Gustavo Gutiérrez’s Mysticism as a Door to Pentecostal Dialogue
Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
Te Movement Toward Mysticism in Gustavo Gutiérrez’s Tought: Is Tis an Open Door
to Pentecostal Dialogue?
Joseph Davis
Associate Professor of Religion, Southeastern University, Lakeland, Florida
Abstract
Over the last few years a distinct shift has occurred within the thought of liberation theology’s most famous proponent, Gustavo Gutiérrez. Specifically, Gutiérrez has ventured into mysticism. With this movement a fascinating question can be posed: Does the incorporation of mysti- cism open up a door for dialogue with Latin America’s other popular theology, Pentecostalism? Conversely, should Pentecostalism reflexively understand itself historically and theologically as a liberating movement of the poor? Placed together, an emphasis on praxis seems to reveal, at minimum, a common starting point. Te methodology of the paper incorporates a detailed historical analysis of Gutiérrez’s position on mysticism and moves to the conclusion that the shift in emphasis opens the door, albeit a small crack, to one of the most exciting opportuni- ties to occur within the history of Christianity: the marriage of Pentecostal spirituality with liberating social action.
Keywords
Gustavo Gutiérrez, liberation theology, mysticism, Pentecostalism
At the 2008 Society for Pentecostal Theology conference, Jürgen Moltmann made a startling statement to commence his talk on the work of “Pentecostals and Liberation Teology.” He said, “I met with Gustavo Gutiérrez in Lima a few years ago, and as we were talking he looked out his window and pointed to the barrios below saying, ‘Out there, it is the Pentecostals who are going into the barrios [to reach the poor].”1 What Gutiérrez meant by the statement was that despite the divide that had separated the two most dominant camps of religious fervor within Latin America, the evidence was clear: it was the
1
Jürgen Moltmann, Statement made at Society for Pentecostal Theology, 15 March 2008, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina.
© Koninklijke Brill NV, Leiden, 2011 DOI: 10.1163/157007411X554668
1
6
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
Pentecostals who were helping the poor. Laden within such a statement are a plethora of both endless possibilities and admittedly speculative projections. In fact, at the onset one must admit that one small statement does not equate to a full-blown theological tour de force. Nor does it mean that the wedding ceremony is about to begin to join these two previously disparate antagonists. What this statement does create, however, is an open door to further scholarly reflection. Tis is particularly true if the aforementioned statement is coupled with perceived changes in Gutiérrez’s stance toward a kindred spirit of Pente- costalism, namely, mysticism. Granted, mysticism is not Pentecostalism and Pentecostalism is not mysticism.2 But it would not be too much to say that there are similarities between the two, and any movement toward the one may have broader ranging implications for the other. Terefore, before venturing further in fruitless conjecture, a number of questions must be answered. First, have there been any changes in Gutiérrez’s theology of liberation that warrant such projections? Tere are some who feel that all talk of change within Gutiér- rez’s theology of liberation is a misunderstanding of his thought.3 Second, what is Gutiérrez’s approach to mysticism? And third, is it possible that praxis itself has created a crack in the door within Gutiérrez’s thought that might integrate two seemingly disparate theologies? Of course, these questions do not stop at Latin America; rather, the prospect of such a provocative fusion has worldwide implications.
Over the past half-century primarily two religious movements have gripped the imaginations and aspirations of the poor in Latin America. Tose two movements are the theology of liberation and the Pentecostal movement.4 Of the two, only liberation theology can be truly said to be indigenous in origin. Pentecostalism is indigenous in another manner; it is the overwhelming choice of the poor in Latin America.5 Daniel Chiquete, commenting on the perceived rise of Protestantism, denied this misunderstanding by retorting that Latin America has not turned Protestant at all; rather, “Latin America has turned
2
Simon Chan has made an interesting case for a structural compatibility between the two. See Simon Chan, “Pentecostal Teology and Christian Spiritual Tradition,” Journal of Pentecostal Teology Supplement Series 21 (2000).
3
One of Gutiérrez’s most recent biographers, James Nickoloff, maintains such a conservative position. See James B. Nickoloff, “A Future for Peru? Gustavo Gutiérrez and the Reasons for His Hope,” Horizons 19 (Spring 1992): 31-43.
4
Te Pentecostal movement originated at the Azusa Street Revival in 1906. Most point to the Medellín Conference in 1968 as the beginning of the liberation theology movement.
5
Laurie Goodstein, “Pentecostal and Charismatic Groups Growing,” New York Times, 6 Octo- ber 2006.
2
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
7
Pentecostal!”6 In his book on Pentecostalism, Allan Anderson confirms this by saying, “Te growth of Pentecostalism in Latin America has been one of the most remarkable stories in the history of Christianity.”7 In fact, a Templeton grant research project confirmed these observations. In terms of the world’s population, two of the top three countries with the largest percentage of Char- ismatics/Pentecostals are in Latin America.8
Interestingly enough, the tie between Pentecostalism and the poor in Latin America is not a local aberration. Te history of Pentecostalism reveals that a disproportionate number of dispossessed and poor are attracted to its message of a God whose Spirit is active and fully invested in the present. Juan Sep- ulveda notes, “From a statistical point of view, Pentecostalism has spread far more in the lower classes of popular sections of Latin American societies” than in the upper or middle classes of society.9 In fact, recent studies confirm not just an interest among the Hispanic poor in the “spiritual” aspects of faith but also a commitment among Hispanic Pentecostals for social change.10 Why? Te answer lies both in Pentecostalism’s derivation and its foundational thesis that God can speak to the common person of any nation, tongue, or tribe. Chiquete notes, “By their very nature the Pentecostals are natural promoters of plurality and inner-cultural contact.”11 In the Azusa Street Revival, one finds the message of a God active in history born among the poor and racially, sexually (gender), and economically dispossessed. From the movement’s inception, Pentecostals were the people “from the other side of the tracks.” Yet, in spite of these humble roots, the exportation of Pentecostalism to Latin America was often viewed with a jaundiced eye among the local religious intelligentsia. Given its origin in the United States, Pentecostalism was sus- pected of being tinged with imperialism.12 As a result, the missions-centered
6
Daniel Chiquete, “Latin American Pentecostalism and Western Modernism: Reflections of a Complex Relationship,” International Review of Mission 92, no. 364 (2003): 38.
7
Allan Anderson, An Introduction to Pentecostalism (Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2004), 63.
8
Tirty-four percent of the population of Brazil and 40 percent of the population of Guate- mala are Pentecostal/Charismatic worshippers. Te Pew Forum, 6 October 2006.
9
Juan Sepulveda, “Future Perspectives for Latin American Pentecostalism,” International Review of Mission 87 (April 1998): 191.
10
Villafane points out that Pentecostals in the Hispanic community in New York City are at the forefront of social concern and outreach. See Eldin Villafane, Te Liberating Spirit: Toward an Hispanic American Pentecostal Social Ethic (Grand Rapids, MI: Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 1993), 110-26.
11
Chiquete, “Latin American Pentecostalism and Western Modernism,” 36.
12
Sepulveda refutes this conception, saying, “Te commonly held accusation that the rapid growth of Latin American Pentecostalism is the result of a sort of conspiracy of the U.S.
3
8
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
Pentecostalism exported to Latin America had the label, “Made in America.” Te label should have read more correctly, “Made among the Poor and Dis- possessed of America.” Here, in Pentecostalism, was a movement that began with the poor and contained in its origins the foundational tenets of breaking down the barriers of social, racial, and gender classifications.
Te early Gutiérrez was clearly one of the students of Latin American theol- ogy who viewed any importation of religion from capitalistic countries with caution. He notes, “Te history of Christianity, too, has been written with a white, Western, bourgeois hand.”13 His primary concern resided in changing the structures of societal oppression, which he called “institutionalized violence.”14 From this starting point, spirituality was seemingly subsumed teleologically under the mandate of effectiveness. Teology itself is formed as “a critical reflection on praxis” as a second step. Gutiérrez affirms this view- point in saying, “From the beginning, the theology of liberation posited that the first act is involvement in the liberation process, and theology came after- ward in a second act.”15 Yet, underneath the definition of praxis is an evalua- tive principle — dissolution of poverty. Gutiérrez notes, “Te criterion mentioned to judge praxis is clearly political effectiveness.”16 As a result of this foundation, the measurement of true spirituality lay within the ethos of social revolution. He says, “We are dealing with two inseparable correlations here and it is important to emphasize this. Te potential of a liberating faith, and the capacities of revolution, are intimately bound together . . . Hence it is impossible to cultivate the one without the other as well, and this is what many find unsettling.”17
Within the criterion of political effectiveness, Gutiérrez also accepted Marx- ist economic theory operationally and coupled it with a heavy reliance upon the social sciences as the proper barometers of societal change. In this, Gutiér- rez believes that Marx’s economic understanding of history is a “scientific understanding of historical reality.” He says:
right-wing to counter the people’s movement and Liberation Teology, has very little basis in the facts.” See Sepulveda, “Future Perspectives for Latin American Pentecostalism,” 190.
13
Gustavo Gutiérrez, Te Power of the Poor in History, trans. Robert Barr (Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books, 1983), 200-201.
14
Gustavo Gutiérrez, A Teology of Liberation: History, Politics, and Salvation, trans. Sister Caridad Inda and John Eagleson (Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books, 1990), xviii.
15
Gutiérrez, Te Power of the Poor in History, 200.
16
Gustavo Gutiérrez, “Notes to a Teology of Liberation,” Teological Studies 31 (1970): 250.
17
Gutiérrez, Te Power of the Poor in History, xx.
4
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
9
Marx deepened and renewed this line of thought in his unique way. But this required what has been called an “epistemological break” (a notion taken from Gaston Bachelard) with previous thought. Te new attitude was expressed clearly in the famous Teses on Feuerbach, in which Marx presented concisely but penetratingly the essential elements of his approach. . . . Basing his thought on these first intuitions, he went on to construct a scientific understanding of historical reality. He analyzed capi- talistic society, in which were found concrete instances of the exploitation of man by his fellows and of one social class by another. Pointing the way toward an era in history when man can live humanly, Marx created categories which allowed for the elabora- tion of a science of history.18
Te early Gutiérrez accented the Marxist aspect in his thought by noting, “Many agree with Sartre that Marxism, as the formal framework of all con- temporary philosophical thought, cannot be superseded.”19 Te accentuating of social and economic liberation led to the misguided perception that the salvation motif in Gutiérrez’s writings was almost exclusively immanistic. Gutiérrez even admitted that
[i]t may seem that we entertain precious little interest in a person’s spiritual attitudes. It could even seem that we disdain qualities of faith or of morality in the poor. We are only seeking to avoid beginning with secondary, derivative considerations in such a way that would confer them with what is primary and basic, creating an interminable number of hair splitting distinctions that in the end only yield ideas devoid of interest and historical impact.20
Given the overt political criterion for evaluating theoretical premises, anyone not involved with immediate political change was viewed axiomatically as part of the problem. Pentecostals fell readily into this category, particularly with a premillennial eschatology as the primary understanding of justice in society. However, the corresponding view from Pentecostals that Gutiérrez’s theology was nothing more than reworked Marxism made the chasm between both diametric. Both assumptions missed the mark in the stereotypical minimiza- tions about the other. Pentecostals misunderstood the theoretical foundations implicit within the ethical imperative of liberation theology, and Gutiérrez minimized the liberating effects of a theology whose historical nexus origi- nated from within the world of the poor.
18
Gutiérrez, A Teology of Liberation, xx. 19
Ibid., 59.
20
Gutiérrez, Te Power of the Poor in History, 95.
5
10
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
Te latter misunderstanding struck at the very heart of the characterizations of each position and proleptically disposed each toward a position on personal religion and, by consequence, on mysticism. Was religion a matter of the indi- vidual before God or was God exclusively in the work to liberate the oppressed? Of course, both realized, at least theoretically, that the question raised is not an either/or question but one of degree, given that humanity is made up of individuals, at least on a certain level. Leaning more to the corporate under- standing of self, Gutiérrez placed the poor and oppressed as the basis from which true spirituality began. He said,
A spiritual experience, we like to think, should be something out beyond the frontiers of human realities as profane and tainted as politics. And yet this is what we strive for here, this is our aim and goal; an encounter with the Lord, not in the poor person who is “isolated and good,” but in the oppressed person. . . . [H]istory, concrete history, is the place where God reveals the mystery of God’s personhood. God’s word comes to us in proportion to our involvement in historical becoming.21
Much of Gutierrez’s approach could easily be ascribed to the overwhelming degradation of poverty and the miniscule attention that the issue had previ- ously received in theological forums. Te problem was that most of Gutiérrez’s socioeconomic presentation gave the impression that personal faith only has value within the liberation process. Consequently, the most personal of spiri- tual evidence, conversion, was also stated in terms of self revelation in the midst of involvement with the poor. Tis, coupled with a perceived dialectical universalism, made God seem more like a Hegelian construct than a savior who was accepted personally.22 Te result was that much of the personal moti- vation for societal change was relegated to filial love as an implicit love for God. In other words, of the two Great Commandments, Gutiérrez’s presenta- tion of liberation theology emphasized the second almost as the sum total of the first and the sole extension of its meaning. Gutiérrez had aimed to link the two by showing how love for the poor was biblically equated with a love for God, which, of course, had plenty of biblical support; however, Gutiérrez’s presentation of love for the poor made love for God axiomatic in that the two were the same. Christ was in the naked, the hungry, and the imprisoned — but seemingly nowhere else. Gutiérrez notes, “And this is precisely why it [spirituality] is not a purely ‘interior,’ private attitude, but a process occurring
21
Ibid., 52.
22
Gutiérrez said, “I was greatly influenced by Hegel in his understanding of history in writing A Teology of Liberation. Personal Interview with Gutiérrez, 5 May 1994.
6
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
11
in the socio-economic, political, and cultural milieu in which we live, and which we ought to transform.”23 Terefore, there was little need to talk about spirituality prior to its implementation in praxis. Te coterminous equation made spirituality seemingly exclusive to one’s neighbor. Anything else was pietistic narcissism.
Something, or more correctly someone, was lacking. To appropriate Martin Buber, the “I” in the “I-Tou relationship” seemed to be unconditionally assumed in the philosophical category of the other presented by Gutiérrez. Te explanation given for this methodology is that theology is a critical reflec- tion on praxis from the viewpoint of the poor. Te flaw in this methodology was that the original application of this definition viewed the poor almost exclusively through a socioeconomic lens. In other words, the poor were defined by a standard that they themselves did not accept. Te poor viewed themselves as more than merely the victims of institutionalized violence. Reli- gion was not an escape from brutality and minimization; it was a full-scale rebellion to negate the denigrating terms of limitation awkwardly placed upon them by their oppressors.
A Shift in Method Is Noticed
In the early 1980s subtle shifts began to occur within Gutiérrez’s thought that revealed a change in his approach to the question of personal spirituality. Pre- viously Gutiérrez had emphasized theology as a critical reflection on praxis accomplished through the prism of sociopolitical analysis. In the early 1980s word began to leak out from Gutiérrez’s summer school sessions that Gutiérrez had begun to change, or at least modify, his approach to liberation theology. Gerhard Hanlon, who had attended the 1982 summer school session, wrote in a journal article:
In its early years liberation theology in Latin America was concerned with analyzing social reality and interpreting the Bible in terms of liberation from social and political oppression. A few years ago interest turned to the study of the popular religiosity of the masses of the oppressed and attempted to see therein values which might contribute to that liberation. Te most recent interest of Latin American theology is spirituality.24
23
Gutiérrez, Te Power of the Poor in History, 53.
24
Gerhard Hanlon, “A Spirituality for Our Times,” Clergy Review (June 1984): 200.
7
12
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
In this article Hanlon suggests that there is a new theme in Gutiérrez’s theol- ogy. Tat theme is the “popular religiosity of the masses.” But is this a different direction for Gutiérrez’s thought? Hanlon seems to think that this is an added emphasis but not necessarily a contrary viewpoint. Others, however, find in this added emphasis a discarding of the older ways of thinking to make way for the new.
One of Gutiérrez’s harshest critics in methodology is fellow liberation theo- logian Juan Luis Segundo. In a lecture given at Regent College in 1983, Segundo made a startling remark about what he perceived as a reversal in Gutiérrez’s thinking. Segundo stated that his old friend and compatriot Gustavo Gutiérrez had abandoned the font of his former thinking. In this lecture Segundo called upon his old companion to return to the philosopher’s stone from which they were both hewn. Tat stone, said Segundo, was the sociopolitical methodology that was liberation theology’s original contribu- tion to the world. But more than this, Segundo maintained that the changes in Gutiérrez’s thought were more than just an added dimension to his thought. Segundo asserted that the changes were so drastic that it did not make sense to talk anymore about a singular continuous train of thought but rather “of at least two types of liberation theology.”25 Along these lines, Segundo sadly con- fessed, “And what is painful to me is that I no longer know whether Gustavo himself would endorse what he said then, or whether he would consider it a mere sin of his youth.”26
In 1989 Arthur McGovern, in his book Liberation Teology and Its Critics, took up some of the same questions raised by both Hanlon and Segundo and reached similar conclusions. McGovern noted, “Te revolutionary excitement has dimmed,” and as a result “Gutiérrez has devoted much of his time and writings to the question of spirituality.”27 Echoing both Hanlon and Segundo again, McGovern also noted that Gutiérrez’s liberation theology had “shifted” from a more sociopolitical agenda to one that now emphasizes more the spiri- tual side. He pointed this out by noting the differences between the two books A Teology of Liberation and We Drink from Our Own Wells. He says, “ A Teol- ogy of Liberation deals almost exclusively with the issue of sociopolitical eman-
25
Juan Luis Segundo, Signs of the Times, trans. Robert R. Barr (Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books, 1993), 67.
26
Ibid., 93.
27
Arthur McGovern, Liberation Teology and Its Critics: Toward an Assessment (Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books, 1989), 87.
8
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
13
cipation, and most of the discussion about liberation from sin deals with eliminating unjust structures caused by sin.”28 Conversely, McGovern notes,
In We Drink from Our Own Wells, Gutiérrez reflects theologically on the journey of the poor in Latin America and the journey of those who have attempted to walk with the poor. When liberation theology first emerged, Gutiérrez wrote about the “revolution- ary ferment” alive throughout Latin America. Te revolutionary excitement has dimmed, but Gutiérrez finds a deeper, more faith centered hope still strong.29
McGovern concludes, “I would clearly designate spirituality as the dominant theme of contemporary liberation theology.”30
Paul Sigmund in his book Liberation Teology at the Crossroads also sees the changes in Gutiérrez’s thought. Sigmund identifies Gutiérrez as the progenitor of what he calls the new line of theological speculation that began to depart from the older, more militant liberation theology of the early years. He says, “Many writers have seen the anticipation of the characteristic elements of lib- eration theology in the writings by Latin American theologians in the middle and early 1960s. . . . However the clearest beginnings of the new line of theo- logical speculation are in the writings of Gustavo Gutiérrez.”31 Why have all these changes occurred? Te answer, for Sigmund, is the times in which Gutiérrez wrote his books. He says,
In A Teology of Liberation, however, the emphasis is much more on the former than the latter in the sense that the structuralist anticapitalism is discussed at much greater length than the participatory populism. Tis emphasis is an understandable product of the time at which the work was written — the late 1960s and the early 1970s. As the book was being completed Chile elected a Marxist president, Salvador Allende, with the support of a coalition that also included Christians and parties of a more secular orientation. Allende’s popular unity seemed to embody the commitment to the poor and the oppressed — and to socialism — that liberation theology argued was the logical conclusion to be drawn from the scriptures.
32
28
Ibid., 82.
29
Ibid., 87.
30
Ibid., 83.
31
Paul Sigmund, Liberation Teology at the Crossroads (Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1990), 28.
32
Ibid., 39.
9
14
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
Te Movement to Mysticism
Had changes occurred within the presentation of a theology of liberation? In A Teology of Liberation Gutiérrez had maintained that “theological categories are not enough. . . . we need a spirituality.”33 With the issuing of the book We Drink from Our Own Wells, Gutiérrez began to make explicit what to many of his followers was implicit, namely, that there was a verdant spirituality within the original coordinates of the theology of liberation schemata. In the fore- word to this long anticipated work, Henri Nouwen stated, “Tis book fulfills the promise that was implicit in his A Teology of Liberation.”34 In this Gutiér- rez was not abandoning his earlier emphasis but “expanding upon the view.”35 In Gutiérrez’s mind, part of the rationale for minimizing the spiritual aspects was that the tenets of spirituality for the poor should germinate from the poor as a part of their own liberation pilgrimage. He notes, “Evangelization, the proclamation of the gospel, will be genuinely liberating when the poor them- selves become its messengers.”36 Tis embryonic spirituality could not be com- plete until the poor were the artisans of their own spirituality: “Te spirituality of liberation will have its point of departure in the spirituality of the anawin.”37 As Gutiérrez warmly anticipated this new type of spirituality, he felt con- strained to contain his own ruminations since the people of liberation would traverse unknown ground in the birthing of a spiritual paradigm. He notes,
Te problem, however, is not only to find a new theological framework. Te personal and community prayer of many Christians committed to the process of liberation is undergoing a serious crisis. Tis could purify prayer life of childish attitudes, routine, and escapes. But it will not do this if new paths are not broken and new spiritual experiences are not lived. . . . Tere is a great need for a spirituality of liberation; yet in Latin America those who have opted to participate in the process of liberation as we have outlined it above, comprise, in a manner of speaking, a first Christian generation. In many areas of their life they are without a theological and spiritual tradition. Tey are creating their own.38
33
Gutiérrez, A Teology of Liberation, 117.
34
Henri Nouwen’s foreword in Gustavo Gutiérrez, We Drink from Our Own Wells: Te Spiri- tual Journey of a People (Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books, 1984), xiii.
35
Tis is the title Gutiérrez gave to his new introduction in commemoration of the fifteenth anniversary edition of A Teology of Liberation, xviii.
36
Gutiérrez, Te Power of the Poor in History, 22.
37
Ibid., 53.
38
Gutiérrez, A Teology of Liberation, 74.
10
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
15
At least in emphasis, Gutiérrez’s liberation spirituality had begun to change. Te question was what would the new changes look like and how would the new emphasis on spirituality cohere with the old expressions of liberation?
A funny thing occurred in the forging of new spiritualities for the theology of liberation. Te new formulations of faith began to look suspiciously like older, more traditional spiritualities within Roman Catholic mystical life. Sigmund commented, “Without admitting that he was doing so, Gutiérrez continued to modify his approach and to emphasize the agreement between his version of liberation theology and the social teaching of the church.”39 Was it a coincidence that the spiritual evolution looked particularly Roman Catho- lic? True, Gutiérrez had previously noted that “without ‘contemplative life,’ to use a traditional term, there is no authentic Christian life.”40 But in its embry- onic development, he had maintained, “what this contemplative life will be is still unknown.”41 Te unknown of the earlier works became known in such traditional Catholic mystics as St. John of the Cross and Teresa of Avila. Monastic pillars of contemplation also began to filter into the thought of Gutiérrez in Augustine and particularly in Ignatius Loyola (contemplation in action). Here, Gutiérrez began to find historical compatriots of liberation who had traversed the spiritual and had never given up the concern for action. As a result, the interior life was seen not as an impediment to liberation but rather as an ally. A recent work by Gutiérrez emphatically embraces spiritual- ity’s help in observing that “spirituality provides strength and durability for social options.”42 In Gutiérrez’s rereading of the mystical and monastic pil- grims, a new vantage point was found to embrace the historical expressions of the faith without losing the present praxis. Te mystical had been demytholo- gized of self-absorbed pietism and had become practical. As a result, Gutiérrez began to mine the deeper recesses of mysticism laden within Christian history. Now Gutiérrez would even become an apostle for the mystical life: “Only within the framework provided by mysticism and practice,” he observed, “is it possible to develop a meaningful discourse about God that is both authentic and respectful of its object.”43 Specifically, the call to contemplation within
39
Sigmund, Liberation Teology at the Crossroads, 171.
40
Gutiérrez, A Teology of Liberation, 74.
41
Ibid.
42
Gustavo Gutiérrez, “Te Teology of Liberation: Perspectives and Tasks,” trans. Fernando F. Segonia, in Toward a New Heaven and a New Earth: Essays in Honor of Elisabeth Schüssler Fiorenza (Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books, 2003), 297.
43
Gustavo Gutiérrez, Te Truth Shall Make You Free (Maryknoll, NY Orbis Books, 1990), 55.
11
16
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
mysticism was now seen as an active participation in the process of liberation as opposed to a fearful withdrawal from the world of need.
Contemplation
What was it about mysticism that attracted the later Gutiérrez? Te answer, of course, is praxis. Gutiérrez had always held to a concept of spirituality that included contemplation, but the adoption of mysticism thrust Gutiérrez into the interior life, which previously had only occupied a footnote in his think- ing. Gutiérrez noted, “Poverty was always a central point in the history of spirituality, and it was always linked to the contemplative life.”44 In Gutiérrez’s life as a parish priest he would often reflect upon the contemplative aspect of the poor, both in merely being within the repose of the church and in active praying. Gutiérrez noted the poor’s abiding presence in the local churches as something more than a place to get out of the rain. He says, “Te poor spend long hours reflecting on their lives [in the church].”45 Reflexively and naturally the poor move from their reflection to prayer. He says, “Tere is perhaps noth- ing more impressive and creative than the praying praxis of Christians among the poor and oppressed. Teirs is not a prayer divorced from the liberating praxis of people. On the contrary, the Christian prayer of the poor springs up from roots in that very praxis.”46
Prayer
Prayer in the spirituality of liberation is not to be thought of as routine, pas- sive, or accepting of degradation. Nor does contemplative silence before God equate to an acceptance of brutality. Gutiérrez states, “Passivity or quietism not only is not a real acknowledgement of the gratuitous love of God, but even denies it or deforms it.”47 Prayer, then, actually questions God about the unac- ceptability of suffering from within the constructs of God’s loving nature: “Teology addresses how to speak about God from the sufferings of the inno-
44
James L. Heff, ed., Believing Scholars: Ten Catholic Intellectuals (New York: Fordham Uni- versity Press, 2005), 45.
45
Gustavo Gutiérrez, “Liberation Teology for the Twenty-First Century” in Romero’s Legacy: Te Call to Peace and Justice, ed. Pillar Closkey (Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield, 2007), 55.
46
Gutiérrez, Te Power of the Poor in History, 107.
47
Gutiérrez, Te Truth Shall Make You Free, 35.
12
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
17
cents, the suffering of the poor.”48 Gutiérrez likewise maintains, “If the ele- ment of injustice be added to this situation of suffering, it can produce resentment and a rejection of the presence and existence of God, because God’s love becomes difficult to understand for one living a life of unmerited affliction.”49 It also maintains the theological structure of struggle before God (coram Deo) as opposed to in atheistic disengagement. Gutiérrez affirms, “Tis painful dialectical approach to God is one of the most profound messages of the book of Job.”50 Te prelude of prayer is central to all God talk because it begins in an attitude of faith from which all talk of God must originate.
True prayer also moves one to action. To pray without a commitment to action nullifies the prayers uttered as faithless. In this dialectical process the surd of suffering moves one to a mystical appropriation of Christ’s suffering. In all unjust suffering the Christian is called to understand that Christ suffers with the victim and “will be in agony until the end of the world.”51 In this suf- fering faith is born — not in a dismissing manner but rather in a mystical paschal participation. From identification with Christ a “hermeneutic of hope” is appropriated that sees in the resurrection of Christ the future redemption.52 Yet, because the suffering is not abated in the present time, there is a need for continued contemplation. Tis discipline of silent meditation beckons the sufferer into an interior life that helps them persevere through the present affliction. Gutiérrez notes, “Teology will then be speech that has been enriched by silence.”53 Yet, the present disciplines and the future hope do not always provide easy answers to the larger, more personal questions of theodicy. In this Gutiérrez confesses, “Tis question is larger than our capacity to answer it. It is a very deep, personal question. Ultimately, we have no answers except to be with the poor.”54 As a result, contemplation continues and compassion follows from the inability (both personal and corporate) to explain God’s love in the midst of evil. Perhaps this is why Gutiérrez was fond of quoting Jose Maria Arguedas’ aphorism, “What we know is much less than the great hope we feel.”55
48
Gustavo Gutiérrez, “How Do You Tell the Poor God Loves You?” Interview by Mev Puleo, St. Anthony Messenger 96 (February 1989): 10.
49
Gustavo Gutiérrez, On Job: God-Talk and the Suffering of the Innocent, trans. Matthew J. O’Connell (Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books, 1987), 13.
50
Ibid., 65.
51
Ibid., 101.
52
Gutiérrez, Te Power of the Poor in History, 15.
53
Ibid., xiv.
54
Ibid.
55
Ibid., 22.
13
18
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
Revelation and Praxis
As part of the liberation imperative, Gutiérrez also advocates the age-old dis- cipline of the reading of the Scriptures. From the beginning of Gutiérrez’s project of liberation, the Bible has held a central position. However, even the Scriptures seem to take on a new dimension within the thought of the latter Gutiérrez. Te early Gutiérrez’s epistemology located truth as a dialectical interaction with praxis. He says, “For what we are concerned with is a re- reading of the gospel message within the praxis of liberation.”56 In this he agrees with Congar in saying, “It [the church] must open as it were a new chapter of the theological-pastoral epistemology. Instead of using only revela- tion and tradition as starting points, as classical theology has generally done, it must start with the facts and questions derived from the world and from history.”57 He also notes that “all truth must modify the real world . . . knowl- edge is thus dialectical starts and returns.”58 By 1983 he had revised his episte- mology to include a more preeminent status for revelation in epistemology. He said, “Te ultimate criterion for judgment comes from revelation not from praxis itself.”59 Correspondingly, Gutiérrez also began to modify his position on the social sciences’ place in epistemology. He wrote, “Te Bible concept is very rich, richer than a purely sociological understanding of the poor.”60
Has Gutiérrez’s Mysticism Created an Open Door for Dialogue?
Is Gutiérrez’s incorporation of mysticism a theological portal through which dialogue with Pentecostalism might commence? Given the chasm that has historically separated them, the answer to such a question is at best tentative. First, while the accentuation of mysticism is without question an elaboration of Gutiérrez’s latent spirituality, the translation from mysticism to Pentecostal- ism is not a seamless transition from either side. Yet, there are voices within Pentecostalism who believe that the chasm is not too deep and that a latent commonality abides between the two. Miroslav Volf is one who implores these two theologies to come together. He states, “It is of ecumenical importance for
56
Ibid., 66.
57
Gutiérrez, A Teology of Liberation, 9.
58
Gustavo Gutiérrez, “Te Praxis of Liberation and the Christian Faith,” Humane Vitae (September 1974): 373.
59
Gustavo Gutiérrez, Te Truth Shall Make You Free, 101.
60
Gustavo Gutiérrez, “Gutiérrez Reflects on 15 Years of Liberation Teology,” Interview by Latinamerica Press, Latinamerica Press 15 (19 May 1983): 5-7.
14
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
19
liberation theology and Pentecostal theology to recognize each other as feud- ing family members,” as opposed to enemies.61 Te reason for this, Volf points out, is an increasing awareness within the Pentecostal movement of both the liberation imperative and the conscientization of socioeconomic need. At first glance, he says, “Liberation theology and Pentecostal theology seem to be prime examples of radically opposing theologies.”62 As Volf notes, however, the two theologies have much more in common than either one of them may wish to believe: “Individual groups of Pentecostalists around the world seem to be slowly discovering the socioeconomic implications of their soteriology, and liberation theologians are becoming more aware of the need for a spiritual framework for their socioeconomic activity.”63 Dario Lopez Rodriguez com- ments on the liberating activity: “Today there is sufficient evidence from sev- eral countries of Latin America that a gradual awakening of the social conscience of a significant sector of the Pentecostal movement is taking place.”64 Doug Peterson agrees: “Ultimately, by empowering people who were previ- ously denied a voice, the Pentecostal Movement in Latin America has acquired a revolutionary potential.”65
On the question of spirituality, Simon Chan also sees a great deal of conti- nuity between Catholic mysticism and Pentecostalism. Within the two tradi- tions Chan sees great possibility in the celebration of the Eucharist as a “central” Pentecostal event.66 Chan also views tongues as, in essence, an expres- sion of Teresa of Avilla’s progression to joy “in which joy becomes so over- whelming that the soul could only respond with all tongues and heavenly madness.”67 Chan says, “Pentecostalism cannot be regarded as a marginal movement, much less an aberration: it is a spiritual movement that matches in every way the time-tested development in Catholic tradition.”68 Chan even believes that the Pentecostal giftings work best in the structure of Roman Catholic and the Episcopal Charismatic traditions. He notes, “In fact I would
61
Miroslav Volf, “Materiality of Salvation: An Investigation in the Soteriologies of Liberation and Pentecostal Teologies,” Journal of Ecumenical Studies 26, no. 3 (Summer 1989): 449.
62
Ibid., 447.
63
Ibid., 460.
64
Dario Lopez Rodriguez, “A Critical Review of Douglas Peterson’s Not by Might Nor by Power: A Pentecostal Teology of Social Concern in Latin America,” Journal of Pentecostal Teology 17 (2000): 136.
65
Douglas Peterson, “Latin American Pentecostalism: Social Capital, Networks, and Poli- tics,” Pneuma: Te Journal of Pentecostal Theology 26, no. 2 (Fall 2004): 306.
66
Chan, “Pentecostal Teology and Christian Spiritual Tradition,” 108.
67
Ibid., 60.
68
Ibid., 71.
15
20
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
like to show that [the Pentecostal reality] is better traditioned in a church that recognizes the constitutive role of the sacraments and the Spirit.”69 But is there a tradition within liberation theology that militates against the indigenous nature of Pentecostalism?
Ecclesiology
In “La Koinonia Eclesial” Gutiérrez proclaims that “the task of the church is as an extension of the missions of the Son and the Spirit.”70 Even in Gutiérrez’s earlier thought he had stated that “spirituality in the strict and profound sense of the word is the dominion of the Spirit.”71 But what does this mean in rela- tion to the ecclesiology? In the formation of the spirituality of liberation, Gutiérrez earlier maintained that he was hesitant to conjecture as to the expli- cation of this “new” spirituality. His reasoning was that the people of libera- tion were “first generation” liberationists; therefore, what liberation spirituality comprised was subsequently in an embryonic and much too formative stage. Gutiérrez has consistently maintained that the poor will not be truly liberated until they are the artisans of their own spirituality. But, as Segundo pointed out, “Something was obvious . . . the common people had neither understood nor welcomed anything from the first theology of liberation, and had actually reacted against its criticism of the supposed oppressive elements of popular religions.”72 Paradoxically, many now have begun to criticize liberation theol- ogy for its lack of indigenous authenticity and for being primarily an academic exercise. Solivan says, “Te power and authenticity present in the early voices of the liberation theologians have been diluted by the process of academic advancement.”73 Charles Self has asserted that “Pentecostalism is truly a faith of the poor and is thus distinct from some liberation theology movements which are for the poor.”74 Tis critique echoes Moltmann’s previous criticism that the theology of liberation had more to do with European theology than it
69
Ibid., 15.
70
Gustavo Gutiérrez, “La Koinonia Eclesial,” trans. David Bustos, Paginas 200 (August 2006): 22.
71
Gutiérrez, A Teology of Liberation, 117.
72
Segundo, Signs of the Times, 74.
73
Samuel Solivan, “Te Spirit, Pathos, and Liberation: Toward an Hispanic Pentecostal Te- ology,” Journal of Pentecostal Supplement Series 14 (1998): 36.
74
Charles Self, “Conscientization, Conversion, and Convergence: Reflections on Base Com- munities and Emerging Pentecostalism in Latin America,” Pneuma: Te Journal of the Society of Pentecostal Theology 14, no. 1 (Spring 1992): 63.
16
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
21
did with any indigenous ecclesiology. In his “Open Letter to Jose Miguez Bonino,” Moltmann remarked that Gutiérrez’s work “offers many new insights — but precisely only in the framework of Europe’s history, scarcely any in the history of Latin America.”75 Gutiérrez often acknowledges his Euro- pean pedagogy as an encumbrance to his own veracity in speaking for the poor. Solivan states, “Without the poor — those who suffer — as subject, theology denigrates into the academic exercise of cognitive praxis.”76 For a privileged theologian educated in first-rate schools, it would be hard to sepa- rate the wineskins of austere academia from the degradation of poverty. To be sure, Gutiérrez has advocated and modeled the incarnational lifestyle, but does this model extend to his theological method? Or theoretically rephrased, does praxis, itself, have a criterion that uncritically incorporates a residual European pedagogy?
Pneumatology
In We Drink from Our Own Wells, Gutiérrez created considerable distance between “popular religion” and liberation theology by juxtaposing those who believe in miracles with those who are involved in the work of liberation: “Te power of the Spirit leads to love of God and others and not to the working of miracles.”77 Here there is a clear divergence from the view of the poor as it relates to both love and pneumatology. Exceedingly little is said throughout Gutiérrez’s works about pneumatology.78 It is an area of immense neglect. As a result, a penetrating criticism must be directed at this lack, and a question of sufficiency must be raised when the most theologically active participant in historical change (the Holy Spirit) is absent. But perhaps this is the point. Does the weakness in Gutiérrez’s pneumatology nuance his entire understand- ing of the Pentecostal movement? And does this lack predispose the theology of liberation to a critique of immanence from which the Pentecostal poor can speak more adequately? Solivan again points out that the two, miracles and
75
Jürgen Moltmann, “An Open Letter to Jose Miguez Bonino,” Christianity in Crisis 36 (29 March 1976): 5.
76
Solivan, “Te Spirit, Pathos, and Liberation,” 65.
77
Gutiérrez, We Drink from Our Own Wells, 63.
78
A quick perusal of the indexes of Gutiérrez’s books reveals the disparity. In Te Truth Shall Make You Free, the index does not have any references to the Holy Spirit. Tere are thirty-seven to Jesus and eleven to Marx. In A Teology of Liberation there are 107 references to Jesus, ten to Marx, and three to the Holy Spirit. All of the books that Gutiérrez has written display this disparity.
17
22
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
liberation imperatives, are not inimical to one another: “For many suffering people what makes God’s promise possible in their present experience is the acceptance of the miraculous. . . .Te experiences of promises fulfilled today serve as first fruits of what is yet in store.”79 Gutiérrez emphasizes only the silent suffering aspect of transcendence. But why is it inconsistent to believe, as the poor do, that God’s identification with weakness is equally as true as the Holy Spirit’s manifestation of power? On an economic level Gutiérrez agrees — it is just in the supernatural aspects where there is resistance. Of course, one might ask how God acting supernaturally now would be any dif- ferent from the Word becoming flesh and dwelling among us long ago. But the fallout does not end there. Systemically there is another more problematic result, namely, liberation itself.
Eschatology
In Acts 2:15-16 Peter exclaims, “Indeed, these are not drunk, as you suppose, for it is only nine o’clock in the morning. No, this is what was spoken through the prophet Joel.” Not only were they not drunk, but the outpouring of the Spirit at Pentecost inaugurated a new era within the life of the church that Joel referred to as the last days (v. 17). In Gutiérrez’s thought there is a great empha- sis on the hermeneutic of hope that creates eschatological longing for change. Gutiérrez is correct in believing in an eschatological hope but does not incor- porate any real pneumatology into his eschatology. As a result, the motivation for change rests primarily within the subject of history, as opposed to the Spirit of, over, and in history. Tis places a heavy weight upon the subject of history, who has hitherto been unable to realize his and her eschatological implica- tions. Granted, the hermeneutic of hope comes through humanity, but it does not originate in humanity. To fill this need, Gutiérrez adopts the methodology of conscientization in what seems to appear more as a Promethean construct than an emphasis upon the Spirit. Tis lack of proper emphasis threatens the entire edifice of liberation in that it places the realization of the movement in the ability of humanity to see. Tis is not the biblical presentation of the noetic effects of sin or the Holy Spirit’s relegation to a subordinate eschato- logical role. Te person who leads into all truth is the primogenitor of the eschatological hope. As a result, the assurance for hope is limited to the ability or inability of humanity to both see and accomplish this hope. And this is a
79
Solivan, “Te Spirit, Pathos, and Liberation,” 91.
18
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
23
major difference between Pentecostalism and liberation theology. To para- phrase Solivan, Pentecostalism has placed its hope for the future upon a pres- ent belief in the Spirit’s workings. In so doing, they have found the impetus for change both on a personal level and in society. Tis is why there is hope for the future. Revealed in the present dispensation is the future realization of abiding liberation.
Hope for the Future?
Is there a crack in the door that allows for dialogue between what, on the sur- face, seems like two antagonistic viewpoints on liberation spirituality? Gutiér- rez has noted that theology will not be free of illegitimate presuppositions until the poor create their own theology. What became apparent with the writ- ing of We Drink from Our Own Wells, however, was that Gutiérrez did have within his own mind the parameters of a certain type of spirituality, namely, Roman Catholic mysticism. As Volf and Chan have pointed out, this does not invalidate dialogue between Pentecostalism and Gutiérrez. Conversely, neither do the similarities between the two extinguish all distance. Simply put, what validates or invalidates the Pentecostal experience, according to Gutiérrez’s theology, is liberating praxis. Te question is, does Pentecostalism qualify according to this criterion? For many, and particularly the poor of Latin Amer- ica, the answer is a resounding yes. But is it enough that the poor have voted with their feet? Gutiérrez maintains, “If we are to find God acting in history, we must have an attitude of faith that is open to novelty and mystery.”80 Where does this openness to mystery lead? Te answer is, a door that was previously closed and is being opened ever so slowly. Yet, difficulties abide when a lack of openness to novelty and mystery persist. Te close proximity of focus and geography could not help but create some expected sibling rivalry. However, this should not be enough to seal the door shut or close it back again. Tus, in order for greater openness to occur, the father of liberation theology must realize that true liberating praxis is occurring within Latin America under the name of Pentecostalism. Tere must also be the realization of the indigenous choice and that the label attached to Pentecostalism “Made in America,” is not accurate. Rather, the “Made in America” label should, as previously noted, more correctly read, “Made among the Poor and Dispos- sessed of America.” Te location of liberating praxis’s nexus should not
80
Gustavo Gutiérrez, Te God of Life (Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books, 1991), 80.
19
24
J. Davis / Pneuma 33 (2011) 5-24
disqualify its extension or incorporation. If Gutiérrez truly believes in a theol- ogy from the poor, then the poor must be allowed to speak, even if their thoughts take them down less traditional and more mysterious pathways. And perhaps they have spoken — in tongues. Te elaboration of a spiritual need is what precipitated Gutiérrez’s movement into mysticism. Te limitation of that elaboration is where the truly liberating prospects come to an end. Te desire to have a “faith that is open to novelty and mystery” is a glorious incarnational goal. However, the constricting definitions of “novel” and, in this case, “mys- terious” prohibit implementation. Where does this leave the hopes of dialogue between the two most potent forms of religious expression in Latin America? Te answer is looking at a ray of light behind a partially opened door wonder- ing what might happen if the door were to open fully.
20
Pentecostal Framework of Primitive Faith: Comparative Insights from Leading Pentecostal Scholars
Gordon Fee: Scripture-Centered Pneumatology
Fee’s scholarship emphasizes the Spirit’s role in New Testament theology, particularly in Pauline writings. While he critiques traditional Pentecostal doctrines like initial evidence, he affirms the Spirit’s transformative presence. Compared to Donev, Fee’s approach is exegetical and text-driven, whereas Donev’s triangle is experiential and restorationist, prioritizing lived encounter over doctrinal precision.
Stanley M. Horton: Doctrinal Clarity and Holiness
Horton’s work, especially in Bible Doctrines, provides a systematic articulation of Pentecostal beliefs, including Spirit baptism and sanctification. His theology is deeply rooted in Assemblies of God tradition. Donev de-emphasizes denominational boundaries, focusing instead on the primitive church’s egalitarian and Spirit-led ethos.
Craig Keener: Charismatic Experience and Historical Context
Keener bridges academic rigor with charismatic openness, especially in his work on miracles and Acts. His emphasis on historical plausibility and global charismatic phenomena aligns with Donev’s praxis-driven model. However, Keener’s scholarship is more apologetic and evidential, while Donev’s triangle is formational and communal.
Frank Macchia: Spirit Baptism and Trinitarian Theology
Macchia’s theology centers on Spirit baptism as a metaphor for inclusion and transformation, often framed within Trinitarian and sacramental lenses. Donev shares Macchia’s Trinitarian depth, especially in Eastern European contexts, but leans more toward neo-primitivism and ecclesial simplicity.
Vinson Synan: Historical Continuity and Global Pentecostalism
Synan’s historical work traces Pentecostalism’s roots and global expansion. Donev builds on this by reclaiming Pentecostal narratives, such as those of Ivan Voronaev. Both emphasize restoration, but Donev’s triangle is more prescriptive, offering a model for future church practice.
Robert Menzies: Missional and Contextual Theology
Menzies focuses on Pentecostal mission and theology in Asian contexts, often challenging Western assumptions. His emphasis on Spirit empowerment for mission resonates with Donev’s praxis element. Yet, Donev’s model is more legitimately communal, drawing from Orthodox and Puritan influences.
Cecil M. “Mel” Robeck: Ecumenism and Pentecostal Identity
Robeck’s work on Pentecostal ecumenism and global dialogue complements Donev’s inclusive vision. Both advocate for Pentecostal distinctiveness without isolation, though Donev’s triangle is more grassroots and revivalist, aimed at local church transformation.
Implications for Church Practice
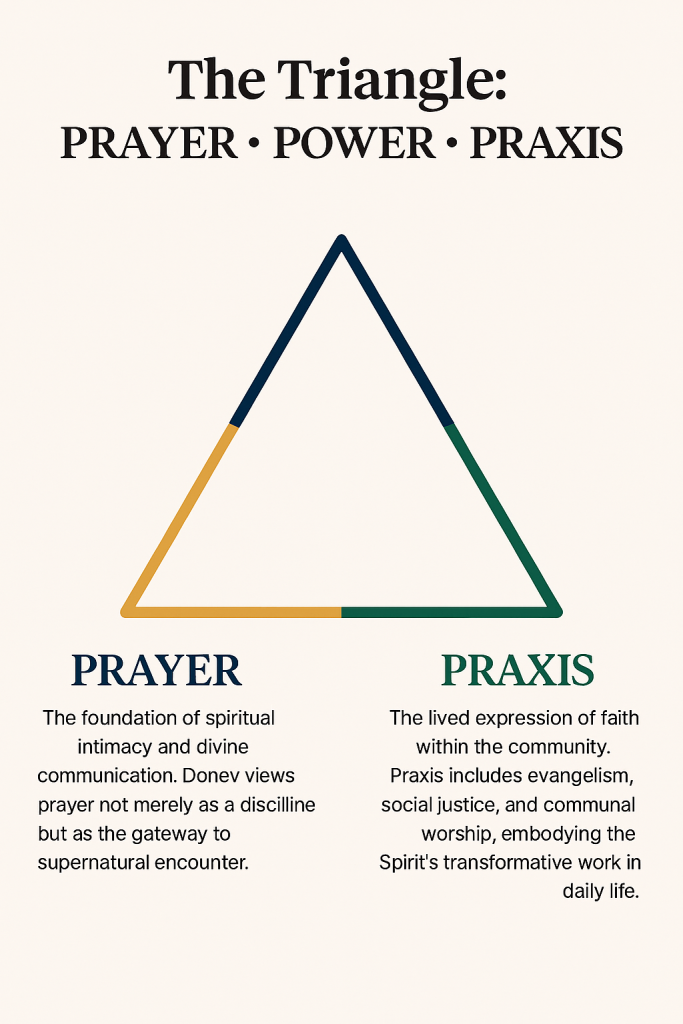
Donev’s triangle offers a practical blueprint for churches seeking renewal:
- Prayer ministries that foster intimacy and prophetic intercession.
- Power encounters through healing services and spiritual gift activation.
- Praxis initiatives like community outreach, justice advocacy, and discipleship.
Compared to other scholars, Donev’s model is less academic and more actionable, designed to reignite the apostolic fire in everyday church life.
Global Mission In Pentecostal Perspective
113 Murray W. Dempster, Byron D. Klaus and Douglas Petersen, eds., Called & Empowered: Global Mission in Pentecostal Perspective (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson Publishers, 1991), 321 pp. $14.95 paper. Reviewed by L. Grant McClung, Jr. Who has the answer to what Pentecostals believe about mission and the description of how they go about doing mission? Coming out of a sense of urgency that caused them to “act now and theologize later,” Pentecostals have been known more for action than reflection. Identifying who the Pentecostals were and how they did the job was a task largely left up to sympathizers from groups such as the Church Growth Movement. Other outside observers, however, were not always so sympathetic. This book is a statement by Pentecostals about Pentecostal missions, a move toward what I have called a “Decade of Self-Definition in the 1990s.” What has emerged since the mid 1980s are signs of a budding “pentecostal missiology,” a development exemplified in this volume. Readers of this excellent new contribution will find that Pentecostals have a broader understanding of wholistic mission issues than the supposed limited agenda of evangelism/church planting via the supernatural. This collection of twelve articles–all from Assemblies of God authors–and three “outside observer” responses has something to say about biblical/theological dimensions, the integration of gospel and culture, response to non-Christian religions, and missiological strategy. It reads well as a text (which I am using) or as a pre-study tool, for example, for a field conference or consultation devoted to understanding the Pentecostal/Charismatic contribution to world evangelization. The three editors are professors at Southern California College in Costa Mesa, California, a Christian liberal arts college sponsored by the Assemblies of God, and are also involved in Latin America ChildCare, an Assemblies of God ministry to underprivileged children in sixteen Latin American countries. The editors introduce each of the five sections of the book with a rationale for the theme of the section and a brief synopsis of each chapter in the section. These sectional introductions give an overall conceptual coherence to the volume, reducing the choppiness and unevenness that often attend multi-authored anthologies. Gordon Fee opens the first section on “Biblical and Theological Dimensions of Global Mission in the Pentecostal Tradition” with a chapter which aims to demonstrate that the roots of the Pentecostal conviction about the global mission of the church are to be found in Jesus’ proclamation of the kingdom of God. In the next chapter, 1 114 Murray Dempster utilizes the concept of the kingdom of God as an integrating center in the development of a wholistic Pentecostal theology which features evangelism, social service and social action. Douglas Petersen in the third chapter of this section adopts and modifies “the hermeneutical circle” of Latin American liberation theologians in order to promote a Pentecostal praxis which applies Jesus’ message of the kingdom within the context of the Third World. Section two focuses on “The Emerging Pentecostal Integration of Gospel and Culture” and features chapters written by Everett Wilson, Augustus Cerillo, Jr., and Del Tarr. Wilson analyzes the phenomenal growth of Pentecostalism in Latin America from a functional perspective, identifying the changing social conditions in Latin culture which encouraged indigenous, national Pentecostal leaders to create “a church of the people.” Cerillo identifies the issues that Pentecostals face in light of the ever-increasing global trend of urbanization, and offers some pertinent suggestions for formulating effective urban ministries. In rounding out this section, Tarr develops a model of communication for preaching the gospel across the different cultural regions of the globe. The issue of gospel and culture is taken up again in section three but the issue is analyzed from the perspective of differing worldviews. Each author describes the worldview under investigation in his chapter from his viewpoint as a participant: Peter Kuzmic analyzes the Marxist worldview, Sunday Aigbe analyzes the worldview of tribal people groups and Sobhi Malek analyzes the Muslim worldview. Given the breakup of the former Soviet Union subsequent to the writing of his chapter, Kuzmic sho.wed great insight in noting: “Anything written about the ‘communist world’ today should be written in pencil. All across Eastern Europe and in the Soviet Union monumental changes are taking place at a breathtaking speed and in most dramatic and unpredictable ways” (143-44). Even though sweeping changes have occurred in the Communist bloc countries, Kuzmic’s study still provides a goldmine of information in understanding what is happening in that part of the world. “Pentecostals and Current Missiological Strategies” is the topic of section four. A chapter by Gary McGee provides a descriptive historical overview of the multiple mission strategies that Pentecostals have used in this century. A jointly-written chapter by Byron Klaus and Loren Triplett documents the historical connection between non-formal/informal national leadership programs and the mushrooming growth of Pentecostalism, warns Pentecostals about their newly found reliance on formal structures of national leadership development and calls for a renewed commitment to indigenous leadership development “in ministry.” Missiologist Larry Pate, in the last chapter in the strategies section, describes the emergence of the 2 115 “two-thirds world missions movement” and assesses its implications for Pentecostal missions efforts. Pate makes a compelling case that theological and practical reflection on the implications of the global shift embodied in the two-thirds world missions movement is the most important strategic issue facing Pentecostal missions today. The fifth and final section of the book provides “Views from Outside” the Pentecostal movement, and according to the editors, the chapters in this section “stress the importance of Pentecostals learning to listen to the broader church as part of its missiological activity” (xviii). Pentecostal mission effort is evaluated from a Church Growth perspective by Peter Wagner, from an ecumenical perspective by Jeffrey Gros, FCS, and from a Third Wave perspective by Charles Kraft. These chapters, designed to provide “dialogical feedback,” are stimulating to read and insightful in both their positive appraisals and constructive criticisms. Hopefully, Called & Empowered will be expanded and revised in a subsequent edition to include a broader participation of missions practice and reflection from a wider variety of Pentecostal and Charismatic missions ministries, along with more contributions from women (all the authors are male) and voices from the “southern world” (only three of twelve essays are from non-North Americans). The book, however, is well-researched and highly readable for those seeking to look through the window into the self-understanding of Pentecostals and their responsibility in world evangelization. Even the casual observer of this tradition would agree that the energy Pentecostals expend in world missions activity flows out of the belief that Pentecostals are Called & Empowered. L. Grant McClung, Jr., is Coordinator of Research and Strategic Planning for the Church of God World Missions and Associate Professor of Missions and Church Growth at the Church of God School of Theology in Cleveland, Tennessee. 3
Pentecostal Theological Education
Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261 Dialogue
“Epistemology, Ethos, and Environment”: In Search of a Theology of Pentecostal
Theological Education, Veli-Matti Kärkkäinen
Professor of Systematic Theology, Fuller Theological Seminary, Pasadena, CA, USA
Docent of Ecumenics, Faculty of Theology, University of Helsinki, Finland
The purpose of this essay is to take a theological look at Pentecostal theological education at the global level. While dialoguing widely with various current and historical discussions of the theology of theological education, particularly with David Kelsey of Yale University, the essay urges Pentecostals to negotiate an epistemology that corrects and goes beyond both modernity and postmodernity. The essay also urges Pentecostals to negotiate several seeming opposites such as “academic” versus “spiritual” or “doctrinal” versus “critical.” The final part of the essay offers Pentecostals some advice and inspiration from the reservoirs of the long history and experience of non-Pentecostal theological institutions.
Keywords
Pentecostal theological education, theology of theological education, epistemology, modernity, postmodernity
First Words: Is Bigger Always Better?
Educators like to imagine that education matters. We like to believe that the leadership of a congregation is improved when that person has a graduate degree and three years of study. We like to think that pouring resources into education is worthwhile. We argue that the more resources we devote to theological education, the better.2
1 This essay is a slightly revised version of my presentation at the World Alliance for Pentecos- tal Theological Education Consultation in Stockholm, Sweden, August 25 2010.
2 Ian S. Markham, “Theological Education in the Twenty-First Century,” Anglican Theological Review 92, no. 1 (2010): 157.
© Koninklijke Brill NV, Leiden, 2012 DOI: 10.1163/157007412X639889
1
246
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
Against this commonsense expectation, the Anglican seminary professor Ian S. Markman bluntly says that in reality, however, it is sometimes the case that denominations such as his own that invest huge amounts of resources in theo- logical education are declining in membership and activity. Markman reports that the Presbyterian Church (USA) with some of the most highly acclaimed theological schools in the world (Princeton and Columbia, among others) has lost two hundred thousand members between 1999 and 2004 — the biggest loss during that time period among all mainline churches! On the contrary, the Anglican Ian S. Markham further observes, Pentecostals with “very limited and informal” training are growing rapidly all over the world, including in some parts of the USA.3
This is, of course, not to establish any negative causality between the high level of education and low level of church activity — an intriguing PhD study topic in itself! — but it should, rather, shake any unfounded belief in the effects of higher education. Indeed, a classic study conducted in the 1960s by the Swiss sociologist Lalive d’Epinay showed that the traditional theological academic training received by mainline Methodist and Presbyterian pastors in Chile was far from making them more effective pastors and church planters than Pente- costal pastors and pioneers in the same location, who had received the mini- mal amount of education.4 Again, it is wise not to draw conclusions too hastily concerning the cause and effects. While it can be the case that theological edu- cation in itself may have a counter-effect on efficacy in church work, it may also true that the counter-effects are due, rather, to a poor theological education. It is well to recall the critical observation offered by a theological schools’ accred- itation official on the effects of seminary education: “There is no other profes- sional organization in the world that is as functionally incompetent as . . . seminaries. Most of our students emerge from seminaries less prepared than they entered, biblically uncertain, spiritually cold, theologically confused, rela- tionally calloused and professionally unequipped.”5
Before Pentecostals start saying “Amen and Hallelujah! I knew that!,” per- haps they should pause to reflect. It seems to me that very few Pentecostal churches suffer from over-education! On the contrary, we could probably com-
3 Ibid.
4 Christian Lalive d’Epinay, “The Training of Pastors and Theological Education: The Case of Chile,” International Review of Missions 56 (April 1967): 185-92.
5 The remark comes from Timothy Dearborn, Director of the Seattle Association for Theologi- cal Education, reported in Jon M. Ruthven, “Are Pentecostal Seminaries a Good Idea?” n.p., avail- able at http://tffps.org/docs/Are%20Pentecostal%20Seminaries%20a%20Good%20Idea. pdf (accessed 7/12/2010).
2
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
247
pile a long list of Pentecostal churches, planted and started well, that have become stagnant because they lacked trained leadership to facilitate and nur- ture congregational and denominational life. Indeed, there is a dearth of aca- demically trained leadership among Pentecostals, not only in the Global South, where most Pentecostal churches (with a few exceptions, such as those in South Korea) suffer from severe lack of economic and other resources, but also in Europe and the USA.6 Let me just take as an example the US Assemblies of God, one of the most established and resourceful Pentecostal bodies in the world. A recent study of educational levels among Assemblies of God clergy revealed that among senior pastors, 12% had no education beyond high school and 4.3% claimed no ministerial training at all. While 30.6% claimed some training in college or at a technical school, 27.4% had taken a certificate course or had completed some correspondence courses in ministerial training. Some 55.6% had attended Bible college, although only 41.3% completed a degree. While 12.4% held a master’s degree, only 9.9% held a seminary degree [often in counseling] and 2.8% held an advanced degree in ministry.7 This example alone tells us that Pentecostals are approaching the task of considering the nature and role of higher education in theology from a very different vantage point than the mainline traditions.
As the title indicates, my focus will be on the theology — rather than, say, pedagogy or philosophy or finances — of Pentecostal theological education. Therefore, I have to leave many things unsaid. My main goal is to urge Pente- costal theologians and educators to collaborate in developing a solid and dynamic theology as the proper ground for theological education. Mainline churches are ahead of us in this work — understandably so, since they have had more time to “practice.” There is much to learn from those explorations and experiments.
My argumentation moves in three main parts. First I will take a look at the epistemological options for Pentecostal theological education. Second, build- ing on that discussion, I seek to discern some key dimensions in the ethos of Pentecostal education. Third, I will offer some reflections as to different envi- ronments for Pentecostal theological education.
6 For a fine essay with ample documentation on the history and current state of Pentecostal theological education, see Paul Lewis, “Explorations in Pentecostal Theological Education,” Asian Journal of Pentecostal Theology 10, no. 2 (2007): 161-76.
7 “Fact* Survey Results: A 2000 Survey of Assemblies of God Churches” (Springfield, MO: Office of the General Secretary, 2000), 9. Copies of this survey are available from the Office of Statistics or from the Office of the General Secretary in Springfield, Missouri. I am indebted to Cecil M. Robeck, my colleague at Fuller, for providing me with this information.
3
248
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
Epistemology: Four “Cities”
In a highly acclaimed and programmatic essay titled Between Athens and Berlin: The Theological Debate, David H. Kelsey of Yale University outlines the underly- ing epistemology and theology of theological education using two cities as paradigms.8 “Athens” refers to the goals and methods of theological education that are derived from classical Greek philosophical educational methodology, paideia. The early church adopted and adapted this model. The primary goal of this form of education is the transformation of the individual. It is about char- acter formation and learning to achieve the ultimate goal, which is the knowl- edge of God rather than merely knowing about God. “It is not primarily about theology, that is, the formal study of the knowledge of God, but it is more about what Kelsey calls theologia, that is, gaining the wisdom of God. It is the transfor- mation of character to be God-like. The emphasis therefore falls upon personal development and spiritual formation.”9 The second pole of Kelsey’s typology, “Berlin,” is based on the Enlightenment epistemology and ideals. (This turn in theological education was first taken at the University of Berlin.) Whereas the classical model of “Athens” accepted the sacred texts as revelation containing the wisdom of God and not only knowledge about God, in the “Berlin” model, rational reasoning and critical enquiry reign. The ultimate goal of theological training is no longer personal formation based on the study of authoritative texts. Rather, it aims at training people intellectually.
It doesn’t take much reflection to realize that, as helpful as this scheme is, it only says so much. There is more to the picture of the underlying epistemology and theology of theological education. Two other models could be added to the equation before an assessment from a Pentecostal perspective is in order.10 My former colleague at Fuller Seminary Robert Banks has suggested a third model, which can appropriately be identified with the city of “Jerusalem,” as it denotes the missionary impulse of the Christian church to spread the gospel from Jeru- salem to the ends of the earth. In an important work titled Revisioning Theo- logical Education,11 Banks argues that if Martin Kähler’s classic dictum “Mission is the Mother of Theology” is true, it means that theology should be missional
8 David H. Kelsey, Between Athens and Berlin: The Theological Debate (Grand Rapids, MI: Eerd- mans, 1993).
9 Brian Edgar, “The Theology of Theological Education,” Evangelical Review of Theology 29, no. 3 (2005): 209.
10 I am indebted to the essay by Edgar, “Theology of Theological Education,” for helping find connections between the four models.
11 Robert Banks, Revisioning Theological Education (Grand Rapids, MI: Eerdmans, 1999).
4
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
249
in orientation. The ultimate goal and context of theological education should thus be missional, which at the end of the day fosters and energizes the church’s mission. It is, however, more than what is usually thought of as “missiological” education as in the training of foreign missionaries. It is about theological edu- cation buildingthe “foundation” that is the mission of the church in all aspects of the church’s life and work. This missional orientation is, of course, in keeping with the current ecclesiological conviction that mission is not just one task given to the church among other tasks, such as teaching or children’s work, but, rather, that the church is missional by its very nature, and thus, everything the church does derives from the missional nature.
Yet one further model can be added to the scheme. Named “Geneva” after the great center of the Reformation, it cherishes a confessional approach to theological education. It seeks to help the students to know God both through the study of the creeds and the confessions and as the means of grace. Forma- tion is focused on the living traditions of the community. “Formation occurs through in-formation about the tradition and en-culturation within it.”12
What would a Pentecostal assessment on this typology be? Pentecostals cer- tainly prefer “Athens” over “Berlin” and “Jerusalem” over “Geneva.” So the ques- tion is settled. Or is it? I don’t think so. We all agree that it would be too cheap to settle on a couple of appealing choices and move from there. The issue is more complicated — and it has to do, I repeat, with both epistemology and theology.
The choice between the classic model of “Athens” and critical model of “Ber- lin” reflects the dramatic intellectual change brought about by the Enlighten- ment. From a Pentecostal point of view, two overly simple responses to the Enlightenment can be mentioned: First, it is bad! Second, it is inevitable! What I want to say here is that even though it would be safe and soothing to be able to go back to the pre-Enlightenment mentality in which the biblical authority, the uniqueness of Jesus, and other key faith convictions could be taken at their face value — and are being taken as such among the common folks, not only among Pentecostals but in almost all other traditions as well — for an aca- demically trained person living in our times it is not a feasible option. To pre- tend that the Enlightenment never happened is the worst kind of self-delusion.
What about postmodernity? Wouldn’t postmodernity’s critique and rejec- tion of modernity’s legacy come as a God-sent aid to those who are troubled about the rule of reason? Indeed, many Pentecostals are enthusiastic about the
12 Edgar, “Theology of Theological Education,” 211.
5
250
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
promises of postmodernity; I myself am much more reserved. Indeed, what is happening in the beginning of the third millennium is that there is a continu- ing debate, at times even a conflict, between three poles when it comes to epis- temology. Following Ernest Gellner’s suggestive book title, Postmodernism, Reason and Religion,13 they can be named as religion, modernity, and postmo- dernity. Whereas “religion” (cf. “Athens” and “Geneva”) builds on authoritative revelation, “modernity” (cf. “Berlin”) seeks to replace all faith commitments for critical inquiry and postmodernity deconstructs all big narratives in turning to everyone’s own stories and explanations. “Religion” is between a rock and a hard place. Neither modernity nor postmodernity looks like a great ally. The lesson to Pentecostal theological education may be simply this: Even though Pentecostals with all other “Bible believers” seek to build on the author- itative revelation of God in Christ (“Athens”), that cannot be done in isolation from the challenges brought about by both modernity and postmodernity. Pen- tecostal theological education should seek to find a way of education in which the challenges of both of these prevailing epistemologies are being engaged in an honest and intellectually integral way. Two other lessons that guide us in reflection on the ethos of Pentecostal theological education in the next main part of the essay follow from this discussion. It is clear and uncontested that Pentecostals should incorporate the missional impulse (“Jerusalem”) into the core of their education. Furthermore, I urge Pentecostals also to consider the importance of a confessional (“Geneva”) approach, not exclusively, but rather as a complementary way.
