. Completed his studies in Frankfurt am Main.
- Kostadin Spasov Bozovayski — age 35. Completed his studies in London — Seminary.
- Krum Georgiev Bumbakov — age 43. Completed his studies at a seminary in Austria.
- Sarkis Bedros Manukyan. Completed his studies in Kingston, Canada.
- Pavel Hristov Nikolov — age 49. Completed advanced theological education in Oxford, England.
- Nikola Borisov Dimitrov — age 42. Completed his studies at a seminary in Bangor, USA.
- Yosif Isakov Danailov — age 49. Completed his studies in Austria and England.
- Atanas Angelov Kremenliev — age 37. Completed his studies at a seminary in the USA.
- Georgi Nikolov Chernev — age 45. Completed his studies in Danzig and London.
- Emanuil Stoyanov Manolov — age 49. Completed his studies in Danzig and London.
- Boris Ivanov Kuzmanov. Completed his studies in Krichona — Switzerland.
- Yoncho Nikolov Dryanov — age 42. Completed his studies in Danzig — Germany.
- Haralan Ivanov Popov — age 47. Completed his studies in Danzig and London.
- Gruy Iliev Kuzmanov — age 54. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Ivan Zerev Angelinov — age 37. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Diko Dimitrov Mavrudaev — age 42. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Yosif Georgiev Kokonchev — age 38. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Enyu Iliev Tsonev — age 39. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Nikola Stefanov Stoyanov — age 40. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Eduard Agop Kuriyan — age 34. Completed his studies in Danzig and London.
- Todor Stoykov Godjorov — age 41. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Ivan Stoychev Ivanov — age 40. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Ladin Ivanov Popov — age 34. Completed his studies in Danzig and London.
- Ivan Mitev Yalamov — age 36. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Stoicho Dimitrov Kupenov — age 38. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Nikola Harlamiev Tsenkov — age 41. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Yanko Nikolov Ivanov — age 47. Completed his studies in Frankfurt am Main.
- Vasil Marinov Popov — age 45. Completed his studies in Krichona, Switzerland.
- Simeon Dimitrov Popov — age 43. Completed his studies in Frankfurt am Main.
- Gavril Tsvetanov Tsvetanov — age 41. Completed his studies in Manchester and at the episcopal academy in Rome.
- Tsvetan Alexandrov Litov. Completed his studies in Frankfurt; currently specialising in America.
- Iliya Yakov Iliev — age 38. Completed his studies in Frankfurt am Main.
- Marin Dobrev Gluharov. Completed his studies at the theological seminary in Frankfurt am Main.
- Zdravko Stefanov Bezlov — age 28. Completed his studies in Frankfurt am Main.
- Nikola Mikhailov Naumov — age 49. Completed his studies in Hamburg — Germany.
- Ivan Petrov Igov — age 48. Completed his studies in Hamburg — Germany.
- Vasil Georgiev Angelov — age 39. Completed his studies in northern America.
- Atanas Andonov Georgiev — age 52. Completed his studies in Hamburg — Germany.
- Mitko Mateyev Dimitrov — age 39. Completed his studies in Wilenest — Germany.
Closing Summary (verbatim translation):
‘In addition to the above-mentioned, a further 7 individuals completed their studies in various countries. Thus, of a total of 115 pastors throughout the entire country, half completed their education abroad — who are accordingly first-class and qualified foreign agents.’
Handwritten annotation at foot of document: ‘до тук’ (‘to here’) — indicating the end of the handwritten portion of the memorandum.
Translator’s Notes
- Entries marked with ✓ in the original document are reproduced here with that symbol. The significance of the checkmarks is not explained in the source; they may denote individuals already arrested, already under surveillance, or prioritised for prosecution at the time of the document’s compilation.
- Underlined text in the original (indicating institutions and cities) is preserved with underline formatting.
- ‘Danzig’ refers to the Free Theological Academy (Freie Theologische Akademie) in the Free City of Danzig (present-day Gdańsk, Poland), which served as the principal training institution for Bulgarian Pentecostal pastors throughout the 1930s.
- ‘Krichona’ refers to the St. Chrischona Pilgrim Mission (Pilgermission St. Chrischona) near Basel, a pietist missionary training institution.
- ‘Wilenest — Germany’ in entry 43 is likely a transcription error or phonetic rendering in the original Bulgarian; the precise institution has not been identified.
- The document bears the archival reference 155/3/177 and is reproduced at pastir.org. The preamble and closing summary are in typewritten Bulgarian; the annotation ‘до тук’ (‘to here’) is handwritten.
- The assertion that foreign-educated pastors are ‘first-class and qualified foreign agents’ represents the operative ideological premise of the 1948–1949 Pastoral Trials — that Western theological education was itself evidence of intelligence recruitment.
THE PASTORAL TRIALS ELIMINATE THE AVANTGUARD OF BULGARIAN EVANGELICALS FOR AN ENTIRE GENERATION (PART 1)
THE PASTORAL TRIALS ELIMINATE THE AVANT-GARDE OF BULGARIAN EVANGELICALS, BEHEADING IT FOR AN ENTIRE GENERATION (Part 1)
[Editorial note: The following text is translated from the Bulgarian original. The documents contain memorandums, archival records, State Security (Darzhavna Sigurnost / DS) interrogation files, survivor testimonies, and secondary scholarly sources. Bracketed insertions in the original are the author’s. Handwritten portions of the source document are noted where applicable. Archival reference: pp. 155–177.]
Archival Preamble
To Comrade [name illegible in manuscript]. Here! … (p. 1), 155–3pp–177
Comrade Director — in order not to speak in generalities [regarding the arrest warrants and the public punitive proceedings against them as enemies of the Party and the people] and to substantiate my claim, I shall append a list of the names of pastors who completed their education in America or in another foreign country. In addition to their religious fanaticism, they have unquestionably acquired the character and mentality of the ‘secular’ Western democracies. For example…
Vasil Georgiev Zyapkov — Age 47
Completed advanced theological studies in Manchester and New York. Interrogated by the State Security Service and driven nearly to madness before he ‘confessed’ to the creation of a spy network that had sabotaged the ‘people’s authority’ and harmed ‘fraternal relations with the Soviet Union,’ thereby becoming a ‘servant and assistant of the interests of England and the United States.’ According to the scenario written in Sofia and Moscow along the model of [Andrei] Vyshinsky, it was Zyapkov who was cast as the ‘sinister mastermind’ of the entire conspiracy (the so-called ‘espionage centre’). He was initially isolated and subjected to pressure to renounce his beliefs, subsequently blackmailed, and finally arrested in early November 1948. For nearly three months he was interrogated in the cells of the State Security Service together with the other pastors, all of whom were compelled to confess to everything imputed to them.