Ethos: Four Polarities
Building on these tentative conclusions based on the epistemological discus- sion, let me continue my reflections on the theology of Pentecostal theological education by discerning and highlighting four dynamic continuums or polari- ties. Polarities are not just opposite ends, they are also processes and orienta- tions in dynamic tension with each other. I think it is important to hold on to the healthy and constructive dynamisms when speaking of the theological education of this movement that was birthed by a dynamic movement of the Spirit. This is what makes the ethos of Pentecostal theological education. I name these four polarities in the following way:
13 Ernest Gellner, Postmodernism, Reason and Religion (London: Routledge, 1992).
6
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
251
• “Academic” versus “Spiritual”
• “Indoctrinal” versus “Critical”
• “Practical” versus “Theoretical” • “Tradition-Driven” versus “Change-Driven”
“Academic” versus “Spiritual”
Everyone who has worked in the context of Pentecostal or any other revivalistic theological training knows that there is a built-in tension between spiritual exercises and academic pursuit. In contrast, the “Berlin” model pretty much leaves that tension behind because only academic excellence is pursued. Every- one who has worked in “secular” theological faculties knows what I mean by this.
The “Athens” models suggest that knowledge and wisdom are not alterna- tives, nor can they be subsumed under each other. Knowledge is the way to wisdom, the true “knowing” of God. The noted American theologian Ellen Cherry describes this in a most useful way as she reflects on the lost heritage of the Augustinian and patristic way of doing and teaching theology: “Theology is to enable people to advance in the spiritual life. Spiritual advancement is the driving force behind all of Augustine’s works. Theories about God and the things of God (i.e., doctrines) are important and wanted, but they are to a fur- ther end: to enable people to know, love, and enjoy God better and thereby to flourish.”14 Augustine is a wonderful example to lift up here because alongside deep spirituality, he is also well known for his highly intellectual and analytic mind. Let me just take up one example. As you read his classic autobiographi- cal Confessions, you will soon notice that in the true spirit of Pentecostal-type testimonials he shares about his life before turning to Christ and the dramatic change he underwent. At the same time, this book also contains one of the most sophisticated inquiries into divinity and theology, including the famous chapter 11 on the theology and philosophy of time! Spirituality and academics seem to go well together with the bishop of Hippo.
Whereas for Augustine and likeminded thinkers theology was spiritual by its nature — an aid to help Christians know, love, and enjoy God — post- Enlightenment academic education as conducted in the university setting has strayed so far from this ethos that recently courses in “spirituality” had to be
14 Ellen T. Cherry, “Educating for Wisdom: Theological Studies as a Spiritual Exercise,” Theology Today 66, no. 3 (2009): 298.
7
252
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
added to the curriculum!15 As if studying God — logos about theos — were not a spiritually nourishing exercise in itself.
“Indoctrinal” versus “Critical”
Pentecostal preaching and testimonies are about persuasion — and often amplified with a loud voice! Not only that, but the Pentecostal way of discern- ing God’s will is geared toward nonmediated, direct encounters with God. In that environment, critical thinking, analysis, and argumentation often sit uncomfortably.Coupled with this is the Bible school mentality of much of Pen- tecostal training that, in opposition to critical academic faculties in the univer- sities, was set up to combat reigning liberalism. In other words, the “Berlin” model doesn’t seem to be a viable option in that kind of environment. Mark Hutchinson describes aptly the dynamic field in which Pentecostal theological education often finds itself in the midst of conflicting expectations:
It would be true to say that most leaders in our movement have little understanding of educational processes, and little expectation about the intelligence of their members. The model of the charismatic leader is to hear from God and then tell the people what he has heard. The concept that they may be in fact serving a community which can hear from God and which is capable of dealing with what they’ve heard is not a common one. And yet, the community model is precisely what a uni-versity is — it is a commu- nity of scholarship. With the prevailing church model, education tends to default towards indoctrination, with more emphasis on character outcomes and opinions than on intellectual formation and knowledge.16
There is a clash of cultures between the church and the academic institution; only the Bible school environment usually avoids this dynamic by going smoothly with the church culture. A Pentecostal academic institution of theo- logical knowledge “exists as a place where definite, charismatic, revelational knowledge and certainty exist alongside and in interaction with the indefinite but progressive search for truth,” whereas a typical church setting calls for a definite, authoritative settling of the issues under discussion. In order to keep this dynamic tension in a healthy measure, “[l]eaders and pastors will have to acknowledge that their revelational knowledge and ecclesial authority is not
15 See further, Cherry, “Educating for Wisdom,” 296-97.
16 Mark Hutchinson, “ ‘The Battle Hymn of the Republic of Learning’: Thoughts on Academic Freedom in a Pentecostal College,” Australasian Pentecostal Theology 9 (July 2005/6): 10.
8
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
253
absolute, while teachers will have to admit that their academic freedom and scholarly knowledge are not absolute goods.”17
A Pentecostal academic mindset should be able to make a distinction between two kinds of understandings of the term critical. The first meaning that usually comes to the popular mind is something like “tearing apart” or “breaking down” beliefs dearly held — as in radical forms of biblical criticism. That kind of use of critical faculties often replicates the naïve and unfounded understanding of rationality à la the Enlightenment whereby one assumes the location to be a context-free “no-man’s land” in which one is able to know something neutrally, without prejudice or bias. That modernist illusion is, of course, thoroughly prejudiced and biased. If postmodernity has taught us any- thing, it is that all of our knowledge is “perspectival”; there is “no view from nowhere.” This takes me to the other, more constructive meaning of critical, which means something like “sorting out” or “weighing” between various opin- ions, options, viewpoints. On the way to a confident opinion or belief, the intel- lectual capacities are put in use to ensure that one’s opinion is justified in light of current knowledge, experience, and wisdom.
The Pentecostal movement at large would be greatly helped by soberly trained leaders who have been taught how to exercise healthy criticism, includ- ing self-criticism. Pentecostals would, for example, learn that “bigger is not always better.” Even though it is not an easy task, by taking the “Athens” model as the basis and the “Berlin” model as a necessary aid, Pentecostal theological education would benefit greatly. In practical terms this means teaching the basics of biblical and doctrinal criticism as part of the curriculum, doing histo- riography rather than hagiography when studying the past of the movement, subjecting prevailing leadership or church growth patterns and ideals to scru- tiny, and so forth.
“Practical” versus “Theoretical”
A recent essay by the newly elected president of Union Theological Seminary (NY), Serene Jones, discloses the depth of the problem that has haunted theo- logical education, particularly ministerial training, from the beginning, namely, how to balance “practical” and “theoretical” aspects. She makes painfully clear just how far academic theology too often has strayed from its practical task. Her title “Practical Theology in Two Modes” is an admission that systematic theol- ogy, her own discipline, needs practical theology by its side as a separate field
17 Ibid.
9
254
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
of study, although at the same time she acknowledges that “everything we do in the divinity school is practical; it’s about faith and people’s lives.”18 The divide between theoretical and practical is another child of modernity, although the distinction, of course, serves heuristic purposes and everyday needs; think, for example, of how useful it is to study first about traffic signs in class (“theory”) before venturing into actual traffic (“practice”). Common sense dictates that in some manner, the distinction should be maintained. In the case of theological education, as long as it has ministerial training as its goal, the separation cannot be accepted. Theological education that does not lead into the adoption of “practices” and virtues relevant and conducive to Christian life and ministry is simply a failed exercise.19
Theology is a peculiar form of cognitive reflection, for its goal is not simply the expan- sion of knowledge. Theology has a quite practical goal — what I would call the forma- tion of religious identity. Theology must once again become an activity forming religious identity and character. For it to play that role, theologians must be engaged in reflection upon religious practices. Some of those practices will be located within reli- gious communities, while others may be broadly distributed within society. Theolo- gians need to attend both to the practices of congregations — worship, preaching and counseling, for example — and to societal practices that have religious and moral dimensions . . . .20
When beginning a new course in systematic theology for seminary students, I usually tell the students that my discipline may be the most “practical” and “relevant” of all fields in the theological curriculum. Students often respond by asking, isn’t systematic theology rather about thinking, argumentation, doc- trines? My counter-response affirms that but also adds that, in the final analy- sis, what else could be more “practical” to pastors, counselors, and missionaries than thinking deeply about what we believe, why we believe, and how we best try to formulate it? That is what shapes sermons, testimonies, worship, coun- seling, evangelism, finances, marriage, and so forth. Although such an exercise may not seem to be as “practical” in a shorter view as, say, basics of homiletics
18 Serene Jones, “Practical Theology in Two Modes,” in For Life Abundant: Practical Theology, Theological Education, and Christian Ministry, ed. Dorothy C. Bass and Craig Dykstra (Grand Rap- ids, MI: Eerdmans, 2008), 195.
19 For an important discussion of “practices,” see Practicing Theology: Beliefs and Practices in Christian Life, ed. Miroslav Volf and Dorothy Bass (Grand Rapids, MI: Eerdmans, 2002).
20 Ronald F. Thiemann, “Making Theology Central in Theological Education,” Christian Century, February 4-11, 1987, 106-8, available at http://religion-online.org/showarticle.asp?title=360 (accessed July 11, 2006).
10
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
255
or church administration, its long-term effects may be far more relevant than one would assume.
This observation is worth repeating: The study of theology that fails to posi- tively shape a person’s identity, faith, character, and passion for God has simply failed its calling. An alternative is not to drop altogether the pursuit of theo- logical education, but rather, to work hard for the revising and rectifying of training.
The focus of the “Jerusalem” model, missional orientation, comes into con- sideration here. If it is true that mission is far more than one of the many tasks that the church does — namely, that the church is mission, mission is some- thing that has to do with everything the church is doing, its raison d’être — then it means that the ultimate horizon of theological education is the mission of the church.21 Pentecostalism with its eschatologically loaded missionary enthusiasm and yearning for the power of the Spirit has all the potential of redeeming that promise. Yet, a word of warning is in order here. While Pente- costals have rightly lifted up the needs of the mission as the key factor in shap- ing education, they have often done so in a way that has shortsightedly promoted merely “practical” tools of effectiveness. The urgency of mission does not mean, therefore, that it need not be theologically grounded or reflected upon. On the contrary, if mission is the mode of existence for the church, it means we should continue careful theological reflection along with praxis of mission, both affirming our praxis and offering needed self-criticism.
“Tradition-Driven” versus “Chang e-Driven”
“Tradition” is a bad word in Pentecostal vocabulary. Indeed, a main impulse that helped birth Pentecostalism was an opposition to the traditions, creeds, and rites of traditional churches. Pentecostalism breathes renewal and revital- ization. As it turned its attention to the future rather than the past, there emerged also a curious view of church history: basically it was a leap from the Book of Acts straight to the beginning of the movement in the twentieth century.
As a result, Pentecostalism is known for innovation, creativity, boldness, and “frontier spirit,” which have helped cultivate spontaneity, loose structures, and the use of unheard-of techniques. Ever-new discoveries in church growth, evangelism, leadership, and the like catch the imagination of Pentecostals.
21 For an important call by a noted ecumenist from India to renew missional commitment in all theological education, see Christopher Duraisingh, “Ministerial Formation for Mission: Impli- cations for Theological Education,” International Review of Mission 81, no. 1 (January 1992): 33-45.
11
256
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
Tradition represents everything stagnant, archaic, irrelevant, and dead. Or does it? For Paul, in what may be the oldest section of the New Testament in the beginning of 1 Corinthians 15, it was of utmost importance to pass on tradition about Jesus and his salvific work. The term tradition, of course, comes from the Latin word to “pass on.” The Johannine Jesus promised his disciples that after his exit, the Holy Spirit would continue working in their midst to help them embrace and gain a deeper insight into Jesus’ teaching, “tradition.” In the Chris- tian view, tradition is but the work of the Holy Spirit as the Spirit helps each new generation to delve more deeply and in a more relevant way into the knowledge, power, and mind of Christ.
Although a Pentecostal approach to theological education cannot be based solely or even primarily on the “Geneva” model, neither should it ignore or downplay its importance. There are two facets to Pentecostalism’s relation to tradition. First of all, the Pentecostal movement stands firmly on the tradition of Christ’s church. Hence, a sufficient study of the whole of the church’s theo- logical, creedal, and historical tradition should belong to the core of the cur- riculum. Second, Pentecostalism in itself represents a growing tradition. As much as new revivalistic movements seek to live in the denial of the inevitable, there is no denying the accumulating effects of tradition and traditions.
Any effective theological education needs to be a good training in the tradition. Given the social reality of knowing, we must work within a framework of texts and commu- nity. Each one of us is born into a family and learns a particular language. From day one, each person looks at the world in a certain way. Knowledge is the result of the hard work of communities that struggle with the complexity of the world and start arriving at a more plausible account.22
As this word of wisdom from Markham illustrates, a proper attention to tradi- tion also helps bring in the importance of community. Communal orientation is needed in order to redeem Pentecostalism, including its leadership, from hopeless individualism. This is nothing but the ecclesiological model of Acts 2.
The important task for Pentecostal theologians is to discern and bring to light the key elements of what makes Pentecostal tradition. What, for example, is the role of the baptism in the Holy Spirit in Pentecostal living tradition?23 Change and tradition, new and old, should be kept in some kind of dynamic balance; that is a continuing challenge.24
22 Markham, “Theological Education,” 159. 23 See Lewis, “Explorations,” 162.
24 See further, Markham, “Theological Education,” 164.
12
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
257
Environment: Four Locations
The term environment in this essay refers to two interrelated aspects of Pente- costal theological education. The first has to do with the setting in which the training is done, whether in a church-based Bible school, theological college, or theological seminary, or in collaboration with “secular” university faculties such as in the Free University of Amsterdam. The second meaning of the envi- ronment relates to whether Pentecostal theological education is “Pentecostal” or, as it most often is alternatively, “Evangelical” with some Pentecostal tinsel. Let me begin with this latter meaning.
Anyone familiar with typical Pentecostal theological schools knows that much of what is taught has little or no direct relation to Pentecostalism; it is, rather, borrowed materials from the Evangelical storehouses. Pentecostal dynamics and philosophy of education are due to the “reliance upon pedagogi- cal and philosophical models that are more Evangelical (or fundamentalist) than Pentecostal . . . [and] written resources on educational philosophy and pedagogy authored by Pentecostals for Pentecostal educators are lacking, espe- cially for higher education.”25 In other words: although Pentecostal students study in a Pentecostal environment, their education is not often distinctively Pentecostal. It is, rather, the extracurricular activities that are more Pentecostal in nature. As a result, Pentecostals become vulnerable to losing their distinc- tive nature and identity.
Behind this malaise is not only the lack of developed Pentecostal theology or textbooks but also a general orientation in much of Pentecostal theological scholarship that often tends to major in repeating uncritically the voices of Evangelicalism, at times even Fundamentalism — even though it is the Funda- mentalists who have been most vocal opponents of anything charismatic! I am thinking here of Fundamentalistic views such as the doctrine of Scripture and inspiration (inerrancy), dispensationalist eschatology, and so on, which have been adopted without a concerted theological assessment of how well, or how badly, these views fit Pentecostalism.26 Henry Lederle of South Africa, himself a Charismatic Reformed, rightly remarks: “It is an irony of recent ecclesiastical history that much of Pentecostal scholarship has sought to align itself so closely with the rationalistic heritage of American Fundamentalism . . . without fully
25 Jeffrey Hittenberger, “Toward a Pentecostal Philosophy of Education,” Pneuma 23, no. 2 (2001): 226, 230; I am indebted to Lewis, “Explorations” (p. 172) for this citation.
26 For an enlightening analysis of the uneasy relationship between Pentecostalism and Funda- mentalism, see Gerald T. Sheppard, “Pentecostalism and the Hermeneutics of Dispensationalism: The Anatomy of an Uneasy Relationship,” Pneuma 6, no. 2 (1984): 5-34.
13
258
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
recognizing how hostile these theological views are to Pentecostal and Charis- matic convictions about present-day prophecy, healing miracles and other spiritual charisms.”27 Now, in principle there is, of course, no problem with bor- rowing from others. It would be only foolish to decline to drink from the com- mon Christian wells and take advantage of other churches’ millennia-long traditions of theological reflection. However, the way in which Pentecostals have done that — and seemingly continue doing it — is what raises concerns. In most cases, I fear, Pentecostal theologians do not acknowledge the fact that what they claim to be presenting as a “Pentecostal” theological view is often nothing more than a “Spirit-baptized” Evangelical, often even Fundamentalis- tic, view taken from others with little or no integral connection to the core of Pentecostal identity.
Pentecostals have much to learn from older traditions. Let me take just one current example. In the above-mentioned essay, Markham carefully considers what are the key elements in his own Anglican tradition and, on the basis of that investigation, lays out three broad theological principles with regard to Anglican theological education: first, it should be creedal because of the cen- trality of the ancient creeds and later Anglican dogmatic formulae; second, it should be liturgical because of the center of the church life in worship and lit- urgy; and third, it should be engaged because of Anglicanism’s deep desire to engage the society at large, including politics, culture, arts, science, etc.28 Now, these are not theological underpinnings for Pentecostal higher education. But I admire the clarity, consistency, and boldness of being true to one’s own tradi- tion without being hostile to others.
Building on one’s own identity and tradition is in no way an excuse or ratio- nale for excluding others or fostering anti-ecumenical attitudes (those are prevalent enough without much training, unfortunately!). On the contrary, from the “foundation” of a clearly formulated identity and belonging to one’s community grows an irenic spirit toward others. In keeping with this goal is the set of guidelines from the global working group of theological educators who prepared a useful document for the Edinburgh 2010 World Missionary Confer- ence in relation to theological educators:
27 Henry I. Lederle, “Pentecostals and Ecumenical Theological Education,” Ministerial Forma- tion 80 (January 1998): 46.
28 Markham, “Theological Education,” 160-62.
14
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
259
a. they should strengthen the denominational identity of future pastors and church
workers, so that graduates will have a very clear understanding of the church to
which they belong (theologicaleducation as denominational initiation);
b. they should introduce students to the wider horizons of the worldwide church so
that they will understand that they also belong to the ecumenical fellowship of
churches (theological education as discovery of catholicity);
c. they should prepare candidates to engage models of church unity, to reflect theo-
logically on ‘unity in diversity’ and to ask how the relation between local or denomi-
national identity and the ecumenical worldwide fellowship can be lived out
(theological education as enabling forecumenical learning).29
As mentioned above, Pentecostal theological training by and large takes place in four different environments.30 Both church-based Bible schools and bibli- cal/theological colleges have rendered an invaluable service to the global Pen- tecostal movement. Indeed, one can safely say that, without this network of grassroots-level training that owes its beginning to the end of the nineteenth- century Holiness and other Evangelical movements’ example, the establish- ment of Pentecostal churches all around the world might not have been possible. Even today these schools play a critical role in ministerial training, as is the case, for example, in most Latin American Pentecostal movements. The mode of rationality in those settings is markedly different from that of higher education proper. Their frame of reference is practical, short-term training of workers rather than academic education based on research and new knowledge.
In this essay, my focus has been on the academic section of Pentecostal theo- logical education as conducted in theological seminaries and theological col- leges with graduate departments; as mentioned, there is also emerging a new breed of Pentecostal theological training, that located in “secular” university faculties.
In the process of seeking a proper balance between the epistemologies of “Athens” and “Berlin” and consequently between the ethos of passing on tradi- tion and critical scrutiny thereof, the important question regarding the relation between the church and academia emerges (“church” here stands for all levels of ecclesiastical life from local churches to global networks of national movements).
29 “Challenges and Opportunities in Theological Education in the 21st Century: Pointers for a New International Debate on Theological Education,” Short version, Edinburgh 2010 — Interna- tional study group on theological education, World Study Report 2009, p. 8, available at http:// oikoumene.org/gr/resources/documents.html (accessed 7/13/2010).
30 In addition, there are locations that are difficult to classify such as the Folkhögskola (“Folk High School”) institutions in Nordic countries, which play an important role, for example, in Swe- den and in Finland.
15
260
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
Unlike university-based theology faculties — unless directly related to the given church, as is still the case in many Roman Catholic settings — that, in the name of academic freedom, resist any kind of supervision from the church, Pentecostal theological institutions better nurture a constructive, mutual rela- tion to the church. As discussed above, this kind of relationship is not without the challenges arising from two different rationalities and intellectual climates. The above-mentioned Edinburgh 2010 document summarizes in a most help- ful way some of the key principles in this regard under the title “Theological education and the church — a relationship of service, ownership, and critical distance.” The document takes as its starting point the overarching principle of closeness and distance, which helps the church to be the church and academia to be academia, yet in a way that makes the relationship mutually conditioning:
a. There is no fundamental contradiction between the principles of academic learning
or intellectual discipline on one hand and a church-related faith commitment on
the other, although at times there may be tension between the two. It is the task of
theological education to strengthen the commitment to Christian faith and to
develop a proper understanding and practice of it, which may include liberating
faith from narrow-minded or uninformed concepts and/or practices.
b. Theological education has a critical and liberating function in relation to the exist-
ing church; with reference to both Biblical and Christian tradition, theological edu-
cation can remind Christian communities of their proper tasks and key mandates. c. The church has a critical and alerting function over against theological education
and the forms of cultural captivity and blindedness theological education can find
itself in due to its particular environment and internal value systems. Serious com-
plaints are being heard that the theological academy in the West has lost its world-
wide, ecumenical perspective and its missionary impact, and that it is not sufficiently
cognizant of emerging shifts in World Christianity today.
d. Theological education therefore needs regular contact with the existing realities of
church life, involvement and close touch with the challenges of mission, ministry
and life witness of churches today, but it also needs critical distance and a certain
degree of autonomy from the daily pressures of church work and from the direct
governing processes and power interests of church institutions.31
Last Words: “An Unfinished Agenda”
Following the title of the late missionary-bishop Lesslie Newbigin’s autobiogra- phy, An Unfinished Agenda, suffice it to say that the continuing work toward a
31 “Challenges and Opportunities in Theological Education,” 6.
16
V.-M. Kärkkäinen / Pneuma 34 (2012) 245-261
261
more coherent and comprehensive theology of Pentecostal theological educa- tion is a task for the worldwide Pentecostal movement.
That said, I would like to come back to the question I raised in the beginning of the essay, namely, is bigger always better? Jon Ruthven formulates this ques- tion in a helpful way: “Could it be that the extreme reluctance of Pentecostal leadership to bow to pressures for the establishment of theological seminaries has merit? Instead of dismissing them as anti-intellectual, perhaps we might pause to consider if these leaders were onto something.”32 Professor Ruthven himself teaches in a seminary/divinity school setting; this surprising question is thus not meant to dismiss or even downplay the importance of highest-level theological training for Pentecostals. The way I take it is that in the midst of many and variegated efforts to update the level of theological education among Pentecostals, it would only be counterproductive to be so carried over by this effort as to lose the bigger perspective. As a bumper put it succinctly: “The main thing is to keep the main thing the main thing.” The key is to work toward a form and content of theological education that bears the marks of an authentic Pentecostal spirituality and identity.
Ultimately, “theological education is part of the holistic mission of the Chris- tian church,” says the World Council of Churches’ Oslo (1996) statement to which Pentecostals can only say, “Amen and Amen.”
There is consensus among us on the holistic character of theological education and ministerial formation, which is grounded in worship, and combines and inter-relates spirituality, academic excellence, mission and evangelism, justice and peace, pastoral sensitivity and competence, and the formation of character. For it brings together edu- cation of:
the ear to hear God’s word and the cry of God’s people;
the heart to heed and respond to the suffering;
the tongue to speak to both the weary and the arrogant;
the hands to work with the lowly;
the mind to reflect on the good news of the gospel;
the will to respond to God’s call;
the spirit to wait on God in prayer, to struggle and wrestle with God, to be silent in penitence and humility and to intercede for the church and the world; the body to be the temple of the Holy Spirit.33
32 Ruthven, “Pentecostal Seminaries,” n.p.
33 Cited in “Challenges and Opportunities in Theological Education,” 5.
A Great Century of Pentecostal Charismatic Renewal
A “Great Century” 81 of Pentecostal/Charismatic Renewal and Missions Edward Keith Pousson Pentecostals and Charismatics missionary-minded segment of dynamics Charismatic to produce a worldwide The following make up what is probably the most world Christianity today. What are the of this century-long movement of both Pentecostal and Renewal that have converged missionary thrust? And on what grounds can we speak of the twentieth century as a “great century” of Pentecostal/Charismatic missions? two questions launch and guide our discussion. will also be addressed: What kind of missionary has emerged from the Charismatic Renewal in particular? has Pentecostal missions impacted Charismatic missions, and what lessons can Charismatic missions learn from Pentecostal missions? What is the emerging Charismatic contribution to mission theology? between renewal and missions is the theme that unites These related questions movement How The relationship this entire article. An End-Time Movement in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. Missions Scott Latourette Christian missions. worldwide religion. century as a comparably “great renewal and missions? What common to Renewal and Missionary This section explores the relationship between renewal and missions against the backdrop of developments Professor Stephen Neill and Yale Historian Kenneth called the nineteenth century the “Great Century” of It was that century that made Christianity a On what grounds may we speak of the twentieth century” are some of the dynamics of renewal both of these centuries that have birthed massive missionary movements around the world? Renewal Results in Mission First, and of primary significance movements every Christian Orthodox, renewed of Pentecostal/Charismatic for this article, spiritual renewal to global missionary in both of these periods gave birth expansion. By the end of the eighteenth century, for example, virtually denomination throughout the Western world, including Catholic and Protestant churches, had been recently in one way or another. Renewal movements in Protestantism included Pietism, Puritanism, Moravianism, England and the related Wesleyan revival, and the Great Awakenings the American Colonies. Though unevenly distributed and timed, it was this church-wide awakening that provided the spiritual impetus for that the Evangelical Revival in in 1 82 which is now called the “Great I Century” of Christian missions, Similarly, renewal pervasive missionary expansion and global country where rapid church Pentecostal/Charismatic decadal growth rates.2 In 1992, Wagner penned this hypothesis: non-militaristic, beginning 1792 and ending 1914.’ in the twentieth century, impacted virtually every renewal has likewise brought church growth. Pentecostal and Charismatic Christian denomination. This about unprecedented In nearly every multiplication is occurring, are leading the way in terms of C. Peter movement has over the past congregations church growth professor “In all of human history not another non-political voluntary human movement has grown as dramatically as the Pentecostal/charismatic 25 years.”3 Without question, as Wagner suggests, Pentecostalism in all its forms is the fastest growing segment of Christianity in the twentieth century. It grew from 16 million worldwide adherents in 1945 to 4.3 billion in 1993.4 Renewal about dramatic changes of that both periods of renewal Protestant institutions, new missionary structures. Protestant the nineteenth century minds of Neill and Latourette Changes Christian Institutions A second comparison from the nineteenth and twentieth centuries is brought in including and especially a vast proliferation The birth and multiplication of these missionary societies is perhaps the leading factor that makes the Great Century of Christian missions in the Once freed from church and state launched more than 21,000 control, these voluntary societies focused exclusively on missions and Protestant missionaries by 1910.6 Thanks to Harper History of ‘ See Kenneth Scott Latourette, A History of Christianity, Vol. 2 (New York, NY: . & Row Publishers, Inc., 1953), 1013-1035; Gary B. McGee, This Shall Be Preached. A Gospel to 1959 History and Theology of Assemblies of God Foreign Missions (Springfield, MO: Gospel Publishing House, 1986), 24; Stephen Neill, A Christian Missions (Second edition revised by Owen Chadwick; London and New York: Penguin Books, 1986), 204, 213-215, 240-245, 286-287, 332-334. 2 C. Peter “Church Growth,” in Pentecostal and Charismatic Wagner, Dictionary of Movements, eds. Stanley M. Burgess and Gary B. McGee (Grand MI: Zondervan Publishing House, 1988), 185-188. [Hereafter cited as Rapids, A1issions, 214; Sydney (New 6 McGee, missionary DPCM.] I ‘ C. Peter Wagner, Warfare Prayer (Ventura, CA: Regal Books, 1992), 48. 4 ‘David J. Hesselgrave, Today’s Choices for Tomorrow’s Mission (Grand Rapids, MI: Zondervan Publishing House, 1988), 119; David B. Barrett, “Annual Statistical Table on Global Mission: 1993,” International Bulletin of Missionary Research 17 (January 1993): 22-23. ‘Latourette, A History of Christianity, 1013-1033ff.; Neill, A History of Christian E. Ahlstrom, A Religious History of the American People Haven and London: Yale University Press, 1972), 422-423. This Gospel Shall Be Preached, I, 21. Examples of early Protestant societies include William Carey’s Baptist Missionary Society (1792), the London Missionary Society (1795), and the American Board of Commissioners for Missions (incorporated 1812). Foreign 2 during Through the twentieth movement has likewise given sending agencies, including 83 living in Asia, the Pentecostal/Charismatic and the world’s largest with some 25,000 of recent their efforts, the percentage of the world’s Protestants Africa and Latin America increased from one percent to ten percent the nineteenth century.’ 7 century, birth to hundreds of new missionary the Assemblies of God Foreign Missions Division with more than 1,500 missionaries, Christian mission, Youth With a Mission (YWAM), missionaries reaching out to nearly every country of the world.’ But the the movement is not its number of missionaries, on the mission field. Eighty percent to Christianity have been the result of according Today at least 66% of the world’s Pentecostals/Charismatics Latin America, and Oceania, including 88% of Assemblies church members and 75% of Church of God (Cleveland, TN) believers, two of the largest Pentecostal denominations worldwide.’° crowning success of but its growth conversions from paganism Pentecostal/Charismatic efforts, Asia, Africa, of God Patterns of Piety fueled the nineteenth produced striking changes piety. Moravian pietism to several researchers.’ live in movement, for instance, of Protestant Renewal Changes A third common feature of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries is that both periods of renewal unleashed new forms of spirituality that aided fresh missionary expansion. The various renewal movements that century missionary in the forms and expressions centered on Christ and him crucified. Wesleyanism called for personal conversion, The Great Awakenings in the Colonies/States stressed the unchurched, preaching. “evangelical” preaching for the need for individual “decisions” holy living, and zeal in resulting responsibility for witness, in the “new birth,” and a prayer for enabled the Protestant strong desire for individual and corporate prayer, including concerts of world missions. These new expressions of spirituality faith to adapt itself and reach out to the ends of History 8 Gary for (Grand Rapids, ‘Paul E. Pierson, “Why Did the 1800s Explode with Missions?,” Christian 11/4 (1992): 20. B. McGee, “Overseas Missions (North American),” DPCM, 614-624; David B. Barrett, “Global Statistics,” DPCM, 814-815, 830; Choices Tomorrow’s Mission, 120, 255n; Edward K. Hesselgrave, Today’s Pousson, Spreading the Flame MI: Zondervan Publishing House, 1992), 88-89; John A. Siewert and John A. Kenyon, eds., Mission Handbook 1993-95 (15th Edition; Monrovia, CA: MARC, 1993), 243, 248, 255-256. 9 Vinson Synan, “Global Consultation on AD 2000 3 Evangelization: AD 2000 the Target,” Together (Spring 1989): 7; Larry Pate, From Every People (Monrovia, CA: MARC, 1989), 129; C. Peter Wagner, Spiritual Power and Church Growth (Altamonte Springs, FL: Strang Communications 1986), 12; C. Peter How to Have a Healing Ministry Without Company, Making Your Church Sick (Ventura, CA: Regal Books, 1988), 68-89. ‘°L. Grant McClung, “The Pentecostal ‘Trunk’ must Learn from its ‘Branches’,” Missions Quarterly 29 (January 1993): 35. Wagner, Evangelical 3 84 our changing movements.” world through many new and unprecedented renewal has produced new and material. Comparing needs-spiritual, Pentecostal Comparatively, Pentecostal/Charismatic and varied expressions of worship and spirituality which have reached to the ends of the earth. One major factor behind the astonishing success of the movement is its appeal to a broader range of human physical to ministry with the Interdenominational Foreign Missions Association (IFMA), missionary theologian Arthur F. Glasser of Fuller Theological Seminary’s School of World Mission emotional, approaches writes, challenge evangelicals… … Pentecostals were willing to tackle the “dark side of the soul” and the growing phenomenon of occultism, Satan worship and demon possession. Whereas IFMA people and other non-charismatic had found it relatively easy to the occasional expose the extravagance of charlatan, they were silenced in the presence of the Pentecostal’s serious confrontation of the hard realities of the spirit world. Here was a spirituality which could not be ignored. 12 Charismatic spiritual guidance, together ministry, dynamic praying movement world. such as exorcisms, worship, healings and spontaneous secularizing “power-encounters,” with expressive and a lively oral tradition make this especially appealing to many peoples of the non-Western Through these and other viable spiritual dynamics, PentecostaUCharismatic missions has curtailed trends of earlier missions that offered people “soul-salvation” but left miracles, healings to the early church.’3 Pentecostal/Charismatic missionaries offer healing, not to “disembodied exorcism and physical souls,” but to whole persons. Renewal expansion global of Changes Leadership Patterns A fourth renewal dynamism giving rise to unprecedented in nineteenth century was the creation of new patterns of leadership, including the service of women, increased participation lay people and of less formally trained clergy, and the unprecedented mobilization of 180,000 student volunteers for missions.14 Similarly, Pentecostals/Charismatics have advanced in missions through hands-on, leadership training models, and the sending of many women evangelists and missionaries. ‘ decentralized training, semiformal Bible institute 11 Latourette, A History ojChristianity, 959-960, 1019-1029, 1043-1047; Neill, A History of Christian A1issions, 202-204, 214, 275. 12 Arthur F. Glasser and Donald A. McGavran, Contemporary Theologies of Mission (Grand Rapids, MI: Baker Book House, 1983), 119-120. “See Paul G. Hiebert, “The Flaw of the Excluded Middle,” Missiology: An International Review 10 A (January 1982): 35ff. 14 Latourette, History ojChristianity, 960, 1020, 1027; McGee, This Gospel Shall Be Preached, I, 24; Neill, A History of Christian Missions, 217-218. “L. Grant McClung, ed., Azusa Street and Beyond: Pentecostal ivissions and 4 example, undesirable, proven growth provided people respond. They “experience” 85 modified Calvinism by making Strong reliance on the laity and multiple routes to ordination have accelerated leadership emergence in areas of rapid church growth. For most Assemblies of God pastors around the world are without so much as a Bible school education. `6 Higher education is not but imposing educational requirements for ordination is a restriction in some cases. And the lack of educational requirements for ordination has not stopped the Assemblies of God from becoming the largest Pentecostal denomination. Renewal Alters Theological Traditions Consider one final comparison between these two “great centuries” of renewal and missions. In both cases, renewed theological reflection motivations for a new thrust in world evangelization. Of great significance for the nineteenth century missions movement was this one fact: renewal reshaped traditional Calvinism with respect to election and predestination. The Puritan fathers, for example, believed that all would hear the gospel and that some from every nation would launched missions to the Indians in all Thirteen Colonies. The Great Awakening in the Colonies broached Arminian-ish ideas, establishing the need for an individual “decision” and a personal of salvation for the elect. And Jonathan Edwards, a leading theologian of the Awakening, for the sinner’s response in accepting God’s forgiveness.” in England, the Evangelical Awakening with its stress breaking up hyper-Calvinism. Even among the Particular Baptists, William Carey’s there was a “slow awakening,” Stutd1fse, Carey, and others planted seeds of a mission theology into In these and many other ways, revival . of traditional theology, providing fundamental convictions and motivations for the nineteenth century missions more room Simultaneously on evangelism was also denomination, the English religious scene.” altered the landscape movement. Topeka, America. the fallow ground of as Andrew Fuller, John in Pentecostalism. The revival in of Pentecostalism in North reflection to Los Angeles, We observe the same pattern Kansas marks the beginning This revival was triggered by fresh theological concerning sanctification, the baptism in the Holy Spirit and speaking in tongues. From Topeka the revival spread to Houston, Texas, and then where the Azusa Street Revival broke out and 76-77; Rapids, Church Growth in the Twentieth Century (South Plainfield, NJ: Bridge, 1986), McGee, This Gospel Shall Be Preached, I, 91-93. 16 J. Herbert Kane, The Christian World Mission: Today and Tomorrow (Grand MI: Baker Book House, 1981), 105. “These and many other theological developments linked to the Great and Awakenings providing missionary motivations are discussed in Latourette, A History of 958-961, 1019, 1043-45. ‘eTim Dowley, ed., A Lion Handbook: The History of Christianity (Oxford: Lion 406-409. Christianity, Publishing, 1990), 5 86 innovations in early motivations and convictions movements. Consider One, Pentecostals Spirit Testament experience. impacted various parts of the world. Theological and mature Pentecostalism have provided powerful that could not help but produce explosive missionary the following three theological innovations. claimed that the personalized power of the Holy is readily available now to every believer just as it was in New Pentecostals discovered that they can receive the sacraments and experience the Spirit, not through the mediation of and the clergy (as in Catholicism), and not only through the ministry of the Word (as in mainstream Protestantism), but through direct and personal access to the Father and to Jesus, the Baptizer in the Holy Spirit.19 Two, Pentecostals emphasized Pentecost expect the supernatural ministering that the purpose of this personal for missions. This claim of the biblical experience of the Holy Spirit is empowerment is a rediscovery by experience of the true purpose (Acts 1:8). Being “baptized” in the Spirit, Pentecostals manifestations or charismata of the Spirit to be there for them in evangelistic and missionary outreach. Three, Pentecostals see themselves as living in the last days and in the same salvation history context as that of the New Testament.2° They have, therefore, recovered the New Testament hope of the soon return of Jesus. This view of things has generated powerful motivation which is characterized by expectancy, urgency, how renewal alters missionary and intensity. These three innovations theological traditions movements. Theological serve to illustrate in such a way as to stimulate fresh missionary reflection concerning the mission of the church has played a vital role across the last two great centuries of renewal and missions. century” above parallels between these of a professional of the School of World Mission Pasadena, California. 21 Although my analysis may lack the nuances historian, I believe that the twentieth century can be called the “great of Pentecostal/Charismatic renewal and missions in that it bears comparison to the nineteenth-century missionary movement. The two periods of renewal and expansion are not only striking but also instructive. They illustrate the following key missionary principles taught by missions historian Paul E. Pierson at Fuller Theological Seminary in First, renewal and missions are interlinked. Missionary expansion is both the natural and the supernatural result of the outpouring of the Spirit of God upon the church (Acts 1:8). Any renewal that is truly Missions “Dowley, ed., A Lion Handbook, 646; Paul A. Pomerville, The Third Force in (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson Publishers, 1985), 65. 2°Pomerville, 21 The Third Force in Missions, 57-58. While Pierson is to be credited for these principles, I do not claim his authority for the ways in which I have adapted and applied them in this article. 6 87 eschatological will eventually turn its focus outward and cross social and cultural barriers to reach the lost, as the biblical Pentecost did. Second, renewal changes the way we do church and missions, creating new structures and patterns for both. Specifically, missions is most effective when local churches and extra-local mission structures cooperate together in a semi-autonomous, mutually interdependent fashion, as seen in both the nineteenth and twentieth century missionary movements mentioned above, as well as throughout church and missions history. Third, renewal creates new and viable forms of spirituality that spur fresh missionary outreach and appeal more effectively to the unchurched peoples of the day. Fourth, renewal creates new patterns of leadership that unleash fresh missionary outreach. And fifth, renewal alters older theological traditions and ushers in new theological insights that provide fresh motivation for evangelistic and missionary outreach. Observing Pentecostal/Charismatic renewal and missions in a general way, we have thus far identified key dynamics or characteristics of renewal that lead almost inevitably to a missions thrust. This analysis provides the foundation, perspectives and presuppositions for all that follows. From here on, however, the emphasis falls more specifically on Charismatic missions of the latter half of this century. The Charismatic Renewal: Creating New Patterns for Church and Missions That the Pentecostal revival has produced a major missionary movement is a well documented fact. By 1990 there were 320,000 classical Pentecostal churches around the world with a total membership of over 45 million. 22 But what kind of missionary movement has the Charismatic Renewal produced? How are the dynamics and principles observed above also working in the Charismatic Renewal? . The Emergence of a “Charismatic” Ecclesia Renewal, we have observed, changes the way we do church. The healing revival of the 1950s formed the bridge between the Pentecostal Movement and the Charismatic Renewal. William Branham, Oral Roberts, T. L. Osborn, Jack Coe, A. A. Allen, R. W. Schambach and hundreds of other healing revival leaders caught the attention of the masses in mainline churches who had more or less ignored classical Pentecostalism. This was the real beginning of the Charismatic Renewal. Dennis Bennett’s public announcement in 1960 of his “nine o’clock in the morning” experience was merely the cutting of the ribbon. After the media publicized Bennett’s announcement, many others in mainline churches admitted their own Charismatic experiences. Many z2 Barrett, “Global Statistics,” DPCM, 812-815. 7 88 Charismatic leaders were able to stay in their traditional churches and cultivate renewal. But hundreds of others were forced out. New wine skins were needed for the new wine. As a result, tens of thousands of independent Charismatic churches were eventually formed across the United States and around the world. For the sake of definition, “independent Charismatic” denotes churches or ministries that have embraced the Charismatic Renewal and, because of their Charismatic experiences and innovations, are not institutionally linked to classical Pentecostalism or any denomination. Although these churches only began to form in the early 1970s, they represent 14% of all Charismatics and now make up the fastest growing segment of Christianity in the United States as well as in many Third World countries.23 There are between 60,000 and 100,000 independent Charismatic congregations in the USA alone. Consistent with observations made in the beginning of this article, independent Charismatic churches are bom out of renewal and have certain characteristics which promote effective missionary outreach. What are these characteristics? First, despite the apparent “babel” of diversity, there is an underlying spiritual unity among these churches. Nowadays old rifts are being forgotten and Charismatic churches and ministers are coming together in “networks”-loose, overlapping ministerial associations without the legal or bureaucratic encumbrances. Well known examples include Charismatic Bible Ministries (1,500 ministers), Christ for the Nations (600 churches), Rhema Ministerial Association (500 churches) and the large, umbrella type Network of Christian Ministries, which brings together leaders of other networks. Second, independent Charismatic churches, like new wine skins, help preserve the witness and the heritage of the Charismatic Renewal. The practical value of this is best seen in light of the fact that most mainline Charismatics become “postcharismatics” after two or three years of involvement in the renewal. 24 Third, independent Charismatic churches have unleashed their laity. They have recruited, apprenticed, and released into ministry and missions thousands of people with little or no formal theological training. Not that professional training is of no value. But Christian history teaches us that God often calls and uses people on the periphery of our religious institutions. “Can . anything good come out of Nazareth?” “Peter D. Hocken, “Charismatic Movement,” DPCM, 144; Wagner, “Church Growth,” DPCM, 181-182; Paul G. Chappell, “Healing Movements,” DPCIU 374; Stephen Strang, “Nondenominational Pentecostal and Charismatic Churches,” DPCM, 640; Barrett, “Global Statistics,” DPCM, 811-813. “For definition and statistics on “postcharismatics” in mainline churches, see Wagner, “Church Growth,” DPCM, 183; Barrett, “Global Statistics,” DPCM, 811-813, 826. 8 Fourth, Charismatic The by leaders, Jesus, people Renewal, powerful strongest and most consistent For an exception the movement’s missions. Many movement. 89 and missionaries are “practical” or mission fields. But some of these love the Lord Missions thrust of the Charismatic Charismatic churches and a major missionary pastors theologians. frame of reference for their theology is provided, not the seminary, but by the context of their ministry and by the hurts, needs and questions of their congregations The lack of theological foundations is sometimes problematic. who are often the subject of a media-inquisition, love their congregations and have led hundreds and thousands of into a liberating experience of the kingdom of God. These and other spiritual and institutional dynamics make the Charismatic and in particular, the independent Charismatic church, a force for world evangelism. The “Slow” Emergence of Charismatic If renewal and missions are linked, then what kind of missionary movement has come out of the Charismatic Renewal, and what kinds of structures and strategies are being used to muster missions activity? While denominational Charismatic missionaries have excelled, the missionary Renewal has come from the independent ministries.’ To this exciting story we now turn. a while, it looked as though the Charismatic Renewal would be to the rule that revival results in mission. Some still question missionary track record. Three things need to be noted. First, not all Charismatic churches are equally interested in are still “bless-me” communities, not yet realizing missions as the reason for revival. Second, the Protestant Reformation was nearly two centuries old before it produced And third, most of what is now being done by Charismatics in missions remains undocumented. But there are indicators of a ground swell of effective missionary activity among Charismatics. the beginnings of a distinctively Charismatic missionary thrust have been relatively slow for the following reasons.26 within the churches. rightly spent much time and energy bringing their own churches and denominations. Structure limitations. Thousands of independent have no connections with organized missions agencies. Many have espoused the ideal of being a “sending church” apart from the expertise and assistance of agencies that specialize in if any, have really succeeded over the long haul. Related to this problem is the spirit of independence that obstructs practical, functional unity and cooperation however, Renewal ministry Charismatic leaders renewal to bear upon churches training and sending missionaries. efforts. Admittedly, Many of the early Charismatic sending Few, in missions 2S 26 Hocken, “Charismatic Movement,” DPCM, 157. Pousson, Spreading the Flame, 79-82. 9 90 Strategy limitations. The emphasis on the Holy Spirit and subjective guidance sometimes preempts practical goal-setting and informed strategy planning. Once a Charismatic minister “felt led” to evangelize a certain Caribbean island. He resigned from his pastorate, raised funds and went to the island, finding nothing but coconut trees. No people. Limited theology of mission. Charismatic anti-intellectualism coupled with the idea of learning by “revelation” apart from theological discipline has taken a toll. Too many churches are built around faith for prosperity, healing and spiritual gifts, often to the exclusion of the biblical basis of missions and the New Testament revelation of the Holy Spirit as empowerment for worldwide, cross-cultural witness to the Risen Lord. Limited missions exposure. Many independent Charismatics have little awareness of recent global mission trends even in their own movement. What is an unreached people group? What is the 10/40 Window? What is the AD 2000 & Beyond movement? What is a career missionary, and how does a person become one? Sad to say, surveys have shown that vast numbers of Charismatics all across the United States are simply unacquainted with these and other mission dynamics. Related to this lack of exposure is the lack of real missionary vision and leadership. These and other bottlenecks account for what some would consider a sluggish start for Charismatic missions. But that is not the whole picture. There are signs that Charismatics, particularly the independents, are seizing a global missions vision and making a global contribution. Charismatics, for example, outnumbered Pentecostals in the number of worldwide annual converts in 1988, according to David Banrett.2′ From the very beginning of the Charismatic movement there were notable missionary pioneers. And through the decades of movement we have seen the emergence of Charismatic sending churches, sending agencies, and a premier association of Charismatic mission agencies and churches called the Association of International Missions Services (AIMS). Charismatic Missionary Pioneers Oral Roberts, T. L. Osborn, Gordon Lindsay, Kenneth Hagin, Sr., and Lester Sumrall are among the few leaders from the Post-World War II healing revival (1947-1958) who also became significant leaders in the subsequent Charismatic Renewal. They have blazed a trail for Charismatic missions. Oral Roberts founded the university named after him which trains Charismatics from all over the world. From 1976 to 1990, Oral Roberts University sent several thousand students into more than 30 countries on “Summer Missions” assignments. T. L. Osborn has played a leading role in Charismatic renewal and missions. By the early 1970s he had already evangelized in over 50 27Barrett,. “Global Statistics,” DPCM, 811. 10 91 countries where his ministry was producing more than 400 self-supporting churches annually. 21 In 1970 Gordon Lindsay founded Christ for the Nations Institute (CFNI) which continues to train and send out Charismatic missionaries to many parts of the world. Kenneth Hagin, Sr. and Lester Sumrall have also founded and led major Charismatic ministries which have launched missionaries and missions efforts in every continent. Pentecostal/Charismatic pioneer Daniel Ost founded Charismatic Ministerial Institute (CMI) in El Carmen, Mexico in 1955. Since then, CMI has trained and launched more than 1,000 ministers throughout Mexico and in ten other countries, including India and France. CMI graduates have founded 120 churches called “Centers of Faith, Hope and Love” which are transforming major cities across Mexico. The school is now challenging its students to go as missionaries to the “10/40 Window,” the least evangelized region of the world, stretching from West Africa to East Asia, 10 degrees and 40 degrees north of the equator. Mexico is no longer just a mission field, but also a missionary force.29 Charismatic Sending Churches Bethany World Prayer Center in Baker, Louisiana is an independent Charismatic church of four to five thousand members. A million dollars annually from their budget supports various projects and over 100 missionaries in 25 countries. One-third of these missionaries were recruited and sent out from Bethany World Prayer Center. The pastor, Larry Stockstill, a graduate of Oral Roberts University, has adopted a strategy which combines crusade evangelism with church planting techniques. With this strategy, several large and growing churches have recently been planted in Russia, Nicaragua, Uganda and India. In 1991, for example, a Bethany team held an evangelistic church planting crusade in Moscow. The result was 5,000 decisions for Christ and 1,000 new believers in attendance at the first service of the Moscow Christian Center. . Another Charismatic church with a serious missionary vision is John Osteen’s Lakewood Church in Houston, Texas. Since its founding in 1961, Lakewood Church has launched effective missions outreaches to more than a hundred countries.3° Tulsa Christian Fellowship, the oldest independent Charismatic church in Tulsa, Oklahoma numbers about 500 and gives $150,000 a year to missions. They have sent out at least 28 David Edwin Harrell, Jr., All Things Are Possible: The Healing and Charismatic Revivals in Modern America (Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press, 1975), 171. z9 Lee Anderson and Christina Tumey, “Mexican Churches Charisma & Growing Christian Rapidly,” Life 19 (October 1993): 68-73. ” Stephen Strang, “Osteen, John Pentecostal Explosion (Altamonte Springs, FL: Creation House, Hillery,” DPCM, 656; Vinson Synan, The Twentieth-Century 1987), 25-29. 11 92 40 of their own people as missionaries involved in just about everything from Bible translation to pioneer evangelism among unreached people groups. Still another example, the 8,000-member Victory Christian Center, also in Tulsa, supports 125 missionaries to 20 different countries. A closer look at a few successful sending churches, including some of those mentioned above, has revealed certain keys to their success. 1) They have a consistently missions-minded pastor and a missions director or a missions committee to steer the church’s missionary involvement. 2) They commit a substantially large percentage, typically from 20% to 30%, of their annual budget to missions. 3) They strongly emphasize the role of the local church in missions, providing consistent missions exposure through literature, preaching and mission conventions. 4) They provide their missionary candidates with both informal apprentice training as well as structured Bible school training. 5) They have loose but functional ties with mission organizations that provide various types of training, helps and services to their missionaries. For example, they may send a missionary through Youth With a Mission or Wycliffe Bible Translators. Some churches relate to Charismatic service agencies that handle the missionaries’ financial matters and newsletters. 6) Sending churches usually have relationships with senior missionaries and/or indigenous Christian leaders in or near to the countries where their missionaries serve. These leaders in the host countries serve as mentors and field directors, especially for new missionaries. 7) Successful sending churches provide pastoral care for their missionaries away from home. This caring support involves correspondence, phone calls, cassette recordings of the pastor’s sermons, and, if necessary, a personal visit from the missions director. These seven factors make up a fairly simple and reproducible methodology, regardless of the size of the church. The Charismatic sending church model has much to offer. It bring their members back to the New Testament conviction that Charismatic experiences are given to the church for the purpose of mission. It emphasizes the centrality of the local church in missions. It produces missionaries that have the local church at heart and believe in church planting. And it helps ease church-missions tensions that exist in many Christian traditions. Despite a highly vocalized ideal of “sending direct” without the aid of so-called “para-church” organizations, I have found that the really successful sending churches usually rely on extra-local entities for help in training, mobilizing, serving and supervising their missionaries. When, however, the church tries to act like a self-contained mission agency, certain weaknesses crop up. Missionaries often become like lone rangers on the frontier without proper supervision or accountability. To the other extreme, some sending churches only get 12 93 involved with persons and projects that they can somehow control from the home front. Furthermore, many churches that try to be the mission agency act more like travel agencies. Short term mission trips to places where churches already exist becomes a substitute for real pioneer missions work. Other weaknesses include the sending of inadequately trained missionaries, haphazard field selection, and duplication or lack of cooperation between missionaries in the same location. The greatest problem with churches that try to become the mission agency is the historically repeating pattern whereby the apostolic function becomes absorbed by churchly concerns. A sudden or gradual shift in missions philosophy or priorities on the part of the sending church can leave missionaries in the lurch. In 1990, for example, a large Charismatic sending church changed its focus from foreign missions to home missions and expeditiously withdrew financial support from 35 overseas missionaries. Many of these had to come home because all their eggs were in one basket. Charismatic Sending Agencies Consistent with the pattern of the Great (nineteenth) Century, whereby awakening resulted in the proliferation of new mission agencies, the Charismatic Renewal has also produced a multitude of new mission structures. Many of the Charismatic networks described earlier in this article have formed creative missionary sending and service agencies which contribute in various ways to the recruiting, training, and mobilizing of cross-cultural missionaries. Other Charismatic mission structures have emerged independently of networks. In the late 1980s, one hundred new agencies surfaced in the Western world, and over three hundred in the Third World.3′ At least ten of the agencies listed as “Charismatic” in the 1993-95 edition of the Mission Handbook are independent Charismatic and represent a total of 646 USA personnel overseas.32 There are many other agencies of various types which represent thousands of Charismatic missionaries. Listed in the Mission Handbook as transdenominational, Youth With A Mission has thousands of missionaries who come from independent Charismatic churches. Not listed in the Handbook, the Oklahoma-based “Teen Mania” has sent hundreds of high school students on summer missions outreaches since 1987. In the summer of 1993, for example, Teen Mania took 1,750 teens to 14 countries, including Mongolia, Egypt and Albania.33 A Charismatic Missions Association In 1985, Charismatic leader Howard Foltz saw that the groundswell Charismatic missionary activity would warrant some kind of 31 32 Barrett, “Global Statistics,” DPCM 830. Siewert and Kenyon, Mission Handbook, 248, 255-256. “1. Lee Grady, “Radically Saved,” Charisma & Christian Life 19 (September 1993): 38-40. 13 94 overarching fellowship or association. So he founded and now leads the Association of International Missions Services (AIMS), a consortium of some 150 Charismatic sending churches, sending agencies and training institutions. Based in Virginia Beach, Virginia, AIMS is devoted to catalyzing the resources of the Charismatic Renewal for world evangelization. It provides a framework for unity, cooperation and the sharing of information between its member organizations. These kinds of developments suggest that the Charismatic Renewal is producing a major missionary thrust, and that the independent Charismatic church is the heartbeat of this thrust. With this in view, we now take up questions raised in the introduction about the relationship between Pentecostal missions and Charismatic missions. The Charismatic Contribution in Relation to Pentecostal Missions Several observers of Pentecostalism agree that the various Pentecostal and Charismatic expressions in the twentieth century all stem from one eschatological renewal movement. The spiritual foundations and impulses for Charismatic missions are traced to the same Holy Spirit revival that began at the start of this century. For all their innovations, Charismatic missions stand in strong continuity with the Pentecostal movement in certain important respects. How Pentecostal Missions Impacts Charismatic Missions First, most of the early pioneers in Charismatic missions, including those mentioned above, either had Pentecostal roots or were influenced by Pentecostalism. Gordon Lindsay, for example, in the late 1960s transformed his revivalistic “Voice of Healing” organization into a Charismatic missionary society devoted to world evangelization. By 1973, Lindsay’s ministry, Christ for the Nations, had helped finance 3,000 church buildings in 83 nations and had distributed 15 million books in 46 languages. 31 Second, Charismatics have also followed many of the strategies of Pentecostal missions. For example, the supernatural calling and recruitment of missionaries, apprenticeship training of missionaries, the use of women in missions, the dependence on the Spirit’s intervention in evangelism, the use of evangelistic crusades to plant churches and the application of indigenous church principles are common strategies in both Pentecostal and Charismatic missions. And third, Pentecostalism’s theological motivation for mission has significantly impacted the Charismatic movement. The Pentecostal emphasis on the Holy Spirit as empowerment for mission is basic to Charismatic missions. Charismatics have inherited from Pentecostals a “Gary B. McGee, “Association of International Mission Services,” DPCM, 30; Pousson, Spreading the Flame, 25-26, 52, 70, 88, 127-128. 35Harrell,A// Things Are Possible, 166-168. 14 95 strong commitment to the literal and plain meanings of Scripture, a Christ-centered approach to worship, preaching, and ministry, a sense of urgency for mission as people living in the last days and a sense of divine destiny.36 Although “Charismatic theology” is still in its formative stages, many Charismatic leaders intuitively know that their Charismatic experiences should lead to evangelism and missions. Emerging Charismatic Contributions to Theology of Mission The Charismatic movement is consistent with historic Evangelical theology with respect to the Trinity, the Incarnation, Christ’s atonement, resurrection, regeneration by the Spirit and other basic doctrines.” Also, as noted above, Charismatics are basically in the same theological orbit as Pentecostals. The Charismatic movement, however, is yet to develop an adequate theology of mission as such. A solid theology of mission would, in fact, be an effective antidote to many of the abuses in Charismatic circles. Nevertheless, there are several tenets of Charismatic “theology-on-the-way” that can or do contribute positively to mission and mission theology. Faith teachings. Despite its many abuses, the so-called “faith movement” honors God and serves mission inasmuch as it cultivates in people a deeply personal, corporate and biblical trust in the Person and power of Jesus Christ. Charismatic faith teaching stresses physical healing, material well-being, positive thinking and confession, divine guidance and the believer’s authority and victory over Satan, principalities and powers. Criticisms and reactions against these teachings abound. Some criticisms are valid. But the spiritual dynamics related to the faith teachings positively account for much of the success in Charismatic evangelism and missions today. Rightly focused faith is central and essential to all successful missions. Howard Foltz of AIMS writes, Faith teaching has elevated the expectations of many believers today to for God and “attempt great things expect great things from God.” When dynamic rhema faith is released in reaching the nations, and not on selfish or material wants, great things can happen. Numerous missionaries from the faith movement have gone to the mission field and believed God for far more than the “average” missionary. 38 Kingdom now. There is another stream of Charismatic thought known as “Kingdom Now.” Leading centers of this emphasis include Earl Paulk’s 10,000-member Chapel Hill Harvester Church in Atlanta, Georgia, and Tommy Reid’s Full Gospel Tabernacle of Orchard Park, New York. These, and others in the “kingdom now” circle, model and 36 McClung, Azusa Street and Beyond, 48-52. “J. I. Packer, “Piety on Fire,” Christianity Today, 12 May 1989, 20. 38Howard Foltz, “Moving Toward a Charismatic Theology of Missions,” paper presented at the 17th Annual Meeting of the Society for Pentecostal Studies (Virginia Beach, VA: November 12-14, 1987), 76-77. 15 96 visible expression of God’s concern on change social conscience Covenant theology. into secular society for the sake of The church is to be a of urge active Christian penetration social service and structural transformation. dominion in the world. Kingdom now theology represents at least a small step towards a theology of social the part of Charismatics. Since internal and external cultural is part of the biblical missionary mandate, the emergence of a in Charismatic circles is praiseworthy. This wing of the Charismatic movement emerged from the controversial discipleship-shepherding teachings the 1970s. Some of these principles continue to find expression in many Charismatic churches today, such as the Fellowship of Covenant Churches and Ministers founded by Charles Simpson and based in Mobile, Alabama. Covenant teachings emphasize self denial, obedience to the commands of Jesus and the need for growth to maturity in the between believers and between spiritual and mentorees. Notwithstanding abuses in discipleship circles, their basic principles are at the heart of the Great Commission and can contribute positively to a theology of mission. context of strong relationships mentors Restorationism. Restorationist Charismatic Carolina based National emphasize the recovery paradigms, teachings are emphasized in several and the Montreat, North groupings, including a nation-wide network of churches known as the People of Destiny International, Leadership Conference. Their teachings of the nine spiritual gifts of 1 Corinthians 12, and the “five-fold ministry” of Ephesians 4:11, especially the apostolic and prophetic dimensions of church authority. Driven by these the People of Destiny movement has developed a creative model of ministry based on Paul’s apostolic team in the book of Acts. The movement is led by a mobile team of four to six “apostolic” team” provides direction for church planting, church nurturing and leadership training, but the relationship between churches is spiritual, leaders. This “apostolic the team and the non-bureaucratic.39 This approach Paul’s missionary band. This semi-autonomous and and its theological convictions display principles and dynamics consistent with those of the apostle “restoration” of apostolic teams is a positive contribution to world evangelism movements. One of the most significant Prayer theological and power developments in the Pentecostal/Charismatic movement 1986): Quoted Prince,” People of Destiny Lfagazine 39Hocken, “Charismatic Movement,” DPCM, 141f; Larry Tomczak, “The World Mission of Every Christian,” People of Destiny Magazine 4 (September/October 15; Larry Tomczak, “Relationship With the Sending Church,” in The Church Planters Handbook, ed. Jim Durkin, et. ai. (South Lake Tahoe, CA: Christian Equippers International, 1988), 105. 40 in 1986 Charismatic leader Derek Prince said, “I’ve also begun to see that in a certain sense the major outreach arm of the Church should be apostolic teams.” from Larry Tomczak, ed., “Unfinished Business, An Interview with Derek 4 (September/October 1986): 23. 16 97 comes under the rubric of “signs and wonders” and “spiritual warfare.” The present proliferation of power literature by Pentecostals/ Charismatics and “third-wavers,” such as Peter Wagner and Charles Kraft,. is making an immense contribution toward our understanding of how effectively to resist and neutralize demonic powers that hinder evangelism and missions. Without these and other spiritual dynamics, missiological techniques and methodologies are like state-of-the-art computer hardware without the software to run it. The current global prayer and power movement which is sweeping into all six continents is introducing new spiritual dynamics for evangelism and missions with documented results in terms of countable disciples of the kingdom. Much of the above may indeed represent formative Charismatic contributions to mission theology and the science of missiology. Most of the hermeneutical problems in Charismatic teachings could be ironed out by the integration of a solid evangelical theology of the kingdom with an understanding of the mission of God. However, theological formulation always lags behind revival and missionary movements. We must remain patient but hopeful. I agree with missions professor, L. Grant McClung’s statement that, . In this “Decade of Definition” there will be a rapid growth in the science of pentecostal/charismatic studies and enough missiological literature to support what I feel is the emergence of a definitive pentecostal/charismatic missiology.” Consistent with precedent patterns of renewal and missions, fresh theological reflection has created fresh missionary motivation among Charismatic believers. What Charismatic Missions Can Learn from Pentecostals If Charismatic churches, especially those of the independent movement, are to maximize their potential for world evangelism, there are several areas where Charismatics need to catch up with their Pentecostal friends. First, Charismatics need to tackle the disciplines of theology and missiology. Charismatics must learn from Pentecostals to overcome their own anti-intellectualism and engage in high-level theological reflection as Pentecostals are now doing. J. Rodman Williams of Regent University in Virginia has made forward strides with Renewal Theology, a three-volume work which takes a fresh look at theology from a Charismatic perspective. But much remains to be done, especially in the area of mission theology. Many Charismatics are yet to learn and embrace what classical Pentecostalism really stands for-that, as a part of salvation history, renewal is essentially missionary in nature and cannot be complete without expansion to the unchurched and the unreached. 41 L. Grant McClung, ” Mission in the 1990s,” International Bulletin Research 14 ofMissionary (October 1990): 153. 17 98 Second, Charismatics must overcome their own aversion to organization. It was not until the forebearers of the Pentecostal movement struck the right balance between Spirit-led spontaneity and strategic organization that their movement became an effective worldwide missionary force. The Assemblies of God denomination, for example, was formed in 1914 as an agency for world evangelization. This organizational move helped provide sorely needed cooperation among pastors and churches, and helped achieve a more effective missionary outreach. Before that time, Pentecostal missions was notorious for a number of fiascoes due to the lack of organization. Charismatics have needlessly repeated virtually every early Pentecostal fiasco: duplication, competition, inadequate training and financial backing for missionaries, lack of structure and the omission of long-term strategy planning. Many are yet to learn the lesson from Pentecostalism that a certain amount of organization is necessary if Charismatics are to fulfill their own missionary calling.” Third, Charismatics need to create, recognize, and unchain more mission structures. Espousing ideals of a “sending church,” some Charismatics all around the world are trying to turn local churches into missionary sending agencies. A related problem is the practice of subjecting mission agencies to the control of sending churches. These practices are contrary to the New Testament pattern and deaf to the voice and verdict of missions history, which teaches us that the authority for mission is not tied to any ecclesiastical institution. The authority- for mission stems directly from the word of the Spirit and from a revelation of Christ in the calling of the missionary. Paul’s apostolic team was not in any way under the direction of the Antioch church. Both church and mission team were under the headship of Christ and the spontaneous leading of the Spirit of God. Where this pattern has been recovered through history, missions has prospered. But where the local church has tried to control missions, it has generally stifled rather than stimulated effective cross-cultural evangelism. Research has confirmed this outcome among Charismatics as well. For Charismatics to unleash a more effective missionary force, they will need to multiply and release more mission structures and provide more and more missionary candidates with a clearly defined career path to missions. Conclusion: “Nine O’Clock in the Evening” The century-old Pentecostal movement, and the one-half-century-old Charismatic movement, and the younger expression known as the “third wave” all represent twentieth-century expressions of the eschatological outpouring of the Holy Spirit which began in the first 42 Howard Foltz, “Bottlenecks Hindering Mission Mobilization,” Ministries 4 (Summer 1986): 42; Pomerville, The Third Force in Missions, 57. 18 engage 99 century A.D. The essential purpose of this and all other renewals is to the church in God’s redemptive mission to the nations. What will it take to make the twentieth century the greatest century of all in even if this achievement takes factors, the history Christian missions, Pentecostals, twenty-first century? theological breakthroughs, needed? Charismatics and other Christians a few decades into the What new institutional and what new spiritual dynamics institutionalization. happens, God always sparks what new are that First, with respect to the above suggestions about organization, both Pentecostals and Charismatics must avoid the trap of over Renewal creates new patterns and structures for ministry and missions. But eventually, these become organizations quench the Spirit. As movements become mature institutions, they tend to “domesticate” the Spirit and the kingdom of God. When this a renewal somewhere on the periphery of the ecclesiastical structures of the day. Then, old wine skins often burst rather than stretch to accommodate the new things God is doing. The and Charismatics is this: how can they the necessary and church spontaneous institutions are increasingly ineffective for cross-cultural Third World models and strategies are multiplying question for Pentecostals continue to provide evangelism, missions spiritual dynamics? informal becoming increasingly effective. 43 overlooked. are Calvinistic thinking think Charismatics reflection structures and strategies for growth without quenching Traditional centralized, hierarchical missions, while and if they to critical Second, the necessity of ongoing theological reflection must not be We have noted that new missionary movements have often been fueled by fresh theological thinking. What theological alterations now needed in Pentecostal/Charismatic communities in order for there to be a fresh outburst of missionary zeal and action? Extreme was a theological barrier in the days of William Carey. Pentecostals and Charismatics are kidding themselves there are no theological barriers today. What are these barriers? How can they be identified and challenged? Are Pentecostals and willing to subject their favorite theologies and scrutiny in order to identify their own blind spots that hinder world missions? And third, what kinds of new spiritual dynamics are needed to launch new and greater missionary movements from Pentecostal/Charismatic communities? Reporting on the 45th General Council of the Assemblies in Minneapolis in August 1993, Peter Johnson asked the question, “Can the world’s largest Pentecostal the revival fires of Azusa Street and go on to greater spiritual heights? of God held denomination reignite Handbook “Bryant L. Myers, “The Changing Shape of World Mission,” in A4ission 1993-95, eds. John A. Siewert and John A. Kenyon (15th Edition; Monrovia, CA: MARC, 1993), 35. 19 100 Or will it degenerate into a bureaucratic dinosaur nourished chiefly by programs, building projects, and committees?”44 Johnson’s question represents the kinds of questions being asked by many Pentecostals and Charismatic leaders today. But my response is, do Pentecostals and Charismatics really want to relight Azusa Street? Some Pentecostal and Charismatics are looking back to what God has done in the past with a kind of “do-it-again-God” nostalgia. But God never quite does it again; his work is often new, surprising, incredible. But a recurring problem with every generation that experiences renewal is the tendency to cling to and perpetuate the forms and expressions of their particular brand of spirituality. When God begins doing new things, they look back to the old ways. My point is this: God is already lighting new fires of renewal and missionary zeal around the world. Many Pentecostals and Charismatics are in the center of it, but some either do not see it or they are standing aloof and looking askance. I am referring to the many multifaceted movements, especially in the Third World, that are now converging under the banner of the AD 2000 & Beyond movement. In all six continents there are the stirrings of an unprecedented transdenominational prayer and power movement which has its focus on the unfinished task of world evangelization. Through this global prayer movement, new spiritual dynamics are being introduced for the “pulling down of strongholds” that hinder evangelism and missions. Prayer concerts, prayer walks, marches for Jesus, spiritual mapping, repentance and reconciliation between pastors and leaders from different denominations and ethnic groups, and a renewed compassion for the lost, especially the peoples of the 10/40 window are some of the new patterns of spirituality that God is using to turn resistant populations into people who are receptive to the gospel.” One of the greatest challenges for the heirs of Pentecostalism will be to recognize the new ways in which the kingdom of God is now advancing and to remain on the crest of that wave until his glorious return. The way home is through harvest. “Peter K. Johnson, “AG Leaders Call for New Pentecost,” Charisma & Christian Life 19 (October 1993): 84. resources for the United Prayer Network of the AD 2000 Movement include: John Dawson, Taking Our Cities for God (Lake the the Mary, FL: Creation House, 1989); Cindy Jacobs, Possessing Gates of Enemy (Grand Rapids, MI: Chosen Books, 1991); C. Peter Wagner, ed., Engaging the Enemy (Ventura, CA: Regal Books, 1991); C. Peter Wagner, Warfare Prayer (Ventura, CA: Regal Books, 1992); C. Peter Wagner, ed., Breaking Strongholds in Your City (Ventura, CA: C. Peter Wagner, Churches that Pray Regal Books, 1993); (Ventura, CA: Regal Books, 1993); George Otis, Jr., The Last of the Giants (Grand Rapids, MI: Chosen Books, 1991). Information is available from: Mobilization of United Prayer Resource Network, 215 N. Marengo Ave., Suite 151, Pasadena, CA 91109. 20
Pentecostal Spirituality: A Passion for the Kingdom
July 25, 2024 by Cup&Cross
Filed under Featured, News, Publication
Pentecostal Spirituality A Passion for the Kingdom Steven Jack Land CPT Press Cleveland, Tennessee
To Peggy Alanna, Laura, Jonathan
Contents Preface Preface to CPT Press Edition Abbreviations Introduction Chapter 1 Pentecostal Spirituality as Theology: A Theoretical Introduction The Pentecostal Movement Then and Now Approaching Pentecostal Spirituality Perspectives on Pentecostal Spirituality An Overview Chapter 2 Pentecostal Spirituality as Apocalyptic Vision: A Narrative-Praxis Analysis Pentecostal Presence: The Inbreaking of the Spirit in the Last Days Pentecostal Narratives: Participating in the Story of God Pentecostal Practices: Worship and Witness in the Light of the End Pentecostal Praxis: Action-Reflection in the Spirit Chapter 3 Pentecostal Spirituality as Missionary Fellowship: An Affective Integration Pentecostal Identity: Liberation for the Kingdom Pentecostal Affections: Embodying and Longing for the Kingdom Pentecostal Prayer: Shaping and Expressing the Affections Pentecostal Passion: Living toward the Kingdom Chapter 4 Pentecostal Spirituality as Trinitarian Transformation: A Theological Revision The Breakup of the Pentecostal Synthesis: Internal Problems and External Criticisms The Re-visioning of Pentecostal Spirituality: The Eschatological Trinity Reaching in to One Another: Remembrance and Repentance Reaching out Together: Learning with the Critics Afterword Bibliography
Index of Biblical References Index of Names Other Books from CPT Press Chapter 1 Endnotes Chapter 2 Endnotes Chapter 3 Endnotes Chapter 4 Endnotes
Preface This work is of, by and for the Pentecostals who have nurtured, exasperated, challenged and encouraged me for the past forty years. I hope they recognize themselves and also find some new perspectives in this interpretation and revision of our tradition. I have sought to be controversial in the best sense of the word. This is almost assured by juxtaposing words like ‘holiness’, ‘Pentecostal’, ‘affections’, and ‘ecumenical’. Because I believe that the whole church is Pentecostal, this study is also, I hope, ecumenical in a sectarian sense. By going deeply into the Pentecostal affections, I hope that other Christians will be able to distinguish themselves from and to identify with Pentecostals. The polemical irenic edges are there, to be sure. I very much want to speak for rapprochement between Pentecostal and Holiness bodies, for a deeper appreciation by Pentecostals of their own heritage, for the crucial importance of religious affections for all Christians (especially Pentecostals), and to put forward a trinitarian re-vision that will provoke and encourage a more socially, missionally, ecumenically, and theologically responsible Pentecostalism. I hope that my liberal Protestant (in the tradition of Schleiermacher) and fundamentalist friends (in the tradition of Warfield and the Scottish Common Sense philosophy) will find things to aggravate and engage their interest in these pages. Pentecostals have much reason to learn from both, embrace neither and to expand, if not radically alter, the label ‘evangelical’ as a self-designation. The antinomy of reason and ‘feelings’ must be transcended; I have tried to show one way of doing that. There are so many persons who have contributed to this work, but I must begin with those who taught me the most fundamental and continually significant theological discipline—prayer. My parents, Jack and Mary Land, have given of themselves to me and many others for over four decades now. My wife Peggy and I served with my parents for twenty years in an urban Atlanta Pentecostal ministry which demanded constant spiritual renewal and theological work. The members of the Society for Pentecostal Studies have through conversation, sharing of ideas, and provocative research, stimulated my development and thought. By their work and example, Leonard Lovett and David Daniels have reminded me of the crucial importance of the black roots and spirituality for a Pentecostalism that would be a folk-liberation movement of
the Spirit. Mel Robeck, Jerry Sandidge, Harold Hunter, Vinson Synan, and Dan Albrecht have all urged me on and their work is reflected in this study. Donald Dayton, who has pioneered in both theological and historiographical fields of inquiry, has freely shared research materials and has chided me and other members of the Society concerning our sometime ‘theological inferiority complex’. I hope I have neither neglected nor proven his point. William (Bill) Faupel, in addition to sharing a great amount of historical data, arranged for an interview with Dr Walter Hollenweger for which I am deeply grateful. Bill’s careful and extremely valuable work undergirds my own and is a prerequisite for understanding North American Pentecostalism. He read a rough draft and made comments which were deeply appreciated. David Bundy, bibliophile and linguist extraordinaire, and Frank Macchia have taught and encouraged me much concerning the Holiness-Pentecostal connections and the larger, deeper meaning of glossolalia. I must thank all Pentecostal leaders who so generously gave of their time, perspectives, homes and hearts over the past fifteen years. Special thanks to Yung-Chul Han in Korea, Margaret Gaines in Israel, the late J. Herbert Walker, Jr and his dear wife, Lucille, in Europe, Andre Weber in France, José Minay (a South American Pentecostal bishop), Rick and Jan Waldrop, David Munguia, Roberto Aldana and Rudi Giron in Guatemala, Miguel and Mireya Alvarez in Honduras (now in the Philippines), Reverend Enrique Guerra in Costa Rica, Reverend and Mrs. Pedro Pablo Castillo in Nicaragua, Arthur Naidoo, James Seekola, Reuben Timothy and Wynand de Kock in South Africa, Neil and Leslie Morrison in Scotland, Brian Robinson, Steve and Kathleen Hall in England, Ivan and Valentina Fedotov of Russia, Hong Yang of China, and a host of international students whom it has been my privilege to teach and from whom I have learned much. President Cecil Knight, Dean Robert Crick, Dr James Beaty (one of my copy editors), the faculty and students of the Church of God School of Theology in Cleveland, Tennessee have understood, encouraged and supported me and my family during these past twelve years. Dr Crick especially has encouraged me in my Pentecostal pursuits and deepened my pastoral care perspective. Rick Moore, Chris Thomas, Jackie and Cheryl Johns have been important dialog partners and friends. Several libraries have assisted me during the past ten years. Barbara McCullough at The William Squires Library in Cleveland, Tennessee and Valerie Watkins of the Woodruff Library of Emory University were especially helpful. The staff of the Pentecostal Research Center and Charles Towler of the
Church of God Publishing House, both in Cleveland, Tennessee, helped me track down some of the early Pentecostal hymnody. I owe special thanks to the editors and staff of Sheffield Academic Press for initiating this series of monographs and to Steve Barganski, whose editorial work has helped to make this manuscript presentable. Several years ago my dissertation advisor, Don Saliers, assigned to me a chapter on ‘Pentecostal Spirituality’ in a book he was editing for Crossroad Press in New York. That became the seed of and impetus for this work. As teacher, mentor, and friend Dr Saliers has influenced me deeply. I look forward to future collaboration. He has been an excellent mentor-director. Theodore Runyon, a member of my dissertation committee, along with my wife, encouraged me to enter the doctoral program in the late 1970s. I have known Theodore and Cindy Runyon for over twenty years now. Their ministry to me and other students has been consistently helpful and always encouraging. Cindy Runyon, Periodicals Librarian at Pitts Theology Library, Emory University, has, by her personable and professional assistance to me and other students at Emory, made the research seem more bearable and the completion that much more enjoyable. Dr. Runyon’s Wesleyan studies, liberation interests, and ecumenical spirit have significantly shaped my theology. He is a friend and colleague, and one of the most challenging professors I have had! Also on my committee were Dr Richard Bondi, Dr Hollis Gause and Dr Hal Knight. Dr Bondi’s background in narrative theology and his extremely insightful critique of the dissertation proved most helpful. His wife Roberta Chesnut prepared one of my doctoral exams. They are both valued colleagues. Dr R. Hollis Gause has taught theology and biblical studies for over thirty years. For the last ten years we have taught together. He and his wife Beulah are adopted grandparents in my family. His criticisms, questions and comments made this a much clearer work. Though I am sure this monograph still needs much more polishing, it is not for lack of laboring on Dr Gause’s part. He has lectured for me and assisted in many other ways during this endeavor. Dr Hal Knight, the last person on the committee, has done more than anyone else to see that I completed this task. He has been friend, copy editor, and dialog partner from start to finish. I deeply appreciate all that he has contributed to me personally and professionally. Next to my family, the members of the Mission Church of God in Atlanta, Georgia have borne the most with me during the gestation and delivery of this work. Their kind understanding, patient endurance, and sincere prayers and
encouragement bore me along when the going was tough. My sister Rosemary and her husband, Steven Lester, have called and urged me on regularly. Susan Harper, a member of the church, one of my former students, and a minis-terial colleague, has decoded my writing and typed this manuscript. She has sacrificed much time and worked hard to make this a presentable piece while completing her own graduate theological studies. But the ones who have given the most are the ones who know me best— Alanna, Laura, Jonathan and my wife Peggy. The children have missed their dad. They have made me tell them over and over why and what I was doing … until I finally understood it myself! They are glad to have their father back. My children have taught me much about Pentecostal spirituality by their questions, doubts, fears, beliefs, prayers and example. They learned this, largely, from their mother. Peggy Goude Land has been a spiritual example, a companion in ministry, and my best friend for twenty-one years. We have ‘talked out’ this research on many long walks and through many late night conversations. The faith and perseverance in her parents Liston and Eunice Goude has come to mature expression in her, and the chief beneficiaries have been myself and our children. With her I give thanks for a work begun, completed, and unfinished.
Preface to CPT Press Edition It’s been almost twenty years, five reprints, and three translations since I completed Pentecostal Spirituality: A Passion for the Kingdom. During this period many persons have been gracious enough to offer critiques, appreciations, and to use it as a springboard into their own investigations and constructions. I hope to issue a revised edition sometime during the next year in which I will respond to my various publics. The book, written as an Emory University doctoral dissertation, continues to show up on textbook lists and for that I am somewhat surprised and pleased. Clearly the book was not meant to be a Protestant scholastic treatment of the traditional Christian doctrinal loci, with the baptism in the Spirit as the unifying hermeneutical center—though that is a worthy enterprise. Instead, this book sought to describe the early Pentecostal ethos, devise a way to explain Pentecostal character (affections) and to prescribe future doctrinal and constitutional projects, some of which have been taken up already. My point was to provide a template for displaying the uniqueness of Pentecostal spirituality as well as its similarities and differences from other Christian approaches. In the process I also sought to get at the nature and proper use of ‘experience’ in Pentecostal spirituality in particular and Christianity in general. The social implications of the spirituality are mentioned but not developed, nor is there sufficient attention to the care of creation and the environment, taken up by other Christians and beginning to be developed by Pentecostals. These and other matters will have to await the revision. In the meantime I have written on other themes, and I hope to further develop the emphasis of holiness shortly. It seems to me that holiness embodies a structure of divine righteousness, a context of divine love, and a dynamic, persuasive, teleological divine power which should inform anyone’s account of what it means to be filled with the Holy Spirit. With hundreds of millions of Christians testifying to such a ‘baptism from on high’, I am confident and thankful for the proliferation of the methods, accounts, and applications of Pentecostal spirituality in the global missional church of our day. I commend this work to the readers not as the last or even best word. But I hope it is still a good word in which many will recognize themselves or aspire to be filled with the presence of God who will one day, soon, be ‘all in all’.
Steven Jack Land President, Professor Pentecostal Theological Seminary
Abbreviations AF . . . . . . . . The Apostolic Faith (September 1906-May 1908) reprinted by F.T. Corum (ed.) Like As Of Fire (Wilmington, MA, 1981) DPCM . . . . . S.M. Burgess and G.B. McGee (eds.), Dictionary of Pentecostal and Charismatic Movements (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1988) HBT . . . . . . . Horizons in Biblical Theology HTR . . . . . . . Harvard Theological Review JES . . . . . . . . Journal of Ecumenical Studies JPT . . . . . . . . Journal of Pentecostal Theology JPTSup . . . . Journal of Pentecostal Theology Supplement Series JSNTSup . . . Journal for the Study of the New Testament Supplement Series NASB . . . . . Unless otherwise stated all Scripture quotations are from the New American Standard Bible (LaHabra, California: The Lockman Foundation, 1960). Pneuma . . . . . Pneuma: The Journal of the Society for Pentecostal Studies RSR . . . . . . . Religious Studies Review SJT . . . . . . . Scottish Journal of Theology TTod . . . . . . Theology Today
Introduction
An Analysis and Re-vision of Pentecostal Spirituality In this work I attempt a fresh and constructive, if somewhat controversial, interpretation and re-vision of the Pentecostal tradition. In the first chapter—the theoretical, methodological section—the fundamental relationship between theology and spirituality takes a distinctively Pentecostal, but interestingly Barthian turn, especially with regard to the role of prayer in the theological task. Agreeing with Walter Hollenweger that the first ten years of the Pentecostal movement form the heart not the infancy of the spirituality, I go on to assert the crucial importance of the Wesleyan, Holiness, and nineteenth-century revivalistrestorationist roots. Spirituality is defined as the integration of beliefs and practices in the affections which are themselves evoked and expressed by those beliefs and practices. The second chapter is a running narrative analysis of certain Pentecostal beliefs and practices using songs, testimonies, and early eyewitness accounts to tell the story. The apocalyptic nature of the spirituality is analyzed, critiqued, and developed to show the relation of revelation, history, and the kingdom of God. The third chapter shows how Christian affections integrate and undergird Pentecostal beliefs and practices. A mutual conditioning is noted among orthodoxy (right praise/belief), orthopraxy (right practice), and orthopathy (right affections). Thus the analysis of Pentecostal spirituality is taken to a new level, transcending in the process the outdated and fruitless antinomy of reason and ‘feelings’. Pentecostal affections are correlated with certain divine attributes, the kingdom of God, and Pentecostal testimony to suggest a kind of Pentecostal faith development characterized by a crisis-development dialectic. The fourth and final chapter offers a trinitarian re-visioning of Pentecostal spirituality, arguing that a passion for the kingdom of God is ultimately a passion for God. Drawing upon the construction and re-vision, certain internal issues and external criticisms of the movement are noted. Further research needs are briefly discussed in the afterword. In summary, this study moves through four stages: (1) the relationship between spirituality and theology, (2) a description-analysis of certain beliefs and practices which characterize Pentecostal spirituality, (3) a demonstration of the integration of the beliefs and practices in Pentecostal affections, and (4) a trinitarian re-vision.
Chapter 1
Pentecostal Theology as Spirituality: A Theoretical Introduction
The Pentecostal Movement ‘Then and Now’
‘Back to Pentecost’: The Fall of the Latter Rain Jesus Christ, in the midst of the intense apocalyptic expectations of his disciples, commanded them to wait for the ‘promise of the Father’. This baptism in and filling of the Holy Spirit was the fulfillment of the prophecy of Joel1 and empowered Christ’s witnesses to the end of the age and the ends of the earth. The coming and mission of Jesus and that of the Spirit was couched in the language of promise and fulfillment in such a way that fulfillment carried an overflow or residue of promise which had personal and global historical implications. Each ‘already’ of fulfillment carried within it the ‘not yet’ of consummation. The waiting for Christ became waiting in Christ for his return. The waiting for the promised Spirit became waiting in the Spirit for ‘the time when, by the Spirit, God would be all in all’. This ‘promise–fulfillment, already–not yet’ is a tensed dynamic which characterizes Christianity’s eschatological passion. From time to time when the tension is resolved prematurely—either in the direction of an other-worldly, ‘not yet’ escapism or a this-worldly, ‘already’ accommodation—there arise movements of restoration, revival, awakening, and renewal to remind the church that it is the ‘eschatological mother’2 whose sons and daughters are meant to prophesy. Pentecostalism was and is such a movement. Pentecostal spirituality sprang forth in North America from eighteenth-century Wesleyan and nineteenth-century Holiness roots. It embodied all the eschatological tensions, turmoil, and blessings of the premillennial revivalism that had swept across the nation in the latter half of the nineteenth century. It was seen as the answer to the earnest prayers of thousands of believers who through global networks of personal associations, periodicals, camp meetings, etc. prayed for a renewal of Pentecost. In 1856 William Arthur, an English Methodist, expressed this longing in the following prayer: And now adorable Spirit, proceeding from the Father and the Son, descend upon all the churches, renew the Pentecost in this our age, and baptize Thy people generally—O, baptize them yet again with tongues of fire! Crown this nineteenth century with a revival of ‘pure and undefiled religion’
greater than that of the last century, greater than any ‘demonstration of the Spirit’ even yet vouchsafed to men.3 Throughout the nineteenth and into the beginning of the twentieth century Pentecostal fires were kindled in England (Irvingites), Germany, India, Russia, 4 Wales and North America (Finney, Moody, the Palmers, and so forth). But it was in the Bible School of Charles Fox Parham in 1901 that Agnes Ozman was ‘baptized in the Holy Spirit’ with the ‘evidence of speaking in other tongues’. This insight of Parham and his students was carried by William J. Seymour to Los Angeles in 1906. Seymour, a humble one-eyed black Holiness preacher who had been Parham’s student, published the first issue of The Apostolic Faith newspaper in 1906. The motto on the masthead of every issue read, ‘Earnestly contend for the faith which was once delivered to the saints—Jude 3’. The first article announced that Pentecost had come to Los Angeles and that there was a ‘revival of Bible salvation … as in the Book of Acts’.5 Seymour joyously reported that
The power of God now has this city agitated as never before. Pentecost has surely come and with it the Bible evidences are following, many are being converted and sanctified and filled with the Holy Ghost, speaking in tongues as they did on the day of Pentecost. The scenes that are daily enacted in the building on Azusa Street and at missions and churches in other parts of the city are beyond description, and the real revival is only started as God has been working with His children mostly, getting them through to Pentecost, and laying the foundation for a mighty wave of salvation among the unconverted. The meetings are held in an old Methodist church that had been converted in part into a tenement house leaving a large, unplastered, barn-like room on the ground floor … Many churches have been praying for Pentecost and Pentecost has come. The question is now, will they accept it? God has answered in a way they did not look for. He came in a humble way as of old, born in a manger.6
Seymour noted that this ‘Holy Roller’, ‘Colored Church’, as some locals referred to it, was in the vicinity of tombstone shops, stables and a lumber yard … You would hardly expect heavenly visitations there unless you remember the stable at
Bethlehem … But here you find a mighty revival going on from ten o’clock in the morning till about twelve at night. In commenting further on the fact that they were meeting in a barn Seymour speculates as to why God chose this place: If it had started in a fine church, poor colored people and Spanish people would not have got it, but praise God it started here. God Almighty says He will pour out His Spirit on all flesh … It is noticeable how free all nationalities feel. If a Mexican or German cannot speak English, he gets up and speaks in his own tongue and feels quite at home for the Spirit interprets through the face and people say amen. No instrument that God can use is rejected on account of color or dress or lack of education. This is 7 why God has so built up the work. It was said that ‘the color line was washed away in the blood’ at Azusa Street. And, remarkably, this was also the case for a short while in the South as evidenced in the reports of white evangelist G.B. Cashwell and the ministry of black Pentecostal Bishop C.H. Mason who was to become the spiritual leader of the Church of God in Christ. Mason ordained white and black ministers, and the first Pentecostal seminary, located in Atlanta, Georgia at the Interdenominational Theological Center, bears his name. But the breaking down of social barriers and beginnings in a humble stable (they also had an ‘upper room’ at Azusa!) were not the only parallels with the New Testament church. This event was interpreted by its adherents as the latter rain restoration of apostolic faith and power for the last days’ evangelization of the world. Everything was determined by the overall expectation of the 8 imminent parousia of Jesus Christ. The ‘full gospel’ for the fullness of times was needed for the filling of saints with the Holy Spirit, so that they could fill the earth with the apostles’ doctrine. This ‘full gospel’ was comprised of five theological motifs: 1. Justification by faith in Christ. 2. Sanctification by faith as a second definite work of grace.
3. Healing of the body as provided for all in the atonement.
4. The premillennial return of Christ.
5. The baptism in the Holy Spirit evidenced by speaking in tongues.
It was the fifth motif that, more than anything else, served as a ‘sign’ that the
‘evening light’9 was shining before the darkness when no one could work.10 The movement was simultaneously restorationist and eschatological. The participants believed that God was restoring the apostolic faith and power for the end times through signs and wonders. God had restored justification by faith through Luther, sanctification by faith through Wesley, divine healing through 11 Dr Cullis and many other nineteenth-century ministers, the blessed hope of Christ’s premillennial second coming through the prophecy conferences of the latter half of the nineteenth century, and lastly the baptism in the Holy Spirit as power for last-days world evangelization. In their view God was calling upon all saints to be godly witnesses in the power of the Holy Spirit. Now the prophethood of all believers could be added to the priesthood of all believers. There were other analogies to the New Testament church. There was an aversion to creeds which divide and thus hinder the mission of the Church. There was a suspicion of organizations which ran by mechanisms and political schemes instead of gifts of the Spirit. In fact the early movement was suspicious of anything which did not have direct biblical precedent or hindered the work of the sovereign Spirit of God. Christ ruled the church tangibly though the ‘whole Bible rightly divided’ and intangibly by the Holy Spirit’s gifts and guidance. There was no single founder of the movement. Like the New Testament days, communication and instruction were carried on through letters, tracts, testimonies and, most importantly, through an ethos growing out of and centered in revivalistic, participatory, populist-oriented worship. All those who had 12 ‘gotten their Pentecost’ were witnesses, tellers of good news. So there were no systematic treatises; that would be a kind of second-order activity removed from the atmosphere of prayer, praise, and witness. Though most of the people were literate—some at Azusa even ‘highly educated’—they were overwhelmingly oral in their worship, witness, and work. As in the New Testament, the sense of urgency to warn the church and to witness to the nations colored all understanding, activity, and affectivity. Now was the time for ‘the everlasting gospel’ (Rev. 14.6, 7), the ‘gospel of the kingdom’ (Mt. 24.14), to be proclaimed in power and demonstration of the Holy Spirit.13 The Bride must be prepared for the Bridegroom. The lost must be brought into the ark of safety before the coming Great Tribulation. This sentiment is captured by Frank W. Sandford, Charles F. Parham’s mentor from Shiloh, Maine, in the change of the title of his periodical from Tongues of Fire to The Everlasting Gospel in 1901. This was to be ‘The Last Solemn Message of the Age’. Sandford declared that
The first gospel message was proclaimed by an angel—‘good tidings of great joy to all people, for unto you is born a Savior’.
The last gospel message will be likewise proclaimed—‘I saw another angel having the everlasting gospel to preach unto them that dwell on the earth … to every nation’.
The first was a message of peace and good will. The latter is to be a message of warning and judgment
The first represented ‘the acceptable year of the Lord’. The latter, ‘the day of vengeance of our God!’
The first brought the glad tidings to a world lost in sin, the ‘whosoever believeth in Him might be justified freely through the redemption that is in Christ Jesus’. The latter warns that same world that it is speedily to give an account for the use or abuse of its privilege, and prepares the way for the time when ‘The Lord shall be revealed from heaven with His mighty angels, in flaming fire taking vengeance on them that obey not the gospel’. The former prepared the way for ‘a Man of sorrows’. The latter for the ‘King of kings’.
The first represents the voice of song singing joyfully, over the hills of Bethlehem, ‘Glory to God in the Highest!’
The second, the voice of divine authority crying aloud to all lands. ‘Fear God and give glory to Him!’
The first heralded One coming meek and lowly, riding on an ass into Jerusalem to die for men.
The latter heralds One coming in ‘great power and glory’ to the City of the King to reign ‘From the river to the ends of the earth’. All hail the power of the everlasting gospel.14
Christ would not come until this message had been proclaimed to all nations in words, signs and wonders. The pace and focus of individual and world history was now quickened and intensified. This movement spread rapidly through all the pre-established networks of nineteenth-century revivalism and the new fields opened by persons who went out immediately, with little or no formal training, to the four comers of the earth.15 The movement grew slowly at first, and within the first fifteen years, was influenced by racial, theological, and social controversies. Nevertheless, Pentecostal churches today represent the largest Protestant grouping in the world
and their spirituality, as transmitted through the Charismatic renewal, has influenced every branch of Christianity. Along with Roman Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy, and Protestantism it may be regarded as a ‘fourth force’ (as opposed to the usual ‘third force’ designation) in Christianity.
The Dimensions of Pentecostal Spirituality
The dimensions of this spirituality’s impact provide a good argument for giving it a closer look. More is needed than an apologetic for Spirit baptism or yet another study of behaviors such as glossolalia. The movement will soon be one hundred years old, and with the years has come the development of creeds, institutions of higher education, elaborate ecclesiastical organizations, and tons 16 of publications per year. Nearing the centenary mark the movement has demonstrated staying power. The dimension of length or longevity is, however, eclipsed by that of breadth. Although it began in North America, Pentecostalism is strongest now in the socalled ‘Third World’. David Barrett estimates that over seventy-five per cent of all members of the over one thousand, non-white Third World indigenous denominations are composed of persons who bear all the phenomenological marks of Pentecostalism. In addition, there are eight hundred explicitly Pentecostal denominations, indigenous to non-white races in the Third World. In addition to the millions of members of the original Pentecostal bodies there are the millions who are part of the charismatic renewal, or the so-called ‘thirdwavers’ who are evangelicals experiencing a renewal of the Spirit but not recognizing it as a separate experience from conversion. ‘Third-wavers’ emphasize signs and wonders, but stay in their churches and do not organize into distinct renewal groups. The members of all three waves of the renewal are now found in eleven thousand Pentecostal denominations and three thousand independent charismatic denominations. They constitute twenty-one per cent of organized global Christianity. As of 1988, there were 327 million affiliated church members of which 176 million were Pentecostal, 123 million charismatic, 28 million ‘third-wave’. The movement grows at a rate of 19 million new members a year or around 54 thousand per day (two-thirds of which are converts/new members). On a worldwide scale, 29 percent are white, 71 per cent are non-white. They are more urban than rural, more female than male, more children (under eighteen years) than adults, more third-world (sixty-six per cent) than
western world (thirty-two per cent), more living in poverty (eighty-seven per cent) than affluence (thirteen per cent), more family-related than individualist.17 18 East Asia, Latin America and Africa are becoming rapidly pentecostalized, whereas Europe remains more charismatic. Some fourteen per cent of all charismatics in mainline churches have ‘gone independent’ each year since 1970, forming some ‘100,000 White-led independent Charismatic churches across the 19 world loosely organized into forty or so major networks’. One fourth of all full-time Christian workers in the world are Pentecostal/charismatic. They are active in eighty per cent of the thirty-three hundred large metropolitan areas of the world. They are ‘more harassed, persecuted, suffering, martyred than perhaps any other Christian tradition in recent history’.20 They are often scorned, imprisoned, tortured and killed by totalitarian dictators or those revolutionaries who oppose such regimes. They usually seek a ‘third way’ of peace in the Third World, and have been 21 characterized as a ‘haven for the masses’ who do not engage in direct sociopolitical action; nevertheless, they have created alternative communities of caring, respect and empowerment and thus developed their own programs of ‘affective conscientization’ toward liberation.22 Although it is impressive that this movement has achieved such breadth in so short a time, the dimensions of height and depth are probably the most theologically significant. By height is meant the dimension of praise, worship, adoration, and prayer to God—this is the most compelling characteristic to most observers and participants. But to this must be added the dimension of depth. This is the reason for the almost century-long sustained growth and breadth of impact. The depth dimension speaks of the ‘deep things’ of the human heart: the abiding, decisive, directing motives and dispositions which characterize Pentecostals. One cannot read the early accounts of the Azusa Street revival or hear the testimonies of Pentecostals today without being struck by this depth of conviction and passion. It is a steadfast longing for the Lord and the salvation of the lost. It is a continuous, joyous exclamation of the inbreaking presence and soon to be consummated kingdom of God. I have observed this on five continents over the last fifteen years. To that extent there is a remarkable continuity from Azusa to Seoul, to Glasgow, to Managua, to Santiago, to Durban, to Moscow. A spirituality of these dimensions demands a closer theological look; it needs an examination of the inner logic of this passion for the kingdom.
Approaching Pentecostal Spirituality
Thesis: The Integration of Holiness and Power
It is part of the unfinished theological task of Pentecostalism to integrate the language of holiness and the language of power—languages spoken by the Holiness and Pentecostal movements respectively. It is a theological and pastoral mistake to dichotomize, confound, or simply to identify love and power. Indeed, in keeping with the earliest Pentecostal soteriology of justification, sanctification, and Spirit baptism, the basic theological challenge and most pressing pastoral need is to show the integration of righteousness, love and power in this apocalyptic movement of spiritual transformation. My thesis is that the righteousness, holiness, and power of God are correlated with distinctive apocalyptic affections which are the integrating core of Pentecostal spirituality. This spirituality is Christocentric precisely because it is pneumatic; its ‘fivefold gospel’ is focused on Christ because of its starting point in the Holy Spirit. Underlying this correlation is a soteriology which emphasizes salvation as participation in the divine life more than the removal of guilt. Indeed, Jesus Christ is the center and the Holy Spirit is the circumference of a distinctive Pentecostal spirituality whose lineaments it is the task of this work to trace. The distinctive apocalyptic affections of Pentecostalism will be shown to be the integrating core for its narrative beliefs and practices. But the decisive context and ever present horizon for most usefully and comprehensibly displaying those beliefs, practices, and affections is eschatological: the presence of God who, as Spirit, is the agent of the inbreaking, soon to be consummated kingdom of God.
Justification: The Distinctiveness of this Study
There is a present need for a comprehensive theological analysis, and constructive explication of Pentecostal spirituality. Until recently most studies of Pentecostalism have been concerned with an apologetic defense of Pentecostal particularities, especially those associated with Spirit baptism,23 or with an analysis of some Pentecostal behavior, especially glossolalia. The former was done by Pentecostals and charismatics whereas the latter was usually done by
someone outside the movement.24 More comprehensive theological works by Pentecostals are essentially traditional outlines of evan-gelical fundamentals with a few extra chapters on Spirit baptism and gifts.25 In recent years Pentecostals have focused on such things as visions and 26
27
testimonies, particular historical figures, branches of the movement, worship, 28 footwashing, and missiology. Gordon Wheelock considered Spirit baptism in North American Pentecostalism and offered a restatement of that doctrine in dialog with the charismatic and mainline challengers. Leonard Lovett considered black-Holiness Pentecostalism and put it into dialog with black liberation thought. There are a few chapters in books, some journal articles, and dictionary entries 29
that deal directly with Pentecostal spirituality, but none that do so with an analytical, constructive theological intent. These works are more descriptive and suggestive. Williams’ book was an early neo-Pentecostal expression of the general characteristics of the spirituality which centered on Spirit baptism. He touched on historical precedent and discussed the contemporary significance of the movement. Spittler’s article in DPCM went into more detail concerning Pentecostal Charismatic practices and defined spirituality as ‘pietistic habits of ordinary individuals’ while theology was ‘systematized, usually written, reflections on religious experience’. His approach, while suggestive and complementary to the one taken in this study, re-emphasizes, by way of contrast to my work, individual experience with experience being understood primarily as emotions or feelings. He sees spirituality as a ‘cluster of acts and sentiments that are informed by the beliefs and practices that characterize a specific religious community’, while my study has emphasized the integration of narrative beliefs and practices in the affections. Chapter 3 of this study will carefully delineate the meaning of ‘affections’. The implicit ‘values’ (experience, orality, spontaneity, otherworldliness, and biblical authority) which characterize Pentecostal practices are cited by Spittler and found earlier in Hollenweger. The latter’s work is especially important for this study in that we are in agreement that the first ten years represents the ‘heart’ and not the infancy of the movement. Hollenweger also has a great appreciation of the orality (I would say ‘narrativity’) of Pentecostal spirituality as well as its Black (via Azusa Street) and Catholic (via John Wesley) antecedents. Hollenweger and I, as over against Spittler and Williams, make more of these points and, as a result, tend to see theology and spirituality in less rationalistic terms. We both have a great appreciation for the older critical tradition of
Pentecostalism.’30 Spittler and Williams also have appreciation for these aspects of spirituality but have been more concerned to provide a cognitive structure for Pentecostal experience. This work also provides a ‘cognitive structure’ but with an affective base which would in turn produce a different theological construction. Carl Henry has been a significant, though by no means exclusive, influence upon Spittler’s early theological development. Williams’s work, while clearly and 31 faithfully delineating Pentecostal themes in volume 2 of his Renewal Theology nevertheless does not show the influence of a Pentecostal hermeneutic throughout. In addition, while going further than many Pentecostals to interact with Wesleyan perspectives, the treatment is extremely brief and not central to his more Reformed roots and interest. He still operates out of the notion of perfection as a kind of philosophical ‘perfectus’. He sees the biblical relations of perfection to blamelessness, righteousness, and maturity but, like so many other writers since Warfield who fail to interact with Wesleyan scholarship, seems to equate entire sanctification with ‘perfectionism’ or to confound it with glorification. Williams’ view is preferable to the traditional Lutheran approach and his work is the best attempt to date at a charismatic systematic theology. Whatever comes later will have to take him into account and build upon his work. He makes more of Spirit baptism and tongues than many classical Pentecostal scholars! While benefitting much from Williams, Hollenweger and Spittler, the approach taken here differs in terms of the view of theology, spirituality and, most especially, the significance of the religious affections. Although several articles in Pneuma: The Journal of the Society for Pentecostal Studies have discussed hermeneutics, eschatology, missiology, and a wide range of historical concerns,32 there have been none which sought to address directly the fundamental theological issue of the relationship between spirituality, theology, and method (with the possible exception of the articles of Michael Dowd and Mark McLean).33 Grant Wacker’s bibliographical work and historical articles do the best job of giving a sense of the milieu and faith of early Pentecostals.34 While most recent efforts have focused on biblical, historical, practical, and ecumenical35 concerns, this work seeks to offer an analysis, integration, and re-vision of Pentecostal spirituality in a manner not attempted until now.
Resources: The Historical Foundations of this Study
There is an abundance of bibliographical resources for the study of Pentecostalism today. The best place to get in touch with this quickly is the bibliographical essay by Grant Wacker in The Dictionary of the Pentecostal and 36 Charismatic Movements. There one finds such indispensable sources as Charles Edwin Jones’ massive two volumes, the bibliographies of Watson Mills and, of course, the dated but still valuable and encyclopedic survey of Walter Hollenweger. Hollenweger, in commenting on his research some twenty years after his groundbreaking dissertation, examines certain phenomenological characteristics of the movement and lifts up the crucial importance of the shift of Pentecostalism and Christianity in general to the Third World majority as we 37 approach the twenty-first century. His work remains important for its comprehensive, global, and Third World advocacy. But by far the most influential works in relation to this study are those of Donald Dayton and William Faupel. Dayton’s ongoing effort to recast the historiography and definitions of evangelicalism so that Holiness and Pentecostal paradigms are not assimilated into Reformed fundamentalist categories provides a crucial standpoint from which to consider Pentecostal spirituality today. Dayton was one of the first to assert that Pentecostalism is a distinctive theological development and not merely an experiential episode in twentieth-century Christianity. His analysis of a Pentecostal gestalt of theological motifs set a new tone for Pentecostal studies.38 William Faupel’s work, like Dayton’s, is heavily supported by historical research. Indeed, there is no more clear, complete, meticulously documented work on North American Pentecostalism available anywhere.39 It is the most significant and careful historical work to be produced on North American Pentecostalism. It surpasses Hollenweger and Anderson and is more deeply in touch with the Pentecostal ethos. It offers a clear insight into the various streams and eddies of North American Pentecostal development, while giving nuanced analyses of the major figures and issues. The theological interpretation of Dayton and the historical investigation of Faupel will be the basis for future Pentecostal self-criticism and construction. Faupel’s thesis, in accord with that of the social-historical approach of Robert Mapes Anderson,40 is that ‘American Pentecostalism can best be understood as the emergence of a millenarian belief system that resulted from a paradigm-shift which took place within nineteenth-century Perfectionism’. Faupel’s massive account concludes by demonstrating ‘that a recovery and reflection of the initial expectations are necessary if Pentecostalism hopes to enter into meaningful dialog with other theological traditions’.41 His work
affords the critical-historical foundation for my own. The foregoing discussion demonstrates that there is nothing in the literature which seeks to analyze Pentecostal beliefs and practices as integrated in the affections—showing the crucial role played by eschatology. But in addition to formal justification, there are purposes which are at the heart of the personal motivation for such a work.
Purposes: The Motivation for this Study
Those who see Pentecostalism as essentially fundamentalist Christianity with a doctrine of Spirit baptism and gifts added on will be disappointed, as will those who see Pentecostalism as an experience which fits equally well in any spirituality or theological system perhaps adding some needed zest or interest. Thus, I argue persistently, if occasionally indirectly, that Pentecostalism cannot and should not be simply identified with a rationalist or scholastic type of evangelicalism. Further, it cannot, without fundamental alteration and accommodation, be assimilated into any and every Christian denomination without eventually bringing fundamental changes. Though recognizably Christian, it is in a period of theological adolescence where decisions are being made about how to use the parental inheritance, whom to court, marry and befriend, what vocation to pursue, and which kind of training and communication is most important for its future. Nevertheless certain aspects of a distinctive Pentecostal self-understanding are emerging already. Pentecostalism flows in paradoxical continuity and discontinuity with other streams of Christianity. Insofar as it retains similarity to the first ten years of the movement, it is more Arminian than Calvinist in its approach to issues of human agency and perseverance. It is more Calvinist than Lutheran in its appreciation of the so-called ‘third use of the Law’ to guide Christian growth and conduct. It is more Eastern than Western in its understanding of spirituality as perfection and participation in the divine life (theosis). In this regard it has much to learn from persons like Gregory of Nyssa, Macarius the Egyptian, and St Symeon, the New Theologian. It is both ascetic and mystical. These treasures could naturally and fruitfully be mined as the line of Wesleyan continuity is traced backwards and forwards. Pentecostalism is more Catholic than Protestant in emphasizing sanctification-transformation more than forensic justification, but more Protestant than Catholic in the conviction that the Word is the authority over the church and tradition for matters of faith, practice, government, and discipline. In its origins Pentecostalism was more Anabaptist than the magisterial Reformation
in its concern for peace and a covenanted believers’ church where discipleship and discipline are essential features of congregational life. Pentecostalism has a more Holiness evangelical hermeneutic than the fundamentalist-evangelical tradition in terms of its actual use of Scripture and understanding of the role of 42 reason. Finally, it is more liberation-transformationist than scholasticfundamen-talist in its way of doing theology as a discerning reflection upon living reality. (This will be explained in greater detail later in this chapter.) Pentecostalism, therefore, exists in continuity but differentiating discontinuity with other Christian spiritualities. To the extent that it has a distinctive spirituality and theology, it may not be seen, used, or identified with an experience or experiential episodes. There may be Pentecostal-like experiences but Pentecostal spirituality is another matter. Other motives for this study have formed in response to fifteen years of contact with Pentecostals from five continents in classes, mission endeavors, prayers, and interviews. They were asking for more Pentecostal literature that was distinctive and integral to their praxis. They were seeking a theological clarity and grounding to serve better the interrelated pastoral, missional, and ecumenical concerns. Mission success has brought in millions of new converts and transfers from other Christian groups. The question arises, ‘How can we disciple such a mass of people?’ Further, and in keeping with the ‘experiences of salvation’ (regeneration, sanctification, Spirit baptism, healing, and so on), what daily disciplines and ways of approaching personal and social crises grow out of and are congruent with this ethos? How must the present approach be supplemented or changed? On what basis? In addition to the dialogue with liberation practitioners in Latin America, Pentecostals have been carrying on their own dialogs and engaging in painful but persistent self-examination concerning the context and extent of mission.43 All this is occurring as a greater number of liberationists begin to construct a liberation spirituality and to recognize the importance of the doctrine of the Holy Spirit. These pressing and painful matters must be addressed in a way that does not compromise the fundamental spirituality but addresses these new challenges, needs, and opportunities. This is especially so in those areas of Latin America and other Third World locations where Pentecostals have a greater and greater influence and responsibility by virtue of the sheer size of the movement.44 Third World Pentecostals are not as preoccupied with the fundamentalistmodernist, personal versus social, conservative versus liberal controversies as are North Americans. This is not to say that they are unaware of liberalism or
radicalism, but they are more open to finding ways to incorporate valid insights and make changes that will help the people. Pentecostals have been ‘Base Communities’ for decades as they have networked and survived in very repressive environments. Theirs is a grass roots ecumenism born of immediate missionary and pastoral concerns. It is the purpose of this study, then, to explicate a Pentecostal spirituality which is apocalyptic, corporate, missional, and essentially affective. After the analysis and integration of Chapters 2 and 3, a constructive ‘re-vision’ is offered which attempts to address some of the Third World challenges, internal problems, and external criticisms. As Chapters 2 and 3 unfold, the contours of the response should become clearer. It is hoped that the re-vision will advance the cause of unity and missionary effectiveness in the body of Christ and that Pentecostals will begin to see liberals as well as conservatives as important dialog partners.45
Perspectives on Pentecostal Spirituality There are certain presuppositions, convictions, and theological commitments which constitute a standpoint from which to approach Pentecostal spirituality. It is not claimed that this is the only basis for such an analysis but only that this one is an especially appropriate methodology for this particular subject matter. The elements of this perspective, this Pentecostal view of the theological task, are discussed under three heads: (1) Spirituality and Theology, (2) Origins and Continuity, and (3) Eschatology and Coherence.
Spirituality and Theology
Theological science is basically a construal of the relationships between God and the world. For Pentecostals, the starting point for such an undertaking is the Holy Spirit who is ‘God with us’. The God who was present among Israel and in Jesus Christ is now present as the Holy Spirit. The God who will one day be ‘all 46 in all’ is at work now in all things, working there together for the good of those who love him.47 The Holy Spirit brings the Father and the Son who, together 48 with the Spirit, abide with and in the believer. To start with the Holy Spirit is not necessarily to become unitarian49 but indicates a theological, practical concern. This can be seen when the New Testament baptismal order of Father, Son, Holy Spirit in Mt. 28.19 is changed so that the Son is mentioned first in the benediction of 2 Cor. 13.14 (‘The grace of the Lord Jesus Christ, the love of God, and the communion of the Holy Spirit’). The order of this benediction is usually followed in the gospel proclamation. However, when discussing life and service in the church (1 Cor. 12.4-6) Paul’s order is Spirit, Lord, God. The alternating order in these three scriptural contexts is not meant to imply a lack of full equality among the three divine persons (as we shall see in Chapter 4).50 Indeed, just the opposite is true. The Pentecostal concern is that of Paul in 1 Corinthians 12—to emphasize the lived reality of the faith, the life and service of the people of God who are organically constituted as the body of Christ by the indwelling of the Holy Spirit. As Newbigin has observed, the Pentecostals focus neither on right structure (Catholic) nor right message (Protestants). Instead, they emphasize that the ‘Christian life is a matter of the experienced power and presence of the Holy
Spirit today … neither orthodoxy of doctrine nor impeccability of succession can take the place of this’.51 In seeking to safeguard the uniqueness, sufficiency, and finality of Christ the Roman Catholic and Protestant approaches often result in ‘a church which is a shell’52 or, as Pentecostals (with Wesley) would say, ‘a form of godliness denying the power thereof’.53 With the Protestants there is agreement on the priority of Scripture over the church and a neglect of visible order and structure. With the Catholics there is a recognition of the Christian life as ‘an actually experienced and received reality, something involving an ontological 54 change in the believer’. In commenting on the first outpouring of the Spirit upon the Gentiles of Cornelius’ household (Acts 10) Newbigin asserts, Nothing could be more plain or unambiguous. The gift of the Spirit was a visible, recognizable, unquestionable sign that God had accepted these Gentiles as His own people and before that fact the most massive and fundamental theological convictions simply had to give way. The Holy Spirit may be the last article of the Creed, but in the New Testament it is the first fact of experience … The Spirit is God’s recognizable witness (e.g. Acts 15.8) to His own presence, and therefore is entitled to right of way before all arguments based on a priori reasoning.55 It was out of a concern for this ‘right of way’ of the Spirit that early Pentecostals disdained and eschewed ‘man-made Creeds’. It was not that they had no fundamental beliefs—their periodicals and testimonies make it obvious that they did—rather, the objection was to a creedalism which they believed brought disunity and rejected the new blessing that the sovereign Spirit was restoring among them. Their primitivism was born out of a desire for apostolic faith, power, and manifestations of the Holy Spirit among ordinary believers. The presence of the Holy Spirit constituted the church. As on the day of Pentecost, the message, structure, faith, and order might all be in place; but it took the power of the new age, the last days’ outpouring of the Spirit, to constitute the church a missionary fellowship which would witness in words, power, and demonstration of the Holy Spirit. The church lives from the Spirit in Christ unto the glory of the Father.56 Creeds must guard the faith not limit the sovereign leading of the Spirit. If God is the living God, the God who in Trinitarian communion is spirit, if the church is a living organism of charisms and signs, and, if salvation is a living relationship with this God among these people who live in last days’ expectancy
and urgency—if all this is the case, then theology must be a discerning reflection upon this living reality, these divine-human relations.57 Theology requires not only discursive reasoning but also the engagement of the whole person within the communion of charisms. The community of the Spirit and Word functions as a worshiping, witnessing, forming, reflective whole; but at the heart of all this is the liturgical life of the community. Ranaghan has concluded that the birth of Pentecostalism cannot be attributed to only the two works of grace theology. He finds that too ‘narrow and incomplete’. Rather, From the field preaching of Wesley to the tents of Aimee Semple McPherson, it has been this one way of worship which has made the theology come alive and given it experiential validity. The worship has provided the vehicle for the theology. One can say further and maintain that the theology has served basically as a commentary on the worship which has always been the central reality.58 Wheelock believes that Pentecostal ‘theology as a whole seeks to convey that an arid, rationalistic, formalistic, unemotional, non-experiential and noncharismatic approach to religious life is unacceptable’. He sees much of this vitality coming from the African- American culture’s emphasis on the nonconceptual aspects of life generally and religion specifically … The whole man should be caught up in the process … the experiential component is viewed as a ‘natural’ element and enthusiastic involvement as a fitting modality of religious expression. It was much of this expectation and practice that was transmitted at Azusa.59 In the context of American restoration-revivalism, it was the ‘black spirituality of the former slaves in the United States’ encountering the specific Catholic spirituality of the movement’s ‘grandfather’, John Wesley, that produced Pentecostalism’s distinctive spirituality.60 Neither Wesley nor the AfricanAmericans did theology in the traditional, scholastic way. Sermons, pamphlets, hymns, testimonies, conferences, spirituals—these were the media of this movement. But this is not so unlike the first hundred years of Christianity. Though some were ‘well educated’, there were not many mighty or wise or noble among them.61 Letters, testimonies, epistles, Gospels, songs, a brief history, and an apocalypse—these were the tools of the first-century house churches. ‘Folk religion’ and ‘populist theology’ carry all the dangers of fanaticism and all the promise of continual renewal in the church. Pentecostalism has experienced and
manifested both tendencies. But it is important to see that theology is not to be identified solely or even primarily with systematic treatises, monographs, and scholarly apparatus in centers of academia. Theology begins in the prayerful response of persons to God. If, then, the Holy Spirit is taken as a starting point and the centrality of worship is given due place of primacy, it must be acknowledged that prayer— individual and corporate, human and ‘angelic’, with sighs and groans, praise and petition—is at the heart of this spirituality. But if it is the heart of the spirituality, it must also figure centrally in the understanding of the theological task. The language of the vocative and the indicative, of prayer and belief, must be seen together. For Pentecostals it is impossible to know God and the things of God without prayer, because in prayer one responds to the Spirit of truth. When one ceases to be prayerfully open, even the light of truth or belief that one has becomes dark, distorted and may soon be forgotten. Theology thus conceived is no mere speculative enterprise; it is urgent, lastdays work. With Karl Barth Pentecostals can affirm that ‘Prayer is an eschatological cry based on acknowledgement of God’s name, will and reign … it is the actualization of our eschatological reality that is possible here and there …’62 Barth discussed the relation of prayer and theology in his Evangelical Theology: An Introduction.63 Four related claims concerning this relation are discussed by Don Saliers in the introduction to the second edition of Barth’s 1949 book, Prayer. 1. The first and basic act of theological work is prayer. Theology itself, while demanding historical knowledge and conceptual reasoning, is radically dependent upon having been addressed by God in such a manner as to respond freely in return … The conception of God must be congruent with the nature of address to the self revealing God, whose revelation is accompanied by the command and invitation to share in the divine life … The essence of prayer and worship, then, is acknowledgement of God and God’s gracious turning in mercy and judgment toward all creation. This response arises from the capacity of the creature, through grace, to love and rejoice in gratitude for who God is … 2. The second claim is that the object of theological reflection is a ‘Thou’ encountered, not an idea to be grasped as the ‘Ultimate God’ or the ‘Ground of Being’, for instance. Doctrinal language about God must be in response
to something actually discerned in God. But this means to thank, to praise, to invoke, and to petition God. This is why Barth can say, ‘Theological work must really and truly take place in the form of a liturgical act’. This is implicit in Barth’s reflection on the fact that we are not only to speak the words Jesus gives us; but we must also receive him and the life of service he confers in and through the words …
3. Thirdly, since theological reflection about God is itself dialogical, we cannot rest content with building upon the certainties of previous systems of thought … To conceive God as living and redeeming the world is humanly possible only by receiving anew through grace the present activity of God. Theology itself becomes an offering to God, and a continuous petition that this offering may be acceptable. 4. Finally, theology cannot guarantee truth, because it cannot in itself guarantee the grace of God … Certainty in our knowledge of God lies not in formulated doctrines, according to Barth, but in acknowledging, invoking, and petitioning that God will truly make the divine Word and 64 being accessible to us.
Upon reading this one is reminded of Barth’s life-long appreciation and sharp disagreement with the theology of Schleiermacher, whom he believed had blurred the distinction between the human and divine by collapsing the Holy Spirit into the human spirit. But Barth thought he might begin his own theological work again, and this time start with the Holy Spirit. There is in the immediately foregoing discussion of prayer and theology the seeds of such a beginning. Pentecostals would find much to recommend Barth in this respect. There is in the first point the recognition of the initiative of God; in the second, an acknowledgment of the personal address (God is Spirit!); the third might serve as a basis for rejection of creedalism, though not of creeds themselves; and, finally, the fourth point emphasizes the sovereignty of the Holy Spirit. For Pentecostals, to know God is to be in a right relation, to walk in the light and in the Spirit. To know and not to do the truth is a lie, to exist in contradiction. In that case even the light one has will become darkness. For example, to say ‘God is with us’ without being with God is to lie or merely to speculate. Christian theology as spirituality must be consistent with, appropriate to, and responsive to its source and object, the living God. This is very much like the theology of the Apostolic Fathers who were
‘essentially practical, unconcerned with speculative theology, unaware of cultural matters …’65 But it is also much like the later patristic-monastic theology in which there was no distinction between prayer and theology. Up until the twelfth century theology was not a manner of knowing but a manner of praying. Theology was not a doctrine to be analyzed intellectually or discussed in school. The purpose of theology was not to explain God, but to know Him in contemplation, adoration, praise and thanksgiving. If theology was a science, it had to do with affections. This prayer conception of theology obtained until the first half of the twelfth 66 century … Therefore, to do theology is not to make experience the norm, but it is to recognize the epistemological priority of the Holy Spirit in prayerful receptivity. Speaking of a pneumatic epistemology, Howard Ervin posits an awareness that the Scriptures are the product of an experience with the Holy Spirit which the biblical writers describe in phenomenological language … the interpretation of this phenomenological language is much more than an exercise in semantics or descriptive linguistics. When one encounters the Holy Spirit in the same apostolic experience, with the same charismatic phenomenology accompanying it, one is then in a better position to come to terms with the apostolic witness in a truly existential manner … in the sense that a vertical dimension to man’s existence is recognized and affirmed. One then stands in ‘pneumatic’ continuity with the faith community that birthed the Scriptures.67 In addition to a distinctive epistemology, other Pentecostal scholars are calling for an ontology and hermeneutic with which to construct a systematic theology ‘worthy of the name Pentecostal’.68 For David Nichols such an approach would involve a ‘spiritual’ ontology with its analogy of love as opposed to analogy of faith or being.69 This ontology would take seriously the transcendent presence of God as the fourth dimension of reality. God who is ‘other’ is not outside the world of time, space and matter.70 Nichols believes that it is time for Pentecostal theologizing to ‘shake free from the shackles of exclusive rationalism, (adaptations of Hodge, Shedd, Warfield, etc.) and from irrationalism, and to stand on its own two feet with a dimensional understanding of spiritual truth’.71 All of this serves to emphasize the importance of the Holy Spirit as a starting point for a distinctive Pentecostal approach to theology as spirituality. Does this,
however, mean that Pentecostals place the Spirit above the Word and thus elevate experience from the category of source for theology to that of norm? The answer is ‘Yes’ and ‘No’. Yes, the Spirit is prior to the written Word of God, but the Spirit inspires, preserves and illumines that Word within the communion of those who are formed, corrected, nurtured and equipped by that Word. Yes, the Spirit does not exist only to illumine Scripture and apply the benefits of salvation to the believer. The gifting and guiding of persons in community and the community as a whole is the ongoing, daily task of the Spirit. The signs and power of the Spirit are not an optional addition for a church that would engage principalities and powers and suffer unto death. However, in a consideration of the relationship of Word and Spirit, the Word as living Word of God in Jesus is, of course, equal with the Spirit. The person and work of the Spirit is in salvific continuity with the person and work of Christ, but it is not exhausted therein. The recovery of dialectical balance or of a proper integration of the Spirit-Word addresses the crisis of authority in the church today and also expresses a central feature of Pentecostal theology. This integration is violated in various ways by differing Christian traditions. Roman Catholic theology, even since Vatican II, still tends in practice to place the church over the Word and then further to place tradition on a level with Scripture. Protestant fundamentalist scholasticism has so subjugated Spirit to the Scriptures that the only significant function of the Spirit is to witness to the Bible which is interpreted by human reason. Other groups which place Spirit over Word and develop private ‘revelations’ beyond and over Scripture— contradicting or correcting Scripture!—clearly err on the other side. Then there is the subtler, supposed subjugation or domestication of the Holy Spirit in which the Spirit serves only to provide zest for ecclesial undertakings, becomes another word for the grace of the sacraments (so that one receives grace and not God the Holy Spirit) or is identified with the light of reason or common human experience as in some more liberal versions of theology. All of these ways of subsuming the Spirit are correlated with an improper understanding of the relationship of Spirit and Word. Agreeing with Calvin and Luther, James Jones, in a neglected but important work, states, the Bible is of little value without the sovereign work of the Holy Spirit. The Bible has no significance when ripped from the context of the experience of the Spirit. Refusing to subsume the Spirit under the Word frees the Spirit to do more than confirm the text and shut up.72 We might also add that this also frees the Spirit to do more than assure the
believer and then shut up. But Jones continues by pointing out, The Spirit does not contradict the Scriptures but his job is more than just repeating what we can find by reading there … John indicates that the Lord expected the Spirit to direct the church in those areas not covered by Jesus’ teachings (John 15.7-12) … The first apostolic council went back to the Old Testament covenant with Noah but justified their decision by saying ‘it 73 seemed good to the Holy Spirit and to us’ (Acts 15.28; 11.15-17). Jones further maintains that the polemics of the past have separated the Bible from the Spirit in community, and therefore destroyed any valid basis for Christian faith: Protestants have the Bible, but the Bible without the Spirit and the community is a dead letter giving rise to arid scholasticism. Catholics have the community, but the community without the Bible and the Spirit becomes only an institutional shell. Pentecostals have the Spirit but the Spirit without the Bible and the community inevitably leads to subjectivism and fanaticism … In the complete Spirit-filled body of Christ, as Paul portrays it, these three partial authorities complement each other. The Spirit inspires the Word and builds up the community; the Word enables us to understand our experience of the Spirit and teaches us the form of our common life; the community forms the context in which the Word is understood and the Spirit encountered. Using the Bible to tear down rather than build up the church, using the church to squelch the Spirit, using the Spirit as a pretext to go beyond the perimeters of the Gospel have destroyed the foundations of Christianity in the modern world more than any external 74 attacks by atheists and skeptics. The wholeness of the body of Christ given in the proper relation of Spirit, Word, and community has as its corollary a view of spirituality which is the integration of beliefs, affections, and actions (of knowing, being, and doing). Indeed for a Pentecostal theology-as-spirituality, with a starting point in the Holy Spirit, it is a necessary correlation. Mark McLean insists, It is simply time to admit that the Pentecostal understanding of the mode of God’s presence among His people in conjunction with our use of Scripture in the common life of the Church results in a Pentecostal hermeneutic and theology that at major points is different from an orthodox non-Pentecostal hermeneutic and theology. The task before us now is to realize and explore the implications of that fact for our understanding of God’s continued
activity in the world and for our understanding of our self-identity and tasks given to us by the living, acting and speaking Creator of all things.75 This theological task demands the ongoing integration of beliefs, affections, and actions lest the spirituality and theology fragment into intellectualism, sentimentalism, and activism, respectively. When theologia is restored to its ancient meaning, the dichotomization that too often occurs or is perceived between theology and spirituality can be overcome. Experience of the Spirit, 76 who is the agent of mutuality and interrelatedness in the Trinity and the church, drives toward and requires this integration of belief, affections, and practice which is at once the definition of spirituality and of the theological task. To state this claim in a more formal way: orthodoxy (right praise-confession), orthopathy (right affections), and orthopraxy (right praxis) are related in a way analogous to the interrelations of the Holy Trinity. God who is Spirit creates in humanity a spirituality which is at once cognitive, affective, and behavioral, thus driving toward a unified epistemology, metaphysics, and ethics. To speak of and long for the full realization of this reality is the privilege and pain of Christian theology. It is in a sense to long for the eschatological Trinitarian realization of the kingdom of God which Jürgen Moltmann has so eloquently described in his Trinity and the Kingdom. Dialog partners in the development of a sense of this realization have been Karl Barth, John Wesley, and Jürgen Moltmann in their distinctive contributions to an understanding of orthodoxy, orthopathy, and orthopraxy, respectively. Karl Barth’s development of the relation of prayer and theological vocation has already been referred to above. However, while insisting that all action must proceed from and be judged by some cognitive awareness of the ‘facts’ of divine revelation, Barth nevertheless indicates something of his wholistic view of ‘knowledge’ and ‘orthodoxy’ in the following discussion: We cannot impress upon ourselves too strongly that in the language of the Bible knowledge yada, ginoskein does not mean the acquisition of neutral information, which can be expressed in statements, principles and systems, concerning a being which confronts man, nor does it mean entry into a passive contemplation of a being which exists beyond the phenomenal world. What it really means is the process of history in which man, certainly observing and thinking, using his senses, intelligence and imagination, but also his will, action and ‘heart’, and therefore as whole man, becomes aware of another history which in the first instance encounters him as an alien history from without, and becomes aware of it in
such a compelling way that he cannot be neutral towards it.77 This statement was put to use by Jürgen Moltmann who, though differing with Barth from time to time, nevertheless remains his student in many ways. In The Trinity and the Kingdom Moltmann develops the doctrine of the Trinitarian history of God in the direction of an eschatological Trinitarian realization of the kingdom. Moltmann sees history in God and God in history without dissolving God into history or leaving history without significant freedom and responsibility. His goal is to enable the church to join God in an orthopraxy (right action) which seeks to be an anticipation, representation, and/or resistance 78 in the light of the kingdom that is coming and now is. Truth is to be done as well as believed, and this requires a passionate commitment to the messianic community of the crucified and risen Lord who, by the Spirit, gives a sustaining, mobilizing, living hope. If Barth emphasized evangelical faith and Moltmann radical hope, John Wesley could be described as the theologian of the love of God. He and Jonathan Edwards represent a deep stream of evangelical thought which has yet to be fully integrated into the North American evangelical establishment. His concern for what contemporary Methodist theologian Theodore Runyon has called ‘orthopathy’ was borne of his years of personal struggle, study, and practice in and among the Methodist societies, bands and classes which were at the forefront of awakening, renewal, and reform in eighteenth-century England. Runyon sees this orthopathy as providing ‘a necessary but currently missing complement to orthodoxy and orthopraxy’. For him orthopathy is ‘religious experience as an event of knowing between the Divine Source and human participant’ involving four interrelated factors: 1. The divine source of experience who makes impressions on the spiritual senses of the human beings. 2. The telos of experience: the intention of the source, the purpose and goal for the human being. 3. The transformation brought about through experience. 4. The feelings that accompany experience.79 His description of these essential components of experience recognizes
the important, powerful, and absolutely necessary contribution which experience has to make to the identity, mobilization and mission of the
Church; and at the same time the checks and balances necessary if experience is to be guided into the most productive channels … experience needs the word of orthodoxy if it is to communicate rightly and the actions of orthopraxy if it is to be the instrument of the sanctification of the world. But both words and deeds need to be fulfilled with the divine power and impact of the motivating Spirit, mediated, received and communicated further through experience … [It is] feelings that focus our energies, enlist us, motivate us and give us passion. Who will fight against injustice, prejudice and corruption who does not have feelings of justice and outrage against injustice? Who will sacrifice for others and engage in acts of mercy who does not feel compassion? Who will spend long hours over a microscope or poring through books who does not know the feelings of joy and satisfaction that come with discovering a new truth or finding new confirmation of an old truth? Who will work hard at great emotional cost putting a marriage back together who does not feel the importance of those relations to all who are touched by them?80 Building on but going beyond the perspective of Runyon, this study uses ‘orthopathy’ to refer to the affections which motivate the heart and characterize the believer. As shown by Saliers, Clapper, and Knight,81 the Christian affections are the heart of the spirituality of Edwards and Wesley. They are likewise the heart of Pentecostal spirituality. The personal integrating center of orthodoxy and orthopraxy is orthopathy, those distinctive affections which are belief shaped, praxis oriented, and characteristic of a person. Affections are neither episodic, feeling states nor individualistic sentiments. There are, of course, attendant feelings or emotions that come and go and intermingle in the affections over time. Unlike ‘feelings’ these affections are distinctively shaped and determined by the biblical story and evidence the marks of particular communal and historical location. In Chapter 3 I will analyze three Christian affections in their distinctively Pentecostal configuration. This will, however, be no mere attempt to balance reason and emotion. Balance is a term often used in the general culture and evangelical mainline churches to refer to a certain kind of mental health or mean of normality. Balance speaks of equal weight given to reason and feeling. Those who speak this way often see the religion of the lower classes, the disinherited, the African-Americans, and Pentecostals as being merely ‘emotional’ and filled with psycho-motor manifestations. Although recognizing the value of feeling as motivation and excitement, they fail to see the crucial and fundamental role of
affections in salvation and, therefore, in the theological enterprise in general. Hence, the word ‘integration’ is deliberately chosen as being preferable to ‘balance’. Integration in certain crises of oppression, domination, and breakthrough may be more like the fusion of a hydrogen bomb. Western society, especially in its white, middle and upper classes, values control and quietness in matters of religion (though not, of course in sports, political campaigns, discotheques, rock concerts, and so on). In contrast, when those oppressed by demonic forces and/or violated and defiled by humanity catch the vision of a kingdom that liberates, sanctifies, and empowers a new existence, there is often, indeed almost inevitably, intensity of response. The joy and exuberance, the depth of sorrow and longing, the courageous wit-ness of millions of such persons cannot simply be written off as hysteria, mass psychosis, or cheap escapism. It is crucial for Pentecostals to consider carefully their beliefs, affections, and practices before they uncritically accommodate to culture, are assimilated into mainstream denominations, or are co-opted by socio-political ideologies. In the words of the Chilean Pentecostal pastor Juan Sepúlveda: We do not propose to reject theological reflection in the Pentecostal context (we are, in fact, reflecting theologically here), but rather we are attempting to repair the road for a form of theological reflection which assumes the richness and specificity of the Pentecostal experience. It is the emphasis on doctrines which has created the idea that Pentecostalism proposes an otherworldly salvation, when what the testimony of the Pentecostal experience 82 shows us is, above all, the opportunity of a salvation here and now. Or again, as Peruvian Pentecostal pastor Bernardo Campos has said recently,
We Pentecostals have always done theology … and as we understand it today it is the living experience and reflection (method) which the Church as a community of faith does (subject), in a social space and a given time (context), concerning the action of God in the world in Jesus and by His Holy Spirit (object, content), with two fundamental purposes to experience and to give account of:
1. The evangelization and reconciliation of the world with God, in the dynamic of the creation and growth of the new person.