Zyapkov completed his studies in literature (not theology, as was erroneously believed) in Manchester. He maintained an extensive network of friends in England and America, including family ties, which the State Security Service deemed dangerous and potentially harmful to Bulgaria. At the insistence of Dimitar Furnadzhiev (1867–1944), he succeeded the latter as religious representative of the United Evangelical Churches (OETs). Zyapkov served as pastor of the central Methodist church ‘Dr. Long.’ He was sent by the Congregationalists to their Union Theological Seminary, where he most likely completed his master’s degree in 1932. His participation in the Bulgarian delegation to the Paris Peace Conference in the summer of 1946 was subsequently used as an argument at trial that he had established espionage contacts.
Zyapkov’s testimony (under the code name “ЧЕРВЕЙ” / “WORM”) reveals the interrogation techniques employed. Reading the document — written in 1951 and entitled My Confession Regarding the Trial, ostensibly submitted as a letter to the Prime Minister requesting a review of the case — one discovers numerous parallels with the memoirs of Haralan Popov (another of the convicted clergymen). The account of the tortures (more psychological than physical in nature) and the manner in which false confessions were ultimately extracted is replicated in both cases.
Zyapkov wrote that he was rarely beaten (‘only once was my head smashed against the concrete wall’), but that the most tormenting aspects were the ceaseless threats of a death sentence and the blackmailing carried out through his family (e.g., ‘your daughter will become a prostitute’). For weeks he was compelled to write confessions until 11:00 p.m., and was then woken shortly after midnight for lengthy nocturnal interrogations. He was threatened that the sentence would be carried out by execution in the cell. Towards the end of these exhausting interrogations, the prisoners began to experience hallucinations. A new narrative was fabricated in which Floyd Black, the director of the American College in Sofia, and his son Cyril Black were presented as the chief conspirators. The strategic intelligence that Zyapkov had allegedly gathered and transmitted to his purported handlers consisted of the numbers and names of Soviet ships docked in the port of Varna — information he had memorised in order not to compromise his confessions during the trial.
Note: Spas Ivanov Asenov, from the village of Malko Belovo, was sentenced to death in the trial of the ‘Free Warriors’ (anarchists). He shared a cell with Pastor Vasil Zyapkov and stated that he was a non-believer. However, when they led him out to be executed, he said: ‘Farewell! We shall meet above, before God’s gates!’
Together with Zyapkov, all of the more influential spiritual leaders were arrested. The agonising investigation was conducted by interrogators who had honed their inquisitorial cruelty through the interrogations of opposition figures. After months of physical and psychological torment, entirely innocent church workers were reduced to clay figures who, in the satanic tradition of the State Security Service, made their ‘confessions’ to having committed ‘espionage, slander against the people’s authority, and preparations for subversive activities.’ For a full three years after his sentencing, Zyapkov barely managed to return to normal behaviour.
Lambri Marinov Mishkov — Age 40
Completed his studies at the Princeton Theological Seminary. According to K. Grozev, he also studied chemistry at the University of Chicago and subsequently theology at Harvard, and worked towards a doctorate at Cambridge during the 1930s, at which point he was obliged to return to Bulgaria to be at his mother’s bedside in her final days. It is improbable, though not impossible, that the young Mishkov managed to complete so many disparate and numerous programmes of study within the span of approximately twenty years. It is equally possible that his name has been confused with that of his namesake Pavel Mishkov, who did indeed graduate from Chicago. The investigative file records only that he received his theological education at Princeton.
Despite being a clergyman, in 1946 he was invited to serve as an adjunct associate professor of philosophy at the newly founded University of Plovdiv. It was at this time that he published his book
Philosophy of Faith — one of the finest philosophical studies of the philosophy of religion ever written in the Bulgarian language.
- Grozev describes him as an ‘old uncle’ — a close friend of his grandfather. He spoke excellent English, would recount stories of Lincoln, and explained the meaning of the expression ‘monkey business,’ as well as one of the proposed etymologies of the well-known acronym ‘OK.’ Mishkov underwent the same interrogations and tortures as the others, but never confessed to having contacted the American Embassy or received money — an accusation that was ultimately dropped, resulting in a reduced sentence. Under duress, he ‘confessed’ to having transmitted information about the quantity of nails produced (in kilograms) at a factory in Plovdiv, as well as the road map from Plovdiv to Peshtera — a map that could in fact have been purchased at any bookshop. It was precisely this map, the subject of interrogations, that had allegedly been passed by Zyapkov to Cyrus Black, who was also considered part of the supposed spy network.
As with all those convicted, his children were barred from universities, forced to take low-paid manual work, and were permitted to visit their father only once every six months or even less frequently. The elder Grozev repeatedly took Mishkov’s children to prison visits when their mother was ill and the next permitted meeting was still months away.
Simeon Petrov Iliev — Age 37
Completed his studies at the American Scientific Theological School as well as a theological seminary in Switzerland. Following the departure of Kr. Stoyanov, at the initiative of the youth fellowship of the church, he was invited to assume the pastoral ministry in Asenovgrad (then known as Stanimaka). During his pastoral tenure, the church experienced a period of growth. He succeeded in uniting several other Evangelical fellowships, which led to a significant expansion of the church community. Despite the hardships of the post-war years, the new (modern) church building was constructed during this period. Furthermore, the headquarters of the Women’s Missionary Union of the Southern Evangelical Churches was established in Asenovgrad, further strengthening the organisational structure of the Protestant community in the region. Simeon Iliev served as pastor until 1949, when he was arrested and tried on charges of espionage.
Konstantin Stoyanov Marvakov — Age 55
Completed his studies at a theological seminary in Austria. Served as pastor of the church in Yakoruda. He was subjected to repression during the Communist campaign against religious communities in Bulgaria. Accused of espionage, the specific charges including the transmission of information concerning the annual harvest in the Chirpan region, as well as the production capacity of the oil-press in the village of Marichleri. These charges were formulated within the same framework as the case against Lambri Mishkov, with all alleged evidence reduced to a single page in the investigative file. This underscores the characteristic method of fabricating accusations in this period, whereby insignificant or publicly available information was interpreted as a threat to state security, in order to justify politically motivated repression.
Kiril Yotov Vladov — Age 43
Completed his studies in Frankfurt. Attended the men’s gymnasium in Pleven, and was subsequently recruited as an assistant pastor at the Sofia Methodist church ‘Dr. Long,’ where he worked and developed under the guidance of Pastor Vasil Zyapkov. He completed his theological education alongside future pastors Litov and Sivriev at the Methodist Seminary in Frankfurt, where he met his future wife, Maria Schmeissner, whom he married in 1931. In 1939 he was transferred to the Pleven Methodist church, replacing Pastor Yanko Ivanov.
As early as 10 September 1944, Soviet soldiers were quartered in the pastor’s residence. Two days later, a group of armed civilians burst into the house and conducted a search, their leader declaring: ‘You are under arrest! Take only the barest essentials — a little food and clothing — for we are taking you to Pleven prison.’ Pastor Yotov asked: ‘May we pray before you take us to prison?’ After the brief prayer, it was as though everything had changed. The leader of the arresting party began to calm those under arrest. The children were taken in by Miss Mara Gaytandzhieva and later sent to the village of Burkach to their grandmother. Before long, Maria returned, but completely changed — the time spent in prison remained with her for the rest of her life. Kiril Yotov spent eight months behind bars, enduring brutal torture and beatings.
In 1948 Kiril Yotov was arrested again in connection with the already-commenced Pastoral Trials. As a local prisoner, he was transferred from the Ministry of the Interior in Pazardzhik to Plovdiv, and ultimately to the investigative detention facility in Sofia. He was accused of supplying information concerning the annual harvest in Aprilsko and Tserov, the annual yield of winter crops, and the grape harvest. Beaten with leather belts and whips that tore entire strips of flesh from his back, in order to compel a confession — yet he did not lose his faith or his optimism. The Communists failed to break him and did not include him in the trial, as he was unpredictable and liable to disrupt their pre-arranged scenario. He was ultimately transferred to the ‘Bobov Dol’ labour camp and subsequently sent to Belene. His home was confiscated by the local authorities and his family was forced to relocate to Sofia. His wife Maria Yotova made extraordinary efforts to support the family, but the children were deemed politically unreliable and expelled from all youth organisations.
As no one could send him money from the outside, he acquired a razor, soap, and a rusty blade with which he shaved and cut the hair of his fellow camp inmates at Belene. In the summer of 1953, after five years in camps and prisons, Pastor Kiril Yotov was released. His family scarcely recognised him. At the time of his arrest he had been a healthy man weighing 85 kilograms; after five years he emerged emaciated, barely 48 kilograms — a frail body, but an unbroken spirit and a smile on his face. He recalled with pain the countless worthy individuals who had been oppressed, tortured, and humiliated.
Kostadin Spasov Bozovayski — Age 35
Theologian. Completed his seminary studies in Kassel and London, England. Born on 11 February 1912 in the village of Stob, Dupnitsa region. He served as pastor in Haskovo, following Vatralski, Furnadzhiev, and Gradinakov, and from 1956 served for three years as pastor in Asenovgrad. Until 1959 he was one of the few pastors not yet affected by the regime’s repression. When the Pastoral Trials commenced, Bozovayski was serving as treasurer at the ‘Pirin’ factories in Kardzhali whilst simultaneously serving as pastor of the Congregational church in the city. Upon his arrest, the charge was raised that he was a committed Germanophile, associating exclusively with reactionaries and the German specialists working in Kardzhali. He received various sums from different parts of Bulgaria, as well as numerous parcels from America, where his two brothers resided, with whom he maintained uninterrupted contact. In 1945 he attended the pastoral gathering of the United Evangelical Churches (OETs) in Burgas. He allegedly supplied ‘information regarding the annual production of the Pirin mine, the warehouses in Kardzhali, and tobacco production.’ The information was said to have been written on a typewriter.
Following the trials, already retired, Bozovayski served as chairman of the Congregational Church in Bulgaria and pastor of the mother church at 49 ‘V. Kolarov’ Street. He was repeatedly summoned before the [State] Committee, where Virchev, Totev, and Timotei Mikhailov were proposed to him as deputies. He refused, as they did not belong to the congregational churches, and Mikhailov was not even an ordained pastor. ‘You will ordain him,’ the director Tsvetkov ordered.
The authorities sought a financial audit with the aim of removing the Kulichev brothers on charges of hooliganism, including breaking down the church door with an axe. The Committee attempted to replace Pastor Bozovayski, but the congregation rejected the new appointment. ‘This question will be resolved definitively this year,’ the Party functionaries warned. ‘The leadership and ordinary membership is considerably aged… the church’s capacity for religious influence is rather weak,’ the Committee’s report noted.
Krum Georgiev Bumbanov — Age 43
Completed his studies at a seminary in Austria. Born in the village of Ognyanov (also known as Banya), he served as pastor of the church in Haskovo, following Vatralski, Furnadzhiev, Gradinakov, and Bozovayski. While serving in Yakoruda, he preached together with Angel Kremenliev in Bansko, Eleshnitsa, and Razlog. Brought as a defendant on the charge that he supplied information regarding the annual production of the dairies and the harvest in the Razlog region, as well as the summer crops in the area. His son, Danail Bumbanov, was arrested together with him in the course of the Pastoral Trials.
Sarkis Bedros Manukyan
Completed his studies in Kingston, Canada. His name appeared on the masthead of every issue of the Evangelical newspaper Zornitsa [Dawn].
Pavel Hristov Nikolov — Age 49
Completed advanced theological education at Oxford. Served as pastor of the church in Plovdiv before Zyapkov.
Nikola Borisov Dimitrov — Age 42
Completed his studies at a theological seminary in Bangor (USA — not the University of Bangor in England).
Yosif Isakov Danailov — Age 49
Completed his studies in Austria and England. A widely published Bulgarian man of letters. In 1952 he was the subject of a notice from the Presidium of the National Assembly: ‘Yosif Isakov Danailov, former resident of the city of Sofia, now of unknown address. I hereby notify you that under Enforcement Order No. 2132/1951, issued by the Sofia District Court, you have been sentenced to pay…’
Atanas Angelov Kremenliev — Age 37
Completed his studies at a seminary in the USA. Maintained close ties with Zyapkov and Pastor Isakov. He is mentioned in an explicit directive of the State Security Service: ‘Demonstrate that the defendants will be held accountable solely for their espionage [activities].’ Immediately following the exile of Pastor Trifon Ivanov, sentenced to eight years, Pastor Kremenliev was sent to the camp near Yakoruda with a rather unusual annotation regarding the conversion of Jews to Christianity.

Translated from the list with pastors from the document above:
LIST OF BULGARIAN EVANGELICAL PASTORS WHO COMPLETED THEIR EDUCATION ABROAD
State Security Service Memorandum, 1948
Archival Reference: 155/3/177
Editorial note: The following is a complete transcription and translation of the archival document photographed at pastir.org. Text underlined in the original manuscript is rendered with underline formatting below. A handwritten annotation reading ‘до тук’ (‘to here’) appears at the foot of the original page, indicating the end of the handwritten portion of the document. Checkmarks (✓) visible in the original against certain entries are noted in brackets. The preamble and closing summary are translated verbatim from the Bulgarian.