2. The creation of a new society (new earth) in the dynamic of the advance of the kingdom of God in history …
The Christian Church has experienced two theological traditions worthy of being taken into account: a systematizing tradition (Aquinas, Calvin, Barth) and an experienced, non-systematic tradition (Muntzer, Kierkegaard, Unamuno, etc.). One must ask, ‘What are the advantages and risks of a systemization and what are the advantages and risks of a theology of 83 experience without divorcing them’.
Campos describes Pentecostal experience as being first of all the ‘community’s mode of being, of doing, and of living’.84 It is a means of understanding that moves from experience to testimony to doctrine to theology and back again in an ongoing dynamic that is more implicit than explicit, more oral than written, more affectively-rational than principled-rational, more narrative than strictly propositional. The affective integration which comprises the Pentecostal affections is the experiential center of a distinctive theology which in less than a century has impacted every continent and every Christian denomination. Perhaps it is the failure of the more Reformed (and especially Lutheran) approaches to appreciate salvation as affective integration (‘the faith that works through love’) that makes it difficult for them to understand and theologically adjust to Pentecostals, Wesleyans, African-Americans, and whole multitudes of Third World indigenous churches. There are, of course, notable exceptions to this;85 but, on the whole, the major contemporary criticisms have come from fundamentalist dispensationalists like John MacArthur86 and the much more informed and nuanced critics such as James Dunn and Frederick Dale Bruner.87 While it is not the task of this study to offer a direct rebuttal, thus adding to and building upon those already offered by Pentecostals, it is hoped that this approach will make clear some of the reasons for misunderstanding and talking past one another. Spirituality as primary theology forms the theoretical standpoint for an analysis of Pentecostalism which will prove recognizable to Pentecostals and afford a basis for revision and dialog. But before that analysis proceeds it is necessary to offer two further observations which are of substantial importance to the development of the thesis. One relates to a limitation and the other to the overall context.
Origins and Continuity
With Walter Hollenweger this study will accept as a historical limitation the first ten years of the twentieth century as the heart and not the infancy of Pentecostal spirituality.88 Hollenweger, one of the leading, if not foremost, authorities on world Pentecostalism’s variety and dynamics, takes ‘the early Pentecostal 89 spirituality as the norm by which I measure its subsequent history’. The streams of Pietism, Puritanism, Wesleyanism, African- American Christianity, and nineteenth-century Holiness-Revivalism form a confluence which has today become a sea of Pentecostal believers.90 Therefore, though there is an incredibly diverse array of Pentecostal denominations as the twenty-first century approaches, yet the original or essential spirituality has left its mark on them all and remains to be re-visioned if the movement is to have theological coherence and continuity. This historical focus or bracketing captures what is perhaps the two most important spiritualities which formed the originators of Pentecostalism: Wesleyan and African-American.91 The Wesleyan spirituality embodied a specific catholic tradition of transformation which included Western and Eastern figures. Wesley translated and abridged many of these sources in a Christian library which he produced for the edification of his lay leaders.92 He taught a second-crisis experience, both preceded and followed by a development, beginning in new birth and maintained only through moment by moment abiding in Christ. Following Wesley, such nineteenth-century Holiness leaders as Finney, Moody, Hannah Whitall Smith, Asa Mahan, and Phoebe Palmer—though from both Wesleyan and Reformed backgrounds—were all in agreement that there was a subsequent ‘sanctification’, ‘baptism in the Holy Spirit’, or ‘overcoming life’ which is the purchased possession of Calvary for every believer. It is generally recognized that the early Pentecostal revival built on this Wesleyan-Holiness foundation in embracing the ‘fivefold’ or ‘full gospel’ of justification, sanctification, Spirit baptism, divine healing, and premillennial return of Jesus; all of these were to be definite experiences flowing from the atonement. That is to say, the Christian could by faith receive the full blessing and benefits, a five fold blessing, if trusting in Christ he or she sought the Lord and ‘paid the price’ of asking, seeking, and knocking. The following song quoted in The Apostolic Faith in 1906, illustrates this desire: ‘Baptized with the Holy Ghost’ (By F.E. Hill)
Do you long to be full of joy and free, To be strong in God and His glory see, Then obey His word and you shall be, Baptized with the Holy Ghost
CHORUS ‘Ye shall be baptized’, Jesus said, Baptized with the Holy Ghost. Tarry then until with power endued, Baptized with the Holy Ghost. Yes, I’ll be baptized with His power, Baptized with the Holy Ghost, ‘Tis the gift I see, the Father’s promise to me, Baptized with the Holy Ghost. Will you consecrate to Him now your all, Let Him have His way while to Him you call, As in faith you wait, the power will fall, Baptized with the Holy Ghost. ‘Tis the gift of God to the sanctified, He will comfort, lead and will be our guide, And will dwell in us, coming to abide , Baptized with the Holy Ghost. Will you gladly fall at the Savior’s feet, Give your doubtings o’er and be made complete There to dwell in peace and communion sweet, Baptized with the Holy Ghost. You can sing God’s praises now, and by and by, You shall speak with tongues, and shall prophesy, In the power of God ye shall testify, Baptized with the Holy Ghost.93
Had there been no eighteenth-century Wesleyan and nineteenth-century Holiness movements there would have been no twentieth-century Pentecostalism; and Pentecostalism is at any rate inexplicable without this theological heritage. Even researchers of the ‘non- Wesleyan’ roots of
Pentecostalism acknowledge its Wesleyan lineage. As Edith L. Blumhofer, whose doctoral dissertation dealt with the non-Wesleyan antecedents of Pentecostalism, has said, ‘Until 1910, most Pentecostals accepted without question the insistence that an experience of Christian perfection preceded Spirit baptism’.94 Non-Wesleyans in the nineteenth-century Oberlin and Keswick movements were ‘Wesleyanized’ and thus ‘Arminianized’. William Menzies, the Assemblies of God historian, has studied the non-Wesleyan roots of the movement but nonetheless has noted that Wesleyanism via the Holiness movement was the cradle of Pentecostalism.95 The importance of the Wesleyan origins of the movement for the understanding and re-visioning of the spirituality cannot be overstated. It is discussed in detail by historians Vinson Synan96 and Melvin Dieter97 and by historian-systematician Donald Dayton.98 Donald Wheelock in his 1983 dissertation on ‘Spirit Baptism in American Pentecostal Thought’ concludes that Wesleyan and non-Wesleyan Pentecostals agree that personal holiness precedes Spirit baptism. For the former it is the definite crisis experience in which the ‘root’ of sin is plucked up, while for the latter it is a matter of victorious consecration which is maintained and deepened by the assistance of the Holy Spirit.99 Further, Wheelock states that almost all American Pentecostals state the following ‘conditions’ for Spirit baptism: obedience to God through separation from all known sin, a request for prayer and unity with others, a praise-filled worship and a faith-filled expectation. Melvin Dieter, aware of the past intense conflict between the Holiness and Pentecostal churches, nevertheless observes that this was, to a large extent, a family dispute between fraternal, if not identical, twins. He concluded that even the largest and more ‘baptistic’ Pentecostal body, the Assemblies of God, has a spiritual dynamic that is at least equally or even more strongly derived from the historical campmeeting perfectionism as it is from any classical Reformed categories. The theological and experiential wineskins of the Keswick low-church Anglicans and others through whom the higher-life message came back to its American home have … been hard put to contain the holiness wine. To use another metaphor, the dominant genes of the vigorous Christocentric pneumatology residing in our common parent, the holiness revival, have left on all the progeny such a unified imprint of spirituality and experience
that each of us will be the loser if we fail to recognize … the ultimate charge that Warfield and his friends leveled against the movement [New School revivalism of Finney, Mahan, et al.] was that it was really ‘Methodist’. The holiness connection is important for Pentecostals because it carries with it the nineteenth-century concern for abolition, prohibition, women’s rights, and the reform of society according to the righteous standards of God. When Pentecostalism and the holiness churches were impacted by the aftermath of the Civil War, Reconstruction, the new higher criticism of the Bible, the ‘liberal’ social gospel and the increasing ‘embourgeoisement’ of Methodism, they were forced to choose between fundamentalism and modernism. By choosing fundamentalism the Wesleyan agenda for ‘spreading scriptural holiness throughout the land’ was reduced to rescue missions, storefront churches, soup kitchens and other kinds of person-to-person involvement. A further result of this alliance has been the presence of both movements at the founding of the National Association of Evangelicals in the 1940’s despite the fact that the word ‘evangelical’ in North America usually excludes or redefines the holiness Pentecostal paradigm in favor of the more Presbyterianfundamentalist paradigm. This drew both movements into battles concerning inerrancy and drew them away from rethinking and further application of their fundamentally transformationalist heritage.100 All of these characteristically Wesleyan concerns can be heard in the words of Frank Bartleman, who was an eyewitness and participant in the 1907 Azusa Street revival: We need deliverance from strife and confusion, a deeper consecration and death to self … God’s fire falls on sacrifice, as in Elijah’s case. The greater the sacrifice, consecration, the more fire. But Ananias and Sapphira are in the mission work today. They are striking the Peters dead with their money and influence. The man who is paying the full price in consecration has very little/voice in the meetings … Preach not to please a ‘party’ but to raise a standard … God gathered a lot of seasoned saints together at ‘Azusa’ in the beginning. They were subdued and purified through months of prayer, and years of experience with God. We live in a light jazzy age. They refuse the fires of purifying, holiness of heart. We have an atmosphere of confusion. There is too much ‘professional’ work, railroading seekers through, like a ‘quack’ doctor’s office. This produces a ‘fake’ Pentecost, with spurious ‘tongues’. The ‘singing in the Spirit’ is also imitated. Men
have learned to do these things without the Spirit, and suggest them to others for their imitation. We have even heard leaders call for any demonstration they wanted from the people. What would Peter say to such a demonstration? … We advertise ‘miracles’, wonderful preachers, etc., and have crowds following bill-board ‘signs’ to the next big meeting. But are the ‘signs following’? Men love the spectacular. What we do not understand is the ‘wonderful’. 101 Dieter and Bartleman, each in his own way, show why the taking into account of the Wesleyan roots is vital. But so is the other stream, black spirituality, because this spirituality was the immediate mediator of Azusa in the person of William Seymour. One of the largest North American Pentecostal bodies today, the Church of God in Christ is predominately Africa-American. It was founded by C.H. Mason, whose name is given to the first Pentecostal seminary in the world in Atlanta, Georgia. This black spirituality was represented by scores of others who were hymn writers and evangelists. Hollenweger says that the reason for the growth of Pentecostalism lies in its African-American roots which he summarizes by listing the characteristics of black spirituality: —orality of liturgy; —narrativity of theology and witness.
—maximum participation at the levels of reflection, prayer and decision making and therefore a form of community that is reconciliatory;
—inclusion of dreams and visions into personal and public forms of worship; they function as a kind of icon for the individual and the community;
—an understanding of the body/mind relationship that is informed by experiences of correspondence between body and mind; the most striking application of this insight is in the ministry of healing by prayer.102
It was the confluence of African-American and Wesleyan spiritualities which gave rise to this movement of participation in the Spirit. A very significant part of the Wesleyan-Holiness inheritance was the ministry of women;103 already in the nineteenth century the language of sanctification as Spirit baptism had proven to be inclusive of women as prophets. Sons and daughters were to prophesy. Women testified, preached, founded churches and witnessed in the power of the Spirit.104 More will be said about this later, but again the importance of the Wesleyan roots cannot be overestimated.
An eschatological equality seemed to bloom wherever the vision and reality of the kingdom of God was experienced in missionary urgency and spiritual zeal. The major metaphor for the church of the last days was the ‘Bride’; she was being prepared for the Bridegroom. This ‘feminization’ of the church by the Holy Spirit was a further affront to society and a warning to the church at large that God was doing a new thing. If the church was going to witness to all nations before the soon coming of the Lord, it appeared that the Spirit’s strategy was to enlist everyone—male and female—in the army. Again, a discerning reflection upon the living reality of the outpouring of the Spirit upon sons and daughters led the Pentecostals to see that the Scriptures concerning ‘silence’ of women in the church had to be reinterpreted. That reinterpretation had already begun in the Holiness movement, as in Phoebe Palmer’s The Promise of the Father,105 but was given fresh impetus in the new ‘Pentecostal reality’.
Eschatology and Coherence For Pentecostals, the Holy Spirit is the agent of the kingdom of God. Christ is the king or regent, and the Holy Spirit is the active reigning presence. It is the Spirit who makes Christ and the Father known. It is in the Spirit that believers are presented to the Father through Christ. The kingdom of God is already present, but not yet consummated. Unlike the dispensationalism of fundamentalism which draws a sharp line between Kingdom Age and Church Age, Pentecostals testified to and rejoiced in the inbreaking of the kingdom of God. Therefore the so-called sign gifts of the apostolic age had not disappeared. Augustine and subsequent dispensationalists had been wrong. With Wesley the Pentecostals affirmed that if the gifts had been withdrawn or were not as much in evidence, it was due not to a divine dispensational bracketing but to the fall of the church under Constantine and the love of many ‘waxing cold’. Pentecostals would have no problem with Barth’s assertion that God would once again bestow his signs and wonders wherever the Spirit is ‘sighed, cried and prayed for’.106 So when the Pentecostals spoke of restoration, it was not primarily a restoration of this or that outward characteristic of the early church, but primarily the apostolic power and expectancy. Indeed the transcendent presence of God among the people in an outpouring seen as the ‘restoration of Pentecost’ is that which gives coherence to the Pentecostal testimony, practice and affections. The Latter Rain restoration of Pentecostal power was for last-days evangelization. Their mission was to warn the church to repent, consecrate, put on the robes of white, and get oil in the lamp before the Bridegroom appeared. The everlasting gospel, the gospel of the kingdom was to be heralded by witnesses whose mouths had tasted the powers of the age to come and whose eyes had seen evidence of that power at work among them. It was urgent that men and women be called from darkness into light because the kingdom age was already dawning. Believers were to be entirely sanctified. With Wesley they could agree that faith in Jesus Christ ‘qualified’ them for heaven and entire sanctification made them ‘fit’ for heaven.107 If believers regarded iniquity in their hearts, they would not be ready for the Rapture and would go through the Great Tribulation. Furthermore, those resistances and hold-outs in their personal lives would hinder their receptivity to the Holy Spirit and they would be poor witnesses for the Lord. The ‘law of love’ required that believers wash their robes and make them white in the blood of the Lamb.
Willful refusal to do so could lead ultimately to one’s name being blotted out of the ‘Lamb’s book of life’. The baptism in the Holy Spirit was to be upon the sanctified life. The same Spirit who would resurrect the dead and rapture the Bride would fill every hungry, obedient seeker. This filling seemed to be a further step toward the realization of the resurrection hope in that yet more power was bestowed and one was ‘sealed’ and made ‘rapture ready’. Healing was in anticipation of the final healing of all things. The material was meant for the spiritual and vice-versa. Healing anticipated a millennial restoration of all things: heaven come to earth and no more sickness or sorrow. This longing for universal healing is expressed in the words of a popular gospel song ‘Our Lord’s Return to Earth’ (based on Acts 2.9-11): 1. I am watching for the coming of the glad millennial day, When our blessed Lord shall come and catch His waiting Bride away. O my heart is filled with rapture as I labor, watch and pray, For our Lord is coming back to earth again. 2. Jesus’ coming back will be the answer to earth’s sorrowing cry, For the knowledge of the Lord shall fill the earth and sea and sky; God shall take away all sickness and the sufferer’s tears will dry, When our Savior shall come back to earth again. 3. Yes, the ransomed of the Lord shall come to Zion then with joy, And in all His holy mountain nothing hurts or shall destroy; Perfect peace shall reign in every heart, and love without alloy After Jesus shall come back to earth again. 4. Then the sin and sorrow, pain and death of this dark world shall cease, In a glorious reign with Jesus of a thousand years of peace; All the earth is groaning, crying for that day of sweet release, For our Jesus to come back to earth again. CHORUS Oh! our Lord is coming back to earth again, Yes, our Lord is coming back to earth again; Satan will be bound a thousand years, we’ll have no tempter then, After Jesus shall come back to earth again.108
Already the Bride was being prepared; already hearts were filled with ‘rapture’ as they labored, watched and prayed. The saints ‘groaned’ with the Spirit and all the earth for the ‘day of sweet release’. Already, many sicknesses were being healed, sins forgiven, sorrower’s tears dried. The peace born in yielded hearts filled with love ‘without alloy’ was already reigning in believers. The faith, worldview, experience, and practice of Pentecostals were thoroughly eschatological. They lived within the tension of the already but not yet consummated kingdom. If the Holy Spirit was at the heart of this tension, He was also the bridge or bond between the ages. As was true for John Wesley, so too Pentecostals traveled in the Spirit forward or backward in time—back to Sinai, back to Calvary, back to Pentecost— forward to the Armageddon, the Great White Throne Judgment, the Marriage Supper of the Lamb. Time and space were fused and transcended in the Spirit, and at the heart of the testimony, expectation, and worship was Jesus the Savior, Sanctifier, Healer, Baptizer with the Spirit, and coming King. God the Father received all prodigals through Jesus in the Spirit. And then he sent them out in Jesus’ name and the power of the promised Spirit, to preach the gospel of Christ to all nations … and then would be the end. Taking due account of this eschatological context renders the spirituality comprehensible and useful for analysis and revision.
An Overview The thesis of this study will be developed in two interrelated chapters. First, taking into account the theoretical, historical, and personal concerns of Chapter 1, the distinctive blend of narrative beliefs and worship-witness practices is analyzed in Chapter 2, as the ethos of Pentecostal spirituality is displayed. It is argued that the ‘already–not yet’ tension characteristic of the eschatological vision is decisively important for understanding the shape and power of this spirituality. The heart or integrating center of the spirituality is located in the affections. Chapter 3 attempts to show how three essential affections—gratitude as praisethanksgiving, compassion as love-longing, and courage as confidence-hope—are ingredient in the Pentecostal understanding and experience of salvation, worship, witness, and, most importantly, prayer. These affections operate by a certain ‘grammar’ and exist in a reciprocally conditioning mode with the beliefs and practices. They may be legitimately termed ‘apocalyptic affections’ since they are constituted by the distinctive eschatological reality and vision of Pentecostals. Having displayed these central beliefs, practices, and affections, Chapter 4 offers a re-vision of Pentecostal spirituality which remains in continuity with the original spirituality of the movement. Certain internal tensions and external criticisms are noted and briefly responded to in the light of the development in the foregoing chapters. These tensions and criticisms also serve as part of the motivation for the re-vision. The construction offered seeks to ground a vision of the Christian life, history, church and mission in an explicitly Trinitarian spirituality which is historically consistent, in keeping with the roots of the movement, internally healing of some of the major divisions, ecumenically responsive, and missionally deepened. Thus the structure of this monograph moves from a distinctive formulation of spirituality and the theological task I have just articulated to an analysis of the constitutive beliefs and practices in Chapter 2, to the integration of the beliefs and practices in the affections in Chapter 3, and finally, to a revision of the spirituality using a Trinitarian hermeneutic in Chapter 4.
Chapter 2
Pentecostal Theology as Apocalyptic Vision: A Narrative-Praxis Analysis Early Pentecostals understood the outpourings of the Spirit in the first century at Pentecost and at the inception of the twentieth-century Pentecostal movement as the fulfillment of divine promises, especially Joel’s prophecy concerning the last days.109 In these instances the fulfillment contained at the same time an ‘overflow’ of promise yet to be fulfilled, and, on both occasions, the interpretation of the event was the proclamation of the gospel which was at once about Jesus and the end. Pentecostalism’s reason for existence was the carrying out of a last-days, global, missionary mandate by those who were Christ-like witnesses in the power of the Holy Spirit. The kingdom of God was at work among God’s people, and the evidence was much the same in the twentieth as in the first century. The wonders and gifts of the Holy Spirit in the ministry of Jesus were being repeated,110 but these were not the only signs observed by the early Pentecostals. The following early exhortation and song indicate the ‘signs of the times’ and the appropriate response: The Lord’s coming is no doubt drawing near. Many signs are now being seen which are in perfect accord with the prophecy of Scripture, but two signs are indeed prevalent just now, and can be noticed by anyone who is on the look out. The love of many is waxing cold because iniquity is abounding. Mt. 25.12.
By actions, if not by words, many are saying, ‘My Lord delayeth His coming.’ Lk. 12.45. In their testimonies they used to express themselves with a glow of heavenly luster beaming forth from their countenance, that they believed Jesus was coming so soon, and were so happy because they felt they were ready to meet Him. Today many of these same voices are silent on that line; Wake up, loved ones, your Lord will come while you are sleeping, if you do not stir yourselves and watch. He will come at an hour that you think not. Come! Awake! Be Ready! You can be ready if you will. Stir up the gift that is in you, by prayer and fasting if needs be, and testimony and praise, until you are all aglow and overflowing with His love again.
No matter what the rest may do, no matter what they say, Keep the fire burning in your soul, fire up! Be true to God, and He’ll reward you at the judgment day, Keep the fire burning in your soul, fire up!
And when your heart is growing cold, you’ll need to fire up. Keep the fire burning in your soul, fire up! Just tarry in the upper room until your heart is stirred, 111 Keep the fire burning in your soul, fire up!
The urgent fervency issuing from the apocalyptic vision of Pentecostals is evidenced by a worship and witness which is crucially dependent upon the witness of the Spirit and therefore constantly concerned with the presence and parousia of Jesus Christ. Though Pentecostalism is often written off as mere emotionalism or an experience safely transplanted into various Christian gardens, this chapter shows the distinctive logic of Pentecostal beliefs and practices as they both express and confirm the apocalyptic reality which did and still does suffuse and inform the corporate life of the community. After a consideration of the original apocalyptic vision and the threefold Pentecostal experience, this spirituality will be examined more analytically by means of four formal categories. Testimonies, songs, articles, pamphlets, and books will be woven into the fabric of this running narrative-praxis account.
Pentecostal Presence: The Inbreaking of the Spirit in the Last Days God, who is spirit, is present in triune fellowship by virtue of the activity of the Holy Spirit in and among the believers. The ‘natural’ person cannot know, love 112 or follow God. It is the spiritually responsive person who can walk in the light, walk in love, and walk in the power of the Spirit as a witness. It is the Spirit who 113 brings the Son and the Father to abide in the believer. The church is made a habitation of God through the Spirit.114 By the Spirit the believers taste the powers of the age to come115 and receive the down payment or pledge of the promised redemption.116 The Spirit is the effective reigning power and sovereign 117 agent of the kingdom whose king is Jesus. The Spirit is the ‘finger of God’ who drives out demons, cleanses lepers, and empowers gospel proclamation.118 According to the early Pentecostals, it was this concrete, visible work of the Holy Spirit in worship and witness which was being received in these last days.
Apostolic Faith: Recovering the Eschatological Vision Pentecostals referred to themselves as an apostolic faith movement due to their desire to recover for the present age the faith and the power of the apostolic church. Paradoxically, it was this primitivistic, backward-looking concern with the early church which was responsible for their passion for the coming of Christ. For them a restoration of primitive faith was a prelude to the restoration of all things. They exhibited three kinds of primitivism, two of which were carried over from the nineteenth century. Their ecclesiastical primitivism led them to be suspicious of ‘man made’ creeds and institutions. Their ethical primitivism called them to an all-consuming passion for holiness. God’s people, the Bride of Christ must wash their robes and make them white in the blood of the Lamb. But it was the experiential primitivism which catalyzed the other two and directed everything toward the soon coming of the Lord. Believers today, they reasoned, can, should, and must evidence the same longing and power as the first Christians, if they are to be in eschatological continuity with the beginning and end of the church of Pentecost. To recover the apostolic faith meant to live in expectation of the coming of Christ in the time of the Latter Rain.
Thus, the outpouring of the Spirit at Pentecost constituted the church as an eschatological community of universal mission in the power and demonstration of the Spirit.119 The tongues at Pentecost and Peter’s subsequent sermon meant that the church in general and each Spirit-filled individual are to be and to give a witness to the mighty acts of God in saving humanity. This witness centers in Jesus Christ and must therefore be given in the power of the Spirit if it is to have continuity with his ministry and fulfill the promise of the Father through Christ. The ‘full gospel’ of the Jesus who is Savior, Sanctifier, Healer, Baptizer in the Holy Spirit, and coming King can and should be proclaimed in the fullness of the Spirit so that the kingdom will be manifested in the midst of the world in words and deeds. When men and women came into Pentecostal services and experienced this eschatological power, this restoration of the apostolic age, they saw the Scriptures, themselves, and the world differently: the resurrection of Jesus as their own resurrection, the first Pentecost as their own ‘Pentecost’, the crucifixion of Jesus as their own crucifixion. All these events were telescoped, fused, and illumined by the expectation that became the message of the entire Pentecostal movement: ‘Jesus is coming soon!’ And how did they know that this outpouring of the Spirit was the Latter Rain, the sign of the imminent arrival of the king? Because they, like those with Peter in Cornelius’s household, heard them speak with other tongues.120 Signs and wonders, even outbreaks of tongues, had occurred throughout history but never as part of such a large-scale restoration of apostolic faith and power. Outsiders focused quickly on the tongues as indicative of a whole movement of irrational, revivalistic, hysterical protest by the disinherited and illiterate. If it was not evidence of demonization, which some fundamentalists still maintain, then it was at best, proof of derangement. The reactions of those who came into direct contact with the movement went from one extreme to the other—from the ‘last vomit of Satan’ to regressive gibberish.121 But this eschatological key, this apocalyptic revelatory experience, was seen by the Pentecostals as the driving force and galvanizing vision of the entire movement. This is beginning to be appreciated today outside the movement. In addition to the massive, carefully crafted, and overwhelmingly persuasive dissertation of William Faupel,122 there are those like the Dominican John Orme Mills who understand that what made the Pentecostal revival in the United States at the beginning of
this century important; what set it against the world and much contemporary religious practice as if it were something startlingly new, something that could transform men’s lives, was not (to take the most obvious example) that people ‘spoke in tongues’. After all, if considered apart from its Christian context; speaking in tongues is not a particularly interesting or unusual phenomenon, let alone something to astonish or disconcert the Christian world.
No, what was arresting about those first twentieth-century Pentecostals was their conviction (a conviction tongue-speaking and the other gifts they had been given irrefutably confirmed, in their opinion) that the new pouring-out of God’s Holy Spirit on them had empowered them to share fully the life of the church of the apostles, the ‘church of Pentecost’. And—so alive was their vision of the New Testament church—this meant that they experienced a fresh, urgent sense of expectation which they could identify with that known by the first generation of Christians. The charismatic manifestations emerging among them—tongues, healing, exorcism, prophecy—they interpreted as signs that they were bringing in the ‘last times’. The Scriptures were being fulfilled: here was the ‘latter rain’ spoken of by Joel and James, portending the coming of the Lord in glory at the world’s end. Is it surprising then, that they had such confidence, such hope? Were they not already seeing around them indications that all things were being made new, as told in the book of Revelation?123
Although Mills may not assign as much significance to the sign of tongues as some early Pentecostals, he nevertheless is on the opposite side from those observers and commentators who classify this as a ‘tongues-movement’. It is only within the gestalt of the apocalyptic narrative, the narrative of which the Pentecostals now saw themselves as being a significant part, that the meaning of the spirituality can be known. To locate the theological center of Pentecostalism in Spirit baptism, as Bruner does,124 or to see tongues as the only thing that distinguishes the spirituality from that of the Holiness or evangelical movements is to miss the point altogether. It is the eschatological shift within the Holiness movement toward premillennialism that signals what is decisive. Dayton and Faupel have described this shift; however it is crucial to note that this is not a shift away from Christ to the Spirit, from love to power, or from gradual to instantaneous change of persons and society.125 These realities are more fused together than split apart or even prioritized. It is an infusion—because of the Spirit’s effusion—of apocalyptic vision and power which alters the way in which
Christ, church, the Christian life, and change are seen. As Käsemann said of ‘all Christian theology’ so it can be said of Pentecostal theology, ‘Apocalyptic was the mother …’126 Pentecostals were adopted by and adopted this ‘mother’ and became sons and daughters, prophets and prophetesses of a new order of the Latter Rain of the Spirit. The social deprivation and functional adaptation to psychosocial strain models of analysis, used to great and informative advantage by someone like Robert Mapes Anderson (Vision of the Disinherited: The Making of American Pentecostalism), tell only the most obvious and superficially interesting part of the story. Grant Wacker, in reviewing Anderson’s book, underscores the point made here as to the importance of apocalyptic discontinuity for understanding the pneumatic continuity of the Pentecostals with the early church. He asserts, Long after the computers have shut down and the behavioral scientists have gone home, the real work of the ‘new’ social historian remains to be done: somehow to understand the dialectic between social forms and the private lives inside. This means, among other things, that the historian who seeks to untangle the origins of a religious movement like Pentecostalism is charged with the task of showing how plain men and women, locked into a particular position in the social system, paradoxically invested their lives with significance by discerning chaos in order as well as the reverse. It may well turn out that the enduring significance of the vision of the disinherited is that it flourished precisely because it was so desperately out of step with the times …127 They would have said that the movement flourished because it afforded an exhilarating vision that life on earth could be a foretaste of heaven. And a warning of the wrath to come.128 The outpouring of the Spirit in the post-Easter community created and sustained that eschatological tension and vision which characterized the early church and the early Pentecostals. Now everything was considered from the standpoint of the imminent parousia. In the transcendent presence of God categories of time and space were fused; and, since Jesus was near, so was the end. The Spirit who raised Jesus, made him present in salvation, signs and wonders and showed things to come. The Spirit who burned as intense hope and energized witness superintended the ongoing mission. To live in the Spirit was to live in the kingdom. Where the Spirit was present in eschatological power, there was the church of Pentecost. In concluding his treatise on The Spirit and the
Bride, G.F. Taylor offered the following advice to those who wanted to be equipped for service and ready for the appearance of the Bridegroom: While you may be greatly helped by following these directions, yet you must avoid all formality. You cannot bring God down to any special form in any matter. The best advice after all is, Get in the Spirit, stay in the Spirit, 129 and follow the Spirit at any cost. This means that eschatology (and especially the apocalyptic vision) is neither an introduction nor a postscript to theology but a constituent part of the whole. It is ‘a conceptualization which is prescribed by Jesus’ proclamation of the kingdom and his appearances after the resurrection’.130 It is an apocalypticism which ‘begins with the special, contingent history of Jesus Christ, the resurrection of the crucified and his Easter appearances, and aims at the universal deity of this God. It inquires after the future of God and proclaims his 131 coming in proclaiming Christ’. In his recent work, Holiness in Israel, John Gammie has found that the apocalyptic writers catch up the themes of the priests, prophets and sages, but integrate them into their own eschatological concerns.132 The holiness of God as well as the end itself is not capable of being co-opted or manipulated by the present. But this very distance creates a new history, new possibilities that are announced, and moved forward by God and those who live in the divine Spirit by the Word.
Apocalyptic Faith: Living in the Last Days
Just as Pentecost was added to the teachings of Jesus in the experience of the early church, the baptism in the Holy Spirit was added to the fourfold gospel (Jesus as Savior, Sanctifier, Healer, coming King) of the Holiness movement. The baptism in the Spirit was a break, a discontinuity, a definite definable, ineffable turning point in the history of the church and the early Pentecostals. It was a break that signaled God’s intervention in and sufficiency for the missionary task of announcing the gospel of the kingdom to all nations before the end. This meant that the nexus of socio-political cause and effect, of demonic and even religious opposition and hindrances—none of this could stop the fulfillment of God’s plan. This gave a new sense of hope to each believer. It was the Father’s will to give them the kingdom.133 This hope would keep them pure, utterly sincere, and
devoted to the mission. The outpouring of the Spirit made them primary and not secondary witnesses of the risen Lord. They could say what they had seen and heard concerning the ongoing work of Jesus Christ to save, to heal, to deliver, and so forth. Hope is not given by and in and for the present world order that is passing away. This does not mean they demeaned this world. It was a hope which had continuity—a new body, a new earth, a new heaven. But this hope was at the same time discontinuous because it is new—a new creation. With one foot in creation and the other in the age to come, the Pentecostals hoped for the salvation of the lost and longed for Jesus to come. His coming was imminent, but no date could be set. Everyday life and events became invested with cosmic significance because God was at work in all things. There were not many adiaphora for Pentecostals; indeed this was not a time for silly, foolish jesting or taking chances with the ways of the world. The Lord was near. The holiness practices and restrictions from the nineteenth century were retained by most North American Pentecostals for almost half a century. Even today they remain conservative on most issues, though of course now that certain luxuries are more affordable they are not seen as quite the compromise with the world that they once were.134 However, with regard to the sense of break, a new hope and the awareness of being involved in a cosmic struggle with powers and principalities—in all these respects Pentecostalism lived and lives in an apocalyptic existence made existentially palpable by the 135 presence, manifestations and power of the Holy Spirit. This longing for the Lord to come, for the Holy Spirit and for the kingdom of God are part of the same thing: it is one passion. And for Pentecostals it is a passion that can change everything. The baptism in the Holy Spirit was the gateway into this eschatologically oriented vocation of witness. Entrance through that gateway might be very forceful, as in the case of universityeducated N.J. Holmes, or very gentle, as in the case of Joseph H. King, one of the early leaders of the Pentecostal Holiness Church. Holmes reports that he fasted for three days, without eating or drinking anything … At times everything was dark, so dark that everything in my experience seemed to go away … One night as my heart was going up for the Holy Ghost, it seemed that the whole room was filling with a mist of heaven, and my whole body was being permeated by it. And a great roll of mist above my head as a waterfall … I felt my tongue slightly moving up and down, the motion growing stronger and stronger. I was conscious that it was not I, that did it, and I was sure it was the Holy Ghost, and immediately my teeth began to
chatter without my effort or control … I recognized the presence and power of the Holy Ghost in all this, and as soon as I discovered the control of my mouth I testified and praised God for Pentecost.136 Holmes’s journey from Presbyterianism to the Holiness movement to Pentecostalism is fascinating in itself, but what is really significant for our purposes is the intense longing for God and the deep satisfaction that obtained when he was visited with his ‘Pentecost’. Changes of denomination were common and so it is no surprise that creeds were not given ultimate authority (a misunderstanding of creeds to be sure). The point, however, is that the coming of the Spirit was so definite and so deep that any change was possible if necessary to obtain the blessing, the equipment, the ‘Pentecost’. Some were like the Methodist minister in Kansas who objected that Pentecostals failed to keep ‘the niggers in their place’. But before he could have his baptism in the Spirit he had to wade through a whole camp meeting made up of mostly African-Americans. He subsequently testified. ‘God surely broke me over the wheel of my prejudice’.137 Continuity with one’s racial, cultural, and/or denominational identity might be disrupted and altered by the discontinuous Spirit baptism. In establishing experiential, pneumatic continuity with the first-century church of Pentecost, one was forced to consider conformity with the church of the end, the holy Bride made up of all races, tongues and nationalities. The early Pentecostals, though noting previous revivals of the Spirit and charismatic manifestations throughout history, did not do so to establish or to legitimate their practice. Rather Pentecostals leap the intervening years crying, ‘Back to Pentecost’ … They do not recognize a doctrine or custom as authoritative unless it can be traced to that primal source of church institution, the Lord and His apostles … If we can so order our lives that they shall fit the New Testament, we care no more for a lack of evidence that the majority of professors of religion did so in the past than we do for the overwhelming evidence that the majority of them are not doing so today.138 In this passage B.F. Lawrence, a Pentecostal pioneer, illustrates what some have called the ahistorical character of the movement—or a desire to leap the ages back to Pentecost. But seen in another way it is a prophetic concern to return to the root, the original covenant, as the prophets of Israel were constantly saying to the religious establishment of their day. The future can only become the promise of God if there is first a word, an apocalyptic convincing of sin,
righteousness and judgment, which gives voice to and makes a space for the cry of the dispossessed, the languishing mass who feel removed from the immediacy of God and victimized by cultural and ecclesiastical forces which tend to shut down their historical process.139 A relativizing of the establishment and its processes is necessary in order to break through, to give voice to the pain of those longing for God and the world that is lost. For thousands of the participants in the more radical Holiness groups, being born again, and receiving a sanctifying filling of love intensified this longing. Back to Pentecost meant back to the Holy Spirit and then forward to the future that God will give soon—not the product of the predict-and-control technology from the culture of evolutionary optimism, critical realism, and ‘embourgeoised’ elitism. The Pentecostals were committed to the fundamental beliefs of Christianity but, in the words of B.F. Lawrence again, were laboring to obtain that supernatural character of religion which was so preeminently a mark of it in the old days. We do not mean to say that others who believe in the new birth have wholly lost this but we desire a return to New Testament power and custom along all those lines of activity which made evident beyond controversy that the church was the living body of a living Christ. We believe that healing for the body, expulsion of demons, speaking in other tongues, were in early times the result of an activity of the Holy Spirit in direct harmony with, nay, stronger still, a direct result of the divine attitude toward the church and world. Further, we hold that this attitude was the only one consistent with the divine nature. If this is true, then with the writer of the Letter to the Hebrews we say. ‘Jesus Christ, the same yesterday, today and forever,’ and expect the immutable nature to maintain an unchanged attitude accompanied by the same glorious results.140 God had not changed. The promises were for the children and the children’s children—as many as God would call.141 The recovery of Pentecostal power—a definite, visible historical occurrence—was a fulfillment of the promise of the Father which was necessary to carry out the global missionary mandate of the church. That having been accomplished and all the nations having heard the gospel in power and demonstration of the Spirit, the promised coming of the King of Kings to catch away the Bride could occur. Pentecostals, to repeat an emphasis of Chapter 1 and the beginning of this chapter, were people of the promise. Of course the Holiness movement of the nineteenth century had also spoken much of the promise of the Father. But for
Pentecostals the fulfillment of the Pentecostal promise in visible, concrete, global manifestations announced something new that God was doing and about to do. It gave a sense of history and directedness to individual lives. The present was passing away, the future was expected, sought, and anticipated. The kingdom of righteousness, peace, and joy in the Holy Spirit was already at work and soon to be consummated. Thus the present was to be lived in hope, obedience, and holiness. God, who has not changed, will keep the divine promises and give surprises, representations, intimations, glimpses of the future along the way through gifts of the Spirit. Each time a believer was filled with the Spirit, each time the power fell in a new assembly or country, history drew nearer its proper end. The church, the individual, the family—everything had to change in light of the new direction, impetus, and focus. This end had begun with the life, death, and resurrection of Jesus. Though elements of apocalyptic faith had been restored after the fall of the church in the Constantinian era, now, with the recovery of the universal ‘prophethood’ and witness of all believers, the restoration of apostolic gifts and power, and the baptism of the Spirit ‘upon the sanctified life’,142 all was in place for the total mobilization of the church. History became mission, and the church was constituted a missionary movement. Believers were agents, not victims; they were harbingers of the coming kingdom. The Bride did not simply wait in the church for the Bridegroom; she went out to invite others to the marriage supper for which each worship service was a rehearsal and anticipation. The historical event of the twentieth-century restoration of Pentecost and the reality of the not yet fully consummated kingdom of God were united in category of promise. The promised Spirit, the promised kingdom, the promised filling with the Holy Spirit, the promised gifts, all these were promises believed and received by the Pentecostals. By believing these promises the believer became a partaker of God’s nature, a citizen of the present and coming kingdom, and a participant in a world-historical process whose end was assured, because God was working in all things for good. This was no occasion for resignation in the face of the ‘fate of God’. Rather one must now walk in the light, walk in love, walk in the power of the Spirit, if one was to walk with God. The kingdom that was coming was one of righteousness, perfect love, fullness of joy in the Holy Spirit, healing for the nations, and a final victory over death and Satan. To believe in that kingdom was to walk according to the nature, will and goal of the king. Salvation was participation in the life of God through transformations by grace through faith.
History was God’s story and each person had a part to play, a gift to offer, a witness to give. There was something of what Moltmann describes as ‘good apocalyptic’, that is a ‘historifying of the world’ and a ‘universalizing of history’.143 But if there was this ‘good apocalyptic’ there was also the ‘bad’ kind. At times, persons who had been so used to being passive would lapse into the view of prophecy as fate. They would see God as only over against the world, especially during times of cultural rejection and persecution. Failing to see prophecy in its historical context they would sometimes develop highly speculative, individualized and fantastic concrete applications which thrilled but did not mobilize. To the extent that they saw themselves as fundamentalist conservatives, as over against the modernist liberals, they forfeited much of the nineteenth-century Holiness birthright of ‘spreading scriptural holiness throughout the land’.144 Soup kitchens, orphanages, rescue missions, and so on were all employed, but the broader societal, global, and cosmic dimensions of the kingdom were limited to one thing: the preaching of the gospel to all nations. Initially the realization of apocalyptic spirituality gave a sense of belonging, dignity and power to many who had seen themselves as victims. Although all Pentecostals fall into the category of the oppressed, many, perhaps most, were from among the poor. Yet the majority of those poor who heard the Pentecostal message did not accept it. Thus, social location cannot adequately account for the movement or the motivation of those who became participants then or more recently. But what is not at issue is that for early Pentecostals the church was to be a witness in the power of the Spirit in the last days. They were a people hungry for God and filled with premillennial expectancy. Today, upward social mobility is clearly affecting the apocalyptic fervor and urgency as the world looks a little better to contemporary, more affluent North American Pentecostals. They often have a guilty conscience and struggle with their roots.145 The early eschatological expectancy and fervent witness activity are seen more nearly in its pristine state among the burgeoning Third World Pentecostals. They, as the early Pentecostals, keep ‘fired up’ by means of the narratives and practices which each missionary fellowship employs to explain and demonstrate the kingdom of God in its worship and witness.
Pentecostal Narratives: Participating in the Story of God
The Biblical Drama and the Christian Life
On the first day of Pentecost, worship and witness marked the entrance of the church, and thus each believer, into a new phase of the salvation-history drama of redemption. Peter’s address to the multitudes who rush together questioning the meaning of this event reveals—in a ‘this is that’ specification—that this is a specific fulfillment of biblical prophecy requiring obedience to the gospel of Jesus Christ. It is confirmation of the exaltation of the risen Lord and an anticipation of his parousia. The promises of the coming of the Spirit and the coming again of the Savior are part of the one promise of God to redeem his 146 creation. On the day of Pentecost Peter announced—in the city where Jesus had been crucified, a city dominated by Rome, the city where he had denied Jesus—that a new chapter was being written. Crucifixion, resurrection, Pentecost, parousia, all formed one great redemption, one story in which they were participants with assigned roles to play. Pentecost meant that the victory witnessed in the resurrection of the crucified one and the promised parousia would not simply be told by those who wait passively for the soon coming of the Lord. No, the power of the age to come was being poured out upon the church for the accomplishment of a universal proclama-tion of the particular redemption in Jesus Christ, a proclamation in word and power and demonstration of the Spirit. The early Pentecostals saw themselves as recovering and re-entering that Pentecostal reality. The vivid presence of the Spirit heightened expectation, propelled into mission, enlivened worship, and increased consecration in preparation for the appearance of the Lord of the harvest. No one could take for granted her or his place at the marriage supper of the Lamb. The wise virgins would have oil in their lamps, would be filled with the Spirit, watching, waiting, working for the Bridegroom.147 The paradox of expecting a sudden event and not knowing when it would occur—waiting in readiness and indeterminacy—was paralleled by the vigorous activity in worship and witness (preparing the saints and the world for his coming) and the abiding rest of the saints.148 Watching and
at rest, witnessing and worshiping, seeking the Lord and waiting on the Lord, these were the rhythms of the early revival. And all of this made sense in the light of what God had done, was doing, and would finish. This story of redemption in the Spirit made sense of the ‘ups and downs’ of the daily life of the participants. In the Spirit they walked with the children of Israel, the prophets, the apostles, and early church believers. In the Spirit they anticipated the great marriage supper of the Lamb at the last day. In the Spirit the blessings and trials of each day were interpreted as part of the one story of redemption. Thus, by interpreting their daily life and worship in terms of the significant events of biblical history, their own lives and actions were given significance. Everybody became a witness to Calvary and his or her own crucifixion with Christ, the biblical Pentecost and a personal Pentecost, the healings of the disciples and his or her own healing and so on. The singing reflected this idea of the present normativity of biblical events and therefore, for that very reason, the necessity of existential appropriation and participation. At the Cross, At the Cross Where I first saw the light And the burdens of my heart rolled away. It was there by faith, I received my sight, 149 And now I am happy all the day. Thus for them Calvary was not only a specific historical event but also a testimony and focus for daily life. From the blood of Christ’s atonement, as it was said over and over, all benefits flow. These benefits of complete redemption were already present as promise, type, and shadow in the Old Testament The Apostolic Faith in September of 1907 proclaimed the ‘Old Testament Feasts Fulfilled In Our Souls Today’: All through the Old Testament we read of the feasts that God appointed to be kept in the worship to Him. There were four feasts: the Passover Feast, Feast of First Fruits, Feast of Pentecost (or Feast of Weeks), and Feast of Tabernacles. They all typify what we get through the cross now, justification, sanctification, the baptism with the Holy Ghost, and then a continual feast Together they typify a complete redemption.150 For those early Pentecostals to abide in the Word, was simultaneously to abide in Jesus and the written Word. Seymour stated that ‘as long as you live in the Word of God, He will always be present’.151 The redemption events live in the
believers and the believers live in them, because they are in Christ and Christ is in them by the power of the Spirit. The Bible as Spirit-Word is the light that shines upon the path illuminating the journey of life as salvation and mission. The Bible was and is inspired. In the community of worship and witness, of praise and proclamation, the Word is written, living and preached. But it is not so much a textbook of propositions as it is the story of redemption in Christ by the Holy Spirit and the journey in the Spirit through Christ to the Father. The doctrines of verbal inspiration and infallibility are precipitants of a spirituality which practiced a much fuller doctrine of the Word of God. To abide in the Word was to use it as the norm for evaluating beliefs and practice. As they dealt with fanaticism and speculation there was a strong emphasis on sticking to the biblical story: if it was not in Scripture, then it should not be enacted. This did not mean that there was no daily specific guidance for the church and individuals from the Holy Spirit. It did mean that Scripture would provide the means to test and direct that guidance and provide boundaries. New experiences would often be the occasion for finding new insights into Scripture. Familiar Scriptures would take on a new meaning. But the beliefs, affections, and practices would all have to be tested by the Word. Thus, the point of Pentecostal spirituality was not to have an experience or several experiences, though they spoke of discrete experiences. The point was to experience life as part of a biblical drama of participation in God’s history. The church was a movement from the outer court to the inner court to the holy of holies, from Egypt through the desert across the Jordan into Canaan, from Jerusalem to Judaea, Samaria and the end of the age (and the uttermost parts of the earth), from justification to sanctification to Spirit baptism, and then in justification, sanctification, and Spirit baptism into the harvest. Whether it was couched in terms of biblical dispensations, discrete personal experiences, or missionary travels, all of this language was meant to speak of the mighty acts of God’s story of redemption in Scripture, in their lives and in the world. It was one seamless fabric. In fact, obedient participation in the story was something like a robe of righteousness worn by the saints who would one day walk with Christ in glory, because they walked with him in service now. Thus their concern was not so much with an ordo salutis as a via salutis. The narrative of salvation provided the structure for formation within the missionary movement. The whole congregation was involved in the process of formation. The singing, preaching, witnessing, testifying, ordinances (baptism, Lord’s Supper,
foot washing),152 altar calls, prayer meetings, gifts of the Spirit—all the elements of corporate worship—prepar-ed people for and called them to new birth, sanctification, Spirit baptism, and a life of missionary witness. These ways of remembering the biblical Word mediated the biblical realities in a kind of Pentecostal sacramentality153 in which there was a constant, mutually conditioning interplay between knowledge and lived experience, ‘where learning about God and directly experiencing God perpetually inform and depend upon one another’. 154 This way of knowing, of forming Pentecostal witnesses, is seen in the Old Testament word for knowledge, (yada), which points beyond the ‘conceptualization of an object’ to the ‘actualization of a relationship’.155 This is why yada is used for marital lovemaking (e.g. Gen. 4.1) and covenantal intimacy (e.g. Jer. 1.5; 22.16; 31.34).156 The force and power with which this often occurred in Pentecostal services indicated that transformation, not mere information, was the goal of the process. Worship was a crisis encounter, an event of meeting with the living God which precipitated certain crises in the life of the believer according to where she or he was in their salvation journey. These crises in the life of the believer flowed from the redemptive accomplishment of Jesus Christ toward the parousia and consummation of the kingdom of God. When Jesus said on the cross, ‘It is finished’, he did not mean that everything that needed to be done by God or believers was over. The ‘finished work of Calvary’ was the completion of his earthly life, teaching, and sacrificial offering. The mission of the Spirit moved within and from that life offering but had its own sovereign purpose. This view is opposed to some more Reformed views which in effect see the ‘finished work of Calvary’ as an accomplished fact whose benefits are applied through personal identification with Christ. This too is an event but not a particularly transforming one and certainly not one which presses toward the kingdom. Though the earliest Pentecostals certainly understood the meaning of imputation and justification, they were more concerned with the impartation of righteousness and sanctification, the transformation of lives and the empowered mobilization of the church. The emphasis of salvation was not so much on ‘standing’ as it was on ‘movement’. It was not primarily a matter of identification with Christ but of conformity to him. It was not so much a ‘position’ as a ‘participation’. This was a direct result of the eighteenth-century Wesleyan perspective which, although diluted and distorted somewhat in its nineteenth-century American adaptations, nevertheless retained the Arminian
sense of personal agency and responsibility (‘respondability’).157 The journey toward God was a journey with God in God. It was walking toward the Father with Jesus in the Spirit. But this journey was also fundamentally a journey into God: a kind of mystical, ascetical journey which was ingredient in knowing God and going further, deeper, and higher. To know God was to be directed by God’s will, motivated by God’s love, and strengthened by God’s power. As Jesus had come to do the will of the Father, so the believer was sent to fulfill righteousness. The point was not only to be declared righteous, pardoned, and forgiven initially in new birth and, thereafter, each day; the point was also and simultaneously to declare for righteousness. The Father drew believers to himself through Jesus by the Spirit. But he drew them in order to set them on the path of righteousness and life, and off the path of sin and death. They must turn, be born again, and set out on the path. There was constant mention among early Pentecostals of the importance of walking in all the light you had. Other believers (non-Pentecostals) would not be condemned, because they were walking in all the light they had. They would, of course, miss the full blessings of Pentecost; but they were, nevertheless, Christians. Some felt that though they may not go in the Rapture because they did not have the seal of the Spirit in his infilling; nevertheless, they could come through the Tribulation through faith in Jesus. There was a great inconsistency in the polemical point being made here. The struggle is evidenced in Seymour who, while teaching the necessity of Spirit baptism in order to be a part of the raptured Bride of Christ, also counseled Pentecostals who were tempted to pride and abuse toward other believers in the following manner: You cannot win people by abusing their church or pastor. As long as you preach Christ, you feed souls; but as soon as you jump on the preacher, you grieve the Spirit … but if you get to preaching against churches, you will find that sweet spirit of Christ that envieth not, vaunteth not itself, is not puffed up, thinketh no evil, suffereth long and is kind, is lacking and a harsh judging spirit takes its place. If you feed them from Christ, you will find the same Spirit burning in their hearts. The main thing is, Are you in Christ? The churches are not to be blamed for divisions. People were hunting for light. They built up denominations, because they did not know a better way … we do not have time to preach anything else but Christ. The Holy Spirit has not time to magnify anything
but the Blood of our Lord Jesus Christ. Standing between the living and the dead, we need to so bear the dying body of our Lord, that people will only see Christ in us, and never get a chance to see self. We are simply a voice shouting, ‘Behold the Lamb of God!’ When we commence shouting something else, then Christ will die in us …
When people run out of the love of God, they get to preaching something else; preaching dress, and meats, and doctrines of men, and preaching against churches. All these denominations are our brethren. The Spirit is not going to drive them out and send them to hell. We are to recognize every man that honors the Blood. So let us seek peace and not confusion. We that have the truth should handle it very carefully. The moment we feel we have all the truth or more than anyone else, we will drop.158
Seymour, then, urged a concentration upon Christ and indicated that persons were responsible for the light they had. The ‘lighted pathway’ of early Pentecostals was the ‘highway of holiness’ whose road signs were clearly marked on the testimony maps so that new sojourners would know the way. These signs were stages or steps which referred to the ‘experiences’ which were to be expected and which in their cumulative and interacting complexity constituted ‘the Pentecostal experience’. The observation is made often by insiders and outsiders that Pentecostals crave personal experience; and, paralleling this either implicitly or explicitly, is the acknowledgment of the centrality of the presence of God in Pentecostal worship.159 The word ‘experience’ is used with varying degrees of care, sometimes referring to no more than certain transient feelings which finally issue in a kind of emotional catharsis. At best it refers to the importance of the living God among his people, and some today are saying that Pentecostalism’s main contribution lies in the recognition of a certain charismatic dimension or vocational enablement to enhance what is already there160 or a release of the graces implanted in baptismal initiation.161 Whatever terminology for these experiences is used, for Pentecostals the category of crisis is important. There is a parallel between the view of the end as a crisis ushering in a new heaven and earth and a view of the Christian life as a series of crises. New birth, sanctification, Spirit filling, healings, prophecies, calls to ministry, all are definite crises or interventions of God; all are present manifestations of the life of the coming kingdom. Of course each crisis exists in some continuity with what has gone before and, most especially, with the
eschatological goal of all things. Nevertheless, it is also true that the crisis often makes possible new and/or supplemental insights into the past, new expectations for the future and, hence, a new present self-understanding. This eschatology is in contrast to that of a traditional fundamentalist dispensationalist who, in agreement with Augustine, Warfield and others, believed that the gifts of the Spirit, the so-called ‘sign gifts’, were limited to the Apostolic era. This dispensational bracketing means that one is now in the ‘church age’ where there is a definite division between the church and the kingdom, between Sermon on the Mount kingdom passages of Scripture and Pauline prescriptions for the church, and between this age and the one to come. For strict dispensational fundamentalists one age cannot interpenetrate another. But for Pentecostals the lines of distinction are drawn differently. Though influenced by Scofieldian dispensationalism, they put a different twist on it.162 Many Pentecostals operated out of three dispensations, instead of seven or twelve; that is, they saw an age of the Father, one of the Son, and one of the Holy Spirit. These three ages roughly corresponded to the history of Israel, the life, ministry, death, resurrection and ascension of Jesus, and Pentecost as the beginning of the present age of the Spirit. There was overlap and interpenetration of these dispensations, and there was a kind of progressive, logical development. The stories told (testimonies) about this development provided continuity not only with what had gone before but, most especially, with the future apocalypse. Indeed the entire unfolding of events, as was sometimes graphically unfolded in thirty-foot-long and seven-foot-high charts in sanctuaries throughout the world, was one continuous process of divine revelation. The last book in the Bible, the Revelation, provided a perspective with which to look back at the whole in much the same way as knowing the last chapter in a mystery novel allows one to read each previous chapter differently. Much mystery remained, but in the end God, a God of righteous love and power, prevailed along with all those who were right with him, loved him, and lived out of his power, while the Beast, False Prophet, and Antichrist were defeated. The spirits associated with these eschatological figures were and are already at work and representations or anticipations of them could be identified in the global political arena as well as close to home. The powers of the age to come were already being poured out over the dispensational walls erected by the traditional ‘charters’ of dispensational history. The church was the new Israel and had a special concern for national Israel because of promises directed to her. However, while there was
a difference between national Israel and the church, the spiritual destiny was the same; the promises of God looked forward to the same kingdom and ‘throne of David’ to be restored when Jesus would sit in the millennial kingdom and rule the nations. So the kingdom was breaking through from the future and the Spirit was being poured out. The Pentecostals did not sell everything and go up to a mountain to await his appearing. They did not retreat to a prayer cave. They did not set dates for his coming, though they, as the early church, were sure it would be soon. No, what was called for was the preaching of the gospel to the nations and getting the Bride ready for the Bridegroom. The crisis experiences within this eschatologically oriented development process were stages along the way, markers along the aisle, toward the altar and marriage supper. They were not experiences for experience’s sake. They were the necessary preparations for a kingdom where all is holiness unto the Lord, a kingdom which even now is righteousness, peace, and joy in the Holy Spirit. There was no consideration of merit or works-righteousness. Faith was the gift of God by grace. But the faith which justified worked through love. In response to the righteousness declared by God for the believer, the believer was to declare for, and walk in, all righteousness. Those who loved Jesus were to love the church and neighbor. Those who were saved by the power of God were to receive power to spread the liberating gospel unto all nations. This meant that the church became a missionary fellowship where testimonies were given constantly in order to develop in the hearers the virtues, expectancy, attitudes, and experiences of those testifying. A typical early testimony (and the services and periodicals were always full of them) would run something like this: ‘I’m so thankful the Lord has saved me, sanctified me, and filled me with the blessed Holy Ghost. I’m thankful to be a part of His Church and on my way to heaven’.163 There would follow then some review of recent or upcoming events which were to be occasions of praise or petition for the body. Healing, trials, temptations, and victories could be reflected upon by the body. By listening to and giving testimonies the congregation was involved in a praxis of theological reflection which, though open-ended, produced great uniformity and carried built-in relevance. There was also congregational control of ‘wildfire’ or fanaticism.164 Consider the following excerpt from a letter dated 27 February 1907 from the widely influential evangelist and church leader G.B. Cashwell in Dunn, North Carolina:
I am receiving letters every day from north, south, east and west from people that have attended my meetings saying that they have received their Pentecost and speak in tongues.
People have been gulled here by take it by faith, reconsecrate, baptism of fire, ‘dynamite’ and ‘lyddite’, till the faith of the people is almost gone. Praise God for Pentecost. Get your justified experience all in good shape, then get the sanctified experience of a clean heart. Then when your faith takes hold of the promise of the Father and Son, and the word of God, you will have great joy as they did that went up from Olivet to Jerusalem. Then you can praise and bless God and the Holy Ghost will come in and praise God Himself in unknown tongue [sic] and you will never doubt it any more, if they burn you at the stake or behead you. He will bear witness of Himself. Let us not come short of the promise.165
Evangelists and congregations who had been ‘burned over’ a few times soon learned to ‘test the spirits’ and recognize what was not scriptural, edifying, or unifying. But if there were counterfeit experiences, that was only because the real thing was so wonderful. The Threefold Pentecostal Experience It will now be profitable to consider the ‘Pentecostal experience’ of the believer in its correlation with the view of God, the means employed, the evidences sought, and the results desired. Recalling Runyon’s analysis of experience in terms of its source, telos, accompanying transformation, and attendant feelings, it will be noted that this discussion builds on his insights with some modifications. God is the source and, in a real sense, the telos of these experiences. God forms persons in and through these experiences in the missionary fellowship for eternal fellowship with himself in the consummated kingdom. The penultimate goal of this formation is readiness or fitness for missionary service. Early Pentecostalism organized its understanding of the Christian life around the three ‘blessings’ or ‘experiences’ of justification, sanctification, and Spirit baptism. Each ‘experience’ is a penultimate realization of an aspect of the coming kingdom and is correlated with an attribute of God. The experiences recapitulate the progressive unfolding of God’s economy of salvation. The manifestation of the gifts of the Spirit confirm that the first-century power is still being given, God is still the source; and, most importantly, the power of the end
is now at work moving all things to their completion in Christ. What did it mean, then, to be justified, sanctified, and filled with the Holy Spirit in light of the imminent return of Christ? Justification. To experience justification was simultaneously to testify to forgiveness, new birth, regeneration, adoption, and being in a new world. To be ‘saved’ in a Pentecostal setting meant an entry into the training program of a missionary fellowship in which, with sins forgiven; one could then continue to walk in the light, make things right with persons whom one may have offended (restitution), and forgive those who had sinned against one. God was a righteous God and righteousness was a word to describe all the requirements of a right relationship or a walk in the light with him. (How can two walk together, except they be agreed?)166 If one were truly justified, one would not walk in darkness and sin anymore. Now, through the power of the Spirit, one could resist the devil, deny the flesh and walk separated from the world. One should ‘walk the talk’ and ‘talk the walk’. To do less was to be a hypocrite at best and at worst to backslide. All ‘experiences’ were amissible, and all were capable of increase as one grew in wisdom and knowledge and strength. In justification one acknowledged the will of God in all the Scriptures as the direction for all of life. As Jesus came to do the will of the Father, to fulfill all righteousness, so each believer was to walk in righteousness, to become the righteousness of God in Christ, so that they would shine as lights in a dark and dying world. It was urgent that the light shine, especially since, in the last days, the darkness would increase and good and evil would grow up together. Rules of righteousness, holiness practices adopted from the nineteenth-century Holiness movement, served to make a difference between the church and the world, the saint and the sinner. As the light of Scripture shined on the path by means of the Word and Spirit, one was to walk in it. Failure to do so meant going back. The choice was to go on to the end or to go back. This view of the Christian life as journey is captured in the gospel song, ‘I Feel Like Traveling On’: 1. My heavenly home is bright and fair, I feel like traveling on, Nor pain, nor death can enter there, I feel like traveling on. 2. It’s glitt’ring tow’rs the sun outshine, I feel like traveling on ,
That heavenly mansion shall be mine, I feel like traveling on.
3. Let others seek a home below, I feel like traveling on, Which flames devour or waves o’er flow, I feel like traveling on. 4. Be mine a happier lot to own, I feel like traveling on, A heavenly mansion near the Throne, I feel like traveling on. 5. The Lord has been so good to me, I feel like traveling on, Until that blessed home I see, I feel like traveling on. CHORUS Yes, I feel like traveling on, I feel like traveling on; My heavenly home is bright and fair, 167 I feel ‘like traveling on.
Many other songs spoke of moving on and implored the Savior to ‘Lead me all 168 the way across the stormy sea of life’. The worshipers would often declare in song that they ‘did not want to get adjusted to this world’,169 because ‘Holiness unto the Lord’170 was their watchword. To be righteous was to heed the voice of God with urgency while the ‘Latter Rain Is Falling’.171 One was called to live as ‘If the End of the World Were Today’.172 Something of the early Pentecostal ethos and social location is captured in the following gospel song, ‘What a Shame on People Who Do that Way’: 1. Some folks go to meeting because they love God, And follow the path which the pilgrims all trod; ‘Tis a peace, ‘tis a peace for the people who do that way. 2. Some folks go to meeting and in it delight, They love to praise Jesus from morning till night;
‘Tis a peace, ‘tis a peace for the people who do it that way.