Preamble (verbatim translation): ‘In order not to speak in generalities and to substantiate the foregoing, I find it necessary to append a list of the names of the pastors who completed their education in America or in some other foreign country, who, in addition to their religious fanaticism, have unquestionably acquired the character and mentality of the “secular” Western democracies. For example:’
THE LIST
- Vasil Georgiev Zyapkov — age 47. Completed advanced theological studies in Manchester and New York.
- Lambri Marinov Mishkov — age 40. Completed his studies at the theological seminary in Princeton, USA.
- Simeon Petrov Iliev — age 37. Completed his studies at a theological seminary in Switzerland.
- Konstantin Stoyanov Marvakov — age 55. Completed his studies at a seminary in Austria.
- Kiril Yotov Vladov — age 43. Completed his studies in Frankfurt am Main.
- Kostadin Spasov Bozovayski — age 35. Completed his studies in London — Seminary.
- Krum Georgiev Bumbakov — age 43. Completed his studies at a seminary in Austria.
- Sarkis Bedros Manukyan. Completed his studies in Kingston, Canada.
- Pavel Hristov Nikolov — age 49. Completed advanced theological education in Oxford, England.
- Nikola Borisov Dimitrov — age 42. Completed his studies at a seminary in Bangor, USA.
- Yosif Isakov Danailov — age 49. Completed his studies in Austria and England.
- Atanas Angelov Kremenliev — age 37. Completed his studies at a seminary in the USA.
- Georgi Nikolov Chernev — age 45. Completed his studies in Danzig and London.
- Emanuil Stoyanov Manolov — age 49. Completed his studies in Danzig and London.
- Boris Ivanov Kuzmanov. Completed his studies in Krichona — Switzerland.
- Yoncho Nikolov Dryanov — age 42. Completed his studies in Danzig — Germany.
- Haralan Ivanov Popov — age 47. Completed his studies in Danzig and London.
- Gruy Iliev Kuzmanov — age 54. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Ivan Zerev Angelinov — age 37. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Diko Dimitrov Mavrudaev — age 42. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Yosif Georgiev Kokonchev — age 38. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Enyu Iliev Tsonev — age 39. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Nikola Stefanov Stoyanov — age 40. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Eduard Agop Kuriyan — age 34. Completed his studies in Danzig and London.
- Todor Stoykov Godjorov — age 41. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Ivan Stoychev Ivanov — age 40. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Ladin Ivanov Popov — age 34. Completed his studies in Danzig and London.
- Ivan Mitev Yalamov — age 36. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Stoicho Dimitrov Kupenov — age 38. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Nikola Harlamiev Tsenkov — age 41. Completed his studies in Danzig.
- Yanko Nikolov Ivanov — age 47. Completed his studies in Frankfurt am Main.
- Vasil Marinov Popov — age 45. Completed his studies in Krichona, Switzerland.
- Simeon Dimitrov Popov — age 43. Completed his studies in Frankfurt am Main.
- Gavril Tsvetanov Tsvetanov — age 41. Completed his studies in Manchester and at the episcopal academy in Rome.
- Tsvetan Alexandrov Litov. Completed his studies in Frankfurt; currently specialising in America.
- Iliya Yakov Iliev — age 38. Completed his studies in Frankfurt am Main.
- Marin Dobrev Gluharov. Completed his studies at the theological seminary in Frankfurt am Main.
- Zdravko Stefanov Bezlov — age 28. Completed his studies in Frankfurt am Main.
- Nikola Mikhailov Naumov — age 49. Completed his studies in Hamburg — Germany.
- Ivan Petrov Igov — age 48. Completed his studies in Hamburg — Germany.
- Vasil Georgiev Angelov — age 39. Completed his studies in northern America.
- Atanas Andonov Georgiev — age 52. Completed his studies in Hamburg — Germany.
- Mitko Mateyev Dimitrov — age 39. Completed his studies in Wilenest — Germany.
Closing Summary (verbatim translation):
‘In addition to the above-mentioned, a further 7 individuals completed their studies in various countries. Thus, of a total of 115 pastors throughout the entire country, half completed their education abroad — who are accordingly first-class and qualified foreign agents.’
Handwritten annotation at foot of document: ‘до тук’ (‘to here’) — indicating the end of the handwritten portion of the memorandum.
Translator’s Notes
- Entries marked with ✓ in the original document are reproduced here with that symbol. The significance of the checkmarks is not explained in the source; they may denote individuals already arrested, already under surveillance, or prioritised for prosecution at the time of the document’s compilation.
- Underlined text in the original (indicating institutions and cities) is preserved with underline formatting.
- ‘Danzig’ refers to the Free Theological Academy (Freie Theologische Akademie) in the Free City of Danzig (present-day Gdańsk, Poland), which served as the principal training institution for Bulgarian Pentecostal pastors throughout the 1930s.
- ‘Krichona’ refers to the St. Chrischona Pilgrim Mission (Pilgermission St. Chrischona) near Basel, a pietist missionary training institution.
- ‘Wilenest — Germany’ in entry 43 is likely a transcription error or phonetic rendering in the original Bulgarian; the precise institution has not been identified.
- The document bears the archival reference 155/3/177 and is reproduced at pastir.org. The preamble and closing summary are in typewritten Bulgarian; the annotation ‘до тук’ (‘to here’) is handwritten.
- The assertion that foreign-educated pastors are ‘first-class and qualified foreign agents’ represents the operative ideological premise of the 1948–1949 Pastoral Trials — that Western theological education was itself evidence of intelligence recruitment.
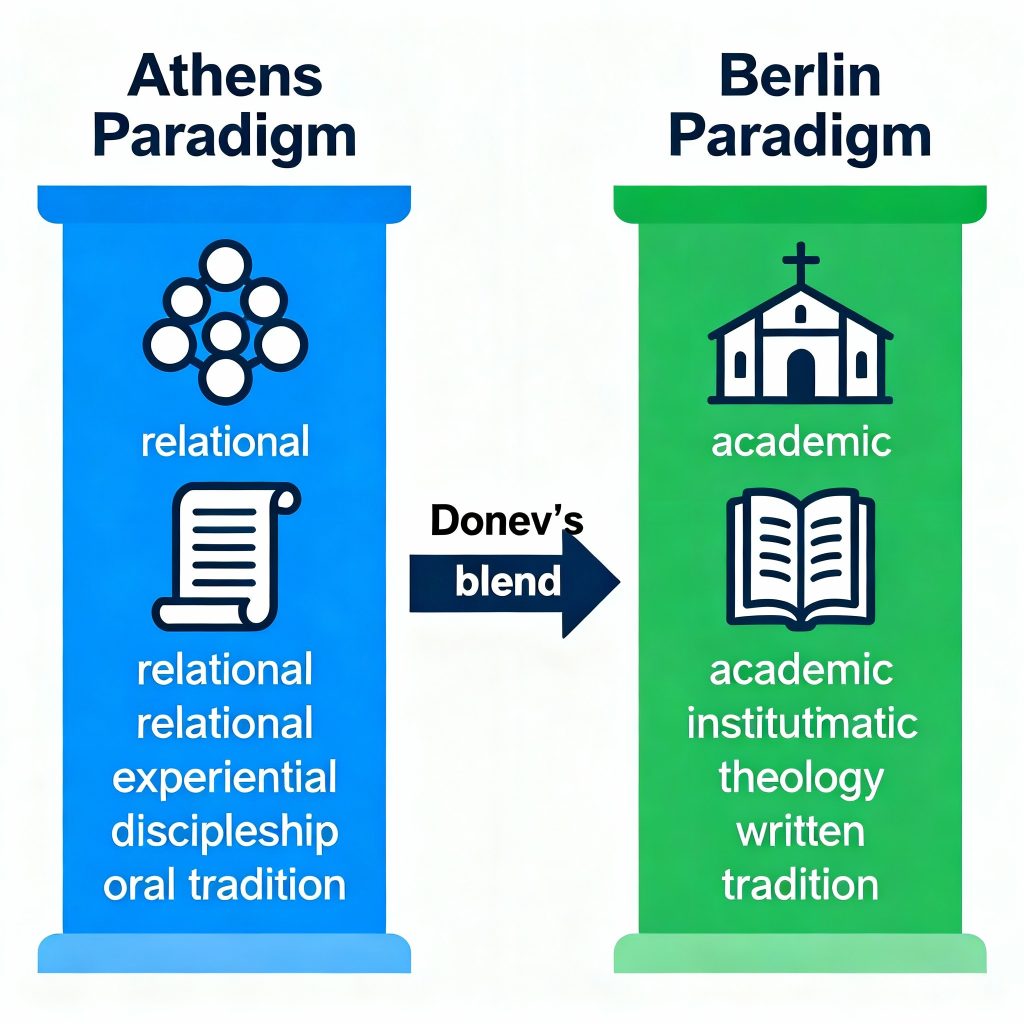
Frameworks and Key Terms by Dr. Dony Donev: Athens vs Berlin Paradigm Shift
Core Theological Frameworks
U.S.H.E.R. Model of Communion
A theological framework coined during the Covid-19 Pandemic in Donev’s Intro to Digital Discipleship course at Lee University. It defines what follows Communion in Christian catechism, identifying five foundational dynamics for disciple growth: Unity, Sanctification, Hope, Ecclesial communion, and Redemptive mission.
Freedom Theology (Theology of Freedom)
Developed through Donev’s research on postcommunist Eastern Europe and the Bulgarian Protestant experience, this framework explores biblical concepts of freedom, liberation from both sin and socio-political oppression, and the church’s transformative mission as a liberator in history. It often appears in his writings as “Feast of Freedom,” drawing connections between national liberation and spiritual renewal.
Primitive Church Restorationist Model
Based in his historical research, Donev advocates for returning to the original practices and structure of the Early (Primitive) Church. This model emphasizes rediscovering authentic spiritual identity, intergenerational faith transmission, and revivalist community rooted in biblical precedent.
These frameworks have had meaningful impact on global Pentecostal studies, digital discipleship, and liberation theology, addressing contemporary challenges in theology, worship, and ecclesial practice.
Effect on Donev’s Models
-
U.S.H.E.R. Model: By anchoring his post-Communion framework in the “Athens” paradigm, Donev prioritizes unity, lived discipleship, and communal mission over purely doctrinal or institutional forms. This perspective shapes the model to valorize shared spiritual experience and relational growth, not just catechetical instruction.
-
Freedom Theology: “Athens” influences Donev’s liberation emphasis by grounding freedom in communal lived reality, while “Berlin” marks the shift toward codifying and structurally analyzing liberation.
-
Primitive Church Restoration: Donev navigates between Athens’ restorationist, dialogical church identity and Berlin’s historical-critical, analytical methodology, advocating an integration that revitalizes spiritual community while acknowledging scholarly insights.
In sum, Donev’s “Athens vs Berlin” usage intentionally blends experiential, relational Christian practice (“Athens”) with disciplined, systematic theology (“Berlin”). This dynamic underlies his frameworks, ensuring they are both deeply incarnational and critically constructive.
2026 Proclamation
Judgment has come to this region!
We were given six years to repent and to change our ways, yet we did not heed the call. We did not hear because we were distracted listening to false reports, following false gods, and walking false paths. Because of this, hardship has come upon us, and greater trials still lie ahead.
What we experienced since the Pandemic has been difficult, but what is coming will resemble the trials of Job. Only those who possess the faith of Job, those who remain steadfast and faithful, will emerge victorious on the other side. Only those who stop complaining and start moving toward conquering the promise will take the land. Only those who believe in the report of the One who brought you out of bondage will receive the blessing of milk and honey.
It does not matter that the enemy is bigger. It does not matter that their army is greater. It does not matter that there is no water or food. He is our provision and will not forsake us even though we feel as if we have been striped down to nothingness.
Stand your ground. Stand tall against demonic works in this region to which we have foolishly opened the door in our weakness. Find your backbone.
Claim your babies, claim your family, claim your promise.
Do not yield to the enemy. Not even one centimeter. Don’t even flinch in fear.
The anxiety and fear you are encountering is a lie from the pits of hell. Rebuke them in the name of Jesus.
BUT if we continue to look the other way, if we continue to welcome sin into our homes and into our sanctuaries, refusing to call sin what it is, then there will be NO hope. There will be no promise of protection. Hypocrisy will not be excused. Grace is not a license for rebellion.
Turning the house of worship into a smoke-and-mirrors spectacle is shameful. The sanctuary must remain holy. It should be a place so sacred, so charged with the presence of God, that one feels conviction even standing upon its floor. A place where no one would dare treat it casually by sipping on their starbucks. No distractions, no performances, no self-promotion.
The church can no longer function as a social club designed to entertain or accommodate the sinful, New Age practices that have crept into our region. Idolatry is wrong. Overlooking that gods have been drowned in our rivers is not acceptable. Bowing in a yoga stance to the gods is wrong.
Playing with magic is wrong. Communicating with the dead is not a game. It is wrong, even if it is your blood dabbling with it. We are to hate the sin, but love the sinner, but this does not mean to turn a blind eye to the manipulation of witchcraft and homosexuality.