3. Some folks go to meeting and grumble and shout, And in a short time Christian folks turn them out; ‘Tis a shame, ‘tis a shame, for people who do that way. 4. Some preachers hold meetings and wear their long coats, But all they are good for is getting our goats; Turn away, turn away, from preachers who do that way. 5. Some folks go to meeting and take the front pew, And after the meeting still smoke, swear, and chew; ‘Tis a shame, ‘tis a shame, for the people who do that way. 6. Some folks go to meeting, all wearing fine clothes, But at the true gospel, they turn up their nose; Turn away, turn away from the people who do that way.173
It was this strong sense of the church as a covenanted, disciplined body of believers (like the Anabaptists of the left wing of the Protestant Reformation) that gave them identity and a sense of belonging; although obviously it could make anyone coming into that ethos feel very uncomfortable! This band of faithful followers construed the wicked as weary and restless and themselves, though very active, as having a divinely given rest of soul: ‘There Remaineth a Rest’ 1. There remaineth a rest for the good and the blest, For the faithful, the tried and the true; And its for us today, who will walk in the way, Jesus tells us just what to do. 2. Let us fear lest we fall, there is rest for us all, Lest we falter beside the way; It is grace for the hour, O, it’s wonderful power, When the Comforter comes to stay. 3. You may find it too late, when you call at the gate, If you trifle the time away; He is calling you now, will you humbly bow, He will save you from sin’s dark way.
4. There is danger I say, should you turn Him away, He so sweetly is calling now; Will you turn Him away ‘till the great judgment day? Why not come and before Him bow? REFRAIN There is rest, sweetest rest, for the good and the blest, And a home in the sky someday; Rich rewards for us there, in those mansions so fair, If we follow Him all the way.174
The paradox of rest and work is caught in even sharper contrast in a selection from the 1908 Songs of Pentecostal Power entitled ‘We’ll Work Till Jesus Comes’: 1. O Land of rest, for Thee I sigh, When will the Moment come; When I shall lay my armor by, and dwell in peace at home? 2. No tranquil joys on earth I know, no peaceful sheltering dome; This world’s a wilderness of woe, this world is not my home. 3. To Jesus Christ I fled for rest; He bade me cease to roam, And lean for succor on His breast, till He conducts me home. 4. I sought at once my Savior’s side, No more my steps shall roam; With Him I’ll brave death’s chilling tide, And reach my heav’nly home. CHORUS We’ll work till Jesus comes, We’ll work till Jesus comes We’ll work till Jesus comes,
And we’ll be gathered home.175 In this song Pentecostal piety portrays the world as a place of weariness and woe. But this same world is a harvest field which is destined to be completely renewed in the millennium. The world at present, however, is a system of interlocking spiritual-institutional realities which are driven by the lust of flesh, 176 the lust of eyes, and the pride of life. When one is born again, one no longer follows the ‘world’s crowd’ but follows Jesus in righteousness. In this present age of moral chaos, to be a disciple was to follow in the way of righteousness and to live by a certain rule or discipline of life. This was more than the mere application of biblical principles to various situations and decisions. It was a discerning, personal following of Jesus in the Spirit. There were conditions to be met if one continued in the way faithfully, and the chief of these was humility. ‘Humble Thyself to Walk’ 1. If thou wouldst have the dear Savior from heaven, Walk by thy side from the morn ‘till the even, There is a rule that each day you must follow, Humble thyself to walk with God. 2. Just as the Lord in the world’s early ages, Walked and communed with the prophets and sages, He will come now if you meet the conditions, Humble thyself to walk with God. 3. Just as a stream finds a bed that is lowly, So Jesus walks with the pure and holy, Cast out thy pride, and in heart felt contrition, Humble thyself to walk with God. REFRAIN Humble thyself and the Lord will draw near thee, Humble thyself and His presence shall cheer thee; He will not walk with the proud or the scornful, Humble thyself to walk with God.177 The justified were to walk humbly in the light, and that requires the Spirit as surely as a flashlight requires batteries. The concern for walking in the Spirit, in
the presence of Jesus, meant that sin was very personal. This is one of the important contributions of the movement even today: a sense of sin not only as transgression but as a personal affront to the Holy Spirit and a hindering of the historical process which is, by the Spirit’s superintendency, moving toward the end in the kingdom of God. Sin is transgression, but it is even more fundamentally a rejection of the conviction or convincing of the Spirit concerning sin, righteousness, and judgment. One cannot be a convincing witness if one is not daily living out of the convictions taught by the Spirit concerning these realities. The Spirit may be grieved, resisted, insulted, quenched, lied to, and, most seriously, blasphemed.178 But in order to walk in the light one had to walk in the Spirit who would lead into all truth, show things to 179 come, make known the things of Christ, and so forth. Walking in the Spirit requires not only illumination—that was foundational to everything—but also calling, appointment, direction, wisdom, and timing of the Spirit. Scriptural behavior required the continual, particular actions of the sovereign Holy Spirit who was also Lord and leader of the saints. This was expressed in the testimonies as a narrative of providence and the Christian life as a conversation involving God, believers, and the world. Pentecostal piety, like Wesleyan spirituality, was very much in accord with the Johannine order: walking in the light, fellowship, and thus ongoing cleansing from all unrighteousness.180 The ordering and directing of life by the Spirit and the walk according to that order and direction was righteousness. This walk began in a regenerative act which gives the believer a new source for life; now he or she could walk according to the Spirit and not the flesh. As a testimony to and a first act of righteousness the Pentecostal believer would ‘follow Christ in baptism’ thus declaring publicly that one was now available to ‘fulfill all righteousness’.181 This was a corporate celebration and carries a special blessing and increase of joy. It was almost always by immersion on profession of faith, and, during the first ten years of the movement, universally in the name of the Father, Son, and Holy Spirit. To be baptized indicated not only conversion but also a willingness to follow all that the Lord commanded. The daily penultimate goal was to walk in the light. Sanctification. The narrative of justification usually involved confessing the resistances and hold-outs in the believer’s life and the desire to fulfill the will of God. Doing the will of God, walking in the light, resisting the devil, and denying the self were all good. But sanctification involved actively seeking all the will of
God for one’s life, loving the Lord with the whole heart, and joyfully bearing burdens without grumbling and complaining. Initial sanctification occurred with justification and the new birth, but entire sanctification was to be expected, desired, and sought. Again, as in the case of justification and new birth, listening to Scripture, testimonies, and songs prepared the way. ‘Is your All on the Altar?’, ‘Cleanse Me’, and Phoebe Palmer’s ‘The Cleansing Wave’ were all sung as was, of course, Charles Wesley’s unsurpassable ‘Love Divine’. The effect of this process of exposure to holiness preaching, teaching, singing and testifying is captured in the narrative song by E.M. Graham: ‘We Will Sing and Preach Holiness’ 1. When I first heard of holiness I thought it must be right; It seemed to fit the Bible, And be the Christian’s light I heard the people singing and testifying too; They seemed to love their Savior, As Christians ought to do. 3. I little thought of joining, I said I could not stand, To be among that people, That’s called the ‘holy band’. The world looked down upon them, And said they were so rash, They often spoke against them, And said they were but trash. 4. But as I went to hear them, And saw the way they did. I saw they had a treasure, From worldly people hid. They seemed to be so happy, And filled with Christian love; When people talked about them, They only looked above. 5. My heart began to hunger. And thirst and burn within: I wanted full salvation. A freedom from all sin. I went to God for holiness, And called upon His name; He cleansed my heart completely, And filled it with the same. 6. And now I’m one who bears that name, That happy holy band; I’ve crossed the river Jordan, And in the Canaan land, The atmosphere is pleasant, And fruit of every kind, When you reach heaven’s portals. I’ll not be far behind.182 If righteousness was a right relationship and direction for life, holiness was the standard for living and the essence of the Christian life. Desire for sin was to be crucified, deeds of the flesh mortified, and sinful stains and tendencies cleansed. If justification signaled a radical break with the world, then sanctification was a
radical dealing with the flesh, the old nature, or the carnal self. The self was denied in justification and was to be so daily thereafter. But in sanctification the self was to come into a new integration of perfect love perpetuated in continual spiritual respiration. Entire sanctification, the complete inner cleansing, would be evidenced in an abiding joy, thanksgiving, and prayerfulness. The Holiness practices were no longer righteous limits to be obeyed whether one felt like it or not. Now they were merely the first steps, the basic training to exercise one in righteousness unto holiness of heart and life. In love the commandments were no longer burdensome or grievous. But what of a second definite experience of sanctifying grace? Even at Azusa there were those who experienced no interval between sanctification and Spirit baptism, but received both simultaneously. Yet, it was important to the leaders at Azusa, W.J. Seymour in particular, to characterize Spirit baptism as the outpouring of the Spirit ‘upon the sanctified life’.183 Justification and sanctification were two separate works of grace. They were the works of grace which had been restored to the church through the Lutheran and Wesleyan reformations, respectively. Spirit baptism was upon the sanctified life. The Spirit witnessed with the human spirit that the work was accomplished. In justification one was to walk in all the light, in the will of the Father. In sanctification the believer was to walk in the perfect love of Jesus. That love filled the heart and without it nothing else profited.184 Since Jesus prayed for the sanctification of his disciples and those who should come after them, believers should pray for their sanctification. As he sanctified himself in total self-offering unto death, so the believer should crucify the flesh with its passions and be completely at rest in the Father’s hands.185 The means of sanctification were the Spirit, the washing of the Word, and, supremely, the blood of Jesus. The Spirit directed the believer to the inner resistances to the will of God. There needed to be a harmony of will and nature in the believer analogous to that harmony that is holiness in God. Indeed, the coming into that harmony and peace in love was the very essence of sanctification. It was a delight in the will and presence of God, and a wholehearted desire to be pleasing to the Lord in all things. When one was sanctified the body of believers rejoiced upon hearing the testimony and then were there to assist the growth in sanctification which would come, now unimpeded by the resistance of the flesh. Faith overcame the world, crucifixion killed ‘the flesh’. But what about the devil and his opposition to the mission that was the very heart of the church’s life?
Spirit Baptism. It was a third experience, the baptism in the Holy Spirit, which equipped the believer to do spiritual battle in tearing down strongholds of the enemy and reaching the lost. How was the power of the Spirit related to the previously mentioned purity of heart and life? In 1908 The Apostolic Faith answered a series of questions on various aspects of Christian living, and many of the first ones had to do with sanctification, Spirit baptism, and the question of evidence. Questions Answered Should a person seek sanctification before the baptism with the Holy Ghost? Yes, sanctification makes us holy, but the baptism with the Holy Spirit empowers us for service after we are sanctified, and seals us unto the day of redemption. Sanctification destroys the body of sin, the old man Adam. Rom. 6.6, 7 … when a man has been saved from actual sins, then he consecrates himself to God to be sanctified, and so his body of sin is destroyed or crucified … What is the real evidence that a man or woman has received the baptism with the Holy Ghost? Divine love, which is charity. Charity is the Spirit of Jesus. They will have the fruits of the Spirit. Gal. 5.22. ‘The fruit of the Spirit is love, joy, peace, longsuffering, gentleness, goodness, meekness, faith, temperance; against such there is no law. And they that are Christ’s have crucified the flesh with the affections and lusts.’ This is the real Bible evidence in their daily walk and conversation; and the outward manifestations; speaking in tongues and signs following: casting out devils, laying hands on the sick and the sick being healed, and the love of God for souls increasing in their hearts … Is it necessary to have hands laid on in order to receive the Holy Ghost? No; you can receive Him in your closet. The gift of the Holy Ghost comes by faith in the word of God. You may receive the Holy Ghost right now, that is if you are sanctified … The baptism of the Spirit is a gift of power on the sanctified life, and when people receive it, sooner or later they will speak in tongues as the Spirit gives utterance. A person may not speak in tongues for a week after the baptism, but as soon as he gets to praying or
praising God in the liberty of the Spirit, the tongues will follow. Tongues are not salvation. It is a gift that God throws in with the Holy Spirit. People do not have to travail and agonize for the baptism, for when all work ceases then God comes. We cease from our own works, which is a very type of the millennium.
Does a soul need the baptism with the Holy Ghost in order to live a pure and holy life? No. Sanctification makes us holy, Heb. 2.11 … The Holy Ghost never died for our sins. It was Jesus who died for our sins, and it is His Blood that atones for our sins … 1 John 1.9, 7 … It is the Blood that cleanses and makes holy, and through the Blood we receive the baptism of the Holy Spirit. The Holy Ghost always falls in answer to the Blood. Is the speaking in tongues the standard of fellowship with the Pentecost people? No; our fellowship does not come through gifts and outward demonstrations but through the Blood by the Spirit of Christ … If a man is saved and living according to the word of God, he is our brother even if he has not got the baptism with the Holy Spirit with tongues.186
Two related questions were asked concerning the possibility of the restoration of a ‘lost Pentecost’ and how to keep ‘the anointing of the Spirit after receiving the Pentecost’. The editor replied with regard to the first that, a person could ‘repent and do the first works, and consecrate to receive sanctification, and wait for the baptism’ again.187 The presumption was that the Pentecostal experience was lost because of ‘falling into temptation and being overcome by Satan’. To the question concerning maintenance of Pentecostal anointing he replied that it could be kept by ‘living in the word of God with perfect obedience’. No antinomianism there! Some had apparently wondered about the place of Bible study after ‘receiving the Holy Ghost’. The editor gave the following caution to the questioner: Yes (we need to study); if not one becomes fanatical or many times will be led by deceptive spirits and begin to have revelations and dreams contrary to the word, and begin to prophesy and think ourselves some great one, bigger than some other Christians. But by reading the Bible prayerfully, waiting before God, we become just little humble children, and we never
feel that we have got more than the least of God’s children.188 These questions and answers, reminiscent of John Wesley’s conferences with his ministers over a century earlier, indicate that very early in the revival there was an ongoing corporate reflection upon the living reality of God in their midst. Scripture, testimonies, songs, prayer vigils, poetry, spiritual gifts, godly lives— all served to form persons who shared a common story. In all this the pre189 eminent authority was Scripture. The Spirit unfolds the Scriptures from ‘Genesis to Revelation and all you do is to follow on’. According to the Scriptures, ‘freelovism’ and anything associated with sexual impropriety is condemned as being from the ‘pit of hell. It is a dragon to devour those who get out of the Word … but He has given His children to know these spirits.’ Since there is no mention in Scripture of writing in unknown languages, then it was not encouraged in the Azusa meetings. Everything was to be measured ‘by the Word that all fanaticism may be kept out of the work’.190 A statement of faith was developed early in the revival at Azusa and published in several issues of The Apostolic Faith. It consists of brief phrases, Scripture quotations, affirmations as to the restoration of apostolic faith, and the ‘old time religion’ practices of camp meetings, revivals, missions, street and prison work, and Christian unity everywhere. This combination of beliefs, declarations, and practices was a definitive list of distinctives made by those who saw themselves as a small but significant band of pilgrims.191
The Way of the Kingdom
In justification, sanctification, and Spirit baptism the believers were enabled to walk in the light, in perfect love, and in power and demonstration of the Holy Spirit, respectively. This was the way of the kingdom. It was a journey into and with a righteous, holy, powerful God who was transforming them and the world by the power of the gospel in preparation and anticipation of the final apocalypse. The unfolding of the biblical drama, church history, and individual history, all of this was the unfolding of God’s historical revelation. The Scripture was the normative prescription and description of these events, but the lives of believers were significant as living epistles and lights shining in the evening light, which signaled the twilight of the old age and the dawning of the new. And through it all, the overriding and determining factor was the final revelation of God: the goal of all history, all nations, and all people. To believe in this righteous, holy, powerful God whose kingdom was righteousness, peace, and joy
in the Holy Spirit was to be transformed unto that end through Christ in the Spirit. The indeterminate but imminent coming of Jesus then, in the first century, and today, among Pentecostals in pneumatic continuity with these early pioneers, was the decisive belief and daily milieu for all the worship and witness practices: ‘Jesus is coming soon’ is the message that the Holy Ghost is speaking today through nearly everyone that receives the baptism with the Holy Ghost. Many times they get the interpretation of the message spoken in an unknown language and many times others have understood the language spoken. Many receive visions of Jesus and he says, ‘I am coming soon.’ Two saints recently in Minneapolis fell under the power, were caught up to heaven, and they saw the New Jerusalem, the table spread, and many of the saints there, both seeing the same visions at the same time. They said Jesus was coming very soon and for us to work as we had little time.192 The Pentecostal narrative beliefs under the influence of this apocalyptic vision of imminent fulfillment called forth distinctive practices, which were themselves signs, confirmations, and celebrations of the power and legitimacy of the beliefs. And, at times, they became the basis for the refining, correcting, and supplementing of the beliefs. The worship and witness were the means of expressing and inculcating the narrative beliefs. All the practices of the nineteenth-century Holiness movement, evangelical revivalism, and early Methodism in the United States and Great Britain (‘personal testimony, speaking in tongues, emotional and motoric outbursts, prostrations, spontaneous prayer, altar calls, prayer room, prophecies, hand shaking, and broader corporate involvement in worship and ministry’)193 appeared in Pentecostalism, as well as many of the more traditional liturgical practices. The difference was the gestalt, that particular mix of eschatological intensification evidenced in the urgency, expectancy, and manifestations of the Spirit which gave rise to a missionary fellowship whose ‘this is that’ (Acts 2.16) affirmation of the Latter Rain turned members of the Holiness movement into members of a global Pentecostal missionary force.
Pentecostal Practices: Worship and Witness in Light of the End
The Last-Days’ Restoration of the Full Gospel
Speaking in tongues and healing had been occurring throughout the nineteenth century. Indeed, Pentecostals were later to show a limited but significant continuity of tongues and other gifts erupting throughout history from Pentecost to the present. In addition there was already a widespread belief in the premillennial coming of the Lord. But speaking in tongues and healing as signs of the eschatological inbreaking of the kingdom of God, signaling the imminent return of Christ, was not so prevalent, and certainly interpreting the ‘fivefold gospel’ as a last days’ restoration for the proclamation of the gospel of the kingdom in all the earth was unheard of before the emergence of the twentiethcentury Pentecostal renewal. This is not to say that eschatology played no role in the theology of the nineteenth-century Holiness movement itself. From the time of John Wesley’s 194 sermon, ‘On the Wedding Garment’, there had always been a concern for preparation and readiness among those teaching Wesleyan sanctification. The gift of healing was the notable nineteenth-century manifestation which both looked back to Jesus’ ministry and forward to Jesus’ millennial reign when there would be no more sickness. Yet, by and large, the whole range of gifts of the Spirit was seen as rare or occurring only here and there, without eschatological significance or import for the understanding of the Christian life, nature of the Church, and missionary witness. The same could be said for the more general notion of ‘power’ for service. The purity and power components of the nineteenth-century sanctification teaching had been like two sides of a coin. They were addressed to the need for personal piety and power for holy living, and the latter included spreading scriptural holiness throughout the land by means of evangelism and various programs of social reform. These practices of personal dedication and social witness were carried out to express and propagate the Holiness emphases, and they were the application of Holiness beliefs. With the eschatological intensification within the so-called more radical wing of the Holiness movement, however, these practices were seen as readiness for and anticipations of the end.
But what necessitated distinguishing sanctification from Spirit baptism? What gave this new impetus and direction to the movement? Yes, the eschatological categories had shifted from postmillennialism to premillennialism. Yes, there was a shift from an emphasis on sanctification to baptism of the Spirit, from purity-power to power for service and holy living. Tongues could have been understood as evidence of sanctification seen as Spirit baptism or vice-versa. There was already a recognition of the difference between purity and power. The central theological reason for this distinction rested on an awareness of the difference between the mission of Jesus Christ and the mission of the Holy Spirit. The Holy Spirit was now not only the Spirit of Christ but also the sovereign Lord. Believer’s lives were to conform to Christ, but their witness was to be like the Spirit’s. This paralleled Jesus’ own witness which was itself by the power of the Spirit. But this also meant that believers had to deal with, wait upon, and seek the Spirit for leading, understanding, and empowering. This represented a shift from what was essentially and functionally a binatarianism to a more trinitarian practice with the accompanying danger of a new unitarianism of the Spirit. Ironically, but with a kind of revivalistic ‘Jesus-centric’ logic, the unitarianism which did develop was one of the second instead of the third person of the Trinity. Perhaps this ‘Jesus name’ or ‘Jesus only’ split within early Pentecostalism was a way of registering a subliminal sense of the danger of tritheism and acknowledging the strong ‘Jesus-centric’ piety of early Pentecostalism and previous revivalism. It was perhaps also a ‘logical’ conclusion from the movement’s fivefold full gospel concentration on Jesus as Savior, healer, sanctifier, Spirit baptizer, and coming king, in which the Spirit was understood as merely instrumental. Whatever the outcome of the historical investigation of the paradigm shift which resulted in Pentecostalism’s separation from the Holiness movement, and whatever the verdict as to the theological reasons or concerns ingredient in that shift, it is clear from an analysis of the ensuing practices that the eschatological presence of God in, among, and through these Pentecostals resulted in a heretofore unseen recovery of the universal call to witness in the power and demonstration of the Spirit in order to carry out the universal mission of the church in the last days. The missionary, charismatic nature of the church, and therefore of the Christian life, was now a central normative issue and concern. Supernatural evidences, leadings, and manifestations characterized the new movement. The hard claim was that every believer in particular and the church
universal was called to be a Christ-like witness in the power and demonstration of the Holy Spirit with an eschatological sense of urgency and passion. Pentecostals were not more emotional than believers in the previous century’s revivals and awakenings. They were struggling to find a new theological integration which would do greater justice to the new experiences, practices, and biblical insights that were emerging. Pentecostal practices were those actions undertaken on the basis of the beliefs, expressive and formative of the affections, and impacted by the inbreaking of the kingdom of God in spiritual power and manifestations. It was important to ‘walk the talk’ and ‘talk the walk’. One cannot understand Pentecostal spirituality apart from exposure to the congregational and individual practices of worship and witness under the influence of the end times. Beliefs about the Bible, the Second Coming, the Holy Spirit, the Christian life, and worship itself are expressed in and shaped by these practices. If, as was stated in Chapter 1, the Pentecostal theological task is understood as a discerning reflection on lived reality, then it becomes apparent that for Pentecostals, like liberationists (though, of course, also different from them), reflection on a distinctive praxis, an apocalyptically informed one, is essential to that task. Rather than merely listing some of the practices, my procedure will be to group a select number of them using four categories which are descriptive of the spirituality and are themselves reflective of the particular eschatological experience of the Pentecostals. These four descriptive-analytical categories are a. Fusion-Fission Tensions. b. Oral-Narrative Formation. c. Spirit-Body Correspondence. d. Crisis-Development Dialectic.195
The fusion-fission category is placed first because it most directly and decisively represents the ‘already–not yet’ tension in Pentecostal apocalypticism. ‘This tension is also reflected in the other three categories and is, therefore, fundamental to any explanation of Pentecostal practices. Fusion refers to those polarities or pairs of concepts which are of equal importance and, in the apocalyptic fire of the spirituality, are fused phenomenologically. Fission, on the other hand, refers to those elements or dynamics which are separate, of unequal value to the believer and are sometimes mutually exclusive. The former (fusion) expresses an integration while the latter (fission) expresses a segregation or
important distinction.
Fusion: The lnbreaking and Transformation of the Kingdom
Space and time are fused in the prophetic reckoning created and sustained by the Spirit of the end. Here and now, there and then are telescoped and traversed by the Spirit so that there is a personal impact of the ‘already–not yet’ tension in the affective response and observed behavior. Pentecostals who are moved deeply and powerfully by the Spirit will laugh and cry, dance, and wait in stillness. In the Spirit they ‘already’ participate in the marriage supper but also live in the ‘not yet’ of a lost world. As has been discussed earlier, the Spirit acts as a kind of ‘time machine’ via the Word, enabling the believer to travel backward and forward in salvation history and to imaginatively participate in the events that have been and are yet to be. The power who raised Christ from the dead is moving all things toward the parousia. The Spirit poured out at Pentecost is filling every believer in such a way that everyday time is kairos for those upon 196 whom the end of the ages has come. But every fulfillment, every ‘already’, has an overplus of not yet or promise. The world and believers are fallen but being redeemed. The body is dying but is now the temple of the Holy Spirit, a part of the body of Christ. In the ‘already–not yet’ time of overlapping aeons believers may speak in tongues and proclaim in the vernacular the mighty acts of God. Doxology is for now and then and reflects the fusion of the worship and witness of the church. Pentecostals in the Third World will often move the worship service into the streets after a full morning of worship. During the afternoon they will sing, testify and pray for persons in the street in a fusion of worship and witness (λειτουργία [leitourgia] and μαρτυρία [martyria]). The power of the kingdom to come is at work through the Holy Spirit to make all places and times serve the glory of God. This intensification of joy means also, at the same time, an intensification of sorrow or longing (see Chapter 3). The longing is the affective recognition of the ‘not yet’ for those who are lost and for the world as a whole. And so there is a pessimism of nature (groaning and sighing in the Spirit) and an optimism of grace (rejoicing in the Spirit). Pentecostal missionary practice seems more like postmillennial optimism (‘We will bring in the kingdom by proclaiming the gospel’). But Pentecostal worship evidences a premillennial pessimism concerning the capability of any human agency effecting the kingdom. Optimism, pessimism or both? It appears that, for them, God will not save the
world on the basis of their works, but he will not save it apart from them either. The kingdom is present and will be consummated. To believe that is to live out of the power of the Spirit who directs and empowers the worship-witness praxis of the church. It is the Spirit himself who is in, and the source of, this joy and sorrow. The Spirit groans and sighs with all creation and within the believer. He creates and sustains this longing. Even though, obviously, the Spirit knows the end and indeed is the sufficient, efficient means of its accomplishment, there is still, in the Spirit, a divine longing. It is impossible to be filled with such a Spirit and to remain passive. It is cause neither for despair nor naive optimism. It is a sober joy, a tearful rejoicing, and a realistic hope. Fusion also describes the relationship of the individual to the community. The body of Christ is a tabernacle made up of living stones for a habitation of God through the Spirit.197 As a communion in the Holy Spirit members respond to one another and the world out of the fundamental and prior response to and in the Holy Spirit. The congregation responds as a whole to the moving of the sovereign Spirit. Corporate, interactive worship is deeply felt and easily observable in Pentecostal settings. The gifts of the Spirit are distributed by the sovereign Spirit as he wills for the good of the whole, and it is the fact that all are responding to the same indwelling, infilling Spirit that makes corporate discernment and receptivity possible. The manifestation of gifts always bears the stamp of the present talents, personalities, and culture of the believer but that is fused with the unmistakable ‘not yet’ eschatological character of the Holy Spirit and his gifts. The Spirit is already poured out and gifting the body, but the believers are not yet as receptive and expressive as they shall be in the consummation of the age. The impact of the Fall upon the understanding, will, and emotions is still felt even and especially among those who are filled with the love of God, sanctified, and fit for the Master’s use. Pentecostals believe that the Bible is the Word of God written. Most subscribe to some form of verbal inspiration, infallibility, and, for almost all North Americans, would espouse inerrancy if asked. The official statements, usually copied from evangelicals, do not accurately reflect the reality of the Scripture as Spirit-Word. The Spirit who inspired and preserved the Scriptures illuminates, teaches, guides, convicts, and transforms through that Word today. The Word is alive, quick and powerful, because of the Holy Spirit’s ministry. The relation of the Spirit to Scripture is based on that of the Spirit to Christ. Even as the Spirit formed Christ in Mary, so the Spirit uses Scripture to form Christ in believers and vice-versa. Anointed preaching, teaching, and witnessing evidence this wholeness, this fusion of Spirit and Word, Spirit, and Christ.
The Spirit is the Spirit of Christ who speaks scripturally but also has more to say than Scripture. The Spirit-Word directs the everyday life and witness of believers and the church as they are led into all truth. Spirit and Word are fused, are married, and can only be separated or divorced at great peril and price to the church and believer. The Word comes in words and in the power and demonstration of the Spirit. If it is not communicated out of the fullness of the Spirit, then the communication is not fully scriptural. If it is not scriptural, then, no matter how apparently charismatic it is, it is not spiritual, of the Holy Spirit. Of course this discernment calls for a body of people who are formed in the Spirit by the whole counsel of God.198 Each person as bearer of the Spirit is hearer of the Word and vice-versa. And all bearers of the Word are those who hear what the Spirit says to the church. If a Pentecostal congregation is not responsive to a preacher, it usually means that he or she is either not anointed or not preaching the Word. Whenever the fusion is violated the congregation will register it by withholding the ‘Amen’.199 The ministry practices, especially of the early Pentecostals, indicated a fusion of clergy and ‘laity’, males and females, races and classes. Clergy and laity are functional distinctions in a gathering in which all have some gift to offer; no one gift is more valued or essential than another. All are needed or they would not have been provided by the Holy Spirit. The Spirit is poured upon male and female, therefore each is called upon to worship, witness, and to manifest the gifts and graces of God. Women would preach, lay hands on the sick, plant churches, prophesy, speak in tongues, and help in all phases of the total ministry. All, in the light of the end, are to submit to one another and assist one another toward that goal. They are to wash one another’s feet in cleansing preparation for that end and in view of their servanthood to one another.200 With regard to salvation and the daily walk of holiness, faith and works, ‘talk and walk’, love and obedience, gospel and law are fused. Love obeys. Those freed by the gospel, from the perspective of the gospel, allow the law to keep them dependent on grace and guided into righteousness. The kingdom that is coming is to be a kingdom of righteousness; therefore, believers must now practice that righteousness in restitution for wrongs committed against others. Faith alone justifies through grace. But the faith which justifies is never alone; it is always, in the Spirit, the faith which works through love. To be in the faith is to be faithful. To be unfaithful is to be an adulterer who has fallen out of love with God. Pentecostals believe that Christians can and have defected or ‘backslid’. They
practice disfellowshipping and restoration in relation to such persons. They call upon those crucified with Christ to crucify the ‘affections and lusts’. The objective is fused with the subjective. They do not see this as worksrighteousness. They see faith as working righteousness but not inevitably or necessarily. Persons can resist the leading of the Spirit, the light of the Word and fall back. Christ’s message to the churches in Asia in the book of Revelation has been used by Pentecostals since the 1906 Azusa Revival to show the importance of hearing what the Spirit says to the churches. For just as individuals can fall away so can churches be deceived into thinking all is well and living on past reputation.201 As a result of this emphasis Pentecostals often practiced a very strict discipline which recognized very few indifferent matters (the so-called adiaphora). Holiness prohibitions against dancing, attendance at movie theatres (worldly amusement), wearing jewelry (worldly luxury and adornment, or vainglorious displays), and so on became tests of fellowship rather than matters for further discussion and cultivation. In an effort to keep the church pure and ready, many persons were offended or taught an ‘all or nothing, now’ approach to church discipline. When the apocalyptic fervor was high, of course, most people were glad to submit to these lists of rules or holiness practices. However, as the fervor subsided and incomes rose, more became affordable; and, as a result, many third and fourth generation believers went to other more lenient churches. For most of the early believers, however, these practices were inherited from the Holiness movement and were seen as being consistent with a full commitment to the God who was looking for a people who were holy and blameless before him in 202 love. These practices also served to give a social identity and sense of distinction between the church and the world. This was further reinforced as a result of a lot of initial persecution, including violence against persons, and destruction of property. Epithets such as ‘holy roller’ served to drive people closer together and cause them to seek even more scriptural justification for those things practiced among them in dedication to God. The plain, simple life of sacrifice, consecration, and witness was consistent with the vision of the kingdom that must shine brightly from within to a watching world. The fruit of the Spirit and the gifts of the Spirit were fused as were the salvation experiences of regeneration, sanctification, and Spirit baptism. It was not just a matter of adding Spirit baptism to sanctification in order have a separate movement. Nor did it seem right to dissociate the two. Spirit baptism as God’s power poured out upon the sanctified life was a reaffirmation of the earlier Holiness insistence on purity and power as two sides of the same coin. Though
logically and experientially separable, they could occur simultaneously, but they should not be dissociated theologically. Being and doing, fruit and gifts of the Spirit, character and personality were to be seen as an integrated whole. God was preparing a Bride who was consecrated and caring, watching and working. The fusion of these elements of the Christian life was consistent with the eschatological fulfillment. One did not have to await the redemption of the body in resurrection to know the fullness of salvation as regeneration, sanctification, and Spirit baptism. The fruit and the gifts together comprised a complete or whole witness to the power of the gospel. The Spirit integrated the inward and outward. These signs or evidences were necessary not only for personal assurance but also for pastoral care and the public witness and influence of the church. In the fusion or union with Christ one was fused or joined to the Father and the Spirit. Indeed the Spirit was the agent of such fusion. Such a union with a righteous, holy, powerful God necessitated and would result in appropriate transformation and development. In this regard justification asked for sanctification which in turn asked for Spirit filling for worldwide evangelism and mission. The justice, love, and power of God became in the believers a deep, motivating passion for the kingdom
Fission: Participating in the Kingdom within a Fallen World
If fusion tends to favor the ‘already’ side of the tension, then fission tends toward the ‘not yet’. The polarities here are unique, sharply separated and, in some instances, mutually exclusive. God and Satan, light and darkness, saint and sinner, church and world are all examples of such mutually exclusive elements. The polarity is seen most clearly in the practice of exorcism, in which the demonized person was separated from the demon by the force of the Spirit driving out the evil spirit. Then the person could hear the gospel and be fused or joined to Christ. The ‘world’ was seen as an interlocking system—socio-political, economic and spiritual—that was passing away. Persons were either of the world or of the Word. To be of the world was to be motivated by the lust of the eye, lust of the flesh, and pride of life.203 Worldliness and godliness were mutually exclusive. To become a Christian is to receive the Spirit of God and to reject the spirit of the world. Men and women were called upon to come out of the world, to be delivered from all binding vices; to leave worldly luxuries, intoxicating beverages, harmful habits (such as smoking) and to cease frequenting worldly
amusements where there were lewd displays contrary to the Spirit of holiness. Pentecostals instrumented separation from this world through conformity to the next. In doing so they radically relativized this world and worldly involvements. The world rejected them, and they rejected the world. They were in the world as witnesses, not as part of the system. Early on pacifism was quite common and the point was often made that they were citizens of the kingdom of God first and last.204 Because they did not retire to a separate geographical location as did the Amish, for example, their differences in conversation, dress, worship, witness, and so on were all the more important to their sense of identity and belonging. Their intense sense of the otherness of God and his coming kingdom seemed to drive them to find ways in which to bear witness to that in their daily life. When someone came from the world into a Pentecostal fellowship there was often a great deal of spiritual energy released in the ensuing fission. Dramatic conversions and deliverances were the rule. It was eventful because of the sharp distinction and the cost that had to be counted. But if there were tears and travail as one was born into the new ‘world’ on the way to consummation, there was also great joy. The tears and joy served to bind the new believer to the body and to reinforce the body’s resolve. They experienced their own conversion again, were urged on in sanctification, and felt a fresh surge of the power of the age to come. Witnessing drew the line between the church and world and invited the world to cross the line. However, there is another type of fission. This time, instead of signaling mutually exclusive polarities, the purpose is to indicate things which are distinguished in that the first item is valued more than the second and takes precedence over it. Examples are revelation and reason, heart and head, Scripture and ‘creeds’. Pentecostals would found Bible schools and institutes to train persons for ministry. These schools, as they developed throughout the century, were places where reason would serve revelation. Reason could not produce revelation, and without revelation reason did not discover what was truly important. The ‘truths’ of secular learning had to be relativized to the larger truth and interpreted within it, that is, within the larger cosmic reality of the kingdom of God. How could one truly know the significance of the past and present or this or that discovery, much less put it to its proper use, without an understanding of the purpose and goal of all existence? Indeed, learning could be dangerous. Plenty of educated persons rejected the things of the Spirit. Many of them attended so-called
Christian schools where they were taught to distrust God and the Bible and the church. The heart was the center of the person; it was the seat of mind, will, and affections. The whole person had to be moved by the Spirit and Word of God. If the head was addressed apart from the heart being aflame with the love of God only pride could result.205 ‘Out of the heart the mouth speaks.’206 The social location, increasing pluralism, and concomitant relativization of all values influenced the Pentecostal response to education. But the foremost concern was to honor what was most important—what ‘thus saith the Lord’. The Spirit-Word of Scripture took priority over church and creeds. Creeds were like fixed fortifications in a battle that required mobility, adaptability and flexibility. Bartleman, who was present at Azusa, quoted Philip Schaff approvingly: The divisions of Christendom will be overruled at last for a deeper and richer harmony, of which Christ is the key-note. In Him and by Him all problems of theology and of history will be solved. In the best case a human creed is only an approximate and relatively correct expression of revealed truth, and may be improved by the progressive knowledge of the church, while the Bible remains perfect and infallible. Any higher view of the authority of creeds is unprotestant and essentially Romanizing.207 Bartleman wanted a unity in Christ not in creeds, because therein all God’s people could be one ‘irrespective of race, color, social standing, or creed’.208 Quoting a prominent preacher who was addressing some Pentecostals as an ‘outsider’ he warned that ‘the beautiful Pentecostal work, so full of promise, where God has designed to come in and fill souls and wonderfully baptize them in the Holy Ghost, is broken and peeled and ruined for lack of love’.209 Further he cites John Wesley’s discussion of ‘opinions’ and ‘bigotry’ and his reminder that when the believers were first filled with the Holy Ghost, they were of ‘one mind, as well as one heart.210 Creeds, according to the early Pentecostals, were designed to keep people out, to divide the body and to say what God could and could not do. They seemed to shut down the sovereignty of the Spirit and to frustrate the desire of Pentecostals to have a church unified in the Spirit for last-days’ mission. It was necessary judiciously to apply scriptural insights to daily decisions and situations. But creeds tended to be exalted to the place of Scripture and that just would not do. The Spirit was over the church. The Spirit was prior to Scripture. So, the order of
authority was Spirit, Scripture, church. Without the Spirit there would have been no Word, incarnate or/written; without the Word, no church. In practice this meant that preaching and prophesying (or its equivalent, tongues plus interpretation) were all to be tested by the Scriptures in the community of Spiritfilled and gifted believers. In this way the church could continue to grow in understanding and be corrected if it got off the track. Ironically, this anti-creedalism became something of a creed itself with the result that some Pentecostals believed that they had the pure Word while others had only creeds and organizations of human origin. They were trying to preserve the sovereignty and priority of the Spirit and in the process often became very inflexible and intolerant. But the intent was to be open and to seek a missionary unity of the Spirit for the urgent task of evangelization. Eventually, however, the Pentecostals, in response to internal dissensions and external accusations, were forced to develop their own creeds, with code names like ‘Statement of Fundamental Truths’ or ‘Declaration of Faith’.211 Pentecostals had experienced something which the creeds had led them neither to expect nor to seek, something, rather someone (the Holy Spirit), who gave them new courage, assurance and power. Thus it was better to place one’s trust in the Holy Spirit who unites than in creeds which divide. They knew they had beliefs, most of them in common with other Christians, but without the dynamic of the Holy Spirit upon and through their lives, the creeds were seen as empty shells and barriers for the missionary unity of the church. R.G. Spurling, early leader of the Christian Union (later to become the Church of God in Cleveland, Tennessee), said that the church fell into ‘creedalism’ when it lost the link of love in the golden chain of redemption. Changing the metaphor, he asserted that love of God and neighbor were the two golden rails upon which the church like a train should run.212 Contrary to much popular misconception, Pentecostals, though suspicious of restrictive creeds, were meticulously concerned, as their internal debates and divisions prove. W.J. Seymour warned Pentecostals of the danger of ‘Impure Doctrine’: We find many of Christ’s people tangled up in these days committing spiritual … as well as physical fornication and adultery. They say, ‘Let us all come together; if we are not one in doctrine, we can be one in Spirit.’ But dear ones, we cannot all be one except through the Word of God. He says, ‘But this thou hast that thou hatest the deeds of the Nicolaitans, which I also hate.’ I suppose that the apostolic church at Ephesus allowed people
that were not teaching straight doctrine, not solid in the word of God, to remain in fellowship with them; and Jesus saw that a little leaven could leaven the whole, and His finger was right upon that impure doctrine. It had to be removed out of the church or He would remain the light and break the church up. When we find things wrong, contrary to Scripture, I care not how dear it is, it must be removed. We cannot bring Agag, which represented satan himself, the carnal nature or old man; but Samuel said Agag must die, and he drew his sword and slew him. Christ’s precious word, which is the sword of Samuel, puts all carnality and sin to death … There are many people in these last days that are not going to live a Bible Salvation. They are going to take chances. But may God help everyone, if their right hand or right eye offend them to cast it from them. It is better to enter into life maimed, than for soul and body to cast into hell fire.
The Lord says. ‘He that hath an ear, let him hear what the Spirit saith unto the churches; to him that overcometh will I give to eat of the tree of life which is in the midst of the paradise of God.’ O beloved, if we expect to reign with the Lord and Savior Jesus Christ, we must overcome the world, the flesh and the devil. There will be many that will be saved but will not be full overcomers to reign on this earth with our Lord. He will give us power to overcome if we are willing. Bless his holy Name.213
In the eschatological context in which the discussion took place, impure doctrine led to impure lives; and the end of that would be either ruin or loss of reward. Some believers would go through the Great Tribulation because of unconfessed, presumptuous, and/or carnal indulgences. There would be a loss of reward. Thus, whether or not one was from a Wesleyan background emphasizing a second definite work of grace (sanctification), one needed power to ‘overcome the world, the flesh and the devil’. The primary pastoral concern was not over this or that creed but that someone should be solid in the Word, teaching straight doctrine—straight out of the Word! In time, however, such pastoral concern hardened. Rules for holy living developed, while under the influence and power of the apocalyptic vision, which prohibited even those questionable things not specifically proscribed by Scripture, but thought to be in violation of scriptural teachings. These are practices which might cause a sister or brother to stumble. These rules (such as dealing with a member who smoked) would be discussed and pastoral admonitions would be offered, usually with advice concerning being merciful and longsuffering toward the carnal, immature or weak.214 Over time, however,
these restrictions became hard and fast laws for immediate enforcement. They became tests of fellowship and requirements for entry into full membership, a kind of holiness catechism which had to be believed and obeyed if one was to be a full participant in the covenanted band of believers. A little leaven could leaven the whole lump. Purity of heart required purity of doctrine and life. Without the pursuit of holiness one could not see the Lord. Also evident in this sort of teaching is the relationship between the Spirit, Christ, and the Word of Scripture. Just as Jesus had specific knowledge of the faults, compromises, faithfulness, and steadfastness of the churches of Asia, so he also spoke to the specific situation of contemporary churches and applied the scriptural teaching by means of the Holy Spirit who searched the hearts and lives of all. Pastoral concern could also lead to disagreement over doctrine. William Durham developed the non-Wesleyan ‘finished work’ view of sanctification to account for those persons, who, though they had no definite crisis experience of sanctification, did ‘have the baptism’. Yet it was also pastoral concern which led Wesleyan Pentecostals to reject Durham’s new teaching and Seymour to lock Durham out of the Azusa mission! For the Wesleyan Pentecostals, power was to be upon and for the sanctified life; thus to turn sanctification into something practically identical to regeneration followed by mere growth was to lose the specificity, dynamic, and event-fulness of the Wesleyan teaching. Growth without crises was not only uninspiring, it was dangerous, for it undercut the hope of real and definite transformations. This division would confirm to many that creeds represented division in the body which could be healed only through arriving at a new consensus in love. Since sanctification was seen as perfect love casting out all fear and binding the body together, the early Pentecostals saw this very painful dispute as striking at two of their most vital tenets: missionary unity and readiness for the coming of the Lord. Yet pastoral concern for sound doctrine seemed to make creeds unavoidable. As Seymour noted, The only way to keep foul and false hellish spirits out of the church of Christ is to have sound doctrine. ‘Fortify the walls’.215 But if Seymour and others offered the ‘sound doctrine’ argument in one hand, they also usually had in the other hand a more pragmatic test for the movement’s legitimacy as a whole: The thing that makes us know that this ‘latter rain’ that is flooding the
world with the glory of God is of the Lord is because we know that the devil is not in such business … This work is not to build up some great machine—not to be some great something but to get souls saved and living in unity with Christ.216 The church is not essentially a machine or organization created by humans; it is an organism. There is a fusion of clergy and laity, male and female, fruit and gifts, but a fission of church and world, and doctrine serves to define those limits. Without those limits there is no clear identity and health. Pentecostals developed different polities, but eventually all—whether congregational, presbyterian, or Episcopal—were qualified by the dynamic leveling of the Pentecostal presence who turned everyone into a priest, prophet, saint, and witness. Offices of the church—ministry gifts such as pastor, apostle, teacher, prophet, and so forth—were to be recognized by the body and could only be effective if the body confirmed the gift. The attraction to evidences and results signaled a shift from the qualitative to the quantitative. But after getting burned by charlatans and the many weird persons that such a movement usually attracts and makes a place for, Pentecostals quickly (as early as the Azusa revival) developed tests of discernment involving sound doctrine and the fruit of the Spirit; these will be discussed in Chapter 3.
Oral-Narrative Formation: The Speech of the Kingdom
In all it was important to observe the fission or distinction between the Holy Spirit and the human spirit. Inducing spiritual experiences was and still is abhorrent to Pentecostals. The Apostolic Faith exhorted, Honor the Holy Ghost. Someone may say, ‘If you can speak in tongues, let me hear you.’ Don’t ever try to do that. The Holy Ghost will never speak in that way. It is not you that speak but the Holy Ghost and He will speak when He chooses. Don’t ever try to speak with tongues or say that the power belongs to you. It is by My Spirit, saith the Lord. When saying or speaking in tongues, your mind does not take any part in it. He wants you to pray for the interpretation, so that you can speak with the Spirit and with the understanding also (1 Cor. 14.16).217 Though Seymour and others were obviously aware that they were speaking, yet it was vitally important to overemphasize the Holy Spirit as sovereign source. If this were true of speaking in tongues it was true of all other gifts; indeed it was true of the whole Christian life. ‘Not I, but Christ. Not my spirit,
but the Holy Spirit.’ That would be a fair characterization of the concerns and affirmations of the early Pentecostals. Speaking in tongues was the point at which the Holy Spirit and the human spirit, the church and the kingdom existed in the most personal yet corporate dynamic tension of the ‘already–not yet’. It is what is most evident to outsiders and it is a practice which paradigmatically and dramatically underscores the oral-narrative character of Pentecostalism. Speaking in tongues was sign, gift, and evidence. When interpreted, it was a sign equivalent to prophecy, to the unbeliever who would often be convicted upon hearing it. It was a sign to the whole church of the restoration of the ‘early rain’ of apostolic power and gifts being restored in a ‘latter rain’ for missionary activity. It was evidence of Spirit baptism. Over the years, in response to charges of demonism or derangement, Pentecostals hardened their claims for tongues as initial evidence. At first, as noted previously, there was a recognition of Spirit baptism apart from tongues, with the gift of tongues usually following at a later time. Early Pentecostals further qualified the initial evidence teaching by emphasizing the importance of the fruit of the Spirit as the sure, lasting proof of Spirit baptism. Speaking in tongues was personal and corporate expression. As personal edification it was available to each believer as an eschatological prayer language, an immediate response to the coming kingdom in which God will be all in all and all speech will be out of hearts aflame with the presence of the Spirit. Tongues underscored the ineffability of God who was the source of wonder and delight. It was also a means to express the inexpressible in the eschatological language of the human heart and heaven. If love was the fount of and gateway into the fruit of the Spirit, then speaking in tongues came to exercise a similar function in relation to the gifts of the Spirit. Here is fusion or union of this world and the next, divine and human, in a communion so intense that initiation and response become a kind of dance with the Holy Spirit leading. There was an obvious Spirit-body correspondence in which that which is most characteristically human and constitutive of human community (i.e. language) required a new speech incapable of being co-opted by the routinizing of church bureaucracies or worldly regimes. Tongues, interpretation, wisdom, knowledge, prophecy, teaching, testimony, praise, and so on, all are intensively personal, intensely corporate and eschatologically oriented. The shape of Pentecostal worship and witness would be incomprehensible without them. Thus in testimonies the apocalyptic telos was the force pulling the testifier
along as she or he told of the providential events, the miraculous happenings, the eventful existence of the journey toward the kingdom of righteousness, holiness, and power which was even then at work. Everyone listened, identified and responded in hopeful longing which served to sanctify and form them as a body of witnesses. Stories merged with the story. What must have seemed a cacophony of sound and a pandemonium of celebration was to the Pentecostals a concert of prayer, a stereophonic praise temple and a proleptic dance of the kingdom. Where the Spirit was, there was liberty. Speaking in tongues, visions, dreams, and so forth under the constraints of 1 Corinthians 12–14 liberate[s] the people of God from dehumanizing cultural, economic, and social forces. They create room for an oral theological debate … unfreeze liturgical, theological and socio-political formulae and replace imported ideologies … with the political literacy of the whole people of God, practiced and learned within the framework of an oral liturgy for which the whole congregation is responsible; this is an authority based on speech, narrative and communication which ‘enters into conflict with authority 218 which is based on status, education money and judicial power’. The dance of joy and the celebration of speech were evidence that victims were freed to become participants in salvation history.219 Music was and is very important in that celebration; it expresses, directs, and deepens that joy. The rhythmic and repetitive nature of much of the singing reflected this joyful celebration or feast of Pentecost in the light of the end, or, to come from the other direction, the marriage supper of the Lamb anticipated in every Lord’s Supper. Hymns of revivalism, of the Holiness movement and of the Wesleyan renewal were sung along with new gospel songs which were usually a testimony, exhortation or chronicle of the journey toward ‘home’. The oral-narrative liturgy and witness of Pentecostals was a rehearsal of and for the kingdom of God. They rehearsed for the coming of the Lord, the final event of the historical drama; and the songs, testimonies and so on were a means of grace used to sanctify, encourage, mobilize, and direct them on their journey.
Spirit-Body Correspondence: The Acts of the Kingdom
When the congregation gathered for worship they moved as one body-mindspirit in response to the Holy Spirit. The interactive patterns of African spirituality and nineteenth-century revivalism were taken over, indeed were
already in place wherever the revival had spread. It was and is a liturgy of, by, and for the people. The correspondence between Spirit and body is evident in a great variety of psychomotor celebration. The Pentecostal believers exist in the Spirit between creation and consummation—on the way to the end where there will be a spirit body in perfect correspondence with the Holy Spirit and freed of 220 all the effects of the Fall. The body is dead because of sin, but it is the cleansed temple of the Holy Spirit. The cleansing of the blood makes possible the indwelling of the Spirit which constitutes Christian existence. To be in Christ is to have the witness of the Spirit. But the conscious, ongoing, abiding of the Spirit requires a clearing of the internal channels of receptivity and a renewal from the tendency to sin, to resist and thus to grieve the Spirit. This is sanctification through mortification and vivification, putting off the ‘old person of sin’ and ‘putting on the new in Christ’.221 Atonement provided redemption, through the body of Christ for his body the church. It was a bodily event that looked forward to a universal resurrection of glory for those joined to Christ. The body is the Lord’s and is to be offered a living sacrifice here and now. Pentecostals had a total ‘body life’ of worship. The whole body responded and each person presented his or her body in receptivity and yieldedness to the Lord. Hands would be raised in praise and longing for his coming as the clouds of heavenly glory descended upon them. Hands would reach out to touch Jesus and by his Spirit receive healing and help. Hands would clap for joy at the mighty and wonderful deeds and presence of God. Hands would clasp and clench as believers reverenced and ‘held on’ to God for a blessing. The right hand of fellowship would be extended to all those coming into full membership in the church. Bodies would sway in the heavenly breezes blowing from the throne of God. Hands would be laid upon those seeking healing, needing encouragement, or being set forth by the body for some particular ministry. The gift of healing was not limited to a healing evangelist. Most healings occurred within the corporate ministry of the church. The healing evangelists simply represented this ministry gift and it was operated through them to touch unbelievers as a sign gift. Hands of the elders would reach to anoint with oil so that the healing balm of Calvary could be applied in the Holy Spirit to the wounded and weary ones. Salvation and healing were for the body—the whole person and were a provision of the atonement.222 They expected everyone to be healed but if they were not, they simply kept praying and expecting the coming of the Lord. Funerals were times of grief and celebration. Thus the regular worship times
of laughter and tears, eschatological joy and longing for the lost, were preparation for the loss of death. Words would be spoken at the funerals concerning the faithfulness of the Lord and often gifts of the Spirit would operate to assure them. God could raise the dead—and there were many reports of this—but if God did not raise them now, he would soon. The body was for the Lord, therefore periods of fasting were to draw nigh to God with one’s whole being. This bodily dedication was necessary, because spirituality involved the whole person and all of his or her life. Fasting was not a punishment; it was a feeding on the Lord and drinking of the Spirit. Spirit-body correspondence was evidenced also in the ordinances: in the washing of baptism, the eating and drinking of the Lord’s Supper, and, for some, the washing of the saints’ feet. Baptism was in recognition of the conversion of the individual and that all righteousness might be fulfilled.223 Great joy and celebration would attend baptisms which were usually, though not of necessity, in a lake, river, or ocean. The Spirit of God would come close and everyone would praise God that another person had come to join them on the missionary journey toward the kingdom. Baptism was not a converting sacrament of initiation, but it was a means of grace in that it represented walking in the light, public witness, remembrance, and following of Christ in public solidarity with the church. Babies were dedicated to the Lord, but would not be lost if they died before baptism.224 Baptism was individual but corporate. It was the acceptance of the call to become a holy witness in the power of the Holy Spirit. It was a death and resurrection ritual of remembrance and hope. For many it was repeated if they had been baptized before conversion or had backslidden. If other churches were offended because of rebaptism, the Pentecostal answer was that of the early Anabaptists: the first baptism was no baptism at all. Baptism did not save; in fact nothing one could do or had done would save. Only the gospel was the power of God unto salvation to everyone who believed. If baptism was the sign of starting out in service to the Lord or the way to the kingdom, then the Lord’s Supper was the sign of ongoing nurture and fellowship. The real presence of God was never an issue. Through the Spirit, God the Father and the Son met them in the Lord’s Supper. Since it was neither a converting ordinance (though that could happen) nor absolutely necessary for daily health, it was not celebrated as often as in most mainline churches — certainly not every Sunday, with a few exceptions.225 Christ was made effectively present by virtue of the Holy Spirit. To eat or drink with unconfessed sin was to court danger, sickness, or even death. Pentecostals took the warnings to the
Corinthians to heart, thus making communion a solemn time of soul-searching and consecration.226 But on the other hand it was a joyous anticipation if one prepared for it properly. Questions for self-examination, hortatory direction, and joyous anticipation were offered as seen in the following gospel song: ‘The Glorious Marriage Supper of the Lamb’ 1. When ‘mid sounds of earthly voices, none your accents ever hear, Will your tones be thrilling or redemption’s psalm? Will your soul in blood-washed garments fair and spotless then appear, At the glorious marriage supper of the Lamb? 2. Will you be among the members who are undefiled, Called from earthly conflict into heaven’s calm? Will you by His Son’s atonement unto God be reconciled, Ere the glorious marriage supper of the Lamb? 3. Now put on the wedding raiment and be ready for the call, With your sin-wounds cured by Calvary’s healing balm; Bow before the blessed Jesus and proclaim Him Lord of all, At the glorious marriage supper of the Lamb. REFRAIN O the glorious marriage supper of the Lamb, O the glorious marriage supper of the Lamb; Robed in garment’s snowy-white, will you meet the saints of light, At the glorious marriage supper of the Lamb?227 Persons could be converted, healed, sanctified, and filled with the Spirit in conjunction with the Lord’s Supper because it was a part of the ongoing missionary worship and witness of the body. But it was definitely not ‘the mass’ or the sine qua non of Christian existence. The Lord’s Supper was important because Jesus was present keeping the Passover and promising the parousia in the Holy Spirit. Those groups which washed feet did so in obedience to John 13 and saw this as a time of cleansing and service to one another. In this way the leveling effect of Calvary was realized and the daily cleansing from sin unto servanthood was
acknowledged, prayed for, and received. Believers were encouraged to confess to one another, especially if they had an ought against someone. All members of the church participated, as could all believers, in the observance of the washing of the saints’ feet. This was usually done in conjunction with the Lord’s Supper and thus the two together constituted a blessing of cleansing, service, and nurture in obedience to the Lord’s commands. To caricature this as a mere remembrance or doing of one’s duty, as the word ‘ordinance’ implies, would be to miss the richness of the actual practice. Pentecostals, they believed, were commanded to do these things just as they were commanded to rejoice and receive the Spirit each day. These were times of great blessing and deepening. At Azusa the Lord’s Supper was memorial, anticipation, and healing, as Seymour testified, We find as we partake of this ordinance, it brings healing to our bodies if we discern the Lord’s body by faith … It also teaches us salvation and sanctification through the Blood. Our souls are built up, for we eat His flesh 228 and drink His Blood. The word ‘sacrament’ was seen as a non-biblical word of Roman Catholic derivation which was associated with mechanical ritual. Never mind that the word ‘ordinance’ was non-biblical also; it was closer to the idea of obeying the specific command of Jesus. To eat, drink, baptize, and wash feet was to do it unto the Lord; and he was present in, with, under, and through these acts. Testimonies would be given during the ordinances to chronicle the narrative journey from the past, through the present and toward the future kingdom.
Crisis-Development Dialectic: The Process of the Kingdom
The narrative journey of Pentecostals in the light of the apocalyptic vision could be characterized as a crisis-development dialectic. Whereas some Christians marked the journey with sacraments which were a kind of crisis, for Pentecostals crisis points were times when God did something decisive which made possible a personal or corporate development that, before that time, was not possible. For example, when an individual was healed (a near universal Pentecostal testimony), their life was radically changed. Now they were living in a world of surprises and divine visitations, as well as daily divine support. No longer could they embrace a strict dispensationalism which bracketed gifts in the first century. Now they were living in the end times. Regeneration, sanctification, Spirit baptism, and various gifts of the Spirit
were crises within and with a view toward an apocalyptic development which was a revelatory unfolding of God’s continual acts of redemption in history. Salvation history was not primarily a matter of ideas, illumination, and belief. It was fundamentally deliverance, turning, listening, watching, walking, waiting on the Lord who had acted, was acting, and would act. God’s activity was the basis or ground for the believer’s acts. Individuals were not alienated from their works by a doctrine of salvation by grace alone which made works seem positively useless if not bad. One worked because God was at work. Works expressed the activity of God in and through and among the people whom he was empowering. Salvation history was an ongoing history of revelation. The Bible was a closed canon but revelation continued because God was not yet all in all. Nothing revealed would be unbiblical, but it was beyond the Bible because salvation history had progressed beyond the first century. All that the Spirit spoke was scriptural, but not all that he spoke was in the Bible. It was not the role of the Spirit only to repeat Scripture. Guidance and gifts would be operated by the sovereign Spirit in edifying the church and witnessing in the world. History was not a series of disconnected episodes but neither was it the smooth unfolding of life as the fruit from a seed in the changing seasons. One would be saved out of darkness into light and then walk in that light. As a person walked in the light, more light would be given. One would make restitution and bring forth ‘fruits meet for repentance’;229 that is, one would leave off sinning and make wrongs right wherever possible. In sanctification there would be a crisis of wholehearted love which concentrated on a complete yieldedness and availability for whatever assignment the Lord of the church might make by the sovereign action of the Holy Spirit. Then, in God’s own time, one could be filled with the Holy Spirit and thus equipped for witness in word and deed, power and demonstration of the Holy Spirit. These three crises committed one to a life of righteousness, purity, and witness in the light, love, and power of God. As God had revealed himself as Fathercreator, Son-redeemer, and Spirit-sustainer in the biblical development of salvation history, so the believer’s life recapitulated the biblical order or the comings of God into human experience. The church itself, though falling away at the time of Constantine, was restored successively through the crises of Luther (justification), Wesley (sanctification), and Pentecostalism (Spirit filling). This whole process would one day be radically altered by the second coming of Christ which would end history but also make possible a new, undreamed of process of adoration and joy.
The crisis-development dialectic was thus characteristic of a view of the biblical drama, the church’s history and the individual believer’s journey. A critique of this will be offered in Chapter 4, but for now at least it can be seen that the Pentecostals were advocating neither a smooth continuity with tradition nor a complete discontinuity. Perhaps it could best be characterized as a continuity in discontinuity. Churches and individuals had been and could be wrong. Presuppositions and traditional views could be radically altered by the intervention of God. What was being called for was a reforming and renewing praxis.
Pentecostal Praxis: Action-Reflection in the Spirit Thus far the significance of the Pentecostal understanding of the presence of God has been assessed and followed by a description of Pentecostal narrative beliefs. The Pentecostal practices, all under the influence of the apocalyptic vision which gave them urgency and focus, have been categorized and briefly described. The presence of the Spirit of the end sets in motion a people with a story to tell. Each chapter of that story reflects the end to which they are called and toward which they press inviting everyone to join them. The ‘already–not yet’ tension must be maintained because, if resolved either way, the mission will be hindered if not forfeited. There can be no escape into the ‘not yet’. It will come to them in God’s time, at any time. On the other hand, there can be no ‘already’ setting up of the kingdom here and now, an accommodative, triumphal venture not requiring the radical inbreaking of God. Persons, churches and world, are presently under the impact and influence of the Spirit who works in all, pressing and driving toward the end. The presence of the Spirit signals a continuing crisis in the development of the world and its history over against the salvation history of the world. In this eschatological praxis of the Spirit as he informs, forms and transforms all things, the Pentecostal believer was called to be like Christ and like the Spirit; or, to put it more accurately, to be like the Spirit in order to be like Christ. Like the Spirit, the believers were to bear witness to Christ and not to themselves. The fruit of the Spirit was the Spirit’s work to manifest Christ in the character of the believers. The gifts of the Spirit were to manifest the power of God in the service of the gospel ministry of evangelism and edification. Like Christ the believers were to depend on the Holy Spirit and not on autonomous human reason or the arm of flesh. Only the Spirit could enable the church to overcome the enemy. Only the Spirit could maintain the unity of the body in the peace of Christ. Only by the Spirit could one see the light, walk in the light and thus walk as Christ walked. Thus Pentecostal praxis was not just the practice of gifts or exuberant worship. It was not merely the stating of a few distinctive beliefs about Spirit baptism or tongues. Rather, it was a corporate action-reflection in the Spirit that sought to bear witness to Christ by the proclamation of the gospel in power and demonstration of the Holy Spirit. At first they were sure that tongues would be for the evangelization of all nations without having to learn the foreign
languages—a kind of short cut before the end. That idea soon was proven wrong. But it was certainly possible; anything was possible with God. Anything was possible except that which violated Scripture and was not Christlike. The praxis of the Spirit, action-learning within his action and teaching, was a missionary praxis which revealed the Kingdom of God.230 The Spirit was and is the supreme missionary strategist. The praxis was evidenced in worship and witness through practices, inherited from the two previous centuries of revival and reform, which bore the distinctive stamp of apocalyptic vision. This stamp or seal of the Spirit could also be seen in the responsiveness, joy, tarrying, longing, and immediate urgent missionary witness. Living in this praxis of the Spirit, the transcendent presence of God, meant living in paradox: in but not of the world, already saved but not yet resurrected, already healed but dying, already filled but longing for the day when God would be all in all, having very limited abilities but the unlimited power and gifts of God, organizing and making faith statements but decrying creeds and organizations, living in expectant readiness in the face of the imminent return of Christ but not knowing when it might be. For those who spoke with the ‘tongues of men and angels’ the only way to survive, thrive, and go forward was in the love of God. They banded together, ‘fortified the walls’ and proceeded to cultivate disciples in a missionary fellowship with an apocalyptic vision. The beliefs and practices taken as a living whole and informed by the presence of the Spirit of the end were distinctive. The powerful, sensed presence of the Spirit led to a clear testimony focused on Christ as Savior, Sanctifier, Healer, Baptizer in the Spirit, and coming King. But these distinctive beliefs and practices as a whole were rooted in distinctive Pentecostal affections which essentially characterized the believers. The affections were normed, shaped, and altered by these beliefs. The practices grew out of and fed the affections. But without these affections there would have been no continuing Pentecostal identity and presence in the twentieth century. It was because of, and in order to nurture, these affections that they were a people at rest yet always at work, watching and ‘Waiting on the Lord’. 1. Waiting on the Lord for the promise given; Waiting on the Lord to send from heaven; Waiting on the Lord by our faith receiving; Waiting in the Upper Room. 2. Waiting on the Lord, giving all to Jesus
Waiting on the Lord, till from sin He frees us; Waiting on the Lord for the heavenly breezes; Waiting in the Upper Room.
3. Waiting on the Lord, longing to mount higher; Waiting on the Lord, having great desire; Waiting on the Lord for the heavenly fire; Waiting in the upper room. CHORUS The power! The power! Gives victory over sin and purity within; The power! The power! The power they had at Pentecost.231
Chapter 3
Pentecostal Theology as Missionary Fellowship: An Affective Integration
Pentecostal Identity: Liberation for the Kingdom
‘Praying through’ from underneath Pentecostals do not emphasize the intensity of feelings, though they are often called upon to defend or explain their strong show of emotion. The Enlightenment view of the opposition of reason and emotion, as well as the fundamentalist emphasis on their ‘balance’, combine to produce a cultural suspicion, if not outright derogation, of ‘Holy Rollers’. Emotions are associated with bodily feelings and motions which are deemed inappropriate for the privatized faith of the middle and upper classes. Therefore when a person oppressed by society and sin ‘prays through’ that oppression to a new identity in the kingdom of God and there is attendant upon this event intense emotion, it has sometimes been slandered as ‘orgiastic’ religion by news reporters and other opinion makers. Poor African Americans and uneducated Caucasians alike are seen as crude and disorderly even though persons of culture may at times enjoy listening to their singing or observing their exuberant celebrations. As Vance Packard, eminent North American sociologist, has observed: it is a long way from Pentecostalism to Episcopalianism in the United States.232 Thus there is the matter of social class as well as the Enlightenment cultural perspective on religion to take into account; these factors merge in a class-cultural bias against movements of the poor in general and Pentecostalism in particular. But in a postmodern era perhaps the dichotomy of reason and emotion, which has characterized much of American historiography, can be transcended, and new, more wholistic, integrative categories devised. Pentecostals, perhaps more than any other group, came to recognize the dangers of mere emotionalism very early in the movement. The strong emotions and the recognition of the dangers were both part of the legacy of nineteenth-century revivalism. But when persons, who had seen themselves (as well as having been perceived by others) as determined by the socio-political, economic, educational, class, and racial forms, broke through by the power of the Spirit into a new existence of freedom and belonging, there were usually tears of joy and shouts of victory in the camp of the prayerful. They were truly liberated and not merely informed. God, who had liberated them, would soon liberate the whole world at the Second Coming of Christ. One was to go about doing good and witnessing in the power of the Spirit
in light of this soon coming kingdom. But who was one supposed to be? What should characterize a Pentecostal believer? Surely not a series of emotional episodes. No, there was a certain vision of what it was to be as well as to give a witness to Jesus Christ; and contained within this vision was an implicit correlation of the character of God and that of the believer, between the Holiness language of love and the Pentecostal language of power.