Holiness is not optional! It is the standard. Period. Judgment has come to this region. Repent, repent, repent.
ENTER 2026…

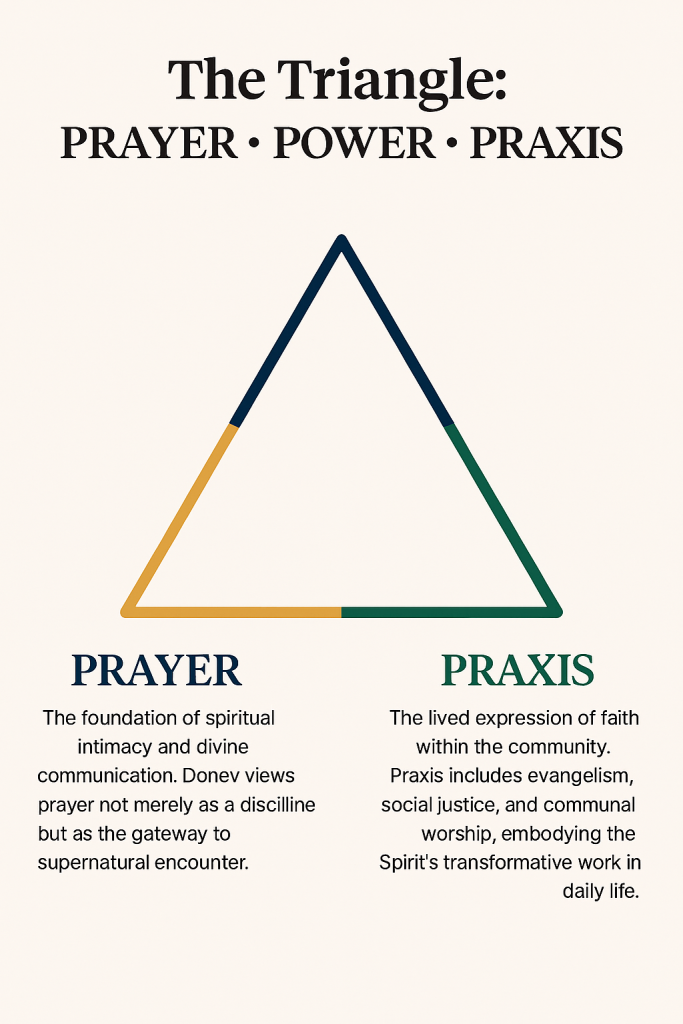
Pentecostal Triangle of Primitive Faith: A Framework of Experience and Restoration
Pentecostal Triangle of Primitive Faith
This is one of Donev’s most recognized frameworks. It emphasizes three core elements of Pentecostal spirituality:
- Prayer: Seen as the starting point of spiritual communication and personal experience with God.
- Power: The manifestation of divine presence through spiritual gifts and supernatural experiences.
- Praxis: The lived expression of faith within the community, reflecting both personal and collective identity.
This triangle encapsulates the holistic nature of Pentecostalism, where theology is deeply rooted in experience rather than abstract doctrine.
Restorationist Theology
Donev builds on the idea of primitivism—a return to the faith and practices of the early church. He critiques Wesleyan frameworks like the quadrilateral (Scripture, tradition, reason, experience) as insufficient for Pentecostal identity, arguing that Pentecostalism goes beyond Wesley to reclaim the apostolic era.
Historical-Theological Contributions
In his book The Unforgotten, Donev explores the theological roots of Pentecostalism in Bulgaria, tracing its development through key figures like Ivan Voronaev and the influence of Azusa Street missionaries. His research highlights:
- Trinitarian theology among early Bulgarian Pentecostals, shaped by Eastern Orthodox pneumatology and Western Pentecostal doctrine.
- Free will theology, emphasizing Armenian views over Calvinist predestination, due to Bulgaria’s Orthodox heritage and missionary influences.
Other Notable Works
- The Life and Ministry of Rev. Ivan Voronaev: A historical-theological study of one of the pioneers of Slavic Pentecostalism.
- Doctrine of the Trinity among Early Bulgarian Pentecostals: Explores how the Trinity was experienced and understood in early Eastern European Pentecostal context
The Pentecostal Triangle of Primitive Faith: A Framework of Experience and Restoration
Introduction
Pentecostal theology has long emphasized the experiential dimension of faith—where divine encounter, spiritual gifts, and communal expression converge. Among the contemporary voices shaping this discourse, Dony K. Donev offers a compelling framework known as the Pentecostal Triangle of Primitive Faith, which seeks to restore the apostolic essence of early Christianity. This essay explores the theological contours of Donev’s model and compares it with other influential Pentecostal and charismatic paradigms.
The Triangle: Prayer, Power, Praxis
At the heart of Donev’s framework lies a triadic structure:
- Prayer: The foundation of spiritual intimacy and divine communication. Donev views prayer not merely as a discipline but as the gateway to supernatural encounter.
- Power: Manifested through the gifts of the Spirit—healing, prophecy, tongues, and miracles. This element reflects the Pentecostal emphasis on dunamis, the Greek term for divine power.
- Praxis: The lived expression of faith within the community. Praxis includes evangelism, social justice, and communal worship, embodying the Spirit’s transformative work in daily life.
This triangle is not hierarchical but interdependent. Prayer leads to power, power fuels praxis, and praxis deepens prayer. Donev’s model thus reflects a restorationist impulse, aiming to recover the vibrancy of the early church as seen in Acts.
Comparison with Wesleyan Quadrilateral
The Wesleyan Quadrilateral—Scripture, tradition, reason, and experience—has historically shaped Methodist and Holiness theology. Pentecostals have often adopted this model, emphasizing experience as a key source of theological reflection.
However, Donev critiques this framework as insufficient for Pentecostal identity. He argues that Pentecostalism is not merely an extension of Wesleyanism but a distinct restoration movement. While Wesley’s model is epistemological, Donev’s triangle is ontological and missional, rooted in being and doing rather than knowing.
Comparison with Classical Pentecostal Theology
Classical Pentecostalism, as shaped by early 20th-century leaders like Charles Parham and William Seymour, emphasized:
- Initial evidence doctrine: Speaking in tongues as proof of Spirit baptism.
- Dispensational eschatology: A belief in imminent rapture and end-times urgency.
- Holiness ethics: A call to moral purity and separation from the world.
Donev’s framework diverges by focusing less on doctrinal distinctives and more on spiritual vitality and historical continuity. His emphasis on praxis aligns with newer Pentecostal movements that prioritize social engagement and global mission.