Becoming a Pentecostal Witness
This chapter analyzes the distinctive Pentecostal experience in terms of religious affections. These affections are shown to characterize Pentecostals and, further, it is demonstrated that they bear the mark or impact of the apocalyptic vision and power of the movement. The transcendent presence of God moves and transforms believers affectively as he conforms them to himself and, therefore, fits them for the coming kingdom. It will be recalled from Chapter 1 that spirituality involves the integration of beliefs, practices, and affections. Christian spirituality as embodied by Pentecostals calls for discerning reflection in the light of the vision of the kingdom of God. This reflection is the heart of the theological task for Pentecostals. Chapter 1 also traced something of the Holiness-transformationist roots of the movement with an explanation of the emergent ‘fivefold gospel’ of the kingdom. Chapter 2 discussed the power of the apocalyptic presence of the Holy Spirit and his effect upon each experienced and enacted aspect of Pentecostal life. Pentecostal narrative beliefs told a story of the restoration of the ‘fivefold gospel’ to the church and the cultivation of the persons who received and believed that gospel as a way of life. Songs, testimonies, gifts, and a variety of other worship and witness practices were categorized and analyzed to show the effect of the ‘already–not yet’ tension. The language of love and the language of power were seeking a translation or fusion that would bring soteriology and eschatology, church and kingdom, Christ and Spirit into a new synthesis. The ‘fivefold gospel’ was Christocentric because of the witness, power, and presence of the Holy Spirit. This gave the movement a shape, direction, and theology which represented an eschatological intensification and pneumatological emphasis within the Holiness movement. While the identification of sanctification and Spirit baptism gave way to an appreciation of the experimental and theological distinction of the two, their interrelationship within the apocalyptic horizon of expectation and preparation remained crucially important in defining the new movement. Both the character
and vocation of a Pentecostal were bound up in the doctrines of sanctification and Spirit baptism, respectively. This character and vocation are captured in the following exhortations to the saints at Azusa: Tongues are one of the signs that go with every baptized person, but it is not the real evidence of the baptism in the every day life. Your life must measure up with the fruits of the Spirit. If you get angry, or speak evil, or backbite, I care not how many tongues you may have, you have not the baptism with the Holy Spirit. You have lost your salvation. You need the Blood in your soul … Many may start in this salvation, and yet if they do not watch and keep under the Blood, they will lose the Spirit of Jesus, which is divine love, and have only gifts which will be as sounding brass and a tinkling cymbal, and sooner or later these will be taken away. If you want to live in the Spirit live 233 in the fruits of the Spirit every day … Sounding very much like the apostle Paul speaking to the Corinthians, Seymour admonished, O beloved, our reigning time has not come yet. We are to be with the Babe from the manger to the throne. Our reigning time will come when Jesus comes in great power from the throne. Until then we are to be beaten, to be spit upon, and mocked. We are to be like His son.234 The character or fruit of the Spirit that should, according to Seymour, characterize those early persecuted witnesses are analyzed in this chapter as Pentecostal affections. The chapter will (1) show that underlying the affections there was an implicit God-salvation correlation, (2) briefly discuss the general definition of Christian affections, (3) describe the apocalyptic affections of Pentecostals, (4) note the important role of discernment and discipline for the identification, cultivation, and preservation of true affections, (5) discuss the Pentecostal understanding of prayer as it shapes and expresses the affections, (6) show that the ruling affection is the passion for the kingdom, and, finally, (7) demonstrate throughout that the missionary fellowship through its worship and witness calls forth, forms, reinforces, and directs the constituent affections of Pentecostalism.
Pentecostal Affections: Embodying and Longing for the Kingdom
An Implicit Correlation: The ‘Theo-Logic’ of the ‘Three Blessings’ Participation in the Pentecostal narratives and practices enabled an affective transformation which was implicitly correlated with certain divine attributes, the apocalyptic vision, and individual testimony. The following chart displays this correlation.
The testimonies, tracts, and songs express a longing to be like Christ, to live a ‘godly life’. The three attributes of righteousness, love, and power are correlated implicitly with the view of Christ as Savior, sanctifier, and baptizer in the Spirit and the Christian testimony to justification, sanctification, and Spirit baptism. The concern for righteousness is expressed in relation to conversion and continuing in the Way. The early statement of faith of the Apostolic Faith Mission at Azusa stood for the restoration of the faith once delivered to the saints … Teaching a Repentance—Mark 1.14, 15. Godly Sorrow for Sin, Example—Matt 9.13. 2 Cor. 7.9, 11. Acts 3.19. Acts 17.30, 31. Of Confession for Sin, Example—Luke 15.21 and Luke 18.13. Forsaking Sinful Ways—Isa. 55.7. Jonah 3.8. Prov. 28.13. Restitution—Ezek. 33.15. Luke 19.8. And faith in Jesus Christ First Work—Justification is that act of God’s free grace by which we receive remission of sins. Acts 10.42.43. Rom. 3.25 … The Blood of Jesus will never blot out any sin between man and man [which] they can make right; but if we can’t make wrongs right the Blood graciously covers (Matt 5.23, 24).235 From this statement it seems that God’s gracious justification or pardon through repentance and faith in Jesus Christ in no way removes the necessity of restitution and reconciliation among persons whenever possible (if they are within range and still living). The believer was sorry for his or her sins against God and thus had a ‘godly sorrow’. But the confession and repentance of sin was
not only a belief in the righteousness of God in Christ but also a declaration to walk in the light, to walk righteously in the world. Indeed, to ‘teach God’s people to observe all things whatsoever He has commanded … practicing every command and living by every word that proceedeth out of the mouth of God’236 is what it means to believe in ‘a full gospel’. Therefore, the ‘full gospel’ was not limited to the fivefold formulation. The ‘full gospel’ was the ‘whole Bible rightly divided’, the whole counsel of God. Old and New Testament Scriptures, as noted earlier, were used in establishing the way of righteousness. The ‘Lord of hosts is exalted in justice and the Holy God shows himself holy in righteousness’ (Isa. 5.16). Walter Brueggemann’s conclusion regarding this Isaiah passage is applicable to the early Pentecostal belief: ‘A social practice of righteousness impinges upon the character of God … Restoration of the covenant between Yahweh and Israel depends on a proper social practice’.237 Pentecostals believed that the practice of some churches had led to antinomianism or to a dead faith without works. Indeed, some churches by their formal, mechanical approach had made the righteous guilty and thus had removed the righteousness of the righteous.238 In contrast, the Pentecostal community mirrored the development of faith in the book of Isaiah as it ‘gathered around the text’ and matured ‘in its embrace and practice of God’s righteousness’.239 But this development of faith was more like a reformation and a new beginning, a restoration to what they believed was a more biblical pattern. This restoration came shatteringly in moves of harsh discontinuity. It was a new development requiring ‘harsh displacement, a breaking of old configurations of power and self-serving value’.240 This discontinuity or displacement was accompanied by intense inner struggle and longing, and this was true whether one was a new convert or a member from another church coming into new light. To come this way was to begin again at the beginning; it was to commit to follow Christ wherever He might lead. It was to agree to walk in all the light God might give as it shined upon one’s path. Justification was pardon but never justification for unrighteousness. Salvation was to become like God. It began with turning toward and walking in the light and it continued just as it had begun. After the light of justification and the requirement of a righteous God more light was given concerning the holiness of God and the sanctification of the believer. This was understood in terms familiar to those out of or influenced by
the nineteenth-century Holiness movement. Again the Apostolic Faith at Azusa affirmed a second work—sanctification is the second work of grace and the last work of grace. Sanctification is that act of God’s free grace by which He makes us holy. John 17.15, 17.—‘Sanctify them through Thy Truth; Thy Word is Truth’. I Thess. 4.3. I Thess. 5.23; Heb. 2.11; 12.14. Sanctification is cleansing to make holy. The Disciples were sanctified before the Day of Pentecost. By a careful study of Scripture you will find it is so now. ‘Ye are clean through the word which I have spoken unto you’ (John 15.3; 13.10); and Jesus breathed on them the Holy Ghost. (John 20.21, 22). You know that they could not have received the Spirit if they were not clean. Jesus cleaned and got all doubt out of his church before He went back to glory.241 Later in the same issue of The Apostolic Faith the following exhortation to purity was given: Blessed are the pure in heart. We do not get this purity till we are willing to let Him have His way to the fullest extent of the word. We are clay in the Potter’s hands. We must have the self well [sic, will] removed in order to receive Him. As long as we have something to say, ‘I don’t like this or that’, we cannot receive the Holy Ghost’.242 Sanctification involved a complete yieldedness and availability to God. Holiness was God’s essential nature and therefore it could be asserted that the object and end of all the precious Scripture is that a definite work may be wrought out in our hearts by the Holy Ghost God’s design through the ages and through all His work with the children of men, has been to implant His own nature-love, in a fallen race … Dear ones, have we got that burning passion for souls of the lost? When we are persecuted and tried for the word of God, can we say in our Hearts, Lord, forgive them, for they know not what they do? It is sweet to have the promise of Jesus and the character of Jesus wrought out in our lives and hearts by the power of the blood and the Holy Ghost, and to have that same love and that same meekness and humility manifested in our lives for His character is love … Dear loved ones, we must have that pure love that comes down from
heaven, love that is willing to suffer loss, love that is not puffed up, not easily provoked, but gentle, meek, and humble. We are accounted as sheep for the slaughter daily. We are crucified to self, the world, the flesh, and everything, that we may bear in our body the dying of the Lord Jesus, that our joy may be full even as He is full.243 Sanctification, which begins in new birth, is actualized in a subsequent definite work. It is a definite work because it is a definite, dynamic reality. Salvation is a partaking of and a participation in the divine life. The character of holiness is love in the believer. It is a perfect love filling the cleansed, emptied vessel and without which the believer’s gifts, sacrifices, and righteous deeds will profit nothing. The measure of love given in new birth, along with the graces therein implanted, come to full fruitfulness in sanctification. ‘This entire sanctification is a ‘burning passion for souls’ that enables one to forgive one’s persecutors. The power of the blood in sanctification is a necessary and logical prerequisite for the power of the Holy Ghost in Spirit baptism. Purity precedes power in the logic of early Pentecostal faith development because one must be a witness in character and deeds. The righteousness of God was to the faithfulness of the believer as the holiness of God was to the love of the saints. The way of righteousness and the burning passion of love asked for the power to make the witness an effective demonstration of the power of God. The baptism with the Holy Ghost was the aspect of salvation corresponding to the attribute of divine power. It was the ‘gift of power upon the sanctified life’.244 The baptism will fade away if one does not walk in the light of righteousness as it shines upon one’s pathway. The Holy Spirit would not continue to empower one walking in darkness and the Spirit could not continue to fill those who did not abide in the perfect love of God. Those who were baptized with the Spirit ‘must die daily that Christ may abide in you. If we begin to get puffed up, God will set us aside, but if we give Him all the glory, He will use us to scatter this light’.245 All the experiences of grace were amissible and required an ongoing moment-by-moment abiding. Nothing could remove believers from the hand of Christ, but they must abide in him in loving obedience by the grace and power provided. The power of the Holy Spirit was given for a specific purpose: [W]hen we get the baptism with the Holy Spirit, we have something to tell, and it is that the blood of Jesus Christ cleanseth from all sin. The baptism with the Holy Ghost gives us power to testify to a risen, resurrected Savior. Our affections are in Jesus Christ, the Lamb of God that takes away the sin of the world. How I worship Him today! How I praise Him for the all-
cleansing blood!246 Praise and proclamation, the presence of Jesus and the Spirit, and the affections in Christ and the power of the Spirit are all fused in a call to Christian character and vocation. Throughout the literature of the early revival there is this explicit correlation of the righteousness, holiness, and power of God and the righteousness, love, and power of the believer. The logic was not that of a formal order of salvation so much as an experiential, dispensational-like development of the believer in righteousness, love, and power. The superlatives of the descriptions of the gospel and the Christian life speak of the implicit correlation of theology, prayer, and salvation: walk in all the light (God is righteous, God is all light, and there is no darkness in him); the full gospel (the fullness of God in Christ); entire sanctification (God is holy, God is love); be filled with the Spirit (God is all-powerful). To relate rightly to God— that is, to know and to follow God—required a progressive transformative development. Participation in the Pentecostal worship and witness over time produced an ‘affective transformation in which lives were formed and shaped’ by their experience of God.247 These Pentecostal testimonies and the correlative view of God were teleologically related to the kingdom of God understood as righteousness, peace, and joy in the Holy Spirit. The righteousness of justification was maintained by walking in the light by grace through faith. The peace of perfect love (which ‘casts out fear’, 1 Jn 4.18) was maintained by walking in love with no inner resistance or ‘hold-outs’. The joy of the fullness of the Spirit was strength and encouragement to believers as they walked in the Spirit and not after the flesh. To believe in the kingdom of heaven, both here and now and there and then, was to long for a kingdom of light and righteousness, holiness, and love, power and demonstration of the Spirit who would fill all things. The Spirit would lead into righteousness. The Spirit would search the heart and, by the Word, point out what was not like Christ and therefore carnal. The Spirit would fill and lead in powerful witness. The Spirit would express himself through gifts and the fruit that was the divine character being formed in the believer by virtue of participation in the divine life. The Father, Son, and Spirit, by the Spirit, came to take up their abode in the believer. If the gifts and fruit were the external witness, then the witness of the Spirit was the internal assurance and evidence for justification, sanctification, and Spirit filling. And speaking in tongues, the eschatological language of heaven,
was at once both internal and external witness, evidence, and assurance. It was a tangible, existential demonstration of that communion, conversation, and intercourse which was what being a Christian was all about. It was a dismantling of the unrighteous Babel of the world in praise, a longing cry of the oppressed for the beloved, and a shout of the eschatological fulfillment already breaking in but not yet fully interpreted. In these ways the early Pentecostals, implicitly at least, correlated their vision of the kingdom, the Christian life, and God. Their beliefs and practices, through the worship, fellowship and witness of the church, were expressive and determinative of certain Pentecostal affections. Before describing these affections it will be well to discuss the general characteristics of ‘affections’ and to show how Christian affections are distinguished from natural ones or mere ‘feelings’.
The Christian Affections: A General Description
Any consideration of affections is complicated by the broad range of meanings and valences of feeling attached to any one of them. Consider the following example. Sue Smith loves her cat, her husband, and her green, two-door automobile. She has had her cat for ten years, her husband for five years, and her green Subaru sedan for one year. Sue takes Samantha, her cat, with her everywhere she goes, and if it is cold outside or the cat is not feeling well Sue tries to stay home and care for it. Sam, her husband comes and goes freely, with or without Sue and Samantha. He has his own small car. Although Sue has told Sam that she trades all her cars after the first twenty thousand miles, he knows that for now she loves this car and does not let anyone, including him, drive it. Her car is a private, personal space for Sue and her cat. Sue, like most people, has several ‘loves’. Each love represents something meaningful and enjoyable in her life and what they represent is shaped by the significance she assigns to them, the amount of time invested, how each ‘object’ of her love has responded to her, what she expects from each, along with the pain and pleasures. Sue also uses the word ‘love’ in relation to chocolate ice cream and trips to the zoo. Often these ‘loves’ will conflict and they have different valences. For example, when Samantha dies, if Sue leaves Sam what does this say about her ‘love’ for the cat versus that for her husband? Sue’s life and ‘loves’ reveal the confusing way that emotions, feelings, and
affection language is often used. The usual response to Sue would be to tell her that she is behaving unreasonably. Her emotions are out of control or balance. This post-Enlightenment dichotomizing or playing off of reason against emotion is characteristic of most of modern Western culture. Public life is usually dictated by reason with the private life reserved for the idiosyncratic and irrational ‘feelings’. This view of reason and emotion is also evident in the evaluation of religious traditions. Everyone knows that Pentecostals are emotional and Episcopalians are reasonable. From animal passions to sweet reasonableness the spectrum of religious ethos is displayed with control, balance, moderation, and quietness among the usual, prevailing criteria for diagnosis and prescription. If the object of the affection is not a cat, spouse, or car but God, then the situation is further complicated in that God is usually construed as the supreme concern or the one demanding overall loyalty. If there are different gods and different construals or ultimate concerns, then the affection will be different. Earlier, spirituality was defined as the integration of beliefs, practices, and affections. This spirituality is a way of life involving knowledge, actions, and affects. These affects or affections are both evoked and expressed by the actions and beliefs. Christians confess that God is love. This love is made known through what God has said and done, is saying and doing, and will say and do. ‘God so loved the world that He gave His only begotten Son’ (Jn 3.16). This says something about the object of God’s love, the world, as well as the source, God. The nature of the gift given says something simultaneously about the source, the object, and the gift. It is not possible to understand this affection, this love, apart from this gift. Indeed it is not possible to receive the gift without love. Scripture further specifies that Christians are to love one another as Christ loved the disciples and others during his earthly ministry.248 This love is shed abroad in human hearts by the Holy Spirit who moves Christians in a compassionate following of Christ.249 If the heart is understood to be the integrative center of the mind, will, and emotions then it is clear that affections are more than mere feelings and Christian affections are meant to characterize a person’s life. For John Wesley and Jonathan Edwards true religion or authentic Christianity was centered in the religious affections. Wesley abridged Edward’s Treatise on the Religious Affections for inclusion in his Christian library for Methodist ministers and leaders. For Wesley, the love of God and neighbor was the heart of true religion without which one was not a Christian.250 His doctrine of entire
sanctification was a way of underscoring the affective transformation wrought in Christ by the Holy Spirit through the means of grace. This fullness of love issued forth in a life of perpetual (even eternal) growth in the grace and knowledge of God as well as the mature manifestation and integration of the fruit of the Holy Spirit. Robert Roberts, Don Saliers, and Hal Knight are contemporary Christian scholars who have emphasized, in varying ways, the constant theme of the importance, if not centrality, of religious affections in understanding the Christian life.251 There is here no mere balancing of head and heart, of thought and feeling; rather there is an integration, an affective understanding which is essential to Christian existence. This faith is constituted by a new disposition of the heart which orders all the powers of emotion, perception, will, and understanding. The affected heart and the intellect are not opposed in true faith, nor are they finally two kinds of capacities which are joined by an act of the will.252 Jonathan Edwards formulates this affective understanding in the following manner: As, on the one hand, there must be light in the understanding, as well as an affected fervent heart, where there is heat without light, there can be nothing divine or heavenly in that heart; so on the other hand, where there is a kind of light without heat, a head stored with notions and speculations, with a cold and unaffected heart, there can be nothing divine in that light, that knowledge is no true spiritual knowledge of divine things.253 There is an epistemological as well as a theological point to be made here, and underlying both is the relationship of Jesus and the Spirit. Jesus is presented to the person through the scriptural testimony by the Holy Spirit. It is the Spirit who moves upon the person to receive Christ. To receive the witness of the Spirit is to receive Christ. But this, then, must also mean that one receives the Spirit. The light and the heat, the truth and love are inseparable because the work of the Spirit and Christ are one work of salvation. To know the truth is to love; to know the truth is to do the truth. Thus to hate, to withhold love is to lie.254 The fanatics of the rationalist or enthusiast types are both addressed and given a deeper understanding of Christian existence from these scriptural and theological perspectives. H. Richard Niebuhr, in a penetrating insight expressed a desire to follow in Edwards’ footsteps more, and undertake an exploration of the land of emotions with a certain hypothesis amounting to conviction … the
hypothesis that contrary to prevalent opinion about the emotions—they put us into touch with what is reliable, firm, real, enduring in ways that are inaccessible to conceptual or spectator reason.255 The conclusion must be that, whatever else it may be, the Christian faith is a pattern of deep emotions. It is gratitude to God for creation and redemption, awe and holy fear of the divine majesty, repentance and sorrow over sins, joy in God’s steadfast love and mercy, and love to God and neighbor. To confess faith in God is to live a life characterized by these emotions.256 These ‘deep emotions’ are the fruit of the Holy Spirit which are formed in some one who believes the gospel of Jesus Christ and construes the world accordingly. Traits like gratitude, compassion, and confidence ‘are what make a person a Christian; they are the definition of Christian spirituality’.257 In the light of the foregoing discussion the following summary statement may be made: Christian affections are objective, relational, and dispositional. To say that Christian affections are objective means that affections take an object. In this case the object is also the subject: God is the source and object of Christian affections. The God who proves righteous, commands righteousness. The God who is love and has ‘so loved’, evokes love. The God who has acted powerfully 258 to deliver, gives power and strength. What God has said and done, is saying and doing, will say and do is the source and telos of the affections. God’s righteousness, love, and power are the source of correlative affections in the believer. The narratives describing these attributes of God evoke, limit, and direct the affections of the believer. God as righteous, loving, and powerful is also the telos of Christian existence and thus of the affections. To believe God is to receive the kingdom of righteousness, peace, and joy in the Holy Spirit and to await its coming consummation. To believe in God and therefore to receive the kingdom is to acknowledge that Christian affections are relational. Christian beliefs and practices shape and express these affections. Christian affections require for their proper genesis and ongoing expression a relationship with God, the church, and the world. This is most obvious in a consideration of that affection which is also the chief theological virtue, love. But as we shall see shortly, it is no less true for other affections. Christian affections cannot be summoned at will. Nor are they a pick and choose kind of emotional smorgasbord for connoisseurs of affective development. They depend on the initiating, sustaining, and directing of the
Sovereign Lord of the church. John Wesley, who spoke of perfect love as wholehearted devotion to God, acknowledged that the Christian life was from first to last a work of the Spirit on a moment-by-moment basis. Wesley asserted, ‘We feel the power of Christ every moment resting upon us, whereby alone we are what we are … and without which, notwithstanding all our present holiness, we should be devils the next moment’.259 For Wesley such a relational understanding of faith entailed regarding spiritual pride as more deeply sinful than any ‘voluntary transgression 260 of a known law of God’. The relationship of faith, obedience, and love was the meaning of faith for Wesley and for those traditions which flow from eighteenthcentury Methodism. Wesley saw this integration in James, Paul, and especially in the epistles of John.261 To be ‘saved’, to be a Christian, was to be rightly related to God and therefore one’s neighbor. If affections are objective and relational, they are and must also be dispositional. Again, for example, God who is love has commanded love for himself and others; and this love which the apostle Paul says ‘abides’ is to characterize Christians. Without it, no matter what or how much they believe, no matter how much they give to the poor, no matter how many gifts of the Spirit they manifest or how great a sacrifice they make, it will profit them nothing.262 Love in particular and Christian affections in general are not passing feelings or sensate episodes. Affections are abiding dispositions which dispose the person toward God and the neighbor in ways appropriate to their source and goal in God. Feelings are important but they come and go, are mixed, and of varying degrees of intensity. Moods too are variable, but affections characterize a person. One might, with adrenalin flowing, heart pumping, and mood considerably elevated, breathe a silent thanks after a near miss on the highway. But this does not mean that one is a grateful person, much less a thankful Christian. How often have Christians been reminded that it is one thing to hear, with assent and tears, a message exhorting to compassion on Sunday and another to practice it on Tuesday? The point is that to have compassion is to be a compassionate person. Further, to be a compassionate person is to construe the world differently. As one considers the plight of the homeless person sitting outside the market where one shops, one is convicted by the life teachings and Spirit of Jesus to act in a personally and socially responsible manner. It is no mere feeling. It is a dispositional, motivational relationship in which the believer, the homeless person, and Christ are implicated by the Spirit in a life of responsible action. Affections are construals of and concerns for the world. As such they are also
‘reasons’ for action. When asked why one acted in a certain way toward the homeless person, the reason would be that one was compassionate. It would be irrational—contradictory of the logic of the Logos—to turn away in unconcerned apathy. The biblical depiction of the identity of God and the world on the way to the kingdom form, shape, and direct the expression of the affections.
The Apocalyptic Affections: ‘On the Way Home’
The differences between Lutherans and Roman Catholics are not only of a theological nature; they are also affective differences. The world is construed differently and the Christian affections are mixed in a different way for Lutherans than for Roman Catholics. One can drink whole milk from different dairies and detect differences in the taste because of the different climates, feed, species of the cows, and processing methods. The ‘sincere milk of the Word’ 263 tastes differently for reasons that are at least analogous. An Anabaptist minister and an Eastern Orthodox priest may be able ultimately to affirm the other as Christian, but at the Lord’s Supper they know that they are different. Pentecostals are not just more exuberant than some other Christians. All the significant Christian affections are there but the profile is different. The apocalyptic vision and transcendent presence of the power of the age to come alters the affective chemistry in significant ways. The sense of urgency concerning the missionary task and readiness for the soon coming of the Holy Lamb of God alters the affections not only in quantitative intensity but also in terms of the qualitative mix or characteristic gestalt. Recalling what was said in Chapter 2 concerning the characterization of apocalyptic in terms of break, hope, and cosmic drama, it is understandable why those accustomed to power through prediction and control, whether in society or in the church, are uncomfortable at least with this spirituality. The sense of the inbreaking of the kingdom of God in Jesus Christ and in personal existence affirms the primacy of grace over against the inexorable, internally conditioned, or socially dominated historical process.264 Such a radical hope protects faith from a more subtle and prevalent threat than radical doubt or error: the trivialization and/or cooptation of faith in modern society. Particular events, specific instances of the gifts of the Spirit operating, in a worship setting or in the market place of witness, these particular occurrences are seen as part of a larger cosmic drama in which one is a participant and not a victim. The sovereign Spirit of God is moving and working in all things for the good of those
who love God. Everyone is playing a part and the final outcome will affect everyone. One’s response to God and one’s neighbor expresses what one truly believes concerning the end. To walk in righteousness is to believe in and be led toward the kingdom of righteousness. To walk in wholehearted love is to believe in and be led toward a kingdom of perfect love and peace. To walk in the power of the Holy Spirit is to walk in joyous confidence and courage in the face of all opposition toward a kingdom in which God will be all in all. One is affected by and toward the kingdom of God that is already at work in and among believers through the Holy Spirit. The ‘not yet’ of the kingdom is known in ‘foretaste’ and ‘down payment’ but nevertheless remains future, new, and something utterly gratuitous—as gratuitous as creation, the incarnation or one’s own new birth. Neither perseverance nor parousia are inevitable.265 Each is gratuitous. For the Pentecostal the power of the Spirit strengthens, sustains, and directs all the affections through all the trials and temptations of life toward the goal of the kingdom of God. It will be neither possible nor advisable to discuss all the Pentecostal affections, and one must also resist the temptation to pick one or more as the ‘essence’ of the spirituality. Robert Roberts gives a clear warning concerning [the] distortion that Christian spirituality is likely to suffer when a thinker alights on some single ‘essence’ of spirituality such as simplicity or openness to the future or authenticity or social justice. Such concepts probably capture something about Christian spirituality, but it is unlikely that any such essence hunting will preserve the richness of the biblical concept.266 And so, this explication will eschew both exhaustive analysis and reductionist essentialization; instead, it will focus on three important affections which are correlated with the view of God, the kingdom, and salvation discussed earlier in this chapter. The three selected are also related to the traditional theological virtues of faith, love, and hope, respectively. The three affections, with certain attendant synonyms or closely related affections, are as follows: 1. Gratitude (praise, thanksgiving) 2. Compassion (love, longing) 3. Courage (confidence, hope) Obviously all Christians are or should be characterized by these affections. Therefore, the effort here is to depict each of these in its distinctive Pentecostal
ethos. The following chart shows something of the structure and interrelationships of the Pentecostal affections.
Gratitude. Since all blessings flow from the gracious action of God, gratitude is the initial and continually relevant Christian affection which, through remembrance and thanksgiving, preserves the believer from the mutually conditioning sins of forgetfulness and presumption. Along with all Christians, Pentecostals give thanks for what God did throughout biblical history to create, call, deliver, and preserve a people for divine fellowship. But Pentecostals lay particular stress on the fact that God not only has acted generally in history, but has done so in their history. Everything good, they acknowledge, flows from Calvary into their lives through the continuing gracious actions of God who seeks and saves the lost. The ongoing action of God is decisive and crucial; it is experienced as a series of events or crises within, and with a view toward, a certain development toward the kingdom. To be ‘saved’ is to be forgiven, regenerated, adopted, cleansed, indwelt by the Spirit, and incorporated into the people of God in the world. Salvation is fundamentally a transformation in conformity with the character and purpose of God. God is righteous and saves in order that believers may walk in the light or walk in the works that were ordained before the foundation of the world.267 The righteousness of God is revealed and made effective in what God has done; the righteousness of believers is given as a gift with and through the faith that works through love.268 Righteousness is imputed in order to be imparted, and it is clear that justification is to be ‘no excuse for sin’.269 One is saved when one repents and receives Christ the Savior through faith by grace. One is declared righteous and simultaneously, by grace, declares for the righteousness of God. Righteousness is everything required for and in a relationship with a just and holy God. At the heart of this relationship is the law of love.
Children, youth and adults can receive Christ. Infants are usually dedicated to the Lord and recognized as part of the covenant community. But at the ‘age of accountability’ when they know right from wrong and consciously experience the conviction and wooing of the Lord they are to receive Christ and be born again.270 Only infants and the mentally handicapped are exempted from this receiving of Christ through faith and repentance. One is responsible only for the light one has! Christ’s atonement avails for them and for all like them. Gratitude, then, is evoked through remembering what God has done in Christ to atone for sins, what God has done to call one out of the world of lost souls, what God is doing to keep and perfect, and what God will do to bring in the kingdom. It is a hedge against forgetfulness. The holiness of God coupled with the divine gracious care fills the believer with thanksgiving, fear, and awe. One shows gratitude through verbal and physical acts of thanksgiving. It is striking how Often one will hear ‘Thank you, Lord’ or ‘Praise the Lord’ in a Pentecostal service. In fact these are perhaps the most frequently recurring phrases. Indeed, the testimonies, songs, prayers, offerings, manifestations of gifts, ordinances, and so on—all the elements of Pentecostal worship—are instrumented for the evoking and shaping of thanksgiving and praise. God is said to dwell in the praises of his people, and through the various means of grace (songs, testimonies, preaching, teaching, prayer, ordinances, and so on) he shapes women and men into grateful persons. But gratitude is expressed not only by what is said but also by what is done. As a hedge against presumption, it is shown by walking in all the light God gives, as the Spirit shines this light of the Lord upon the path of the pilgrim. This is not righteousness of works. As The Apostolic Faith asserted, This is not a ‘do, do’ religion, but it is the religion of the Lord Jesus Christ. Man has got to be born again. You cannot get it through moral culture, refinement, or giving up, but you must be born into it. It is through God’s beloved Son who washes you, cleanses you, and makes you a fit subject for heaven.271 The believer remembered in song that ‘Love lifted me … out of the angry waves … when nothing else could help’.272 Believers were ‘in a new world’ since the Lord saved them.273 In gratitude to God they must, when Scripture illuminated by the Spirit shined on their path, ‘go forward or else backslide’.274 As they received ‘more’ of the Holy Ghost, they would be expected, if it were authentic, to express more love, humility and praise.275
God thus has a purpose and plan for each life and each church. Gratitude means attending to the light of Scripture and the everyday voice of the Spirit, so that the general shape and specific directives of the Lord of the church may be realized in Christian service and witness. The life of faith is a life of faithfulness which is borne of grace and has its constant end in gratitude. The grace of God and the gratitude of the believer are personal. The Holy Spirit is God’s gracious presence, God’s active favor, and God’s effectual working in the believer. The Spirit personally orders the grateful heart so as to conform the individual to Jesus Christ. Although, ‘Thank you, Father’ and ‘Thank you, Holy Spirit’ are commonly heard in Pentecostal worship, it is ‘Thank you, Jesus’ that most frequently expresses gratitude. All blessings flow from the Father in the Spirit through Jesus. To be grateful is also to remember where you have come from. The Apostolic Faith in January of 1907 exhorted its readers to recall when they were ‘poor and ugly’ in their own sight, because that was when God ‘exalted and used’ them. But when they ‘got to be some great Nebuchadnezzar’, then God will turn them 276 out ‘to eat grass like an ox. Keep little and God will use you.’ Humility is the companion of gratitude. One is grateful to be a part of the holy people of God and to be out of the world that is blind and bound. Friendship with the world will dull and eventually destroy thankfulness and praise to God because one of the chief marks of a ‘worldly’ person is that he or she is unthankful. The ways of God are not the ways of the world. Their methods are different. The ‘world’ rejected Jesus, and has persecuted his disciples throughout history. Pentecostals are one of the most persecuted and martyred bodies of twentiethcentury Christians. In some Central American countries for example, they have been killed by the ‘right’ and the ‘left’. This does not mean they have tacitly endorsed the status quo. It means they have taken a third way and disavowed the ways of the world. One of the deep sources of ongoing thanksgiving and gratitude is the sense of belonging to the church of the living God and no longer being a part of the world which is passing away. Even when Pentecostals cannot tell the time and place when the Lord saved them, they still have a definite sense of being called out of the world and into the church on the way to a kingdom of righteousness. Every time someone is born again and waits with the church, the believers remember, rejoice, and look forward to the final homecoming. The source is the
righteousness of God, the way is a walk in the light, and the goal is a new heaven and new earth wherein dwells righteousness. This ‘faithful faith’ is the victory that overcomes the world. Gratitude is a powerful reason and motivation for witness. The sharp delineation between church and world heightens the pain of separation which the church in general and the believer in particular feels. Though believers hate evil and are not friends of the world, they nevertheless remember that God so loved them while they were in the world. Indeed they are now in and not of in order to love the world as God does. The world is an enemy to be loved. They are, to use Niebuhr’s terminology without buying into all his conclusions, against the world in order to be for its transformation which has already begun in them. Christ is against, and the transformer of, culture.277 In most Pentecostal services prayer requests will be offered for the lost— neighbors, relatives, fellow workers, and so on. Neighbors are lost and deluded, but God is graciously at work convicting, blessing, judging, and drawing them to Jesus Christ. Anger because of the binding of Satan, sorrow for the lost condition of these persons, and joy over their deliverance, and a celebration of life and mission of the church are all in evidence. When someone is saved, and there are millions of such testimonies during this century, there is great rejoicing. In summary, gratitude is grounded in and shaped by the gracious righteousness and merciful faithfulness of a holy, compassionate God. To be saved, pardoned, justified or born again is to be taken out of the unrighteous ‘world’ and placed in the body of Christ so that one may, with all the believers, become the righteousness of God in him toward the world. One gives thanks by walking in the light, being a light (in terms of Christian character) and doing deeds of righteousness so that others will believe and glorify God. Gratitude as thanksgiving and praise is characteristic of Pentecostal worship and is a passionate reason for the shape and content of the worship and witness of Pentecostals. To construe God as gracious, the world as lost and oneself as delivered or rescued is to be gratefully disposed toward God, in worship and for witness. Compassion. If gratitude is the foundation of the Pentecostal affective structure, the interior of the building is a compassionate, longing love. Pentecostals, emerging as they did from the nineteenth-century Holiness movement, have a concern for holiness as perfect love or wholehearted devotion to God. Though they have been noted for their fierce doctrinal disputes, it is nevertheless widely recognized that Pentecostal congregations have a deep love
for God, for one another, and for the lost. Objectively, they would acknowledge that God is love; therefore, believers must love as God does and must be, to that extent, holy. This is what it means to have the mind of Christ.278 If righteousness is fundamentally but not exclusively associated with the covenant faithfulness of God the Father to the creation, then love as compassion is primarily associated with Jesus. For Pentecostals, as for John Wesley, their sins nailed Jesus to the cross and could, if returned to, even now represent a crucifying afresh of the Son of 279 God. Just as God in righteousness by grace creates a new people who belong to him and to one another, so God in holy love will create a new heart which is aflame with holy zeal and longing for the kingdom. If one is stirred to righteous indignation at the sight of the unrighteous violations of the world, then to this is joined a compassionate longing for the salvation of the lost and the coming of Christ. In the fullness of the kingdom everything will be holiness unto the Lord and without holiness no one will see the Lord.280 This holiness is not that which is given in the article of death or at the resurrection and glorification of believers. It is, rather, a cleansing of the heart,281 a washing of the robes and a cleansing ‘from all filthiness of flesh and spirit perfecting holiness in the fear of God’.282 Though the world had been abandoned, yet it remained in the form of evil thoughts, tempers, desires, and ways. As Wesley would have said, though sin remained, it no longer reigned. The believer wanted to do the right thing and to walk in the light. Pentecostals want to witness in the power of the Spirit. But the desire for holiness or sanctification is at heart a desire for God himself, to be like Christ in love. To have this love requires self-denial; indeed self-will is often construed as the heart of the problem. The sinful desires and tempers have to be mortified, put off and expelled by the love of God. The blood of Christ, the Word, and the Spirit are collectively the agents of cleansing. What keeps one from being moved toward the lost and suffering mass of humanity? Inner resistances, the cares of this life, carnal desires, all these are hindrances to the notion of compassion and the infilling of the Spirit. The desired purity of heart is given when believers ‘are willing to let Him have His way to the fullest extent of the word’. Then they will be ‘clay in the Potter’s hands … and ‘self’ will be removed’.283 Indeed this emptying is necessary if one is to be filled with his Spirit; when the filling occurs, then the first thing that can be told is that ‘the blood of Jesus Christ cleanses from all sin’.284 The believer has his or her affections in Jesus Christ, the Lamb of God
that takes away the sin of the world.285 One must stay in the cross and die daily if power is to rest upon one’s life and witness.286 Sanctification was the center or heart of ‘Bible Salvation’ for the believers at Azusa and millions subsequently. It was ‘God’s design through the ages and through all His work with the children of men … to implant His own nature—love, in a fallen race’. It was ‘sweet to feel the tender thrills of that love, going through every part’ of one’s being.287 Jesus is the center and model of compassionate love. To be compassionate is to be moved toward others as he was. The Spirit moves upon those who are emptied out and yielded to manifest the character of love which is described in the following short exhortation from Azusa: The Character of Love It is sweet to have the promise of Jesus and the character of Jesus wrought out in our lives and hearts by the power of the Blood and the Holy Ghost, and to have that same love and that same meekness and humility manifested in our lives, for His character is love. Jesus was a man of love. The people flocked to Him to hear His words. Women lugged their babies in the hot sun and spent days listening to the words of Jesus. Men got into boats and went across the sea to see Jesus and hear His precious words. While there were many that followed for the loaves and fishes, many followed Him for healing. Yes. He was a man of love. He was the express image of the Father, God manifest in the flesh.
Dear loved ones, we must have that pure love that comes down from heaven, love that is willing to suffer loss, love that is not puffed up, not easily provoked, but gentle, meek and humble. We are accounted as sheep for the slaughter day by day. We are crucified to self, the world, the flesh and everything, that we may bear about in our body the dying of the Lord Jesus, that our joy may be full even as He is full.288
If they were going to fill the world with the doctrine of Christ before his soon coming, early Pentecostals realized that they must be emptied of all that would hinder their availability and character as witnesses. As faith is the victory over the world which secured the believer in righteousness for walking in the light, so crucifixion is the biblical strategy against the flesh with its hindering passions and desires. The passion of Christ for one’s sins becomes, when struggling against those same sins, compassion. The compassion for those bound in sin, enslaved in the passions, is possible only in Christ. Like all the Christian affections, compassion is sustained by abiding in Christ.
Without the compassion of Christ one cannot face, confess, and mortify one’s own sinful passions. As love grows, so does hatred of these passions and a desire to reach the sheep scattered with no shepherd.289 To construe one’s heart as having the same sorts of evil passions, selfish motives, and senseless resistance to grace as those in the world is to move toward the world with humility. When there is no known hold-out or resistance but only a consciousness of love it is a wounded love which, even when it grows, recognizes how totally dependent upon the faithfulness, longsuffering, and love of God one is. Fallibility, neurotic fears, and repressed resistances remain. Only in constant openness to the compassionate love of God, in searching of the Spirit, and in faithful fellowship of the saints is it possible to avoid self-deception or immobilizing despair. Compassion moves one to respond according to the pattern of Christ. Compassion is the reason and the motive for that response in and by the Spirit. Compassion longs for all to know the love of God and for the kingdom to come. Compassion is borne of inner peace with God based on and flowing from the peace made at Calvary. It is the healing of the heart that makes one like God and therefore for others.290 Compassion is suffering love wounded by the suffering of others who do not know or have rejected Christ. When Pentecostals ‘pray through’ about their resistances or holdouts and ‘kill’ the untoward affections, God’s love fills their hearts. This is usually attended by tears and laughter, by sorrow and joy, by delight in and longing for the Beloved. These feelings are common among Pentecostals. In this way one acknowledges affectively the death, crucifixion of self with Christ, and the resurrection. This is a deepening of those changes which were brought about in the new birth. The progression or logic of the soteriology is reflected in the affections. Justification and new birth ask for sanctification which asks for Spirit baptism. So then the gratitude and thanksgiving associated with initial salvation, when the love of God is shed abroad in the heart by the Holy Spirit, ask for or tend toward the fullness of love which is called entire sanctification. The crucifying and putting off of the deeds and carnal affections is not so as to merit entire sanctification; they are necessary in order to be filled with or to be decisively determined or moved by love. Initial sanctification, associated with the real change accompanying new birth, reaches its goal in entire sanctification. The fullness of freedom associated with new birth moves forward the fullness of love in entire sanctification as one walks in the light of the Scripture. The sin tendency as resistance, hold-outs, self-will and so forth is to be acknowledged, confessed, hated, mortified, and put away even as one reads the Word, yields to
the searching of the Spirit, and does all the good he or she can. The old is replaced with the new. It is good to be moved by gratitude toward the lost, hurting and oppressed. In this way one shows that one is grateful. On remembering those in need one remembers whence one has come. But compassion is a deeper binding to the crucified one and to the lost. Compassion moves with urgency, pity, longing for the lost. Compassion moves the believer toward the world and draws the world into the sphere of redemption. Gratitude looks up to God continually; compassion looks out to the lost longingly. If gratitude is the hedge against presumption, forgetfulness, and mere duty, then compassion is the safeguard against hardness of heart, complacency, and sentimentality. Compassion sings, ‘Rescue the perishing … care for the dying’.291 The holiness of God in Christ by the Holy Spirit cleanses and consumes with holy zeal. To become compassionate is to carry daily in one’s body the dying of the Lord.292 Pentecostals characteristically travail in prayer for the lost, afflicted, and oppressed. Pentecostal songs would be used to call believers to prayer, typically during an ‘altar service’ and to guide these prayers toward consecration and cleansing. Compassion could and did move the regenerate, and all were called upon to be witnesses. Nevertheless, carnality would hinder their witness, imperil their salvation, and be a stumbling block to others. If compassion toward others was to come to full expression then love for God must be as complete as possible. The capacity for this love would increase but the hindrances must be removed and selfishness rooted out. A few representative songs will illustrate this desire to be sanctified, fully yielded, and available for the Master’s use. The first are selections from an Assemblies of God collection entitled Melodies of Praise.293 In the selection ‘Jesus I Come’ the congregation sings, Out of unrest and arrogant pride, Jesus I come, Jesus I come; Into Thy blessed will to abide, Jesus, I come to thee; Out of myself to dwell in Thy love, Out of despair into raptures above Upward for aye on wings like a dove, Jesus, I come to Thee.294 The connection between consecration and Spirit filling is made explicit as
believers are urged to Be filled with the Spirit Yield completely to the One Who cleans’d And made you whole; Be filled with the Spirit You need the precious love of God To fill and flood your heart; Until there is no room For carnal self to have a part.295 In ‘Bring your Vessels not a Few’ those who are seeking for the infilling and blessing of the Lord in their heart and life are instructed, Bring your empty earthen vessels, Clean thru’ Jesus’ precious blood, Come, ye needy, one and all; And in human consecration wait Before the throne of God, Till the Holy Ghost shall fall.296 As they seek the ‘Pentecostal Blessing’ they pray that God will cleanse their ‘hearts from sinful leaven’.297 In ‘Waiting on the Lord’ for the promise of the Father, they acknowledge that the power of Pentecost ‘gives victory over sin and purity within’.298 The Pentecostal soul longs for ‘Higher Ground’299 and to go ‘Deeper, Deeper’ in the love of Jesus every day.300 Deeper, deeper in the love of Jesus Daily let me go; Higher, higher in the school of wisdom More of grace to know.
CHORUS O deeper yet, I pray, And higher every day, And wiser blessed Lord, In Thy precious holy Word. Deeper, deeper! Blessed Holy Spirit, Take me deeper still, Till my life is wholly lost in Jesus
And His perfect will.
Deeper, deeper! Tho’ it cost hard trials, Deeper let me go! Rooted in the holy love of Jesus, Let me fruitful grow. Deeper, higher ev’ry day in Jesus, Till all conflict past, Finds me conqu’ror, and in His own image Perfected at last. Deeper, deeper in the faith of Jesus, Holy faith and true, In His power and soul exulting wisdom, Let me peace pursue.301
This gospel song is important for several reasons. It shows that the holy life is a daily pursuit requiring divine wisdom from the Word of God. It indicates that the depth dimension is reached when the Holy Spirit, who searches the deep things of God, takes the believer deeper into Christ—lost in him and his perfect will. This will perhaps cost ‘hard trials’ but it is necessary to be rooted deeply if one is to be fruitful. Apparently love is the ground or fundament from which all the fruit of the Spirit springs; to go deeper in love is to go deeper in faith (the faith of Jesus) and to pursue peace. This is reminiscent of the passage often quoted among Pentecostals, ‘Pursue peace with all, and holiness without which no one shall see the Lord’ (Heb. 12.14). As early as 1908 the Pentecostals were singing ‘Is Your All on the Altar?’, ‘None of Self and All of Thee’, ‘His Way with Thee’, ‘The Cleansing Wave’ and ‘Higher Ground’.302 There are tensions between a thoroughgoing Wesleyan and other formulations of sanctification in these songs. But through them there is a richness and a struggle to articulate a deep, abiding longing for God and a fullness of love which is not fully appreciated by merely reading the early and somewhat meager Pentecostal statements of faith. This all-consuming love for God was finally a longing for the coming of the Lord. Pentecostals’ love was a ‘Longing for the Dawning’ of the day of the Lord when all conflict would be past.303 The object of this affection was most often Christ himself and the great ‘Meeting in the Air’ with all the saints of old.304 As they sang ‘O, I Want to See Him’305 they beseeched the Savior, ‘O Lord, How
Long?’306 In the meantime the agenda was captured in such songs as, ‘I’ll Go Where You Want Me to Go’,307 ‘Sitting at the Feet of Jesus’, and ‘We’ll Work till Jesus Comes’.308 Such longing kept one separate from the world but moved one toward the lost. The peace of sanctification did not lead to complacency because sanctification as love must necessarily become compassion in a world that is lost and suffering. In such a world the ministry of healing expressed and evoked compassion and longing. At Azusa Seymour linked sanctification of soul and body and asserted that both, along with all other blessings of salvation, were provided in the atonement. Seymour was a literalist when it came to healing. God would sanctify ‘bodies from inherited disease … Every drop of blood we received from our mother is impure. Sickness is born in a child just as original sin is born in the child. He was manifested to destroy the works of the devil. Every sickness is of the devil.’309 Though not all Pentecostals since then would share this metaphysics, most would continue to affirm and practice a joint ministry to soul and body. As the sick come forward for prayer the congregation often sings ‘The Healing Waters’, which focuses not on physical healing, but forgiveness, bliss, ‘precious perfect love, and rest!’310 There are thousands of testimonies all over the world to healings. Some see healing as one of the major emphases, if not the characterizing aspect, of the movement. But be that as it may, it is true that when one was healed, there was joy and sorrow. The joy was obviously because of the miraculous help given to the afflicted and the assurance given to all the witnesses. But everyone was reminded of his or her mortality. All were never healed; some were. And the ones who were not were always in substantial enough numbers to create a longing in the fellowship for the great day of final salvation and universal healing. The healing evangelists may have had their theories as to why this or that person was not healed, but the masses of believers knew it was a mystery.311 They, along with compassionate pastors, cared for and comforted the afflicted, who joined with them in rejoicing with the healed. The doubts and struggles created by the formulas of faith, then and now, would only yield to the compassion of the body of believers who, as a whole and individually, knew that all would eventually die. Compassion for the sick and suffering was always most intense among those who had the least medical care
available or who could least afford it. This compassion was rooted in fundamental notions of creation of the body, resurrection of the body, a millennial kingdom of a new heaven and earth, and, most of all, the ministry of Jesus. The love of God shed abroad in the believer’s hearts at regeneration grew in the ‘hungry’ until it filled them with longing for God and compassion for the lost. The songs, testimonies, sermons, altar services, healing services, rescue missions, soup kitchens, orphanages, and missions both evoked and expressed love, longing, and compassion. Gratitude turned one toward the world in thankfulness and a desire to tell others the good news. Compassion moved one toward the lost, afflicted, and perishing in obedience to the pattern of Christ’s ministry. The world was overcome in the faith that was at once a personal victory and a corporate commitment. The flesh was crucified, and through consecration and cleansing, compassion could move one back into the world from which one had come. But the evil spirits would not be moved by gratitude or compassion. The rejection, hostility and persecution of the world could soon wear down compassion. The wounded and weary realized there were real dangers to be faced and real evils to be overcome. The grace of regeneration had given power to resist the evil inclinations from within and allurements from without. The grace of entire sanctification gave the inner freedom which delighted in the will of God and longed for the salvation of the world. But walking in the light or righteousness and walking in love was not the same as walking in the power of the Spirit. Believers needed courage and fortifying to sustain their battle against powers and principalities. They needed the full panoply of gifts and graces to proclaim the gospel in word, power, and demonstration of the Spirit. This power —this authorized power of God would bring courage to witness and, if necessary, to suffer and die. With this courage they would, could, and did go all over the world witnessing to the lost and warning the church to get ready for the kingdom of righteousness, peace, and joy that would soon dawn upon the world. The move toward a new integration of the affective life, one that seeks to incorporate new power, courage, and confidence into a life of active gratitude and compassion can be seen in the following testimony which is quoted at length from The Apostolic Faith paper in 1908. Miss Antoinette Moomean of Eustice, Nebraska narrates her journey from the mission field of China to the Azusa Street Revival. This testimony conveys the ethos, affective tone, and something of the instrumented means used to effect affective transformation. It is clear from this account that baptism in the Spirit meant a strengthening of all that had gone
before in her Christian development and a discovery of ‘the secret of the endurance of the martyrs’. It is an interesting weaving together of doctrine, affect, gifts, practices, and self disclosure. There were and are hundreds of thousands of testimonies like this one. It provides a good transition from the preceding discussion of gratitude and compassion to the succeeding and final affection to be considered, courage: On leaving China, October, 1906, I was asked to investigate the Apostolic Faith Movement in Los Angeles, where they claim to have manifested the same gifts of the Holy Ghost as of old (1 Cor. 12.8-10). I heard such contradictory reports that I kept away for some time, but praise God. He had His hand upon me for this wonderful gift, and I had no rest until I went and heard and saw for myself. It only took a short time after the beginning of the first meeting, to know it was of God. And when the altar call came, I went forward. Before this I had asked God to turn His great searchlight upon my heart and was astonished to find so much worldliness, spiritual pride, vanity, insincerity, lack of love, selfishness, and other things. When I had left for the foreign field seven years before this, I thought I had died to everything; but when the Spirit began to deal with me in preparing me for the fullness of the Spirit, I found I was very much alive, in fact had scarcely begun to die to self. Although the Lord had given me wonderful victories in my life and what I thought was the baptism of the Spirit, yet when God began to search me as never before, I had to confess that I had never even been sanctified. I had been taught the suppression theory and now and again the ‘old man’ would pop up in greater or less degree; sometimes harsh words did not escape, but I would feel them boiling up inside. But God showed me that His word meant just what it said, that provision was made in the atonement —not only for our sins but our sin, the old Adamic nature (Rom. 6.6, 18, 22). How I did rejoice at the last, the longing of my heart to be rid of that which had kept me from being entirely free from sin, was to be satisfied. I had sought my baptism of the Spirit three times, when the Lord told me that I must be sanctified before the Spirit could take full possession of my body. Just so were the disciples sanctified before Christ left them (John 17.17, 19), that they might be ready for the baptism of the Spirit
After some of the saints had prayed for me, one of them asked me if I had the witness of the Spirit to my sanctification according to Heb. 10.14, 15. For some years back when I had been taught of the Spirit to keep ‘short accounts’ with the Lord, and there was nothing left to do in the way of restitution; and having laid all on the altar. I knew I had met the condition, and that God had fulfilled His promise; although there was no other feeling than the assurance that God had done the work because of His Word. I then began to praise God audibly, and in a few minutes I was flooded with billows of glory, and the Spirit sang through me praises unto God. Besides this witness of the Spirit, was the witness of the fruits; for under whatever provocation, there is no uprising, for there is nothing to rise up. Glory to Jesus.
When sanctified, I was filled with such glory that I felt sure it must be the baptism, which did not come for three weeks. In the meantime, the power was upon me almost continually, sometimes lying under the power for hours, while I consecrated myself to God as never before. At last after a real dying out, as I never dreamed could be possible on earth, in the upper room at Azusa Mission, the promise of the Father was made real to me, and I was charged with the power of God and my soul flooded with glory. The Spirit sang praises unto God. Glory to Jesus. He gave me the Bible experience, speaking through me in other tongues. The Lord showed me that the cross was going to mean to me what it had never meant before. One morning the Spirit dealt with me, singing through me—
Must Jesus bear the cross alone,
And all the world go free;
No, there’s a cross for every one,
And there is one for me.
The last line He just seemed to burn into my soul by repeating it over and over again. Sometimes the Spirit would sing a line and then sob out a line. Although I wept and was in anguish of soul, it was all in the Spirit The life of Jesus passed before me, and He asked me if I was willing to follow Jesus in living absolutely for Him in ministering unto others. I thought I had known something of what this meant in China; but now to preach the everlasting Gospel in the power and demonstration of the Spirit
and to truly go out on the faith line and to minister day and night, sometimes unto the hungry multitudes in the face of fierce opposition, meant far more than ever before. But He enabled me to say, ‘By Thy grace I will bear this cross’.
The Garden scene came up before me next, as the Spirit again sang, ‘Must Jesus bear the cross alone?’ And He seemed to say, ‘Your friends will forsake you, your own family will misunderstand you, you will be called a fanatic, crazy; are you willing to bear this cross?’ Again I answered, ‘By Thy grace, I will’. The crucifixion scene then came before me and it seemed as if my heart would break with sorrow, and I could only wait in silence. Then I said, ‘Lord, if it was to be beheaded. I could; but’—I could go no further. Later in the day, the Lord spoke to me again as I was under the power. It seemed as if I would perish in soul anguish. I was unconscious of the workers all about me. It seemed as if Jesus Himself stood beside, looking down upon me. I could only say, ‘Jesus, Jesus, Jesus. I will, I will, I will’. His promise came to me as distinctly as if audibly [and] said, ‘My grace is sufficient for you’. And in a flash, He gave me to understand the secret of the endurance of the martyrs who were burned at the stake with the glory of heaven upon their faces, and seemingly free from pain. And He enabled me to say, ‘Yes, Lord, your grace is sufficient’. Then the Spirit began to sing in a joyful strain, repeating over and over again the last line until I could almost see the crown:
The consecrated cross I’ll bear,
Till Christ has set me free;
And then go home a crown to wear,
For there’s a crown for me.
To sum it up, the baptism of the Spirit means to me what I never dreamed it could this side of Heaven: victory, glory in my soul, perfect peace, rest, liberty, nearness to Christ, deadness to this old world, and power in witnessing. Glory to His name forever and forever!312
Courage. The faithfulness of the grateful and the zeal of the compassionate are deepened and strengthened by the courage associated with Spirit baptism. In regeneration one belongs to the new people of God and gives thanks; in
sanctification one receives a new heart of compassionate love for God and others; and in Spirit baptism one receives an ‘authorized strength’ to be a courageous witness in word and demonstration of the Spirit.313 The faith of the new people of God overcomes the world as the redeemed follow the leading of the Spirit-Lord. The discipline of crucifixion or mortification neutralizes the inner hindrances to the fullness of love and compassion that is the essence of sanctification. The infilling of the Spirit enables the believer and the church to resist the devil and to assault spiritual strongholds with spiritual weapons.314 We have already seen how righteousness and sanctification, along with their corresponding affections of gratitude and compassion, are thoroughly apocalyptic in orientation. The deepening of love in sanctification is the result of and issues in a further intensification of a yearning for the consummation of the kingdom of righteousness where everything will be ordered according to the covenant purposes of God. Perfect love longs for all God’s children to be home with the Lord, so that the Pentecostal vision of heaven is at once theocentric and anthropocentric.315 The deeper peace with God associated with the mortification of the carnal desires and fullness of love is an anticipation which looks forward to the perfect peace (shalom) and well-being associated with the new heaven and earth. The power given in Spirit baptism strengthens all the other fruits of the Spirit and gives courage and boldness borne of confidence in God. This brings great joy in believing because the believer can, in addition to standing and suffering for the gospel, also take the offensive and engage the forces of unrighteousness, hatred, and oppression in prayer, service, and witness. The confidence of this courage looks at what God has done and already is doing. This confidence in God, because of the fulfilled promises and ongoing guidance, builds a hope which looks forward to the day when God will be ‘all in all’.316 Just as the Spirit fills the reconciled, sanctified believer who then praises and proclaims God, so also one day everything and everyone will praise God. These three affections can also be seen as safeguards against certain dangers. A grateful, thankful walking in the light guards against presumption or mere mechanical duty. Grace is the foundation for everything given and promised; and every day is experienced as a gift of forgiveness, cleansing, and enablement. Gratitude disposes toward obedience, while a wanton, lascivious disregard for scriptural limits and directives is guarded against when the heart is truly thankful. Compassionate, wholehearted love in and through Christ guards the soul against sentimentality, apathy, and hardness of heart. The believer at peace
through the cross is a peacemaker through compassion. The courage that is given to the grateful, compassionate seekers after righteousness is a hedge against despair. Believers are called to take up their cross and follow, and not merely to be victims. However, they are to follow courageously. It is important to wait upon the sovereign Spirit, because to go forth without the Spirit’s leading is to go without his power. Techniques may be used to induce ‘sensations of power’ but real power belongs to the Spirit alone. Power, like holiness and love and grace, is the believer’s possession only in a derivative and relational sense. The Spirit is ‘the Faithful Guide’317 and ‘Bishop of the Church’.318 It is His office and work ‘to preside over the entire work of God on earth’ (Jn 10.3). Jesus has sent the Holy Spirit to be the chief bishop and ‘not men’ (Jn 14.16; 15.26; 16.7-14). It is the Holy Spirit who infuses with divine power and invests with heavenly authority and, therefore, no ‘religious assembly is legal without his presence and his transaction’. He is the ‘Teacher of teachers’. So many of God’s people are without divine power and ‘experiential salvation’ today because they do not accept him as their teacher, leader, and comforter. It is the power of the Spirit that gives bishops and elders their authority today. His ‘credentials’ must be put in their hearts if they are to be coworkers with and partakers of him. The enduing of power is their single most important qualification for office. Without this the leaders cannot witness to the uttermost parts of the earth with the people. The Spirit ‘takes the members into the church … [and if] they commence sinning, the Holy Ghost, the chairman and bishop, the presiding elder, turns them out’. There can be no power in the church and hence in the members unless the Holy Spirit is heeded. No one can take the place of the Spirit: Many people today think we need new churches … brick structures, modern improvements, new choirs, trained singers right from the conservatories, paying from seven to fifteen hundred dollars a year for singing, fine pews, fine chandeliers, everything that could attract the human heart to win souls to the meeting house is used in this twentieth century. We find that they have reached the climax, but all of that has failed to bring divine power and salvation to precious souls. Sinners have gone to the meeting house, heard a nice, fine, eloquent oration on Jesus, or on some particular church, or on some noted man. The people have been made glad to go because they have seen great wealth, they have seen people in the latest styles, in different costumes, and loaded down with jewelry, decorated from head to foot with diamonds, gold and silver. The music in the church has been sweet, and it is found that a good many of the church people seem
to be full of love, but there has always been a lack of power. We wonder why sinners are not being converted, and why it is that the church is always making improvements and failing to do the work that Christ called her to do. It is because men have taken the place of Christ and the Holy Spirit.319 The Spirit is the Lord who leads the church into battle and devises the tactics that will be effective in bringing glory to God and sinners unto the kingdom. Pentecostals tend to see themselves as an army of the Lord. Each one is a ‘Soldier in the Army of the King’, and the church moves like a mighty army on 320 ‘the Tribulation Way’ as it is ‘Marching to Our Home on High’. In courage and hope the church is ‘Waiting for a Blessing’, while serving in the ‘Armies of Zion’.321 Each soldier is confident that ‘When the Roll Is Called Up Yonder’322 she or he will be there. Confidence and hope are respectively the ‘already–not yet’ polarities of courage. The believers’ confidence is built as new persons are born into the kingdom and they witness healings, exorcisms, and other answers to prayers. Corporate worship is ‘joy unspeakable and full of glory’.323 As confidence in the leading and presence of the Spirit builds, so does the vision of hope as believers 324 sing, ‘O, What Joy It Will Be’. Many Pentecostal believers are arrested and many have been imprisoned, tortured, and killed. But it is common for them to sing, preach, and witness in the prisons, even founding prison churches. From the Pentecostals imprisoned in Los Angeles at Azusa to the more recent Soviet Pentecostal prisoners, to Chinese, African, South and Central American believers, all have undergone persecution and frequently have paid with their lives. Pedro Pablo Costillo, the current overseer of the Church of God in Nicaragua was imprisoned under the Sandanista regime. He preached to and baptized prisoners in each and every section of the prison in which he was placed. Upon his release he elected to stay in the country and lead his people in ‘evangelistic and social ministry’ to the needs of the Nicaraguans.325 It takes courage to eschew the ‘right’ and the ‘left’ and find a ‘third’ way of peace. In the most oppressive environments the joyful praise of the Pentecostals can be heard. While it is true they provide a ‘haven for the masses’, it is nevertheless also true that their courage is by no means a passive resignation. What was said at Azusa could still be said throughout the Third World today— they are ‘ready not only to go to prison but to give our lives for Jesus’.326 As at the beginning of the movement, the poor, the young, and the formally
untrained go out to local and foreign fields to serve. A short article in The Apostolic Faith paper of October, 1906 captures this populist uprising of the Spirit: Back to Pentecost What mean these salaried preachers over the land that will not preach unless they get so much salary? People have wandered from the old landmarks … Get back. You have no time to lose. We must all be up and doing something for perishing souls around us. Do you want to be blest? Do you want the approbation of God? Be a servant to humanity. The loaves and fishes did not multiply in the hands of our blessed Redeemer till he began to give out to the hungry.
God does not need a great theological preacher that can give nothing but theological chips and shavings to people. He can pick up a worm and thrash a mountain. He takes the weak things to confound the mighty. He is picking up pebble stones from the street and polishing them for His work. He is using even the children to preach. His Gospel. A young sister, fourteen years old, was saved, sanctified, and baptized with the Holy Ghost and went out, taking a band of workers with her, and led a revival in which one hundred and ninety souls were saved. Salaried ministers that are rejecting the Gospel will have to go out of business. He is sending out those who will go without money and without price. Glory to God ‘for this Apostolic 327 day.
The faithful everywhere reported and still report ‘signs following’ which hold the faith and hope, confidence and courage of the witnesses.328 Individuals would have dreams and visions and be called to foreign fields. In 1906 Lucy Leatherman of New York City reported to The Apostolic Faith that she had been called to Beirut. God asked her if she would be willing to ‘go with him to the wild Arab of the desert’ and she said ‘yes’.329 Yet, those who trust in dreams or manifestations or tongues of the Spirit were cautioned to maintain a guard because these could not be the ground of their confidence. The Spirit is not a permanent possession of theirs or their church: Those who receive the baptism with the Holy Ghost and speak in tongues and then backslide from this state may retain the speaking in tongues for a while after divine love is gone, but gradually this gift will melt away. A very little harshness or a critical suspicious statement about a brother will grieve the tender, sensitive Spirit. A careful and constant guard must be
made, lest the flesh arise and destroy the fragrance and sweetness of this Spirit walk. Preachers often go too far and try to emphasize in fleshly vehemence a good point made by the Spirit. All such conduct will receive a gentle rebuke of the Spirit and, if heartily repented of, will soon be overcome, and result in greater confirmation of God’s power in one’s life.330 The courage to be a witness in the world in opposition to the demonic spirits was borne of the power of the Spirit who, by his constant, searching presence, strengthened the affections, manifested the needed gifts and drove the enemy out of the possessed and back from the believer. The grace of forgiveness and mercy gave the believer the courage to face the world and their own sins in responsibility and humility. The grace of sanctification gave confidence and joy as believers gained victory in the inner struggles with the flesh. The grace of Spirit filling continually gave courage and strength to oppose and to discern the enemy of the saints.331 Gratitude, compassion, and courage grow from the righteousness, love, and power of God and are construals of the world in the light of the kingdom of righteousness, peace, and joy in the Holy Spirit. Believers are to be continually grateful to God, compassionate through Christ, and courageous in the Holy Spirit. But since they are still in though not of the world, still in flesh though not of the flesh, and still opposed on every hand by a crafty and cunning adversary, the possibility of deception is very real. Cultural, carnal, and demonic elements can only be distinguished by the Holy Spirit.