Comparison with Charismatic Theology
Charismatic theology, especially within mainline and evangelical churches, often emphasizes:
- Renewal within existing traditions
- Broad acceptance of spiritual gifts
- Less emphasis on tongues as initial evidence
Donev’s triangle shares the Charismatic focus on spiritual gifts but retains a Pentecostal distinctiveness through its restorationist lens. He seeks not just renewal but recovery of primitive faith, making his model more radical in its ecclesiological implications.
Eastern European Context and Trinitarian Theology
Donev’s work is also shaped by his Bulgarian heritage. He highlights how early Bulgarian Pentecostals embraced a Trinitarian theology informed by Eastern Orthodox pneumatology. This contrasts with Western Pentecostalism’s often fragmented view of the Spirit.
His emphasis on free will theology—influenced by Arminianism and Orthodox thought—also sets his framework apart from Calvinist-leaning Charismatic circles.
Conclusion
Dony K. Donev’s Pentecostal Triangle of Primitive Faith offers a rich, experiential, and historically grounded model for understanding Pentecostal spirituality. By centering prayer, power, and praxis, Donev reclaims the apostolic fervor of the early church while challenging existing theological paradigms. His framework stands as a bridge between classical Pentecostalism, Charismatic renewal, and Eastern Christian traditions—inviting believers into a deeper, more dynamic walk with the Spirit.
Comparative Insights from Leading Pentecostal Scholars
Gordon Fee: Scripture-Centered Pneumatology
Fee’s scholarship emphasizes the Spirit’s role in New Testament theology, particularly in Pauline writings. While he critiques traditional Pentecostal doctrines like initial evidence, he affirms the Spirit’s transformative presence. Compared to Donev, Fee’s approach is exegetical and text-driven, whereas Donev’s triangle is experiential and restorationist, prioritizing lived encounter over doctrinal precision.
Stanley M. Horton: Doctrinal Clarity and Holiness
Horton’s work, especially in Bible Doctrines, provides a systematic articulation of Pentecostal beliefs, including Spirit baptism and sanctification. His theology is deeply rooted in Assemblies of God tradition. Donev diverges by de-emphasizing denominational boundaries, focusing instead on the primitive church’s egalitarian and Spirit-led ethos.
Craig Keener: Charismatic Experience and Historical Context
Keener bridges academic rigor with charismatic openness, especially in his work on miracles and Acts. His emphasis on historical plausibility and global charismatic phenomena aligns with Donev’s praxis-driven model. However, Keener’s scholarship is more apologetic and evidential, while Donev’s triangle is formational and communal.
Frank Macchia: Spirit Baptism and Trinitarian Theology
Macchia’s theology centers on Spirit baptism as a metaphor for inclusion and transformation, often framed within Trinitarian and sacramental lenses. Donev shares Macchia’s Trinitarian depth, especially in Eastern European contexts, but leans more toward neo-primitivism and ecclesial simplicity.
Vinson Synan: Historical Continuity and Global Pentecostalism
Synan’s historical work traces Pentecostalism’s roots and global expansion. Donev builds on this by reclaiming Eastern European Pentecostal narratives, such as those of Ivan Voronaev. Both emphasize restoration, but Donev’s triangle is more prescriptive, offering a model for future church practice.
Robert Menzies: Missional and Contextual Theology
Menzies focuses on Pentecostal mission and theology in Asian contexts, often challenging Western assumptions. His emphasis on Spirit empowerment for mission resonates with Donev’s praxis element. Yet, Donev’s model is more liturgical and communal, drawing from Orthodox and Puritan influences.
Cecil M. “Mel” Robeck: Ecumenism and Pentecostal Identity
Robeck’s work on Pentecostal ecumenism and global dialogue complements Donev’s inclusive vision. Both advocate for Pentecostal distinctiveness without isolation, though Donev’s triangle is more grassroots and revivalist, aimed at local church transformation.
Implications for Church Practice
Donev’s triangle offers a practical blueprint for churches seeking renewal:
- Prayer ministries that foster intimacy and prophetic intercession.
- Power encounters through healing services and spiritual gift activation.
- Praxis initiatives like community outreach, justice advocacy, and discipleship.
Compared to other scholars, Donev’s model is less academic and more actionable, designed to reignite the apostolic fire in everyday church life.
Dr. Dony K. Donev: Introduction to John 5
-
Focus on a small part of Chapter 5; full chapter will be addressed in another talk.
-
Expository Bible study principle: do not omit what the author intends; understand the context.
-
John’s Gospel narrative in brief:
-
Chapter 1 – Creation and beginning.
-
Chapter 2 – Christ’s first miracle (water to wine).
-
Chapter 3 – Nicodemus and questions of faith.
-
Chapter 4 – Woman at the well.
-
Chapter 5 – Paralytic man (focus of this study).
-
Application: We see ourselves in these stories:
- At the well with the woman.
- With the paralytic, facing sickness or oppression.
- In creation, asking questions about beginnings.
- John’s Gospel speaks to our lives and experiences.
Verse 1: Context & Significance
-
“The Feast of the Jews” = Passover (second recorded Passover Jesus attended).
-
Chronology: Jesus ministered ~3–3.5 years, not four.
-
Johannian phrase: “After these things…” (Greek: meta tauta). Contextually links back to previous events (Samaritan woman, previous miracles).
Verse 2: Present Continuous Action
-
“Now was” vs. “there was” → emphasizes ongoing reality.
-
Location: Sheep Gate, Pool of Bethesda (“House of Mercy”), five porches.
-
Historical significance: gate restored by Nehemiah; miracles happen through preparation and prior work.
-
Water symbolism: continuous in John’s Gospel.
Verse 3: The Multitude at Bethesda
-
People lying on porches: sick, blind, lame, paralyzed, waiting for the stirring of the water.
-
Place functioned like a hospital or hospice, offering mercy but not healing.
-
Importance: highlights the need for action, faith, and not just passive waiting.
Verse 4: Angel’s Stirring of Water
-
Angel stirred water; first to enter after stirring was healed.
-
Greek: “troubling” of water → divine or angelic activity.
-
Step of faith required to enter: miracle is available, but effort is needed.
Verse 5–7: The Paralytic Man
-
Man had been ill for 38 years.
-
His theology: “A man have I none…” → depended on others, not God directly.
-
Lesson: don’t wait on another; God can act directly.
-
Human tendency: self-pity, victim mentality.
-
Jesus asks: “Do you want to be well?” – Highlights awareness, desire for change, and personal responsibility.
Verse 8: Jesus Commands Healing
-
“Rise, take up thy bed and walk.”
-
Immediate healing, resurrection-like command (Greek: anistemi).
-
Significance: ignores self-pity, performs the miracle directly.
-
Steps in healing: man immediately rises, strength restored, carries his bed/stretcher.
-
Application: miracles require obedience and action; prior failures don’t prevent success.
Verse 10–12: Testing by Religious Leaders
-
Sabbath controversy: “It is not lawful to carry thy bed.”
-
Misplaced focus: rules over divine action.
-
Observation: miracle transcends human rules; legalistic thinking may blind people to God’s power.
-
The healed man didn’t initially know who Jesus was → possible to receive miracle without knowing fully, but sustaining it requires knowing God.
Verse 14: Warning Against Sin
-
Jesus instructs: “Sin no more, lest a worse thing come unto thee.”
-
Connection: healing is not just physical but spiritual; continued obedience sustains the miracle.
Key Observations & Theological Lessons
-
The man who had no human helper was found by the Son of Man who created all men.
-
Healing is a believer’s right; Jesus administers it within the covenant of creation, restoring balance to the universe.
-
Miracles point to Christ as the central figure (water symbolism, “man of the hour”).
-
Faith, obedience, and direct encounter with God are crucial.
Practical Applications
-
Everyone can receive a miracle.
-
God makes healing and restoration possible.
-
Personal faith and obedience maintain the miracle in daily life.
-
Step of faith is often required; God provides directly.
365 Daily Thought Stirring Stories from the Field
In 1999, Dony and Kathryn established Cup & Cross Ministries International with a vision for restoration of New Testament theology and praxis. Today they have over 50 years of combined commitment to Kingdom work. This book invites you to spend a few moments each day on the field sharing their experiences of serving as pastors, evangelists, chaplains, consultants, church trainers, researchers, missionaries and educators of His Harvest around the globe.


Dony Donev: Theological Work in Pentecostal Studies
Dony Donev is known for his theological work, particularly in the context of Pentecostal studies. While he may not have a widely recognized catalog of specific terms or frameworks that have achieved broad usage, he has contributed significantly to the academic field through his research and writings.
Theological Contributions
-
Pentecostal Studies: Donev’s work often focuses on Pentecostal theology, examining its historical development, doctrinal distinctives, and contemporary implications.
-
Contextual Theology: He explores how Pentecostal theology interacts with cultural and societal contexts, particularly in Eastern Europe.
-
Pentecostal Hermeneutics: Donev might have contributed to discussions about how Pentecostals interpret the Bible, emphasizing a Spirit-led reading of the Scriptures.
Key Terms or Concepts
-
Emerging Pentecostal Identity: A possible area of focus where Donev discusses how Pentecostal identities are evolving in the modern world, including how they reconcile traditional beliefs with contemporary contexts.
-
Cultural Engagement: A term that may be used to describe his analysis of Pentecostalism’s role in engaging with and transforming culture.
For more specific terms or frameworks coined by Dony Donev, it would be beneficial to consult his published works or academic papers.
Pentecostal primitivism is a concept within Pentecostal theology emphasizing a return to the faith and practices of the early Christian church. Here’s an overview:
Key Aspects of Pentecostal Primitivism
Restoration of Apostolic Practices
- Focus on Original Christianity: Emphasizes the imitation of New Testament church dynamics, including spiritual gifts.
- Spirit-Led Worship: Encourages direct experiences with the Holy Spirit, akin to early church practices.
Doctrinal Simplicity
Primary Framework: The USHER Model of Communion

The U.S.H.E.R. Model of Communion (or USHER Model)
-
Creator: Dony K. Donev, D.Min.
-
Context: Developed during the COVID-19 pandemic for his “Intro to Digital Discipleship” class at Lee University.
-
Core Purpose: To answer the question “What follows communion?” in Christian practice and catechism. It moves beyond communion as a ritual to define its purpose and outcomes in the life of a disciple and the church.
-
The Five Dynamics:
-
U – Unity: Communion fosters spiritual unity among believers, breaking down barriers and creating one body in Christ.
-
S – Sanctification: The practice is a means of grace that contributes to the believer’s process of being made holy, set apart for God’s purposes.
-
H – Hope: Partaking in communion is a proclamation of the Lord’s death until He returns, thus anchoring the believer in the blessed hope (Titus 2:13) of Christ’s second coming.
-
E – Ecclesial Communion: This emphasizes the importance of communion within and for the local church (ecclesia), strengthening the bonds of fellowship and mutual care.
-
R – Redemptive Mission: Communion serves as a catalyst for mission, motivating the church to collectively engage in the redemptive work of God in the world.
-
Other Associated Frameworks and Concepts
Dr. Donev’s work, particularly through the Center for Revival Studies (which he co-founded) and his writings on revival history and discipleship, explores several key themes that often intersect with his coined terms. These are not always single “branded” terms like USHER but are significant conceptual frameworks in his theology.
-
Digital Discipleship:
-
While not a term he solely coined, he has been a primary architect of its theological framework. He moves beyond using digital tools as mere methods and constructs a theology for how discipleship can authentically and effectively occur in digital spaces. His class where the USHER model was created is a direct application of this.
-
-
Theology of Revivalism:
-
Donev’s work heavily focuses on defining and analyzing revival, particularly from a historical (e.g., Balkan, Slavic, and Pentecostal) perspective. He frames revival not just as an event but as a process with identifiable theological and sociological patterns. His book “The Covenant of Peace: God’s Dream for the World” delves into this.
-
-
Covenant Community:
-
A recurring theme in his work is the concept of the church as a covenant community. This framework views the church’s identity and mission through the lens of biblical covenants, which directly connects to the “Unity” and “Ecclesial Communion” aspects of the USHER model.
-
-
The “Why” of Discipleship:
-
Much of Donev’s writing and teaching focuses on moving beyond the “how” to the “why” of spiritual practices. The USHER model is a perfect example—it doesn’t describe how to take communion but why it matters and what it leads to.
-
Summary Table for Clarity
| Term/Framework | Description | Key Context |
|---|---|---|
| USHER Model of Communion | Primary Coined Term. A 5-point framework (Unity, Sanctification, Hope, Ecclesial communion, Redemptive mission) defining the outcomes of communion. | Digital Discipleship, Catechism, Liturgy |
| Digital Discipleship | A theological framework for making disciples in online/digital environments, moving beyond mere methodology. | Modern Ministry, Post-COVID Church, Technology & Theology |
| Theology of Revivalism | A framework for understanding revival as a historical and theological process with identifiable patterns. | Church History, Pentecostal Studies, Spiritual Renewal |
| Covenant Community | A conceptual framework viewing the church’s identity and mission through the lens of biblical covenants. | Ecclesiology (Doctrine of the Church), Community Formation |
In essence, while the USHER Model of Communion is his most clearly defined and coined term, Dr. Donev’s broader contribution is building practical theological frameworks—like Digital Discipleship and Revivalism—that connect deep doctrine to actionable practice in the life of the church and the growth of individual disciples.