A Disciplined Discernment: Word and Spirit
The early Pentecostals were accused of being demonic, deranged, deluded, and/or divisive. Those making the charges usually did so on the basis of Pentecostal claims to spiritual gifts that clearly, to them at least, were limited to the first century. Others criticized the strong emotion, mixing of races, and prophesying of women and men.332The Apostolic Evangel published in Royston, GA in 1907 responded by advancing ‘Some Infallible Evidences that the Modern Pentecost Is of God’. The article listed four evidences which could assist in discerning the spirit of Pentecostalism; in addition, the article gave two brief exhortations to the Pentecostals themselves. The evidences were: (1) the intense hunger for righteousness in those who were filled; (2) the deep crucifixion of self, which is what the devil puffs up and uses; (3) the continual praises to God; and (4) the increase of the ‘unspeakable love of God and one another that
accompanies Spirit baptism’.333 The admonitions to Pentecostals had to do with judging others and power. The Evangel suggested that when they got their Pentecost they would be ‘just as true to God and His Word as even on outward as well as inward things, but you will be forever done measuring the height of people’s experience by the cut of their clothes’. In addition, Pentecost will, supposedly, cure them of their stress on ‘noise as power … God will not give His glory to noise; although He reserves the right to make all the noise He 334 pleases’. If the admonitions deal more with matters of style and taste, the firm evidences are more substantial tests of authenticity. Coming out of a perfectionist, revivalist background, Pentecostalism, from the first, had to oppose fanaticism while striving to ‘let the Spirit have His way’. Those gathered at the Azusa Mission in 1906 developed guidelines for recognizing fanatics: Fanatics are marked by harshness towards those who do not fall in line with them, an [sic, and] Jesus is not held up. Sooner or later the fruits of the flesh appear in a lack of holy living. We note these things because some honest souls have feared that this Pentecostal movement was fanaticism. So we mark some of the features of the meetings which are the opposite of fanaticism. Divine love to all, especially to the church, the body of Christ, of which every justified soul is a member. Humility: this is a humble work in a humble place and we are glad that it is. We humble ourselves under the mighty hand of God and constantly search the scriptures to know His whole will and plan. Holy lives: these people are living holy lives, separate from the world, the flesh and the devil, and rescuing other souls to a life of purity and holiness. There is a Holy Ghost shine on the faces of the workers. Is this the work of the devil?335 A few insights can be gleaned from the foregoing quote. In keeping with 1 John 3, Pentecostals looked at the source and results of supposed spiritual manifestations and persons. If Jesus was ‘not held up’ then the manifestation was fanatical. Harshness was clear proof that the chief characteristic of Jesus, divine love, was missing. Next to love in importance was humility and humble, submissive searching of the Scriptures for ‘his whole will and plan’. Holy lives of witnesses who have a ‘Holy Ghost shine’ of glory and joy are also highly valued. So in addition to the very important inner witness of the Spirit, believers could check their and others’ lives for the confession to Christ which sought to
edify the church in love, further the mission and manifest the fruit and gifts of the Spirit and not the flesh. Those who were ‘walking in the light’ would recognize darkness. So it was 336
important to walk in all the light one had. Those who had crucified the flesh and were guarding their heart and desires in wholehearted love to God and compassion to the lost would be most sensitive to carnality arising from within or masquerading from without. They were not to trust themselves but trust the cross of Christ. In this way through searching the Scriptures and their hearts everything could be kept under the blood. The Apostolic Faith exhorted the faithful to remember that [w]hen men and women are saved and sanctified, they need the Blood just as much as they ever did. We should not trust ourselves in half a second; we need the Blood every moment.337 Yielding to the Spirit for a daily filling so that his presence and leading is decisive for the manner and direction of life enabled one to recognize more readily another spirit and detour off the ‘highway of holiness’. The gift of discerning of spirits was operated in the church body whenever there was a need. It was not equated with prudence, although experience and maturity were highly regarded. Exorcisms were performed whenever the body determined by the Spirit that a demonized person was present. They were exorcized in the name of Jesus and there are to this day thousands of testimonies of persons thus delivered and taken into the fellowship.338 The norm which was and is referred to over and over again in Protestantism was the written Word of God, the Holy Scriptures. It was important to ‘rightly divide the Scripture’, interpret properly and ‘compare scripture with scripture’.339 This was the same safeguard against the deceptive spirits, which since the days of the Corinthian church, had sought to bring in fanaticism.340 Reading and studying the Word was to be balanced, however, with prayer and singing of praises. Prayer would keep the one who read too much from being ‘too argumentative’, while singing would revive the heart. But the saints could not live without the blessed Word.341 The discipline of the church followed the lines of the discernment of the Spirit. The Spirit took people into the church and turned them out. It was the church’s responsibility to discern the condition of the life according to the Spirit and Word and to restore those who might fall away. Discipline was for the purity of the body. Without purity the unity would be compromised and without unity the mission would be hindered.342
Discernment of spirits then seeks to determine the source and evaluate the results of spiritual manifestations and teachings by means of the gift of the Spirit and the Word in the body of believers.343 The affects of gratitude, compassion, and courage serve as the existential prerequisite for being fully open to and benefiting most deeply from the work of the Spirit and the Word in the church. Some spirits must be cast out and the chief protection against them is the Christian character yielded to and sustained by God. The fruit of the Spirit and the gifts of the Spirit belong together. Christ is both a fruit and supreme gift of the Spirit. His life, ministry, death, and resurrection were all due to the formation, leading, and empowering of the Spirit. Every spirit from God will testify in word, deed, and character to the incarnate Son who had the Spirit without measure. The Spirit-filled community is the best safeguard against deception of the world, flesh, or devil. The Scripture is the story of righteousness and truth. The Spirit creates hunger and thirst for righteousness and leads into all truth. Canon and charisma as given in the Spirit and received in the body of Christ are mutually conditioning. Neither can be explained or benefited from without the other. Ultimately, without the Scripture there is no path; without the Spirit there is no light. The fruit of the Spirit is the character of God and therefore is depicted fully and narratively for believers in the life of Jesus. But the acts of Jesus must be taken together with the acts of the Spirit and the story of God the Father throughout Scripture, for all three of these are parts of the one story which should evoke and shape the Christian life for the kingdom of God. Prayer is the fundamental vocation of the community and each believer. It is the belief and practice which shapes and evokes the affections and is essential to discernment and every other gift. Out of the heart affected toward God the Father, through God the Son, and in God the Holy Spirit the mouth speaks.
Pentecostal Prayer: Shaping and Expressing the Affections
Praying in the Missionary Fellowship
The Pentecostal affections are given shape and expression in prayer which is offered to, through, and in God. The traditional way of expressing this is to note the procession of all things from God through Christ in the Holy Spirit. But then all things are offered and returned in the Spirit through Christ to God. Each of the Christian affections is correlated with an attribute of God. All the divine attributes are integrated in the living unity of God who is the ground and source of the unity and continual renewal of Christian character. Thus, [each] affection is a facet of the life of prayer and is correlated to various attributes of God … In the final analysis, neither God nor the one who prays can be analyzed into a discrete series of attributes … unlike the being of God, our experiences are always partial and therefore subject to tension and one-sidedness. Fear and love of God may coexist, not because of the strength of our affectional understanding, but because of the nature of God toward whom these emotions are directed. Prayer turns us back again and again to praise and thanksgiving, to awe and confession, to rejoicing and intercession and unifies these in the love of God.344 Pentecostal affections are shaped and expressed through the prayers of missionary fellowship. There the heart is formed for worship and witness as mutually conditioning aspects of Christian discipleship. The corporate and individual prayers are shaped by the preaching and teaching of the Word, the singing of songs, the giving and hearing of testimonies and prayer requests, the fellowship of the believers before, during, and after the services, the constant praises and thanks offered throughout the service and the operation of the various gifts of the Spirit, and the intercessions of the saints. All these activities shape the prayers and the prayers in turn shape the affections. Prayer in the missionary fellowship is the primary means of participation in worship and is a rehearsal for witness. One remembers, acknowledges, and anticipates the mighty acts and faithfulness of God in prayer. It is this memory and anticipation which evokes gratitude, informs compassion, and undergirds
courage. Often the testimonies of the believer, usually offered in regular ‘testimony services’, will be in the form of a prayerful meditation on the individual’s life. These testimonies usually end with a request that the body pray for certain needs, that the believer’s life will be a blessing and that he or she will finally ‘make heaven’ their home. The believers give thanks to the Lord continually and enjoy seasons of praise for the excellency and greatness of God toward them. Compassion is expressed through the cries and groaning intercessions commonly heard throughout the sanctuary, through ‘holy laughter’ believers rejoice in the Lord. As past deliverances, preservations, and healings are remembered, thanksgiving and praise increase, making the memory, expectation, and longing more intense and deeply ingrained. In seasons of ‘concert prayer’ it sounds as if the congregation is an orchestra warming up for the concert rather than playing the same musical arrangement. The unity of this sort of prayer derives from the common response to the one Spirit. Believers have a deep sense of joy together. They are flowing together in the same stream, a unifying flow which bears one along, guided by the Spirit and the scriptural narratives. To use another metaphor, at times it is like a jazz performance with first this one and then that one improvising from a common theme; and at other times it is as if all are playing one great symphony of praise. There are praises, silences, and periods of waiting on the sovereign Spirit. Sometimes the body will come together for hours to intercede for a special need. Or they will go on an extended fast or vigil,345 this accentuating the idea of prayer as ‘waiting on the Lord’. Such waiting is essential for focus and affective transformation. There is no patience, steadfastness, or meekness without ‘waiting on the Lord’. Prayer is the primary theological activity of Pentecostals. All worthwhile knowledge must be gained and retained prayerfully because only the Spirit can lead into all truth. Even correct knowledge will lead to presumption without constant, prayerful thanksgiving, intercession, and praise. A church that rejoices, waits, and yields in the Spirit, a church that loves the Word and will tarry as long as it takes to pray through to the will of God, the mind of Christ, and the leading of the Spirit, that church is Spirit filled. Prayer, therefore, is the most significant activity of the Pentecostal congregation. It suffuses every other activity and expresses the affective richness of the believer and the church. All prayer is in the Spirit, and all who truly pray continually open themselves to and receive what the Spirit is saying and doing in
and among them. To receive and to be indwelt by the Spirit of Christ is to be a Christian. This indwelling and constant receptivity constitutes the church as a fellowship or participation in God and, at the same time, a missionary force. All who have the indwelling witness of the Spirit to Jesus Christ are to be witnesses to him. Being a part of the missionary fellowship is like being in God’s home. It is like learning from an earthly parent who gives you a vision of how things are going to be and leads you in his or her way, rewarding your obedience and chastening your waywardness but through it all nurturing you and giving you peace. There is a spirit that moves in God’s home; it is the Spirit of God. And getting possessed by this Spirit is what happens to those who dwell in the home of the Lord all the days of their life—who are nurtured by the environment of hope, compassion, and peace. Because Christian spirituality is a kind of intercourse, prayer and the church are its central foci: prayer as conversation with God, and the church as God’s ‘home’, the place where he especially dwells, his earthly presence, his ‘body’.346 The Pentecostal Church is very much like a family with fathers and mothers in Zion and sisters and brothers in training for their fundamental Christian vocation —witness. The affections of gratitude, compassion, and courage cannot be developed apart from the activity of the Spirit nor can an authentically Christian witness be given without the same Spirit’s power. The gospel of the crucified, risen, and coming one must be proclaimed in words, power, and demonstration of the Spirit. Worship in spirit and truth must be according to the nature and will of the missionary God who constitutes the church a missionary movement of transformation.347 And prayer, the heart of true worship and witness, must always and continually be in the Spirit.
Praying in the Spirit
Pentecostals could agree with most Christians that prayer is the fundamental act of faith, the central act of worship, and the deepest meaning of human existence. Humans are made for God and thus for prayer. The human is spirit, made in and for the God who is Spirit. Faith, as the establishment of a proper spiritual responsiveness by grace, believes the promises of God and lives in hope. But the heart of faith and hope is love. The Spirit is traditionally recognized as the bond of love between the Father and the Son and the point of contact between God and humanity. The Spirit of God and not human consciousness or pious feelings
is the noetic ratio of faith. The Holy Spirit is the knowability of God who gives his self-knowledge to humanity as a gift.348 Theology may depart from the Spirit through skepticism, fear of fanaticism, presumption, or the attempted domestication of the Spirit. Persons also may attempt to cultivate Christian character as a self improvement exercise. But this attempt is as doomed as that of a spouse who tries to develop the requisite affections for a good marriage apart from his or her beloved. The Christian affections are relational and thus spiritual in that they are the fruit of the Spirit. The means must be spiritual if the result or goal is to be spiritual. The goal of the Christian life is not the achievement of a certain personality profile but a participation in the life of God. When the means become the end the believer is susceptible to one of the greatest dangers to the Christian life, spiritual pride. Central to the Pentecostal practice of prayer is the view of fullness or filling with the Spirit. All Christians pray in the Spirit. But what do Pentecostals mean by Spirit-filled prayer? The possibility, some would say inevitability, of spiritual pride is a clear and present danger, because this would seem to imply a greater development of the fruit of the Spirit, and a greater openness to and desire for spiritual gifts. This subsequent experience of filling would seem of necessity to create two classes of Christians: the indwelt and the filled. Perhaps a brief discussion of filling or fullness will show how Pentecostals seek to avoid this danger. Part of the problem, of course, is the notion of ‘filled’. If this refers to an objectivization and quantification of the Spirit, then the believer would feel full and satisfied, perhaps something like one feels after a hearty meal. While there is often a deep satisfaction attendant upon spiritual blessing there are no normative feelings. Notions of the Spirit as a force or a substantial quantity have as their primary referent not the Spirit but the effects which the Spirit produces. In a similar manner the biblical words for Spirit which refer to wind or oil, flowing waters, or fire, all are used to refer to some effective property and not the essential nature of the Spirit. Earlier discussion noted the importance to the early Pentecostals of emptying out, putting off and mortifying the flesh. All these disciplines were not in order to become worthy to receive a blessing from God, to be a kind of spiritual elite. They were designed to give God more of the heart and to eliminate those things contrary to his nature and will. To be filled was to be determined in a decisive way by the Spirit. This is analogous to the idea of being filled, for example, with fear. When this happens one will either flee or fight—or perhaps be totally
immobilized. Fear fills the heart and thus decisively orients the entire person. Thus, to be filled with the Spirit is to be decisively determined by and oriented to the things of the Spirit, to what the Spirit is saying and doing. The fruit of the Spirit’s indwelling is given a deeper intensity and, in the eschatological community of Pentecostalism, a new urgency. To be filled with the Spirit and opened to greater fruitfulness has implications for the character and vocation of the believer. Others who claim no such filling or baptism in the Spirit may appear and actually be more stable personalities. Many have made more converts and many have greater Christian knowledge and insight. The first Pentecost, like those subsequently, took what the disciples were and set it on fire. They still had much to learn and unlearn. There were still going to be differences of opinion, depression, and struggles. But there is no denying the dynamic impact and charismatic character of the post-Pentecost community. Pentecostals testify that they are stronger, more open, more useful than they used to be prior to the baptism and infilling of the Holy Spirit. They continually seek the filling of the Spirit. For, though they speak of one Spirit baptism, they testify to repeated fillings. Saying that one wants to grow and that one wants to be filled with the Spirit may or may not be the same thing because Spirit baptism is fundamentally for the vocation of the believer as witness in the power of the Holy Spirit. But to say that the fruit of the Spirit has no relation to the witness of the believer would be similar to saying that holiness had nothing to do with the Spirit. The deepening of the believer’s life through cultivation of the fruit of the Spirit is directly related to concern for and effectiveness (as a yielded vessel) in witness. Some views of power and gifts tend to ignore this, emphasizing how God used Samson even during his initial compromises or how God used Balaam and even spoke through an ass (a somewhat humbling observation for all gifted preachers!) But the point of Spirit baptism is not how many or what kind of gifts have been manifested. The point is to walk in and live out of the fullness of God, to exist in radical openness, meek yieldedness and passionate zeal for the things of God.349 When the Spirit comes to indwell the believer in regeneration, he brings the Son and the Father.350 The living of God in the believer and the believer in God —a mutual indwelling—makes of the Christian, and the church as a whole, a habitation of God through the Spirit. Praying in the Spirit is intercourse and deep communion with God. Being filled with the Spirit is being yielded to, directed, and empowered by God to give a witness more consistent with his Spirit to Jesus
Christ. Sins against the Spirit hinder that witness, divide the missionary fellowship, and distort the Christian affections. Indeed a consideration of sin in relation to the Spirit adds a needed corrective to the one-sided view of sin as transgression with its resultant moralism. In Scripture the Holy Spirit may be resisted (Acts 7.51), grieved (Eph. 4.36), insulted (Heb. 10.29), quenched (l Thess. 5.19), lied to (Acts 5.3, 4) and blasphemed (Mt. 12.31; Lk. 12.10; Mk 3.21, 29). So sin is not only transgressing the law, it is also something deeply personal. To think of opposite kinds of responses would indicate something of what it would mean to be filled with the Spirit. Instead of resisting, yielding; instead of grieving, rejoicing evermore; instead of insulting, revering in honor; instead of quenching, being inflamed and provoking others to love and good works; instead of lying to the Spirit, speaking the truth in love in order to edify and preserve the missionary fellowship; instead of blaspheming, blessing, treasuring and proclaiming the witness of the Spirit as the witness of God. If these responses were forthcoming in the Spirit, the resultant affections would have God as the source, goal, and means of fulfillment, and self-fulfillment would be a by-product. In the final analysis, the fruit of the Spirit cannot be cultivated by anyone but the Spirit in persons who constantly submit to his reminding, leading, searching, and enabling. As Karl Barth, who can hardly be accused of promoting enthusiasm, has said, ‘Only where the Spirit is sighed, cried and prayed for does He become present and newly active’.351 Indeed, the best defense against enthusiasm is the continual filling of the Spirit. In this way humble gratitude, compassionate love, and courageous hope will dispose one toward reproof, rebuke, correction, or resistance, opposition, and rejection of everything that is unscriptural, unedifying, and antithetical to Christian witness. Pentecostals have often used the strategy for detecting counterfeit money as an analogy for discerning spirits: ‘Be so familiar with the authentic, that the false is readily detectable’. This can only happen in ongoing yieldedness and openness to the Spirit. It is a life lived in and from the Spirit, in Christian discipleship, in the missionary fellowship that is lived in the truth. The Spirit leads into this reality, this faithfulness of God with us. A relationship with God is only possible actually, continually and ultimately in the Spirit of God. Prayer is the way to acknowledge this means to fruitfulness, and the prerequisite for discernment as the Spirit’s gift. Pentecostal prayer is offered in three forms which shape and express the
affections each in its own way. These forms are: with words understood, without words, and with words not understood. One of the three affections discussed earlier will be paired with one of the modes of prayer to illustrate this diversity. The first and most obvious mode of prayer is with words understood or prayer in the vernacular. Pentecostal prayers have been shaped primarily by the Bible and the understanding of the Christian life which has been mediated through the early Holiness movement. Gratitude has been the most commonly expressed prayer in the Pentecostal congregation. Thanks for what God has done and praise for who God is are continually offered in Pentecostal worship. The presence of the Spirit is most characteristically responded to in this way. But sighs, groans, and laughter also express and shape the affections. Compassion is the most obvious example. In intercessory prayers Pentecostals weep over the lost and afflicted and long for the coming of the Lord. Prayer as sighs is evoked by the Spirit who groans and sighs even as all creation for the full and final manifestation of the sons and daughters of God.352 ‘Holy laughter’ is also common as believers experience the comfort and joy of the Spirit and meditate upon the eschatological promise and vision. Indeed all of prayer is eschatologically qualified by the ‘already–not yet’ tension previously discussed in Chapter 2. Thanksgiving, love, and confidence are indicative of the ‘already’ of what God has done, is doing, and will do, whereas petitionary longing, rejoicing, and praise because of the promised victory, and courageous waiting through hard trials are more indicative of the ‘not yet’ pole of the affections. Speaking in tongues, the most studied and discussed aspect of Pentecostal piety, is a form of prayer which is especially edifying to the individual; it gives assurance, confidence, and courage. This eschatological speech indicates that the power of the end is breaking in now in this way, though of course it is only one of the ways this is happening. The end began in Jesus Christ and is coming to consummation. This speech creates and sustains a community whose culture is situated simultaneously in the ‘already’ and ‘not yet’ of eschatological existence. Tongues, when interpreted, are, like prophecy—good for the whole body. All will not exercise this gift in tongues in the body; but for Pentecostals, all may speak in tongues in self-edification which will, in the unity of the body, ultimately if indirectly edify the whole. All prayer, as noted earlier, is in the Spirit. The three modes suggest that the whole of the personality is to be engaged in prayerful dialog and communion with God. Further, the threefold shape of prayer indicates that affections are not only complex, cognitive integrations but that they also operate on and are
expressions of different levels or dimensions of human consciousness. This is true whether one’s culture is oral-narrative or literate. First World and Third World participants are in need of such searching, formative, and multidimensional prayer. All three modes of prayer are interdependent and mutually conditioning. In prayer the Holy Spirit continually sanctifies believers so that the structure, content, and dynamics of God’s holiness are reproduced in Christians as righteousness, love, and power. These three correspond to the gratitude, compassion, and courage used earlier to characterize Pentecostals. The modes of prayer are modeled and practiced in the missionary fellowship as the fundamental means to form and express the distinctive affections. The witness, fruit, gifts, and filling with the Holy Spirit contribute to a single unifying passion which orders the affections and directs them to a single goal: the kingdom of God.
Pentecostal Passion: Living toward the Kingdom Just as Pentecost is larger than a single day, so Pentecostalism is larger than a single experience. Pentecost, originally a spring harvest festival (the Feast of Weeks), became a commemoration of the giving of the Law at Sinai. This Law was a way of life, a covenant established by words written on stone by God and the voice of God speaking out of the fire and cloud that covered the mountain. Pentecost, like Sinai, represents a dispensation to live by and not simply a ‘kickoff event’ inaugurating the church. For one thing, the church as the people of God, the people of faith, hope and love, is much older than Pentecost. For another, the people at Pentecost continued in the apostles’ doctrine, fellowship, and breaking of bread.353 The prophetic fulfillment of that day opened history in a new and decisive way for the church’s witness to Jesus Christ in the power of the Spirit. In the words of José Comblin, Catholic liberation theologian, Christianity has two sources: the ‘Jesus event’ and the experience of the Spirit—Easter and Pentecost … intimately bound up in one another, but neither can absorb or reduce the other. The tradition of Western Christianity has never given enough importance to the Spirit. There was one Easter; there are millions of Pentecosts.354 The message of millions of Pentecostals today is that the kingdom of God is breaking in, through the gospel ministry of words, power, and demonstration of the Holy Spirit. For them Pentecost has become a liturgical paradigm, an existential reality, and a dispensation of the Spirit in the last days. Earlier in this chapter it was shown how these Pentecostals have operated out of an implicit correlation between God as righteous, holy, and powerful, and the Christian life as gratitude, compassion, and courage. This was a correlation of divine attributes to Christian affections. The Holiness parentage and apocalyptic orientation of Pentecostalism gives these affections, common to all Christians, their distinctively Pentecostal configuration. Through prayer in particular, in the three modes mentioned above, the believer is shaped for and expresses the foretaste of the kingdom.
A Passion for the Kingdom
For Pentecostals the kingdom, at least their being a victorious part of it in the
future, is by no means inevitable. They remember that the kingdom was taken from Israel and given to others who brought forth the proper fruit (Mt. 21.43). This introduces another tension in Pentecostal spirituality in addition to the characteristic ‘already–not yet’. Seen in this light, the fruit of righteousness, peace, and joy and the correlative affections of gratitude, compassion, and courage are indispensable as dispositions requisite to faithful participation in the reign of God. Indeed, since for most Pentecostals there is no place of unqualified or ‘eternal security’ other than abiding in Christ, there is therefore no static, abstract vision of the Christian life which will suffice. They are a goal-oriented or teleological community on the way to the kingdom. As Robert Roberts has observed concerning the requisite earnestness of seekers after the kingdom, I have to yearn for the kingdom, seek it, treasure it, desire it, before the vision it gives me will amount to Christian spirituality—that is, will amount to hope, peace, joy, compassion and gratitude as genuine emotions. If I am content with my present worldly life, successfully denying the prospect of death and complacent about the evil in the world’s heart and in my own, then the message of the kingdom will not bear these fruits in me even if in some sense I believe it.355 Therefore, to live before and in the presence of God through Christ is absolutely necessary if all is not to be in vain and fruitless.356 The kingdom of God is God’s rule or reign. It is that society and situation in which persons, created by God in the divine image, love God and their neighbor with their entire being. The kingdom is ‘present and future’, ‘already and not yet’, ‘in but not of this world’. The community of Christ acknowledges and agrees to submit joyfully to this reign. The Holy Spirit is the reigning power who forms persons in accordance with the requirements of the kingdom. These requirements correspond to the nature of the king and what it means to be rightly related to the king and others. To be filled with the Spirit, therefore, is to be disposed toward the kingdom with all decisiveness, longing, and earnestness. As Paul has said, the kingdom is not a matter of meat and drink (moralism) but of righteousness, peace, and joy in the Holy Spirit. These three fruits of the Spirit require and envision a society or community of the king.357 The representative Pentecostal affections discussed in detail earlier are dynamically and teleologically related to this society on the way to the end. The fellowship of the Holy Spirit and the affections of individuals mutually require and condition each other. But the passion for the kingdom of God is the organizing principle, the integrative center of the affections.
This passion may be construed as a ruling affection in the following manner. Praying for the kingdom of righteousness and walking in the light are ways of shaping and expressing the affection of gratitude. Giving thanks is a fundamental recognition that one’s life and the kingdom are God’s gift. Praise and gratitude mean living to the praise of God’s glory and walking in the works ordained from the foundation of the world to glorify God.358 Notice that to walk in the light, to be grateful, and to long for righteousness in the whole world are what it means to believe in a righteous God. To know this God is to be made righteous by faith, then to become the righteousness of God in the world in anticipation of a consummated kingdom of righteousness. The Spirit guides into all truth and empowers the believer to proclaim the gospel message. Righteousness means missionary faithfulness. Righteousness speaks of the ordering of all of life according to the will of God. It describes the structure, limits, and contours of that relationship. There can be no peace with God and no true joy without righteousness. But righteousness will never be perfectly realized in this world because of human fallibility and worldly rebellion. The interim fulfillment of the Law and thus of all righteousness is love. The heart of Pentecostal spirituality is love. A passion for the kingdom is a passion for the king; it is a longing, as has been shown already, to see God and to be at home. When the heart is whole in its love for God there is a profound peace. It is the peace purchased on Calvary and applied through the blood of Jesus to the believer to cleanse from all filthiness of flesh and spirit, perfecting holiness in the fear of God. This deep fear and reverence for God, with the realization that salvation is a dynamic relationship and not a static inevitability, gives an edge to Pentecostal spirituality. There is little peace and rest for the double-minded person who regards iniquity or resistance in his or her heart. The awareness of this struggle, the vigilance, consecration, and the travail of praying through to peace, all contribute to the compassionate drive of Pentecostals toward the world; their neighbors are not only transgressors, but also, like themselves, are defiled and inwardly alienated from the life of holiness and happiness. This peace borne of perfect love and reverence, is a moment-bymoment abiding in Christ through the Spirit and the Word. The saints at Azusa were deeply aware of this dimension of spirituality: When men and women are saved and sanctified, they need the Blood just as much as they ever did. We should not trust ourselves a half a second; we need the Blood every moment.359 In the Spirit, the blood, or life given and being given, keeps on cleansing daily as
believers submitted themselves to God in confession and repentance. The kingdom is for those who pursue peace and holiness without which no one will see the Lord.360 The passion for the kingdom means yielding to the Spirit as he searches, fills with love and sighs and groans for the kingdom. When one sighs with the Spirit in longing expectation, then one is disposed rightly. Several times it has been noted that living in the presence of God was crucial to Christian spirituality and especially Pentecostal piety. This does not entail living with certain constant sensations, nor is it merely a mental exercise. There is a daily vital experience of placing one’s self at the disposal of the Spirit as the 361 source of and direction of life. The disciplines of private and corporate prayer, living in the Scriptures, walking in fellowship, the Lord’s Supper, fasting, all are ways of learning to attend to the Spirit in following Christ. Living in the presence of God, walking in the light, and delighting in the Lord are all aspects of the same thing. This is what it means to know God. For Pentecostals being baptized in or filled with the Spirit is a way of speaking of the integration of these aspects of the Christian life. The joy of the Lord is a strength, encouragement, and source of hope. This joy is the fruit of the Spirit who gives the believer a ‘taste’ of the power of the age to come. Sometimes even a taste will cause the believer almost to lose consciousness. The ecstasy of Pentecostals is not a possession or loss of self-control. It is a relinquishment of control in a trust that believes that the kingdom—like salvation is a gift of God that has nothing to do with self-willed and technique-manipulated progress but has everything to do with the power of the God who raised Jesus and sends the Spirit with witness and wonders into the community of hope. The enjoyment is most often a quiet, constant, abiding sense of God’s leading and providence. But it is also—and the two are mutually reinforcing—characterized by moments of unspeakable joy. All gifts of the Spirit are eschatological, proleptic signs of a kingdom of joy where sorrow, death, and sin are put down and banished once and for all. Speaking in tongues may express the painful longing of joy or its exultant victory, but true joy always instills courage to press on to the kingdom. Healings, from a headache to a heart attack, are provisional, temporary inducements to rejoice because the Father is going to give the kingdom to the poor who seek first the kingdom and his righteousness. When it is kept in mind that most Pentecostals are poor, non-white, Third World, young adults, it is no wonder that this renewal in the Spirit, this anticipatory celebration of the kingdom, is so often characterized by laughing, leaping, and praising God. They believe the kingdom
is theirs. They could heartily agree with Wesley who, in his comments on Rom. 14.17 and 1 Cor. 4.20, proclaimed, The kingdom of God … that is true religion, does not consist in external observances but in righteousness … the image of God stamped on the heart; the love of God and man: accompanied with the peace that passeth all understanding, and joy in the Holy Ghost … For the kingdom of God … real religion does not consist in words, but in the power of God 362 ruling the heart. The passion for the kingdom is the ruling affection of Pentecostal spirituality and not the mere love of experience for experience’s sake. There are several ways of justifying this statement, but for now the most important one is to observe that Pentecostal spirituality is not developed in solitude but requires a Pentecostal community of witnesses.
The Community of the King
The Pentecostal passion for the kingdom of God is formed and expressed in and through a Pentecostal community. This community exists in the pronounced eschatological tension of the ‘already–not yet’. The strategy of the Holy Spirit in announcing and previewing the kingdom is to form and sustain the community of the king. This strong tension explains why Pentecostals to this day have no strongly developed ecclesiology. In some way the church as a human organization, a polity with policies and procedures, is a great disappointment. This is a strength and a weakness. It is a strength because it is an ongoing critique of the tendency of the church toward an involuted institutionalism. The church is a church on the way to the kingdom and is thus more a movement of the Spirit than a structure wedded to the present age. It is an obvious weakness, because it means that there are often not sufficient biblical and theological controls and directives worked out for the church’s life outside the worship and witness settings. Pentecostals have often divided over minor points of doctrine and personality clashes. They are serious about doctrine but often lack the interest and will to give sustained attention to the ‘politics’ of the church. The community, in its desire to be separate from the world, often uncritically takes on elements of its culture. This is even more true as Pentecostals experience ‘redemption and lift’ into a higher socio-economic status. But my purpose here is to note the relation of the church to the kingdom in the
Spirit’s strategy. Pentecostals do not believe that worldly politics, manipulation, and coercion will ever bring in the kingdom. They are often criticized for their lack of social consciousness and responsibility. There are historical, social, and theological reasons for this. From the revivalism and social reform of the nineteenth-century Holiness movement to the great reversal among evangelicals of the late nineteenth and early twentieth century there was a complex shift culturally, socially, and theologically which influenced Pentecostals.363 There was a shift from cultural optimism to pessimism, from postmillennial optimism to premillennial pessimism, from sanctification as purity to sanctification as Spirit baptism for power. Coupled with these shifts was the rise of the radical, historical-critical approach to Scripture, the assertion of evolutionary progress, and the devastating aftermath of the Civil War. Many Pentecostals at the beginning of the twentieth century were a part of the proletarian masses of people who had joined the more radical Holiness groups. Faced with the choice of liberal, social-gospel activism or conservative fundamentalism the latter seemed more socially and theologically appropriate. This was unfortunate for both the liberals and the Pentecostals—to say nothing of the fundamentalists! At any rate, given that kind of historical, social, and theological location, Pentecostals eschewed politics. After all, why should those of the disenfranchised masses, then or now, try to play the game of the power elites? Jesus would reward covenant faithfulness to his Word and to the neighbor, but the world would never do this. The church was a community on the way to the kingdom; this world was not home. This did not mean that Pentecostals had no social significance however. They, of course, were and are very much involved in rescue missions, medical help, orphanages, schools, feeding the hungry, and clothing the naked. They cared for each other and those around them who needed the love and care of the Lord. The church was to spread the gospel, relieve suffering, and prepare the faithful for the coming of the Lord, not crush social injustice. Many early Pentecostals were pacifists and quite critical of society. The mixing of the races, leveling of persons in the ‘democracy’ of the Spirit and his gifts, and the ministry of women, all were countercultural, to say nothing of the practices of dress, speech, and behavior which further manifested the social ethic and narrative of holiness that characterized them! Nevertheless, this counterculture trained men and women to be courageous, articulate, and patient. The community was the Spirit’s strategy for transforming the world and them with it. As such the ‘works of the flesh’ were destructive of
unity, therefore of mission. Those who practiced these things could not inherit the kingdom of God. The world, the flesh, and the devil were enemies of the kingdom of God. The fruit of the Spirit, on the other hand, tended to unify and, coupled with the gifts, build up the community and qualify it for effective witness. In later years, as economic fortunes and the social location of North American Pentecostals have risen, their sense of eschatological passion has often declined.364 If the tendency of the early years was toward rejecting society or ignoring it, the tendency of later years has been to accommodate. With respectability has come new perils. But now many Pentecostals are becoming interested in the roots of the movement. They are in dialog with other theological traditions and, with some evangelicals, are rediscovering something of the apocalyptic and revolutionary potential of Pentecostalism. The eschatological tensions (already–not yet, church–kingdom, church–world) must be heightened and given new theological direction if the spirituality is to recover something of the original radical vision, deepen affectively and open out to give to and receive from the richness of the larger body of Christ. Even more importantly for Pentecostals, the missionary expansion, so stunning in the twentieth century, is in danger of stalling out and being betrayed by a strictly pragmatic lust for quantity and effectiveness which lacks the theological concern for quality—that is, for a responsible Christian discipleship and ecclesiology. The passion for the kingdom of God with the attendant attention to affective transformation and integration could offer one way to move forward. But first, attention must be given to certain crucial internal tensions and external criticisms; new theological paradigms need to be constructed to address these tensions and criticisms and to unify elements of the spirituality which tend toward individual fragmentation, ecumenical isolation, and missionary narrowness. This will be the agenda of the fourth and final chapter.
Chapter 4
Pentecostal Theology as Trinitarian Transformation: A Theological Revision
The Breakup of the Pentecostal Synthesis: Internal Problems and External Criticisms
The Logic of the Argument Perhaps it would be helpful now to step back and look not only at the structure but also, and especially, at the logic of this presentation. The following chart may be referred to as the explanation unfolds.
This study has sought to demonstrate a certain correlation, implicit at least, between a particular view of God (divine attributes) and a distinctive Pentecostal spirituality whose integrating core is found in certain apocalyptic affections. These affections are shaped and expressed by certain beliefs and practices and represent the existential integration of those beliefs and practices. It was shown that this spirituality is Christocentric (the fivefold gospel) because of its pneumatic starting point. In the Spirit Christ saves, sanctifies, heals, baptizes in the Holy Spirit, and is coming soon as king. It was asserted and demonstrated that, given the nature and history of Pentecostalism, the theological task is best understood as a discerning reflection by the eschatological missionary community upon the living reality of God with us.
Since spirituality, the fundament of all theology, was construed as the integration of beliefs and practices in the affections, and further, since these affections were characterized as ‘apocalyptic’, it was important to portray the apocalyptic ethos which is the immediate context and horizon of believer and doer of the Word. The good and bad elements of this apocalyptic were assessed. Next the fivefold gospel, and three-blessing scheme of salvation were seen to constitute the core of early Pentecostal orthodoxy. Salvation was a narrative journey, and pilgrims practiced their faith in the light of the inbreaking kingdom through worshiping, walking (ethics), and witnessing in the Spirit of the end. The walk was a living out of a cosmic drama in which the testimony to Christ and the testimony about one’s daily life were processed in and with the eschatological community. The orthodoxy and orthopraxy of the Pentecostal community were shown to be interdependent in Chapter 2 and integrated in the affections (orthopathy) in Chapter 3. It was at this point that the divine attributes of righteousness, love, and power—sometimes implicit, sometimes explicit in the previous chapter— were seen to be correlated with the salvation testimony (saved, sanctified, and filled with the Spirit) and the biblical understanding of the kingdom of God as righteousness, peace, and joy in the Holy Spirit. Following a discussion of the fundamental characteristics of affections (objective, relational, dispositional), the apocalyptic affections of Pentecostal spirituality were explicated in such a way that their correlation with the divine attributes was made explicit. The affections were shown to be shaped by and expressive of the beliefs and practices. Though not the only ones, gratitude, compassion, and courage were selected as central Pentecostal affections. Connectedness with each other and some other affections were shown in order to indicate the kind of ‘grammar’ necessary to speak the language of Pentecostal spirituality or, better still, to understand something of the ‘rulishness’ of the way Pentecostals speak the language of the Christian faith. Pentecostal prayer was shown to evoke and express the affections, and its various modes were explored. Prayer was seen to be the primary and essential theological act of the community as well as the continual milieu of its worship and witness. The beliefs and practices are integrated in the affections, which are correlated with God and salvation. But then the affections are focused toward the kingdom of God, which was shown to be the ruling affection or passion of Pentecostal spirituality. This passion at the heart of the beliefs and practices gave definite direction, depth, and intensity to the affections.
The view that Christianity is fundamentally, though not exclusively, a matter of certain affections, which form the existential core of the spirituality but are not merely self-generated pious feelings—the view held more or less by Jonathan Edwards and John Wesley, with ample biblical precedent—is especially appropriate for the study of Pentecostalism whose corporateindividual spirituality is marked by living in and from the eschatological presence of God. In addition to the claim that this is an especially appropriate approach to Pentecostalism there was, in Chapters 1 and 2, an argument that this was true for Christianity in general and crucially important in a consideration of the theological and pastoral task of the church. Though not central to the argument itself, this theological claim underlies everything done herein. Theology is the reflective, prayerful business of working at the interrelationship of orthodoxy, orthopraxy, and orthopathy, or beliefs, actions, and affections, respectively. This view is taken to be over against that of an overly rationalistic fundamentalism or a liberalism, rooted in human reason or experience, which is not decisively shaped by Scripture. For the early Pentecostals the in-breaking of the kingdom with all the signs of the Latter Rain required a re-vision of the Christian life, the church, and missionary priorities. This was in continuity with the nineteenth-century Holiness and revivalist themes but represented an eschatological intensification of those restorationist, perfectionist, premillennial motifs. The resulting Pentecostal synthesis with the attendant signs, wonders, holy affections, and missionary explosiveness was vibrant, powerful, and widely influential. But it was not yet established. Within five to ten years of the Azusa Street Revival, problems would arise which were so severe and so deep that they would mark and fragment the movement for the rest of the century.
The Nature of the Problem
Into the ‘Pentecostal pot’ of the first decade of the twentieth century were added several different and potentially explosive ingredients which needed careful, slow cooking. Persons of different racial, regional, and theological backgrounds were brought together in prayer, renewal, and communal care. Men and women, African- American and Caucasian, north and south, east and west, all converged in ‘upper rooms’ in Topeka, KS, Los Angeles, CA (Azusa), Dunn, NC and Atlanta, GA. Their suspicion of organization and naïveté concerning the revivification of the church through a deeper sanctification and last days’ empowerment set them up for trouble. In addition, there was an excitement and
hunger for new insights and experiences. While not bad in itself, and almost always qualified by seeking biblical precedent for everything, it was nevertheless contributory to the entire volatile ethos which developed. Like the book of Acts there was no developed ecclesiology or polity for adjudicating differences—especially those that might require more than a few days or weeks to consider. Although there were many periodicals, and people gathered to discuss matters in a Christian conference reminiscent of Acts 15, nevertheless, the fact remained that the new movement, though strong on transforming experiences, lacked experience in adjudicating theological and interpersonal differences and moving toward a consensus.
In 1910 William H. Durham began to challenge the predominant threeblessing view of salvation and within four years the movement was split along soteriological, theological (doctrine of the nature of God), and racial lines.365 Durham held that sanctification began in regeneration and continued as growth. The second crisis was Spirit baptism and not sanctification. He could not find a second work of sanctification in Acts nor did he experience one before his Spirit baptism. He rested upon the ‘finished work of Calvary’. This, of course, was more acceptable to many fundamentalists; but nevertheless, not enough to cause the more conservative elements among them to embrace or even tolerate the Pentecostals. When the controversy became ‘carnal’, some persons, like Frank Bartleman, parted company with Durham even though they agreed with most of his concerns. Durham’s rejection of subsequence and eradication in relation to sanctification put Pentecostals even more at odds with the Wesleyan Holiness movement which had been its cradle. Sanctification now became positional (imputed) and progressive. Holiness would continue as a concern, a consecration in readiness for the return of Christ and an ideal to be sought. And indeed much of the altar theology of Phoebe Palmer could be embraced by Finished Work advocates, at least the emphasis on claiming one’s sanctification in faith. But there was no real consideration of what in fact Wesley had taught, and Wesley’s safeguards against Pharisaism and moral complacency had not been carefully considered. Denying the attainability of entire sanctification there was a tendency
to accept some compromised ideal as the goal itself. For denial of the attainability of an enjoined moral ideal leads inevitably to the practical repudiation of that ideal. If realism determines that only compromise is possible, then compromise becomes the goal. It is sought for, acceded to, enshrined; acquiescence displaces aspiration.366
The fivefold gospel became the fourfold once again, with Christ as sanctifier dropping out, and the possibility of a new soteriological integration vis-à-vis a reappropriation of deep Wesleyan insights was lost. It seemed to many Wesleyan-Holiness Pentecostals to be a betrayal of the original vision and tantamount to a disastrous disjoining of purity and power. This was ironic since the Holiness movement had seen purity and power as two sides of the same coin; for them sanctification was Spirit baptism. Many of the Wesleyan Pentecostals had become Wesleyan before receiving the Spirit baptism and had been
persecuted because of it (e.g. R.G. Spurling and N.J. Holmes); thus they were very disturbed over abandoning a spiritual reality which they had earlier maintained in the face of opposition. C.H. Mason, the bishop of the Church of God in Christ (Wesleyan-Pentecostal body), nevertheless did not see this as a reason to disfellowship the Finished Work proponents or divide the movement. Others were not so sure. J.H. King of the Pentecostal Holiness Church pronounced the Finished Work to be ‘Antinomianism, Darbyism dressed up in a Zinzendorfian garb and going throughout the land doing its old destructive work among believers’.367 Within weeks of Durham’s death in July of 1912, the new Issue or ‘Jesus Only’ controversy erupted. This was a unitarianism of the second person of the trinity which sought to establish, in order, the correct baptismal formula (Acts 2.38 over Mt. 28.19), the correct name (Jesus = Joshua = Jehovah saves, therefore Jesus is Jehovah and all the names of God are unified in him), and the correct nature of God (Jesus as united designation for Father, Son, Holy Spirit). Three factors contributed to the rapid development of this doctrine, in addition to the immediately precipitating historical events:368 the already prevailing Jesucentric experientialism, the openness to and search for special revelations, and the intense focus on the book of Acts. The Finished Work and New Issue controversy, along with a desire to unify the many scattered missions, storefronts, and churches of the movement, led to a call for an assembly in Hot Springs, Arkansas, 2-12 April 1914. The group assembled was almost entirely white; though C.H. Mason attended, he had not been invited. The opening address by M.M. Pinson was entitled ‘The Finished Work of Calvary’, and the preamble to the Bases of Union, while mentioning redemption and Spirit baptism, was explicitly silent on entire sanctification. Though the words ‘entire sanctification’ would later appear as a doctrinal heading in the 1916 Statement of Fundamental Truths, its wording and the memory of the 1914 meeting clearly signaled that the movement was divided. The Finished Work, New Issue, racial controversies, all were swirling around in the air at the birth of what was to become the largest Pentecostal denomination. Women were not prominent in all these controversies as protagonists, adjudicators or (with the exception of Florence Crawford and later Aimee Semple McPherson) as formers of new movements. For the most part women, though continuing to found churches, pastor, prophesy, missionize and so forth, were increasingly left out of polity and leadership matters. They had been elders at Azusa. In the ensuing years their numbers in the ministry were to decrease
though their spiritual influence and importance to the movement was immeasurably great.369
The Force of the Criticisms
In addition to the fierce internal debates over doctrine and the frequent personality clashes, there was, from the beginning, severe criticism of the style and substance of Pentecostalism.370 The criticism of the revivalistic, emotional activity was nothing new really. Dancing, yelling, leaping, prostration, crying out to and waiting upon the Lord were all part of the revivalism of the previous centuries. The prominence of African-Americans, poor whites, and women was a source of shock and embarrassment to many. The combination was startling, to say nothing of the gifts of the Spirit. Speaking in tongues was especially targeted and used to label the movement. The Pentecostals were, to use the kinder, gentler terms, ‘Holy Rollers’, and ‘tongue talkers’; the less kind referred to the movement as the ‘last vomit of Satan’ before the end of the age. Pentecostals were variously characterized as demonized, deranged, regressive, orgiastic, divisive, elitist, escapist, and anti-intellectual.371 With the rise in socio-economic and educational standing, the emergence of Pentecostals into the Evangelical mainstream through the National Association of Evangelicals in the 1940s, and the explosion of the charismatic renewal from the 1960s onward, some of the criticisms have softened. But other more pointed theological criticisms have emerged372 having to do with subsequence, worksrighteousness, and the alleged exegesis of experiences; the old criticisms are still around’ in North America and the Third World. Richard Quebedeaux, though making his critique a little less severe in a later work, nevertheless contrasted classical Pentecostalism and the charismatic renewal, respectively, in the following manner:373
Of the seven criteria above, the last is probably the most telling: class location
contributed to his negative and one-sided analysis of Pentecostalism. Early Pentecostals and those in the Third World would evaluate themselves using different categories. He ameliorated the severity of his analysis after conferring 374 with some more formally educated Pentecostals. In North America, though accommodation is not the total picture (giving of time, talents, and treasures usually exceeds that of most other Christian bodies), there has, nevertheless, been a price to pay as Pentecostals move into the middle and upper classes. Movie stars, money, and megachurches have often eclipsed tongues as evidence of spiritual fullness and blessings. Though denominational officials lament the changes and condemn the ‘name it and claim it’ prosperity gospel, nevertheless, from Jim and Tammy Bakker to Jimmy Swaggart, the record leaves little doubt that Pentecostals have not tried very hard to resist the temptations of the good life. Describing this latter aspect of contemporary Pentecostalism as a ‘veritable Amway movement’, historian Harrell notes that it offers not healing for the sick, but security for the well; not consolation for the poor, but confirmation to the successful … as Martin Marty perceptively noted … in times past Pentecostalism ‘was “true” because it was small and pure but now it is “true” because so many are drawn to it’.375 Grant Wacker believes that even though the trend may be toward accommodation, now the first and second generation pioneers are best understood, not in terms of theories of compensation for low social status or poverty, but in terms of a radical perfectionism which was not a means of escape from but a means of transcending life’s difficulties. They ‘tried to cope with sin and suffering by forging a new vision of what the gospel was all about’. Wacker goes on to observe, In crucial respects, the Pentecostal movement is less mature today than it was in the early years. Modern Pentecostals do not need to romanticize their past in order to learn from it. The first generation resisted the blandishments of secular society in order to preach a gospel that challenged the culture in more than superficial ways. Modern Pentecostals might recover that vision. They might discover as church historian George Marsden has put it, that grace is not cheap and forgiveness is more than good manners. They might discover that in the beginning, the movement survived not in spite of the fact that it was out of step with the times, but precisely because it was.376
The logic of the initial spirituality of Pentecostalism (still present though distorted), the nature and number of internal problems and external criticisms, as well as the emerging class differences and accommodations of modern Pentecostalism, all point toward the need to reconsider Pentecostal spirituality.
The Need for Re-vision
The Pentecostal movement is in a period of theological adolescence. Tempted to forget or selectively remember the past, dangerously accommodated to North American middle and upper class culture, and having its supposedly distinctive experience, the baptism in the Spirit, marketed in every church or induced for the bored and impatient, Pentecostals are being asked to choose whom they will be. It is neither possible nor desirable merely to repeat the past, and pragmatism soon leads to cynical detachment and withdrawal. The call for re-vision is coming from various quarters. Some speak of the movement as being at a ‘crossroads’.377 Margaret Poloma in her detailed sociological analysis of the Assemblies of God, one of the largest Pentecostal denominations, asserts that Pentecostals should pay attention to their core values (she focuses on the ‘holiness ideal’ or the closing of the ‘ideal-real gap’). She notes that power and success rather than simplicity and sacrifice are now looked upon as synonymous with holiness. She concludes that if they abandon ‘dynamism for relativism, the supernatural for the natural, the ideal for the real, and ambiguity for rigidity’ the church’s distinctive identity will be destroyed.378 These observations could easily apply to most North American Pentecostals who have moved into the middle and upper classes and are third and fourth generation members. Along with several inside observers, she believes that charisma or Pentecostal distinctiveness will be diminished in the marriage of the movement to the powerful and famous or to conservative fundamentalism. As the charismatic movement begins to lose its novelty, the mainline denominations work to ‘conservatize’ and accommodate it; and while the independent charismatic movement is growing, there may be a decline in overall growth in North America.379 Meanwhile, as the explosive growth of the Third World continues, new and urgent questions of theology, discipleship, and suffering press for a careful response. While personal televangelism kingdoms fall in public view and private despair, there is a growing desire to re-vision the past, to look with realism and respect upon the fathers and mothers of the movement. Those who share this
concern are convinced that Pentecostalism is more than a feeling, more than an episode in church or individual history, more than an added option for Christians whose personality profile happens to match. They seek a second naiveté, and a rekindling of the apocalyptical vision—expanded so as not to be so 380 individualistic—of the kingdom of God. Along with Roman Catholics, Eastern Orthodox, and Protestants, Pentecostals too are being called to a renewed vision which addresses global and local pastoral issues. The Pentecostal spirituality which has been the concern of this monograph represents one of the most significant and far-reaching developments in the modern church. On one level gifted, careful leadership is needed more than ever, but on an even deeper level theological work alone will bring unity, focus, and renewed power so that the movement can both give and receive gifts in the body of Christ. The pioneers were not afraid to risk and to sacrifice. If sons and daughters are going to prophesy and not merely speculate they must do likewise. And part of that risk will be in the area of serious, sustained, theological discussion within and without the movement. If apocalyptic is in some sense the mother of theology and especially of this spirituality, then it is time to get to know her better; it is time to wait for fresh interpretations of what the Spirit of the end is saying to the church.
The Re-visioning of Pentecostal Spirituality: The Eschatological Trinity Let us recall the definition of the theological task put forward in Chapter 1 and illustrated in Pentecostal history with varying degrees of faithfulness: theology, for Pentecostals, is a discerning reflection by the eschatological missionary community upon lived reality. The story and testimony of this community lives by the power of the Spirit within and all around the believer. The Spirit of the end groans, sighs, and pressed within in order to drive out toward the world in witness and toward God in worship. Prayer is the first act of discerning reflection, engaging the whole person and involving the whole community as context and example. The living reality of God and the kingdom calls forth a wholistic response which in turn leads to deeper reflection and further response. The spirituality of the community as an integration of beliefs, practices, and affections is the precondition and ongoing result of this discerning reflection. When the integration begins to fragment there are intellectual struggles, affective distortions, and practical dilemmas which cry out not merely to be solved one at a time but also to be interpreted as symptomatic of deeper need.
Unification and Fragmentation
The Apostolic Faith Mission at Azusa Street stood ‘for the restoration of the faith once delivered to the saints—the old time religion, camp meetings, 381 revivals, missions, street and prison work and Christian unity everywhere’. From the Christian Union of 1886 to the Azusa Street Mission there was a cry for unity as they sought to ‘displace dead forms and creeds and wild fanaticisms with living, practical Christianity’.382 But as seen earlier in this chapter the disagreements and divisions over the number of crucial salvation experiences, the name and nature of God, and the unity of all peoples and races throughout the body, globally and locally, was soon at issue. Splits over doctrine, personalities, race, and regionalism were common. Along with the fusion of Christian love was the fission into varying groups as the power and impact of the movement intensified and swept all outward to the world and forward toward the end. In spite of attempts at unity, a polity and process for consensus did not emerge. Things were moving too fast; the pressures were too great. And perhaps
also there was a need for greater sanctification in terms of love and patience. But the concern for truth in every part of faith’s formulation placed strain on the best of motives. If unity could not be assured by ‘man-made’ creeds, neither could it be guaranteed by good intentions. Everyone agreed that unity as love and biblical belief was crucial for carrying out the last days’ mission of the church. But with so much emphasis on revival and the church as an event, there was not much inclination or interest in building the kind of organization that could serve the vibrant organism. Having rejected not only ‘man-made’ creeds, but also being suspicious of ‘man-made’ organizations, they were left to the improvisations, imitations, and pragmatism of leaders of varying ability and maturity who often fought each other as much as they fought the devil. In addition to ecclesiastical fragmentation there was a splitting or lack of integration of the stages of salvation. They became almost like the strict dispensational divisions which the Pentecostals had inherited (and read about in their Scofield Bibles) from the Fundamentalists.
Speculation and Determinism
Although Pentecostals generally had a different kind of dispensationalism than Fundamentalists, they were nevertheless influenced by their use of Fundamentalist publications and speculations concerning end-time events and characters. Pentecostal dispensationalism was more like that of John Fletcher or Joachim of Fiore (they were familiar with Fletcher but not Joachim). According to this schema there were three overlapping interrelated ages of the Father, Son, and Spirit, respectively. They were living in the age of the Spirit before the final day of glory following the return of Christ and the making of all things new. As the first decade of the twentieth century passed and the first generation began to die out, so too the apocalyptic fervor began to wane and interest in detailed charts grew to an all time high.383 Speculation as to ‘who’, ‘when’, and ‘how’ in Daniel, Ezekiel, Revelation, and Matthew increased, and sermons and paperback books on prophecy proliferated. Along with the continuing missionary concern there was, among the Pentecostals who stayed home, a longing for heaven and a strong prayer and financial support for missions which continues unabated to this day. But, because of their association with the evangelicals who had rejected the modernist social gospel, the Pentecostals and others with nineteenth-century
Holiness roots were in many ways cut off from that century’s social witness and larger view of the kingdom of God.
Renewal or Realization
In the 1940s the renewal of apocalyptic ardor and desire for apostolic order returned with great force in a movement competitive with and condemned by most Pentecostal groups: the New Order of the Latter Rain.384 It was premillennial and, arising basically among the lower middle and working class poor, was a protest against the embourgeoisement of Pentecostalism. In addition to new apocalyptic zeal there was a renewed emphasis on healing and other gifts, and on the fivefold ministry gifts of apostles, prophets, evangelists, pastors, and teachers. These had been in some decline in the decade before this revitalization occurred. Many of those involved in the Latter Rain of the mid-century went on to contribute to the genesis of the charismatic movement of the 1960s and 1970s. In contradistinction to the New Order of the Latter Rain, which was working class, premillenial, and pessimistic concerning bringing in the kingdom of God on earth, the Kingdom Now movement of the 1980s is optimistic, postmillennial, and socially located more in the middle to upper class. While similar in many ways to the Christian Reconstructionist movement which wants to apply the law of God to society so as to compel righteousness, the rationale of the Kingdom Now movement is the infiltration of the structures of the world so as to transform them from within. Coupled with a strong emphasis on pragmatic faith or principles of kingdom living (in the K-Dimension), this movement represents the other end of the spectrum of response to Pentecostal apocalypticism. It is activist, but thus far not revolutionary. It is more often than not a part or reflection of the ‘can-do’ optimism and ‘positive thinking’ which pervades much of conservative American piety. In addition to the Kingdom Now move toward realization of the kingdom there is yet another significant movement challenging Pentecostalism with a form of realized eschatology; that is the ‘faith formula’ or ‘name it-claim it’ approaches associated with, but by no means limited to, Kenneth Hagin and Kenneth Copeland.385 Although divine healing in the atonement was taught before, during and after the Azusa revival there were qualifications, explanations, and retractions of extreme statements occurring as early as 1910 in the Apostolic Faith paper. While the movement would continue to be assaulted by ‘hyper-faith’ healers, there would also always be a pastoral temperament
which countered these extreme claims. Just as they had to admit that they were wrong about tongues as missionary languages so the early Pentecostals had to admit that God did not always, immediately, heal, and certainly that all die in Adam. Nevertheless, healing as a crucially important gift, sign, and ministry became yet another focus for the tendency toward human as opposed to divine sovereignty, toward technique as opposed to waiting upon the Lord, and toward inducement as opposed to gift. Enough healings occurred to keep the hope and joy alive; enough did not occur to keep the faithful questioning, struggling, hopeful, and compassionate. Although some built clienteles, the pastors who lived among the people built communities of those who suffered, were healed, were sick, and died together. The resolution of the renewal-realization tension evident in the New Order, Kingdom Now, and ‘faith formula’ strategies are indicators of what happens when the ‘already–not yet’ tensions of the kingdom are pushed too far in either direction, toward the imminent end or the realizable present. What is needed is a revision of the old models, a reappraisal of dispensational association, an integration of soteriological ‘experiences’, a concerted effort toward unity and inclusiveness, and an expanded definition of mission which will move Pentecostalism away from some of the more individualistic understandings of the past.
Correlation and Transformation
It is evident that there was and is a distinct apocalyptic, Pentecostal spirituality, but it is equally clear that it needs some fresh attention. What is offered here can and should be only a suggestive, programmatic statement which, while having continuity with the past, will nevertheless offer the possibility for future developments and innovation. Theology is concerned with the relation between God and creation, and Pentecostal theology conceives that relation to be a living dynamic, requiring discerning discursive reflection, that is gifted by and attuned to the things of the Spirit. Since Pentecostalism is an apocalyptic movement of the Spirit, it will want to have the eschatological context and horizon prominently displayed in its approach. In this sense Pentecostal theologizing is not only a reflection upon but also a reflection of and within reality; the Godsalvation correlation with its attendant affective transformation was discussed in Chapter 3. What was implicit in Pentecostal history and thought must now be made explicit, but grounded in a slightly different way. What follows are five
interrelated loci for a new correlation and expanded view of transformation. These loci are God, history, salvation, church, and mission. God. God is the last thing. Therefore Pentecostals should focus their attention and theological efforts on an understanding of God as the eschatological trinitarian presence and not on speculative end-time sequences.386 This does not necessarily mean giving up on premillennialism; but it does entail a shift of focus. There is one presence but three persons whose unity and identity consists and is given in perichoretic interrelatedness, in which each person fully participates in the life of the others; the unity is in the community. But the distinctiveness is seen in the appropriation of certain works to each, though all by virtue of their coinherence are involved in each work. Thus, the work of creation is sovereignly appropriated to the Father; the work of reconciliation, to the Son; and the work of sustaining and unification unto glory, to the Spirit. Appropriation and perichoresis are ancient doctrines of the church which were formulated to be faithful to the biblical narratives and the lived reality of the redeemed. Today they may serve the re-visioning of the Pentecostal spirituality as a way to guarantee the unity and diversity of the church, the crisis and development of soteriological transformation and the recognition of the eventfulness of the one work of God in creation revealed from Eden to the end: redemption from beginning to end. To live in the presence of the God of redemption is to live as a participant in the divine drama; to be created in God’s image is to be made for love and fellowship with God and each other. God is a communion who creates us for communion and moves us toward ultimate full participation in the divine life. Heaven is theocentric and therefore anthropocentric; in the Pentecostal imagination it is home, reunion, and family celebration with all the redeemed around God’s throne. History. But revelation is not of some idea or static reality. It is a revelation (like the last book of the Bible) of the God who speaks to the churches, works in all things, and brings all things before his throne. History, then, is eschatological trinitarian process. This does not mean that God, in Hegelian fashion, is dissolved into history; it means that history is in God. God works in history, in the world, for the good of those called according to his purpose. As God is the eschatological trinitarian presence who is the goal and limit of all things, so history, as God’s great theater, moves by God, in God, to God. A dispensational understanding of history like that of Joachim of Fiore,387 the Cappadocians, John
Fletcher, and Jürgen Moltmann is more compatible with and suitable for Pentecostal theologizing and spiritual formation.388 It is fascinating to find an association of trinitarian ‘deepening’ or revelation with Spirit baptism in the early Pentecostal writers B.H. Irwin (1896) to D. Wesley Myland (1906), and Bishop J.H. King (1914). Irwin testified that the ‘blessed baptism [of the Holy Spirit and fire] deepens and intensifies our love toward God and … gives us a clearer insight into the nature of the adorable 389 Trinity’. Myland showed perichoretic sensibilities when he exhorted believers, Do not think that all these displays are of the Spirit alone; the Father is there, the Son is there, and the Holy Spirit is there. Whenever God has come to anyone, the whole Godhead is manifested therein; it is the dynamic of the Godhead; the things of the Spirit are displayed in His sovereign working. This movement must be saved from saying that there is never any Spirit until there is Pentecostal fullness, and also after we get Pentecost, from saying it is the Spirit only. It is God! The Father, the Son and the Holy 390 Spirit. The outpouring of the Holy Spirit on the day of Pentecost was a decisive revelation of the Trinity according to Bishop J.H. King of the Pentecostal Holiness Church. This revelation he took to be essential for the ‘Church’s message and self-understanding’. His personal Pentecost was an ‘inward revelation of the Trinity which was unknowable to anyone outside of the Pentecostal experience … this knowledge of the Trinity was essential, in order for the Church as a whole and the believer in particular, to be truly apostolic’.391 God acts in and is affected by history. Jesus and the Spirit ‘sigh and groan’ as do creation and the believer who share in the eschatological trinitarian process. God creates, gathers in Christ, and leads forward in a process that is in actuality a processional into the new heaven and new earth. Pentecostal spirituality narrates this journey and acts in God in the light of the goal of the consummated kingdom reign begun in Jesus and carried forward in the Spirit. This procession, as noted earlier, has two sources: the ‘Jesus Event’ and the experience of the Spirit—Easter and Pentecost. The two events are intimately bound-up in one another, but neither can absorb or reduce the other … There was one Easter; there are millions of Pentecosts.392 Thus salvation history is a progression from the Father through the Son in the
Spirit, then in the Spirit through the Son to the Father. But then God is all in all and the Godhead opens as we ‘know as we are known’. Moltmann calls the three movements the monarchical, eucharistic, and doxological, respectively; all refer to God as the trinitarian origin, presence, and goal of Christian existence. This is no modalistic interpretation of history because the kingdom sovereignty of the Father, Son, and Holy Spirit are ‘continually present strata and transitions in the kingdom’s history’.393 This means that the Spirit is not limited to inspiration of Scripture and illumination and empowerment of the believer. The Spirit is also creator and is intimately involved in all things, providentially sustaining and directing them toward their goal in God. The goal of creation is not annihilation but transformation; just as the goal for humans is new creation.394 By the Spirit the creative intention of the Father and the redeeming passion of the Son are communicated to all creation in a prevenient grace which is the source of all that is good and true and beautiful. Pentecostals, it will be recalled, spoke of a restoration of apostolic faith. This approach acknowledges that through Luther, Wesley, and then the Pentecostal movement, things vital and good were restored to the church. But this process of restoration is part of the larger restoration of all things which will finally issue in that which is greater than the initial creation. It is a ‘restoration plus’, for God will be ‘all in all’. According to this understanding of history as eschatological trinitarian process, all of history is missionary history, and to become a Spirit-filled Christian is to become a part of the teleological process of suffering, healing, hope, and victory which presses toward the kingdom in God. Salvation. Even as history may be characterized in terms of a kind of crisisdevelopment eventfulness in which new possibilities are created by God, so also the individual Christian lives in a crisis-development process which moves forward, not passively but passionately. Eschatological salvation as participation in the divine life of historical mission requires affective transformation. Salvation is not fundamentally an accomplished event, though it is grounded in what God has done for us. But the ‘for us’ is grounded in the ‘in himself’, the pro nobis in the a se. Because God is trinitarian eschatological presence in history, and because humans are made for love and fellowship with God and each other, what God has done for us in Christ he accomplishes in us through Christ in the Spirit. Salvation is a passion for the God who is at work in all things moving history toward the consummation.
The holiness of God speaks of the fact that God’s presence is like no other in that he alone is the source of the divine order, the divine unity, and the divine power to reveal and effectuate, both in creation and redemption. Therefore, the structure of holiness is righteousness, the content of holiness is love, and the dynamic of holiness is the power of the Spirit who enables the giving of one’s self to justice and love in the world. To be filled with the Spirit is to delight in the will, love, and service of God. This salvation means first of all the giving and the ordering of life. The resurrection was the justification of the life of Christ and thus the world of sinners. This was the vindication of the life, teaching, and death of Christ and the setting right of human life. ‘To be born anew is to live from this new source of life which has overcome sin, death, and hell. He declares righteous those who turn and acknowledge by grace his Lordship that they may become the righteousness of God in him. To receive a declaration of righteousness requires a declaration for righteousness. Since the Spirit is at work ordering all things according to this word of righteousness and moving all things in judgment and grace toward the end, therefore to be saved is to receive the Spirit of righteousness and to be led into all truth as it comes to be unto the end. But to be saved is also to love. This is the integrating center, because salvation as participation requires that all be done in love or it profits nothing. Love is the center of affective transformation. There is no question of eradication of an evil substance, no question of the sentence of death still in effect because of the Fall and fallenness of humanity. Love as union means all will die in God and therefore live; as one lives, one dies. Death is the final validation of the direction of a life. It is the acknowledgment of solidarity with all creation under the curse; but, because it is also solidarity with Christ in the Spirit who groans, it is a filling up of what remains of Christ’s suffering. The question of entire sanctification then is not so much a question of subsequence or eradication. Rather, it becomes a question of the kind of measure of love appropriate or adequate to one who ‘so loved’ the world. Nothing but a wholehearted love is adequate to this. Resistances seen in this light are confessed as they come into consciousness. The ‘flesh’ is mortified as thoughts and desires come to light in a participatory following of Christ and are renounced as ‘not I’ but the ‘old I’, which found its integrating center in the ‘flesh’ and not the Spirit.395 In this sense Wesley’s instinct was correct. If God is love, the love of one who ‘so loved’, then the fulfillment of the Law and all righteousness in Christ was unto holiness, which is in this life essentially wholehearted devotion
to God and one’s neighbor. This requires an affective transformation. Without this, the righteousness received and declared for will be resisted and the unrighteousness not fully and deeply repented—since love wounds and heals. Sin in the believer is not, in its most serious guise, some lack of perfect conformity to all the will of God as God knows and acts. That is the ultimate goal. But penultimately (and crucially for Pentecostal spirituality) sin is a betrayal, a willful resistance of that purpose for which we were called. The passion of Christ ‘on the cross’ is finished. The passion of the believer and the church in Christ is not. In him that passion becomes compassion, a wholehearted longing to see all and everyone redeemed, and a pursuit of peace and holiness without which no one will see the Lord. To speak of power without the integrating center of love is to run the risk of becoming a ‘sounding brass and a tinkling cymbal’ or worse to pursue justice to the letter while excluding mercy and humility born of wholeheartedness toward God. Wholeheartedness as simplicity of intention and desire will direct power toward self offering witness rather than domination or presumption.396 The power of Pentecost should be seen as historical, existential, habitual, and extraordinary. The power of the Spirit forms a life for God as Christ was formed in Mary’s womb. This power is a person, the Holy Spirit who must then be existentially invoked, received, and welcomed. To receive the Spirit is to receive the Spirit’s witness and accede to the Spirit’s leading, fruit-production, and empowering for witness. The Spirit’s filling must be invoked daily because the point is to live out of his fullness and by his direction and not that of the world, the flesh, or the devil. The Spirit’s continual filling is a penultimate and proleptic realization of the filling of all things when all confess that Jesus Christ is Lord to the glory of God the Father. This filling means that the Spirit’s life and power and fruit unto holiness are decisive. One is filled with the Spirit, not fear, lust, or greed. Extraordinary filling is analogous to the Gethsemane crisis of Jesus’ life. He who had the Spirit without measure cried out for strength to offer himself as he struggled and suffered. So there are extraordinary times of suffering which many Pentecostals have had to endure, when an extraordinary filling and enabling of the Spirit is necessary to make an offering of one’s self. This is the gift and witness of martyrdom. For fourth and fifth-generation Pentecostal children and new converts in Pentecostal churches, perhaps this view of salvation as eschatological trinitarian passion could be thought of simply as a developmental process with three dimensions. Each of the three may become a moment of crisis or be a source of
continuing direction and inspiration or judgment, depending on one’s background, knowledge and present spiritual condition. The new believer or child is received into the community and belongs to God and the family of God. Whether baptism or dedication is used (and Pentecostals have done both) to indicate this reception and claiming of the child and God’s reception and claiming of him or her, it is still a time that looks forward to an existential saying of ‘yes’ and turning toward God in repentance and love with full assurance of forgiveness of sins. But as the new believer grows or the child enters adolescence, new situations and temptations present themselves. A new awareness of self and the world, coupled with (in the new believer) an acknowledgment perhaps of known hold-outs or resistances to the love and will of God, call for the internalization of the righteousness by which one was received and in which one has been directed. Now is the time to become affectively, wholeheartedly identified with Christ and the mission of the spiritual community. Moral integration will be an ongoing, daily gift of grace through all the means of grace (prayer, Scripture, worship, fellowship, counsel, confession, Lord’s Supper, footwashing, and so on). It is this abiding in Christ wholeheartedly in love that is the core of the spirituality. But if the righteous path toward the kingdom is to be followed in love in the world, one must be empowered daily not only to will and to walk but also to wage war against the principalities and powers. Pentecostals desire the filling of the Spirit because they understand the present age or world to be under the spell of evil: the demon spirits must be fought with spiritual weapons, spiritual strategy, and in spiritual might and power. In order to fill the earth with the gospel, in order to do justice, in order to love and defend others, believers need the continual filling of the Spirit. As they speak in tongues in the eschatological missionary fellowship, the praise of the kingdom that has come joins with that which is coming in a proleptic celebration of God’s victorious grace. But, and this is equally as spiritual, one will also sigh, cry and groan as that very joy and victory makes the lostness and need of the world stand out in bolder relief. This development is a progression from belonging to a community ordered by and for righteousness, to being identified with Christ wholeheartedly in order to fulfill all righteousness, to being empowered to actualize the missionary purpose of God in the world as led and filled by the Holy Spirit who gives his fruit (character of the witness) and gifts (special equipment for the witness). This is a movement which emphasizes the new people of covenant righteousness by grace through faith, the new heart of wholehearted integration by grace through faith, and the new vocation as witness by grace through faith. These three dimensions
of salvation are constantly present and interrelated in a way analogous to the perichoretic trinitarian relations. These dimensions correspond to the resurrection, the cross, and Pentecost. As these are central events of continuing significance, so these dimensions are ongoing crises or landmarks of the faith development of Pentecostal believers. As Calvary is central in salvation history so sanctification as moral integration or wholehearted love is central in salvation as participation in the divine life.397 The Church. The Church is a communion of diversity and unity in the Spirit. Just as God is one in three so the church is one and many in God. The church as eschatological trinitarian fellowship is a communion in God—a people of God, a body of Christ, and thus a communion in the Holy Spirit. What is fellowship but participation? In this fellowship gifts and office coincide and theology is the discerning reflection of the whole as each offers his or her gift, recognizes the other’s gifts, and is built up to disciple and love the neighbor. The fruit of the Spirit is one because the Spirit is the sole source and the fruit is the character of God. But the church is the milieu or garden for that cultivation. The fruit is cultivated by the Spirit so that the church as a whole and each believer may be witnesses who represent something of the divine character and care of God in the world. The gifts are diverse, differently applied, sovereignly distributed (not ‘discovered’ or ‘cultivated’ or ‘operated at will’), and different in each manifestation. But the gifts are for the whole body which is for the kingdom. Thus the gifts simultaneously serve an ‘inner’ edificatory function and an ‘outer’ evangelistic one. The church that is caught up in the divine fellowship is one because of the same divine presence from whom it lives; the church is holy because that presence is the holy and only presence which sanctifies. To be set apart unto God, for believer and church, is to be set apart for union, for that which is joined to God is holy. To treat the church anywhere as profane is to profane the church everywhere. The holiness of the church demands unity. All who pray to and in the same presence are one, are holy and thus should strive to show the world how they love one another. But this church that is one in the divine presence and holy in divine union is apostolic and catholic in its power and universal mandate, respectively. The church in the trinitarian eschatological presence of God moves into all the world in the power of the Spirit who is moving all the world toward the end. The apostolic power is authority and strength to proclaim the one gospel in word and demonstration of the Spirit.
All believers are part of one another as they are part of Christ’s body. They coinhere as children of God. God is the divine mother who has begotten them and brought them forth as dear children in the same family by creation and 398 redemption and destination. The church lives from God through Christ in the Spirit, and in the Spirit exalts Christ to the glory of the Father. Mission. The mission of the church in the light of all that has been said is, therefore, eschatological trinitarian transformation. The church is being transformed by and for God and thus bears witness in what it is and what it does to the kingdom. The mission is to do justice, love mercy, and walk humbly with God. In keeping with what was said before, the church is to recognize the divine presence at work in creation and providence as well as in the more immediate soteriological dimensions. This means that the sanctification of the believer and of the church is to be the motive and analog for the sanctification of the world, not by dissolving the church into the world but by calling the world to repentance and to righteousness. The church, where possible, must work to make structures more adequate to the life as righteously ordered and intended by God. Structures cannot be sanctified in the same way as individuals, but, since the Spirit is at work in all creation, discerning action of the church can bear witness to and participate in those activities which more nearly embody righteousness, dignity, and love for people.
Defense of the weak and prophetic denunciation of sin and oppression are part of the church’s mission to love the neighbor. There is no dichotomy between the command to love one’s neighbor and the Great Commission to disciple the nations. These commands are to be neither confounded nor dichotomized, because love is the character of God and of the Christian in God. However, to refuse the mandate to disciple is to hate, or worse, to be indifferent. To seek to disciple only those who seem to be likely candidates for church membership is to deny the global care and providence of the Spirit. In this regard also the Spirit is not to be grieved or quenched. The personal, social, and cosmic implications of Pentecost are only now beginning to be grasped in the movement, especially in the Third World and among some North American Pentecostals.399 The love which pursues righteousness and presses the demands of God on all structures and people faithfully is the love which, full of hope, seeks to liberate the captives, because the Spirit of the Lord is poured out upon the church.400 Thus Pentecostal liberation brings great joy because peace, not violent coercive manipulation, is the means and the goal as fruit and gift of the Spirit, respectively.401 The early Pentecostal pacifism, in a nuclear age of extensive poverty, is the best strategy for the church today.402 The vast needs of Third, First, and Second World believers alone would stagger the church to its knees, much less the affliction, hatred, and bondage of millions of others. The original vision of unity through sanctified hearts for last-days mission in the power of the Spirit is still valid. And the end is as near and as imminent as God; it is as urgent as God’s passion. But before the unity of the whole church can be addressed, Pentecostals, drawing upon the resources of their spiritual journey and God’s way with them thus far, must themselves come together in a new way. After all, the church cannot very well ask the world to consider the justice, peace, unity, and love of God if it is not itself living out of practicing these things with visible zeal.
Reaching in to One Another: Remembrance and Repentance Based on the foregoing suggestive sketch of a new direction or revision of Pentecostal spirituality, the following observations are offered in order to show what possible impact such a programmatic endeavor might make on the contemporary Pentecostal scene.
The Vision and the Disinherited
From Niebuhr’s work on the Social Sources of Denominationalism to Robert Mapes Anderson’s classic social history of Pentecostalism, The Vision of the Disinherited, it has been accepted that the movement was of and by the poor and working class.403 Although there were educated persons and members of the middle class present at Azusa and scattered throughout the early movement (e.g. J.H. King and N.J. Holmes) it is nevertheless true that the greatest part of the constituency then and now has been drawn from the poor and working classes. This is very much true in the Third World today although there, of course, the overwhelming majority of the people are poor. So, in the beginning of the movement in North America and in other parts of the world the liturgy has been of, by, and for the people404 and characterized by maximum participation of races, sexes, and classes. There was thus racial integration and the full ministry of women in a church of the poor and working classes. The reason for this overcoming of social and economic barriers was the eschatological perspective which accompanied the fall of the Latter Rain. Such an understanding was already found in the nineteenth-century Holiness movement, where writers such as Phoebe Palmer (The Promise of the Father) defended the ministry of women. Now women had a vital ministry as elders, pastors, missionaries, teachers, and so forth. And for a while it did seem as if the color line had been washed away in the blood. Everyone was needed and appreciated in the great task of world evangelization: whosoever was called and gifted by the Spirit was acceptable as long as they evidenced the fruit of a godly life. Due to the work of C.H. Mason and W.J. Seymour, Pentecostalism was, in the beginning, one of the ‘most powerful expressions of Black religion in the world’,
a movement in which black piety had exerted its greater direct influence on American religious history. But very soon there was an accommodation to the racism of American culture instigated by the Whites, leading to racial separation among Pentecostals. Although Mason maintained, and usually initiated, close fellowship and preaching assignments within the Church of God and the Pentecostal Holiness Church, Pentecostals worshiped and fellowshiped in increasingly segregated flocks. As the decades passed, the increasing association with fundamentalist evangelicals meant that it seemed less plausible to ordain wo-men. Although they still could pastor or evangelize, their ministry was classed at a lower rank than men and the polities were careful to indicate that they were under the supervision of men, thus not ‘usurping authority’. Today the racial divisions continue inter- and intra-denomina-tionally. The Church of God in Christ, for example, is almost completely black while the Assemblies of God in North America is mostly white. There are denominations with more African Americans and other ethnic representations, but they are not really equal in terms of access to leadership ministries. The gifts of leadership distributed by the Spirit are not yet reflected in the politics of most North American Pentecostal churches. Pentecostals have moved into middle-class respectability but they are still ambiguous about the ministry of women.405 A restoration of the eschatological missionary vision wedded to vigorous common study of the relevant Scriptures would go a long way to a reunifying of what has been fragmented and stratified. Challenges are very great in terms of mission fields and human need. In the last days the curse and divisions of the Fall are having to be overcome in anticipation of the coming kingdom. The unity and distinctiveness of the Godhead reflected in the male/female atonement bound in Christ means that each has a distinctive and equally important part to play in ministry. Ordination becomes recognition of the Spirit’s assignment for the ministry which one is set apart to accomplish.
The Doctrines of Division
In the beginning of the movement there was a rather unified view of salvation, the Godhead, and the kingdom. Salvation was understood in terms of the fivefold gospel and three blessings. The triune presence was manifested in gifts and wonders which signaled a fresh inbreaking of the kingdom of God. With the emergence of the Finished Work view, the fivefold gospel was
effectively reduced to fourfold again, leaving out the distinctive emphasis on sanctification. Victory replaced sanctification, and power categories were dominant over purity and cleansing ones. But there was an ongoing ambiguity regarding holiness. The Assemblies of God retained a statement on ‘entire sanctification’ in their initial ‘Declaration of Fundamental Truths’ and continued to emphasize consecration for greater service, effectiveness, and readiness for the Rapture of the saints. When the Pentecostal Fellowship of North America (PFNA) was formed, the ‘Statement of Faith’ was exactly that of the earlier National Association of Evangelicals with the exception of Article 5: ‘We believe that the full gospel includes holiness of heart and life, healing for the body and the baptism in the Holy Spirit with the initial evidence of speaking in other tongues as the Spirit gives utterance’. It is perhaps significant that there was an ongoing struggle and ambiguity concerning holiness. The holiness codes of conduct remained in effect for decades, with the Assemblies of God being one of the first groups to modify their statements and the Church of God being one of the last. In keeping with the roots and spirit of the PFNA ‘Statement of Faith’, Pentecostals need to retain the fivefold gospel and something like the threedimensional understanding of salvation developed previously in this chapter under ‘Correlation and Transformation’. The use of three dimensions affirms the necessity of crisis experience in the development of a morally committed, integrated and empowered life while avoiding the necessity of choosing between two or three crises. Sanctification as moral integration within a lifelong process of discipleship and growth may offer a way to begin to address this longstanding impasse. Moral integration would make desirable, but would not imply, maturity. It would help guard against moralism and presumption by centering the spirituality not in righteous deeds or in powerful manifestations but in humble love through abiding in Christ. Moral integration under these circumstances, though requiring struggle and mortification, would nevertheless be neither a works righteousness, nor a sentimental episode. If the demands of New Testament discipleship as found in the Gospels are taken seriously, then it will be seen that nothing short of revolutionary, affective transformation is called for if one is to deny the self, take up the cross daily, follow, love as he loved, and walk as he walked (Mt. 16.2426; Mk 8.34-38; Lk. 14.26-35). By considering the demands of radical discipleship and the shape of the Christian life, Pentecostals could develop a spirituality which correlates more closely with the fivefold gospel’s emphasis on Jesus.
The issues raised by the New Issue or Jesus Only movement are more difficult and complex because they go to the heart of the original and especially the revisioned spirituality. To their credit, the Jesus Only churches warn against tritheism. But by following the Jesucentric emphasis of early Pentecostalism to its logical conclusion, this modern form of modalistic monarchianism undoes the logic of the progressive revelation of salvation history and violates the plain sense of Scripture. These Scriptures are given special interpretation by the Oneness Pentecostals when perspicacity would seem to demand otherwise (for example John 17 or the passages dealing with the baptism of Jesus). Unity is not identity. An ongoing, in depth dialog on the pastoral, soteriological and missional dangers of tritheism and modalism is needed between Oneness and other Pentecostals. This dialog has begun in the Society for Pentecostal Studies but needs further denominational sanction and support. The New Order of the Latter Rain and the Kingdom Now movements represent, respectively, the protest against and evidence of the embourgeoisement of Pentecostalism.406 They are representative of the pessimism of nature and optimism of grace present in the broader Pentecostal movement. But over against both, the tension between the ‘already–not yet’ of the kingdom must be maintained. Premillennialists have never, at least in Pentecostal circles, sat around and wanted to escape in a secret Rapture; they have been anything but passive. But sometimes their expectations of grace were overblown and they forgot they were still in this world. The kingdom is breaking in but still to be consummated, thus combining optimism and pessimism in an active missionary waiting—as in John Wesley, who is claimed by both the premillenialists and postmillenialists!
Passion and Polity
A passion for the kingdom of God was the unifying center of the movement. Even in their divisiveness the Pentecostals still share this passion. With the exception of the Oneness groups, the differences have not prevented contemporary cooperation and pulpit exchanges. They have had a shared passion but not a shared polity. Ironically, following the initial divisiveness of the earlier part of the century, Pentecostals only began talking officially to one another again in 1943 when they, along with several Holiness and Protestant groups were invited to join the National Association of Evangelicals (NAE). The first World Pentecostal
Conference (WPC) was organized in 1947 and the Pentecostal Fellowship of North America (PFNA) came into being the next year. African Americans are not participants in the PFNA but they are involved in the WPC. But the WPC is nothing like a really representative or inclusive body of Pentecostals worldwide. It is dominated by North American and European Pentecostals who are now in 407 the minority in terms of the global movement. Pentecostals are, nevertheless, beginning to talk to one another and to cooperate somewhat in the areas of mission strategy, publishing, chaplaincy, and academic interchange. The latter was initiated in 1970 with the formation of what is now quite an ecumenical, scholarly group, the Society for Pentecostal 408 Studies. With the great number of Pentecostal Bible Schools, several liberal arts colleges and a few seminaries, there should be a greater exchange taking place in the future, if there is to be a genuine re-visioned revitalization of Pentecostalism in North America. The Third World membership is burgeoning and still there is no polity to bring representatives together with administrators and Pentecostal theologians to reflect on their common praxis and to re-envision their spirituality. The traditional Pentecostal suspicion of organizations and the protection of ‘turf’ by the existing bureaucracies make competition, redundancy, and ‘re-inventing the wheel’ a problem. What is needed is for something like the WPC to become a more vigorously inclusive forum for theological, pastoral, and missional concerns. Pentecostal missionaries are coming now from all over the world and going to all parts of the world. Increased leadership and participation of Third World Pentecostals and mergers or close association with First and Second World Pentecostals is encouraging greater effectiveness and theological deepening of one another through narrative exchange and common worship. These promising dialogues and mergers could go a long way toward healing more of the divisions of the past and avoiding further needless fragmentation or fanaticism. Until recently there was no single international publication in which Pentecostals could speak to each other across cultures and socio-economic, racial and national boundaries. A re-visioned Pentecostal spirituality requires such a global interchange. A common end in the consummated kingdom of God requires a common process of shared hopes. A spiritual result (unity) requires a spiritual process, a shared praxis of witness, fellowship, testimony, and searching the Scriptures. These are old Pentecostal strategies which once worked locally and made the movement strong. To emphasize the merely quantitative aspects of
growth to the neglect of the qualitative issues of identity and contribution to the larger body of Christ grieves the Spirit of unity.
Reaching out Together: Learning with the Critics
Subsequence and Sectarianism The charges of subsequence, elitism, and divisiveness have been lodged against Pentecostals from the beginning. And, as we noted earlier, these were some of the milder charges! It is said, for example, that Pentecostals disintegrate the unity of Christian initiation, especially through their lack of understanding of baptism, the rite of initiation in mainline churches. All this is laid to the account of the subsequence doctrine. As a result of claims to subsequent blessing—whether of entire sanctification, Spirit baptism or both—Pentecostals are further charged with an elitism which divides Christians into before and after or the ‘haves’ and the ‘have-nots’ of redemptive experiences. Special claims have been made by Pentecostals concerning the preparation of the Bride (having on the spotless wedding garment and/or having oil in the lamp) and those who are ‘sealed’ by the Spirit for the Rapture. Finally, the critics said that all of this leads naturally, if ungracefully, to division by encouraging people to leave ‘dead, formal churches’ for the free and lively worship of Pentecostal communities of faith. The divisive spirit is also seen in continuing subdivisions of Pentecostals. To understand subsequence, one needs to consider the eventfulness of salvation history itself. Why Pentecost after Calvary and the resurrection? Was it just a formal inaugural event for the new church which was waiting for its birthday to arrive? No, just as in salvation history, so in personal history there are crises or events which make possible new developments or intensify the development in a way unimagined before the event. Christian initiation is not generally understood as terminal, and even the critics admit to subsequent sacramental actions and events which, however continuous with the initiation, are nevertheless decisive for ongoing development. Here Pentecostals, still very immature theologically, could learn with the critics in a discussion of the meaning and significance of confirmation, theosis, and Spirit baptism, for example. What is the difference in remembering one’s baptism and remembering one’s new birth? What are the similarities? How might they be construed together? These questions and others need to be a part of a common spiritual project. It might also be helpful to realize that whereas God is received in Christian initiation, one does not receive all that one needs from God. That requires a
walking in the light and prayerfully seeking fuller understanding and development—both chronologically and spiritually. When the bored, cynical, and unfruitful become renewed, joyful, and fruitful, does that make them elitist? Or does that occur only if they testify to it? Surely not. It is only when exclusivist claims are made which make it incumbent on all to receive just what others have and just the way they have. Grace is a many splendored and multi-faceted reality, at least in the application to and transformation of lives by the Spirit. The hard claim to a particular experiential filling with the Spirit is still not a claim to greater spiritual maturity, nor greater scriptural understanding. Surely here there is room for discussion and learning together. All churches have special claims and believe that their distinctive gift is important enough to justify their corporate existence and individual efforts. Each must first recognize the church in his or her own church and then in other churches. The presence of God made known through a confession to Jesus Christ in word, deed, and fruit is the basis for such a mutual recognition. In that recognition and the ensuing mutual exchange, one can discover what is ‘better’ or ‘worse’ in each. Finally, it should be remembered that in addition to ‘come-outers’, there were just as many Pentecostals who were ‘crushed out’ or ‘pushed out’ of their churches because of their testimony and claims to sanctifying and empowering experiences. Associated with these departures were, of course, theological differences, but there were also at the same time race, class, and cultural conflicts and often a perception that the church existed for and was ruled by a clerical elite who saw themselves as not needing to learn anything new with the people. These clergy would neither weep nor rejoice with others in their spiritual struggles and victories. Such actions by the clergy too often gave the impression that the church was a ‘closed shop’ whose nonnegotiable rules and liturgies existed for the benefit of the few. This is to say nothing of the lack of missionary sacrifice and concern or compassionate involvement in the needs of the hurting and the hungry. Quick judgment, misunderstanding, and lack of communication led to many needless divisions. The rediscovery in each age of the radical discipleship of Jesus and the potency of the Holy Spirit makes it necessary for the church to accommodate its own Pentecostal brothers and sisters with at least as much patience and attention as it gives to the accommodation of its culture. When the disinherited and powerless who have become enfranchised and enabled by the gospel in the
power of the Spirit hear from non Pentecostals that they are elitist for teaching a subsequent work of grace, they gladly reply, ‘Yes, of course!’, or simply, ‘Hallelujah!’
Mission and Unity
For Pentecostals, it is consistent with their spirituality and their distinctive way of being Christian to say that shared missionary passion is the means to unity today. Pentecostals could heartily agree with the perspective of Harry Boer, who in his influential work Pentecost and Mission reminded all Christians that the Spirit was not given to church organizations, ‘to many desperate individuals’, or even to the organism. No, the Spirit has been given ‘to the organization as it serves the organism, and to the organism as it comes to expression in the organization’. Boer further observed concerning the Great Commission that the ‘outpouring of the Spirit is in and by reason of its very nature the effectuation of the Great Commission in the life of the Church … It is not, like the commands of the law, a command which men are impotent to obey’. And rather than preaching it as a command to obey, Boer asserted that the Great Commission must be presented ‘as a law that expresses the nature and that governs the life of the church’. Boer further warned that if the church was seen as a body that meets for edification and praise which also has the task of obeying the missionary command, no great deployment of missionary power is to be expected. Nor can the Spirit enter upon a full exercise of His function in the Church so long as He is regarded as the Spirit of regeneration and sanctification who must also provide the Church with a missionary donun superadditum.409 Pentecostals do not feel that their movement or the baptism in the Holy Spirit is a donum superadditum. All authentic Pentecostals are witnesses who can start meaningful ecumenical exchange at the point of that missionary concern. There is a growing need for expanded contacts through structures and practices that will allow and enable a merging of horizons of hope in the context of narrative exchange and reflection on missionary praxis. In this regard there are many hopeful signs today which would have been unheard of a few decades ago. These signs include an ongoing and rich Roman Catholic-Pentecostal dialog;410 a National Council of Churches of Christ in the United States-Pentecostal Dialog; several Pentecostal Churches that have joined the World Council of Churches (primarily from the Third World);411 large
Pentecostal-Charismatic National Conferences in Kansas City and New Orleans during the past decade;412 ongoing Pentecostal participation in the National Association of Evangelicals;413 Pentecostal participation in the World Evangelical Fellowship; and innumerable smaller but equally significant grassroots efforts. In all this there are practices arising out of Pentecostal spirituality which have facilitated and will advance future ecumenical encounters. If the large conciliar organizations want to dialog with Pentecostal leaders representing millions of believers today, then testimony, intercessory prayer, and praise, and some common missionary praxis is the way to proceed. There can be a merging of horizons and a shared hope as each person narrates his or her faith journey. Catholics often complain that they do not have the dramatic crises and events reported by Pentecostals, but as they narrate their journey new mutual insights are gained, making the encounter itself an event if not a crisis! Praying together, and not just for one another, bearing burdens and confessing to one another is essential for any Christian community and especially for meaningful ecumenical fellowship. Finally, with regard to missionary praxis, perhaps a fruitful, specific place to start would be with a shared healing ministry. In prayer for and ministry to the sick, oppressed, demonized, and suffering, Pentecostals could participate with other Christians in a missionary praxis which would be at once a sign of the last days’ ministry, a gift of the Holy Spirit, a sacrament symbolizing the mystery of redemption by the wounded healer and an expression of the most central and most needed of the affections for the time between the times: compassion. As Pentecostals reflect on these practices of testimony, prayer and healing with other believers, new insights and openness can emerge as God’s gift. This is the presupposition for any meaningful progress in other areas. A shared spiritual formation is the fundament of a shared theology, at least from the Pentecostal perspective.
Theology and Passion
This study has claimed that there is a distinctive Pentecostal spirituality which should be reflected in the process and results of the theological task. Prayer is necessary and not a mere ‘pious addition’ if that task is taken to be a discerning reflection upon lived reality by the eschatological, missionary community. Prayer expresses and evokes the apocalyptic affections which integrate and
motivate the beliefs and practices of the community. What is given to the Pentecostal community in Scripture is opened to the future in God and ‘set on fire’ with a passion for the kingdom which precludes those private experiences or involuted corporate indulgences which only invite the judgment of God.414 This means that faith and love are opened to the world and strain forward in hope. Spirit baptism and ongoing filling intensify and focus 415 that hope which saves even as it reaches to lift, save, and encourage others. This hope gives courage in the face of the world and the devil, and confidence toward the God of all hope. The Pentecostal outpouring in the first and twentieth centuries resulted in the increase of faith, hope, and love for millions of disinherited but not abandoned men, women, and children. But Pentecostals must see the connection between this passion for the kingdom and theology lest they lose both through neglect or dissipation. Theology itself is a kind of passion for God, and passion for God requires ongoing theological work as part of its inner logic and worldly vocation. The merging of the two is the mark of a true theologian—one who truly prays for the kingdom. There arose in Israel during the several hundred years of the intertestamental period an apocalyptic movement which sought to recapitulate the concerns of the priests, prophets, and sages for cultic, social, and personal holiness within their eschatological horizon of hope for cosmic transformation. Perhaps God has raised up the rough-hewn, largely immature but passionate Pentecostals in this century to remind the church of the apocalyptic power and force of the gospel of the kingdom and to prepare the world for the end—the triune God who is to be ‘all in all’. The church which is filled with the Spirit and immersed in the compassionate care of a lost and afflicted humanity has one common longing, one unifying cry, one joyful shout: Come, Lord Jesus!
Afterword It is time to say what must be said of all such interpretive-constructive studies: this is a work begun but unfinished. In the writing of this monograph I have often had the sense of being borne along, as if in a mighty river. Having come ashore and had an opportunity to look back, there are at least seven tributaries that need to be explored further. First of all, Pentecostalism raises anew the question of the relation of theology and spirituality. That issue, discussed in Chapter 1 but implicit throughout, is not a merely sectarian or parochial concern. It has to do with theology’s object, objective, context, and goal. By starting with the Holy Spirit, the living reality of God with us, certain methodological and hermeneutical commitments and presuppositions are laid on the table. These need to be drawn together in a separate piece using the work of the new Pentecostal theologians of North America to be sure, but especially taking account of the Third World majority who are only just beginning to be published. Central to these hermeneutical, methodological concerns is a second matter: the role and meaning of experience. If Edwards’ and Wesley’s approaches to the reason-emotion debate are taken as offering a primal evangelical paradigm, what new light might that throw upon the current evangelical debates over balance, cognitive structure, and the role of the Holy Spirit? Will fundamentalists continue to see the concern with affections discussed in this study as a dead-end approach which is hopelessly mired with feelings? If so, should not Pentecostals begin at least to question the labels ‘fundamentalist’ or ‘evangelical’ when applied to themselves? Perhaps Pentecostals would be well advised to construct their own distinctive rendition of the Wesleyan quadrilateral (Scripture, reason, tradition, and experience). This third line of inquiry is related to the second but is more comprehensive. It would afford a means to re-establish contact with the Wesleyan roots of the movement. If the word ‘integration’ not ‘balance’ is more appropriate for Pentecostals, how can this be demonstrated using the quadrilateral? What are the implications of the Spirit-Word formulation used in this presentation for a fresh understanding of the meaning of Scripture and how should the hermeneutic take into account and reflect the apocalyptic context and horizon with its attendant ‘already–not yet’ tension? With regard to reason in
such an eschatological fellowship, it would be important to explore what has been implicit in this work: the critical, communal discernment of a Pentecostal community. Surprising to some will be the use made of tradition. Contemporary Pentecostals should explore what it would mean to be in experiential continuity with the early movement in light of the claim to be in continuity with the apostolic church. Apostolic succession takes on new meaning in this light. Luther and Wesley, often mentioned in the early literature, are vitally important today. Of the two traditions, why are Lutherans almost always the most vociferous critics? Why do they find it so hard to accept the Pentecostal denials of Pelagianism and enthusiasm? Here the Wesleyan connection is extremely important; the two traditions should make common cause. Pentecostals should examine Wesley’s creative Protestant-Catholic construction and then follow Wesley’s sources, both Eastern and Western, back into his main source, Scripture. Wesleyans and Pentecostals seem to be in agreement with regard to a particular integration of Scripture, tradition, and reason in the sanctified, Spiritfilled life. Further work on the Christian affections would perhaps enable Pentecostals to appreciate more and more their sectarian distinctiveness and ecumenical import. But this raises a third matter for consideration. Given the vast expansion and diversity of Pentecostalism today and the importance of narrative to the tradition, is there some common, foundational narrative which might serve to identify, unify, and direct the future development of at least a majority of its adherents? Such a common narrative might serve in much the same way as the ‘canonic’ narrative of the first ten years; that is, it would unify those who differ in terms of geography, race, class, culture, and gender. The biblical account of Pentecost, the present reality, the apocalyptic goal; all would be elements in such a contemporary reformu-lation of the Pentecostal testimony. A fourth set of issues clusters around the doctrine of the church. Pentecostals have been clear enough in their rejection of institutionalism but have failed to produce a viable ecclesiology which could allow for ongoing change and debate without schisms. A polity for the development of consensus has yet to be constructed (perhaps the World Pentecostal Conference, the European Pentecostal Theological Association, the Pentecostal Fellowship of North America or the Society for Pentecostal Studies could pursue this). Some way must be found to talk and study with the Independent and Oneness groups; this is vital for Pentecostal self-understanding as well as the reunifying of the movement. Can Pentecostals, among themselves and in dialog with other
churches, discover another model for ecumenical discussion, development, and mission? Another internal ecclesiological issue will be a consideration of what structure of the church is best correlated to the shape of the Christian life. If Pentecostal faith development is to proceed, what is there about exclusively hierarchical, mass revivalist, or autonomous congregational approaches which is either inadequate or inimicil to the health of the church or the individual believer? If the logic of Pentecostal affections and gifts is followed, how would that alter traditional ecclesiological formulations? There is, fifthly, an acute need for new metaphors for crisis experience. Eschewing the exclusively substantialist, supplementing the exclusively relational, and working toward an affirmation of a truly ontological change in the believer, can a soteriology be developed which reflects the eventfulness of the biblical narratives, historical and human development? Perhaps affective transformation and integration will prove to be new and useful metaphors for crises within and with a view toward a certain eschatological development. This work is a step in that direction. If Pentecostal theology is a discerning reflection upon living reality in the light of the end, then the shape of the eschatological expectation is crucially important. The sixth area of further research would center on the question of how Pentecostals can live within the tensed dynamic of the ‘already–not yet’ while avoiding the fragmentation of a wholistic, integral mission to souls, bodies, and structures on the one hand, and accommodation to the optimistic, seemingly omnicompetent technological society on the other. Seventh, Pentecostal eschatology, while premillennial and apocalyptic, is qualified by the Latter Rain doctrine. There is an emphasis on the power and sovereignty of God, but because the Holy Spirit brings the life of the kingdom of God into the present, passivity and cultural pessimism are minimized as people are empowered for ministry. It is not postmillennial; it avoids presumption and cultural accommodation. The kingdom of God is larger than the church and therefore there is an implicit ‘post-millennial’ activism contained within the premillennial expectancy. Indeed the expectancy of the coming fullness of righteousness, peace, and joy feeds the activism. This can, by means of further development of the trinitarian perspective of Chapter 4, be expanded to include socio-cultural concerns without a loss of evangelistic commitment. As a work begun but unfinished and a movement that just passed its first centennial, Pentecostalism holds much promise for the future, if it remains open
to the Spirit who indwells the people of God and moves all things toward their consummation in Jesus Christ.
Bibliography
Abel, T.D., Better Felt Than Said: Pentecostal Experience in Southern Appalachia (Waco, TX: Markham Press, 1982). Abraham, W. The Logic of Evangelism (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1989). Albrecht, D.E., ‘An Investigation of the Sociocultural Characteristics and Dynamics of Wallace’s “Revitalization Movements”: A Comparative Analysis of the Works of Four Social Scientists’ (unpublished paper, Graduate Theological Union and The University of California at Berkeley, 1989). Aldana, R., D. Munguia and R. Waldrop. Interview with author. Centro Guatemalteco de teologica Practica, Quetzaltenango, Guatemala. 3 October 1989. Alexander, D.A., ‘Bishop J.H. King and the Emergence of Holiness Pentecostalism’, Pneuma (Fall. 1986), pp. 159-83. Alexander, D.L. (ed.), Christian Spirituality: Five Views of Sanctification (Downers Grove, IL: IVP, 1988). Alvarez, C.E., Santidad y compromiso (Mexico: Casa Unida de Publicaciones, n.d.). Anderson, E.P. (ed.), Melodies of Praise (Springfield, MO: Gospel Pub. House, 1957). Anderson, R.M., Vision of the Disinherited: The Making of American Pentecostalism (New York: Oxford University Press, 1979). Arrington, F.L., The Acts of the Apostles: An Introduction and Commentary (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1988). Arthur, W., The Tongue of Fire; or the True Power of Christianity (New York: Harper, 1856). Barrett, D.B., Cosmos, Chaos, and Gospel: A Chronology of World Evangelization from Creation to New Creation (Birmingham, AL: New Hope-Foreign Mission Board of Southern Baptist Convention, 1987). Barrett, T.B., In the Days of the Latter Rain (London: Simpkin, Marshall. Hamilton, Kent and Co., 1909). Barrios, Magdalena de, and Elizabeth de Gomez. Interview with author. Centro Guatemalteco de teologia Practica, Quatzaltenango, Guatemala, October 1989. Barth, K., Evangelical Theology: An Introduction (New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston. 1963).
—Church Dogmatics (Edinburgh: T. & T. Clark, 1975-1977). —Prayer (ed. D.E. Saliers; trans. S. Terrien; Philadelphia: Westminster Press, 1985). Bartleman, F., Azusa Street (South Plainfield, NJ: Bridge Publishing, 1980). Beaman, J., Pentecostal Pacifism (Hillsboro, KS: Center for Mennonite Brethren Studies, 1989). Beasley-Murray, G.R., Jesus and the Kingdom of God (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1986). Bell, R.H. (ed.), The Grammar of the Heart (San Fransisco: Harper and Row, 1988). Berkhof, H., Christian Faith: An Introduction to the Study of the Faith (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1979).
Boer, H.R., Pentecost and Missions (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1961). Bowman, R., G.S. Hawkins and D. Schlesinger, ‘The Gospel according to Paulk: A Critique of “Kingdom Now Theology”’, Christian Research Journal 10.3 (Winter/Spring, 1988), pp. 9-13, and 11.1 (Summer/Fall, 1988), pp. 15-20. Bowdle, D.N. (ed.), The Promise and the Power (Cleveland, TN: Pathway Press, 1980). Bowers, J.P., ‘Sanctification in the Church of God: A Shift from the Three Blessing Paradigm’ (unpublished paper, Southern Baptist Theological Seminary, 1985). Brewster, P.S. (ed.), Pentecostal Doctrine (Gloucestershire: Grenehurst Press, 1976). Bridges Johns, C., Pentecostal Formation: A Pedagogy among the Oppressed (JPTSup, 2; Sheffield: JSOT Press, 1993). Brown, D., Understanding Pietism (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1978). Brueggemann, W., ‘II Kings 18-19: The Legitimacy of a Sectarian Hermeneutic’, HBT 8 (1985), pp. 1-42.
—Hope within History (Atlanta: John Knox, 1987). Bruner, F.D., A Theology of the Holy Spirit: The Pentecostal Experience and the New Testament Witness (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1970). Burgess, S.M. (ed.), Reaching Beyond: Chapters in the History of Perfectionism (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1986). Burgess, S.M., and G.B. McGee (eds.), Dictionary of Pentecostal and Charismatic Movements (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1988). Campos, B.L., ‘From Experience to Pentecostal Theology’ (unpublished paper, trans. J. Beaty and S.J. Land, paper presented to the Encuentro Pentecostal Latinoamericano, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1989). Carr, W., ‘Towards a Contemporary Theology of the Holy Spirit’, SJT 28 (1975), pp. 501-16. Cassidy, M., Bursting the Wineskins: The Holy Spirit’s Transforming Work in a Peacemaker and His World (Wheaton, IL: Harold Shaw Pub., 1983). Cassidy, R.J., Society and Politics in the Acts of the Apostles (Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books, 1988). Castegeda, J.M., Interview with author. Centro Guatemalteco de Teológica Practica, Quetzaltenango, Guatemala, October 1989. Castillo, P., Interview with author. Managua, Nicaragua, 15 October 1989. Chikane, F., No Life of my Own: An Autobiography (London: Catholic Institute of International Relations, 1988). Christenson, L., Speaking in Tongues and its Significance for the Church (Minneapolis, MN: Bethany Fellowship, 1968). Clapper, G.S., John Wesley on Religious Affections: His Views on Experience and Emotion and their Role in the Christian Life (Metuchen, NJ: Scarecrow Press, 1989).
—‘Orthokardia: The Practical Theology of John Wesley’s Heart Religion’, Quarterly Review 10.1 (Spring, 1990), pp. 49-66. Clark, S.B., Confirmation and the ‘Baptism of the Holy Spirit’ (Pecos, NM: Dove Publications 1969). Clayton, A.L., ‘The Significance of W.H. Durham for Pentecostal Historiography’, Pneuma: The Journal of the Society for Pentecostal Studies 1 (Fall, 1979), pp. 27-42. Colllns, J.J., The Apocalyptic Imagination: An Introduction to the Jewish Matrix of Christianity (New York: Crossroad, 1989). Comacho, H., ‘Involucramiento del laico en la revitalización de la vida congregacional’, Pastoralia 7.15 (December, 1985), pp. 55-68. Comblin, J., The Holy Spirit and Liberation (Mary Knoll, NY: Orbis Books, 1989). Conn, C.W., A Balanced Church (Cleveland, TN: Pathway Press, 1975).
Cooey, P., Jonathan Edwards on Nature and Destiny (Lewiston, NY: Edwin Mellen, 1985). Corum, F.T. (ed.), Like As of Fire, a collection of The Apostolic Faith, 1906-1908 (Wilmington, MA: F.T. Corum, 1981). Cottle, R., ‘Tongues Shall Cease’, Pneuma: The Journal of the Society for Pentecostal Studies 1 (Fall, 1979), pp. 43-49. Crews, E.M., Jr, ‘From the Back Alleys to Uptown: A History of the Church of God (Cleveland, Tenessee)’ (PhD dissertation, Harvard University, 1988). Date, Henry, and E.A. Hoffman, Pentecostal Hymns Number Three: A Winnowed Collection for Evangelistic Services, Young People’s Societies and Sunday-Schools (Chica-go: Hope Pub. Co., 1894). Dayton, D.W., Discovering an Evangelical Heritage (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1976).
—‘Declaración de la consulta de lideres educacionales de la Iglesia de Dios: Desarrollo de un modelo pastoral pentecostal Crente a la teologia de la liberación’, Pastoralia 7.15 (December, 1985), pp.99-106.
—‘The Holiness Witness in the Ecumenical Church’ (unpublished paper, Wesleyan Theological Society, 1987).
—The Theological Roots of Pentecostalism (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1987). —‘Yet Another Layer of the Onion: Or Opening the Ecumenical Door to Let the Riffraff in’, The Ecumenical Review 40.1 (January, 1988), pp. 87-110.
—‘Pentecostal/Charismatic Renewal and Social Change: A Western Perspective’, Transformation 5.4 (October/December, 1988), pp. 7-13. D’Epinay, C.L., Haven of the Masses (London: Lutterworth Press, 1969). Dieter, M.E., The Holiness Revival of the Nineteenth Century (Metuchen, NJ: Scarecrow Press, 1980).
—‘The Development of Nineteenth Century Holiness Theology’, Wesleyan Theological Journal 20.1 (Spring, 1985), pp. 61-77.
—‘The Wesleyan-Holiness and Pentecostal Movements: Commonalities Confrontation, and Dialogue’ (paper presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Pentecostal Studies, 1988). Dorman, D.A., ‘The Purpose of Empowerment in the Christian Life’, Pneuma 7.2 (Fall, 1985), pp. 147-65. Dowd, M.B., ‘Contours of a Narrative Pentecostal Theology and Practice’ (paper presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Pentecostal Studies, 1985). Drayer, J.R., ‘The Significance of Apocalypticism in Contemporary British Eschatology’ (ThD dissertation, Southern Baptist Theological Seminary, 1970). Duffield, G.P., and N.M. Van Cleave, Foundations of Pentecostal Theology (Los Angeles: L.I.FE. Bible College, 1983). Duggan, M.W., ‘The Cross and the Holy Spirit in Paul: Implications for Baptism in the Holy Spirit’, Pneuma 7.2 (Fall, 1985), pp. 135-46.
—‘Implications for Pentecostal-Charismatic Theology’ (paper presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Pentecostal Studies, Gaithersburg, MD, 1985). Dunn, J.D.G., Baptism in the Holy Spirit (Philadelphia: Westminster Press, 1970).
—Jesus and the Spirit (Philadelphia: Westminster Press, 1975). Dupree, S.S. (ed.), Biographical Dictionary of African-American, Holiness-Pentecostals 1880-1990 (Washington, DC: Middle Atlantic Regional Press, 1989). Durnbaugh, D.F., The Believers Church: The History and Character of Radical Protestantism (New York: Macmillan, 1968). Elbert, P. (ed.), Faces of Renewal (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1988).
Elliott, W., ‘Continuity/Discontinuity Between Protestantism and Pentecostalism’ (paper presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Pentecostal Studies, 1989). Ervin, H.M., ‘Hermeneutics: A Pentecostal Option’, Pneuma 3.2 (Fall, 1981), pp. 11-25.
—Conversion-Initiation and the Baptism in the Holy Spirit (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1984). —Spirit Baptism: A Biblical Investigation (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1987). Fahey, S.McM., Charismatic Social Action (New York: Paulist Press, 1987). Farah, C., From the Pinnacle of the Temple: Faith Versus Presumption (Plainfield, NJ: Logos, n.d;). Farah, C., Jr, ‘A Critical Analysis: The “Roots and Fruits” of Faith-Formula Theology’, Pneuma 3.1 (Spring, 1981), pp. 3-21. Faupel, D.W., The American Pentecostal Movement: A Bibliographical Introduction (paper presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Pentecostal Studies, 1972).
—‘The Function of “Models” in the Interpretation of Pentecostal Thought’, Pneuma 2.1 (Spring, 1980), pp. 45-71.
—‘The Everlasting Gospel: The Significance of Eschatology in the Development of Pentecostal Thought’ (PhD thesis, University of Birmingham, 1989). Fedotov, I., and V. Fedotov, Interview with author. Maloyaroslavits, Russia, October 1989. Fee G.D., ‘Baptism in the Holy Spirit: The Issue of Separability and Subsequence’, Pneuma 2.1 (Fall, 1985), pp.87-99. Finger, T.N., Christian Theology: An Eschatological Approach (2 vols; Scottsdale, PA: Herald Press, 1985). Fletcher, J., The Portrait of St Paul (New York: Hunt and Eaton, 1889). Gaetan, A., ‘Teologia de la Liberacion: Perspectiva de una majer pentecostal’, Pastoralia 7.15 (December, 1985), pp. 87-98. Garnmie, J.G., Holiness in Israel (Minneapolis: Fortress Press, 1989). Garcia, P., Interview with author, Guatemala City, Guatemala, October 1989.
‘Gathering of Latin American Pentecostals: Summary report’ (unpublished paper, Salvador, Brazil, 6-9 January, 1988). Gee, D., Trophimus I Left Sick: Our Problems of Divine Healing (London: Elim Publishing, 1952). Gerlach, L.P., ‘Pentecostalism: Revolution or Counter-Revolution?’ in L.L. Zaretsky and M.P. Leone (eds.), Religious Movements in Contemporary America (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1974), pp. 669-99. Gerlach, L.P., and V.H. Hine, People, Power, Change: Movements of Social Transformation (New York: The Bobbs-Merrill Co., 1970). Giron, R., ‘Analisis de la pastoral pentecostal en America Latina’, Pastoralia 7.15 (December, 1985), pp. 55-68. Goff, J.R., Jr, ‘Fields White unto Harvest: Charles F. Parham and the Missionary Origins of Pentecostalism’ (PhD dissertation, University of Arkansas, 1987).
—‘The Faith that Claims’, Christianity Today (February 19, 1990), pp. 18-21. Hamilton, M.P. (ed.), The Charismatic Movement (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1975). Hanson, P.D. (ed.), Visionaries and their Apocalypses (Philadelphia: Fortress Press, 1983). Haynes, E., and M.S. Lemons (eds.), Church of God Songs No. 3 (Cleveland, TN: Church of God Publishing House, n.d.).
—Church of God Songs No. 4 (Cleveland, TN: Church of God Publishing House, n.d.). —Church of God Songs: Tears with Joy (Cleveland, TN: Church of God Publishing House, 1920).
Hine, V.H., ‘The Deprivation and Disorganization Theories of Social Movements’, in Zaretsky and Leone (eds.), Religious Movements, pp.646-64. Hocken, P., ‘The Pentecostal-Charismatic Movement as Revival and Renewal’, Pneuma 3.1 (Spring, 1981), pp.31-47.
—‘The Meaning and Purpose of “Baptism in the Spirit’’’, Pneuma 7.2 (Fall, 1985), pp. 125-34. —‘Signs and Evidence: The Need for Catholic-Pentecostal Dialogue on the Relationship between the Physical and the Spiritual’ (paper presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Pentecostal Studies, 1989). Hollenweger, W.J. ‘The Black Pentecostal Concept: Interpretations and Variations’, Concept 30 (1970), pp. 16-17.
—The Pentecostals (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1972). —New Wine in Old Wineskins (Gloucester: Fellowship Press, 1973). —Pentecost between Black and White (Belfast: Christian Journals, 1974). —‘After Twenty Years’ Research on Pentecostalism’, Theology 87 (November, 1984), p. 404. —‘After Twenty Years’ Research on Pentecostalism’, International Review of Mission 75.297 (January, 1986), pp. 3-12.
—Interview with author. Asbury Theological Seminary, Wilmore, KY, February 1990. —‘The Critical Tradition of Pentecostalism’, JPT 1 (1992), pp.7-17. Holmes, N.J., and L.S. Holmes, Life Sketches and Sermons: The Story of Pentecostal Pioneer N.J. Holmes (Royston, GA: Press of the Pentecostal Holiness Church, 1920). Howell, J.H., ‘The People of the Name: Oneness Pentecostalism In the United States’ (PhD dissertation, Florida State University, 1985). Hunter, H.D., Spirit Baptism: A Pentecostal Alternative (Lanham, MD: University Press of America, 1983).
—‘Reflections by a Pentecostal on Aspects of BEM’ (unpublished paper, prepared for the NCCUSA Dialogue, 1990). Irwin, B.H., ‘Pyrophobia’, The Way of Faith (28 October 1896). Jackson, R., ‘Prosperity Theology and the Faith Movement’, Themelios 15.1 (October, 1989), pp. 16-24. Johns, J.D., and C. Bridges Johns, ‘Yielding to the Spirit: A Pentecostal Approach to Bible Study’, JPT 1 (1992), pp. 109-34. Jones, C., G. Wainwright and E. Yarnold (eds.), The Study of Spirituality (New York: Oxford University Press, 1986). Jones, C.E., A Guide to the Study of the Holiness Movement (Metuchen, NJ: Scarecrow Press, 1974).
—Perfectionist Persuasion: The Holiness Movement and American Methodism, 1867-1936 (ATLA Monograph, 5; Metuchen, NJ: Scarecrow Press, 1974).
—A Guide to the Study of the Pentecostal Movement (Metuchen, NJ: Scarecrow Press, 1983). —Black Holiness: A Guide to the Study of Black Participation in Wesleyan Perfectionist and Glossolalic Pentecostal Movements (Metuchen, NJ: ATLA, 1987). Käsemann, E., New Testament Questions of Today (London: SCM Press, 1969). Kenyon, H.N., ‘An Analysis of Racial Separation within Early Pentecostalism’ (MA thesis, Baylor University, 1978). King, J.H., From Passover to Pentecost (Memphis, TN: H.W. Dixon Printing Co., 1914).
Kirkpatrick, D. (ed.), Faith Born in the Struggle for Life (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1988). Knight, H.H., III, ‘The Relation of Narrative to Christian Affections’ (unpublished paper, Emory University, 1987).
—The Presence of God in the Christian Life (Metuchen, NJ: Scarecrow Press, 1992). König, A., The Eclipse of Christ in Eschatology: Toward a Christ Centered Approach (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1989). Ladd, G.E., The Presence of the Future (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1974). Land, S.J., ‘Pentecostal Spirituality and Disciplines’ (unpublished paper, Guatemala Center for Practical Theology, 1989).
—‘Pentecostal Spirituality: Living in the Spirit’, in L. Dupree and D. Sailers (eds.), Christian Spirituality: Post-Reformation and Modern (New York: Crossroad, 1989), pp. 484-90. Larkin, C., Dispensational Truth or God’s Plan and Purpose in the Ages (Philadelphia: Rev. C. Larkin Est., 1920). Lawrence, B.F., The Apostolic Faith Restored, in D.W. Dayton (ed.), Three Early Pentecostal Tracts (The Higher Christian Life Series; New York: Garland Publishing, 1985). Lederle, H.I., ‘An Ecumenical Investigation into the Proprium or Distinctive element of Pentecostal Theology’, Theologica Evangelica 21.2 (June, 1988), pp. 34-41.
—Treasures Old and New: Interpretations of Spirit-Baptism in the Charismatic Renewal Movement (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1988). Lovelace, R., ‘Baptism in the Holy Spirit and the Evangelical Tradition’, Pneuma 7.2 (Fall, 1985), pp. 10123. Lovett, L., ‘Black Holiness-Pentecostalism: Implications for Ethics and Social Transformation’ (PhD dissertation, Emory University, 1979). MacArthur, J., Jr, The Charismatics: A Doctrinal Perspective (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1978).
—Speaking in Tongues (Chicago: Moody Press, 1988). McClendon, J.W., Jr, Systematic Theology: Ethics (Nashville: Abingdon Press, 1986). McClung, L.G. (ed.), Azusa Street and Beyond: Pentecostal Missions and Church Growth in the Twentieth Century (South Plainfield, NJ: Bridge Publishing, 1986). MacDonald, W.G., ‘The Cross versus Personal Kingdoms’, Pneuma 3.2 (Fall, 1981), pp. 26-37. McDonnell, C., and B. Lang, Heaven: A History (New Haven: Yale University Press, 1988). McDonnell, K., ‘The Experiential and the Social: New Models From the Pentecostal/Roman Catholic Dialogue’, One in Christ 9 (1973), pp. 43-58.
—‘The-Distinguishing Characteristics of the Charismatic-Pentecostal Spirituality’, One in Christ 10.2 (1974), pp. 117-28.
—Presence, Power, Praise: Documents on Charismatic Renewal (Collegeville, MN: Liturgical Press, 1980), I-III.
—‘The Determinative Doctrine of the Holy Spirit’, TTod 39.2 (July, 1982), pp. 142-61. McGee, G.B., ‘Apostolic Power for End Times Evangelism: A Historical Review of Pentecostal Mission Theology’ (unpublished paper presented to the International Roman Catholic and Classical Pentecostal Dialogue, 1990). McGinn, B. (ed. and trans.), Apocalyptic Spirituality (New York: Harper & Row, 1977). McLean, M.D., ‘Toward a Pentecostal Hermeneutic’, Pneuma 6.2 (Fall, 1984), pp. 35-56. MacRobert, I., The Black Roots and White Racism of Early Pentecostalism in the U.S. (New York: St Martin’s Press, 1988).
Maddox, R. (ed.), Aldersgate Reconsidered (Nashville: Abingdon Press, 1990). Marshall, I.H. (ed.), Christian Experience in Theology and Life (Edinburgh: Rutherford House, 1988). Masserano, F.C., ‘A Study of Worship Forms in the Assemblies of God Denomination’ (ThM thesis, Princeton Theological Seminary, 1966). Menzies, R.P., The Development of Early Christian Pneumatology (JSNTSup 54; Sheffield: JSOT Press, 1991). Mills, W.E., Speaking in Tongues: A Classified Bibliography (Costa Mesa, CA: Society for Pentecostal Studies, 1974). Moberg, D.O., The Great Reversal: Evangelism versus Social Concern (Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1972). Moltmann, J., The Church in the Power of the Spirit (New York: Harper & Row, 1977).
—The Trinity and the Kingdom (New York: Harper & Row, 1981). —‘The Fellowship of the Holy Spirit—A Trinitarian Pneumatology’, SJT 37 (1984), pp. 287-300. Moonie, P.M., ‘The Significance of Neo-Pentecostalism for the Renewal and Unity of the Church in the United States’ (ThD dissertation, Boston University School of Theology, 1954). Moore, E. LeR., ‘Handbook of Pentecostal Denominations in the United States’ (MA Thesis, Pasadena College, 1954). Moore, R.D., ‘Approaching God’s Word Biblically: A Pentecostal Perspective’ (paper presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Pentecostal Studies, 1989).
—‘Canon and Charisma in the Book of Deuteronomy’, JPT 1 (1992), pp. 75-92. Morris, P.C., ‘The Holy Spirit in the Music of the Church of God’ (unpublished paper, term paper, Church of God School of Theology, 1989). Myland, D.W., The Latter Rain Covenant and Pentecostal Power, in D.W. Dayton (ed.), Three Early Pentecostal Tracts. Nelson, D.J., ‘For such a Time as this: The Story of William J. Seymour and the Azusa Street Revival’ (PhD thesis, University of Birmingham, England, 1981). Newbigin, L., The Household of God (London: SCM Press, 1953). Nichols, D.R., ‘The Search for a Pentecostal Structure in Systematic Theology’, Pneuma 6.2 (Fall, 1984), pp. 57-76. Niebuhr, H.R., The Social Sources of Denominationalism (New York: World Publishing, 1929).
—Christ and Culture (New York: Harper & Row, 1951). —‘Theological Unitarianisms’, TTod 40.2 (July, 1983), pp. 15-57. O’Connor, E., The Pentecostal Movement in the Catholic Church (Notre Dame: Ave Maria Press, 1971). Oosthuizen, G.C., Moving to the Waters: Fifty Years of Pentecostal Revival in Bethesda 1925-75 (Durban, South Africa: Bethesda, 1975). Palmer, P., The Promise of the Father (Boston, MA: H.V. Degen, 1859; repr. Salem, Ohio: Schmul, 1981, and New York: Garland, 1986). Pearlman, M., Knowing the Doctrines of the Bible (Springfield, MO: Gospel Publishing House, 1937). Peters, J.L., Christian Perfection and American Methodism (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1985). Pluss, J.-D., Therapeutic and Prophetic Narratives in Worship: A Hermeneutic Study of Testimony and Vision (Bern: Peter Lang, 1988).
—‘Pentecostal Visions of Peace between Ecclesial Authority and Secular Society’ (paper presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Pentecostal Studies, 1989). Poewe, K., ‘Links and Parallels between Black and White Charismatic Churches in South Africa and the States: Potential for Cultural Transformation’, Pneuma 10.2 (Fall, 1984), pp. 141-58.
Poloma, M., The Assemblies of God at the Crossroads: Charisma and Institutional Dilemmas (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 1989). Pomerville, P.A., The Third Force in Mission (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1985). Poythress, V.S., Understanding Dispensationalists (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1987). Quebedeaux, R., The New Charismatics II (New York: Harper & Row, 1983). Ranaghan, K.M., ‘Rites of Initiation in Representative Pentecostal Churches in the United States, 1901– 1972’ (PhD dissertation, University of Notre Dame, 1974). Reed, D.A., ‘Origins and Development of the Theology of Oneness Pentecostalism in the United States’ (PhD dissertation, Boston University, 1978). Reeves, M., and W. Gould, Joachim of Fiore and the Myth of the Eternal Evangel in the Nineteenth Century (Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1987). Reid, D.G. (ed.), Dictionary of Christianity in America (Downers Grove, IL: IVP, 1990). Rhodes, J.S., ‘Karl Barth and the Base Communities: A Dialogue on Praxis and Interpretation’ (PhD dissertation, Emory University, 1987). Robeck, C.M., Jr, ‘Pentecostalism and Ecumenical Dialogue: A Potential Agenda’, Ecumenical Trends 16.11 (December, 1987), pp. 185-88.
—‘Pentecostal Perspectives on the Ecumenical Challenge’ (unpublished paper prepared for the Pentecostal/COFO dialogue, 1989). Robeck, C.M., Jr (ed.), Charismatic Experiences in History (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1985). Roberts, R.C., Spirituality and Human Emotion (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1982).
—The Strengths of a Christian (Philadelphia: Westminster Press, 1984). Roebuck, D., ‘From Extraordinary Call to Spirit-Baptism: Phoebe Palmer’s Use of Pentecostal Language to Justify Women in Ministry’ (paper presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Pentecostal Studies, 1989). Rosato, P.J., The Spirit as Lord: The Pneumatology of Karl Barth (Edinburgh: T. & T. Clark, 1981). Runyon, T., ‘System and Method in Wesley’s Theology’ (unpublished paper, American Academy of Religion, 1982). Runyon, T. (ed.), What the Spirit is Saying to the Churches (New York: Hawthorne Books, 1975).
—Sanctification and Liberation (Nashville: Abingdon Press, 1981). Saliers, D.E., and L, Dupre (eds.), Christian Spirituality, III: Post-Reformation and Modern (World Spirituality 18; New York: Crossroad, 1989). Sandidge, J.L., Roman Catholic-Pentecostal Dialogue, 1977-1982: A Study in Developing Ecumenism (Studies in the Inter-cultural History of Christianity, 44; Frankfurt: Peter Lang, 1987). Sauls, N.D., Pentecostal Doctrines: A Wesleyan Approach (Dunn, NC: The Heritage Press, 1979), 1. Sepúlveda, J., ‘Reflections on the Pentecostal Contribution to the Mission of the Church In Latin America’, trans. J. Beaty and S.J. Land, JPT 1 (1992), pp. 93-108. Sheppard, G.T., ‘Pentecostalism and the Hermeneutics of Dispensationalism: Anatomy of an Uneasy Relationship’, Pneuma 6.2 (Fall, 1984), pp. 5-34. Shopshire, J.M., ‘A Socio-Historical Characterization of the Black Pentecostal Movement in North America’ (PhD dissertaion, Northwestern University, 1975). Showalter, A.I., The Best Gospel Songs and their Composers (Dalton, GA: A.I. Showalter, 1904). Smeeton, D.M., ‘Perfection or Pentecost: Historical Comparison of Charismatic and Holiness Theologies’ (MA thesis, Trinity Evangelical Divinity School, 1971). Smith, H.B. (ed.), Pentecostals from the Inside Out (Wheaton, IL: Scripture Press, 1990).
Smith, T., Revivalism and Social Reform (Gloucester, MA: Peter Smith, 1957). Snyder, H.A., The Community of the King (Downers Grove, IL: IVP, 1977). —The Divided Flame (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1986). Spittler, R. (ed.), Perspectives on the New Pentecostalism (Grand Rapids: Baker, 1976). Spurling, R.G., ‘The Evening Light and Church of God’, Evangel 1.1 (1 March 1910); Evangel 1.6 (15 May 1910).
—The Lost link (Turtletown, TN: Farner Church of God, 1920). Stafford, G.W., ‘Experiential Salvation and Christian Unity in the Thought of Seven Theologians of the Church of God, Anderson Indiana’ (ThD dissertation, Boston University School of Theology, 1986). Stockard, P.D., ‘Modern Kingdom Theology: A Brief Review and Critique of the book, Held in the Heavens Until: God’s Strategy for Planet Earth by Earl Paulk’ (unpublished term paper; Church of God School of Theology, 1989). Stockwell, E.L., ‘Pentecostal Consultation’ (unpublished paper, Salvador, Brazil, 6-9 January 1988). Stoll, D., Is Latin America Turning Protestant? (Los Angeles: University of California Press, 1990). Stronstad, R., The Charismatic Theology of St Luke (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1984).
—‘Pentecostalism, Experiential Presuppositions and Hermeneutics’ (paper presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Pentecostal Studies, 1990). Stroup, G.W., The Promise of Narrative Theology (Atlanta: John Knox, 1981). Stylianopoulos, T., and S.M. Heim (eds.), Spirit of Truth: Ecumenical Perspectives on the Holy Spirit (Brookline, MA: Holy Cross Orthodox Press, 1986). Swaggart, J., ‘The Coming Kingdom’, The Evangelist (September, 1986), pp. 4-12. Synan, V., ‘The Role of the Holy Spirit and the Gifts of the Spirit in the Mystical Tradition’, One in Christ 9 (1973), pp. 193-202.
—‘Theological Boundaries: The Arminian Tradition’, Pneuma 3.2 (Fall, 1981), pp. 38-53. —‘Holiness and Pentecostal Traditions in Dialogue’ (paper presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Society for Pentecostal Studies, 1988). Synan, V., The Holiness-Pentecostal Movement in the United States (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1971).
— (ed.) Aspects of Pentecostal-Charismatic Origins (Plainfield, NJ: Logos, 1975). —In the Latter Days (Ann Arbor, MI: Servant Books, 1984). Taylor, G.F., ‘The Spirit and the Bride’, in D.W. Dayton (ed.), Three Early Pentecostal Tracts. (New York: Garland Publishing, 1985), pp. 90-91. Thielicke, H., The Evangelical Faith (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1974), 1. Thomas, J.C., ‘The Spiritual Situation of the Disciples Before Pentecost’ (paper presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Society for Pentecostal Studies, 1984).
—Footwashing in John 13 and the Johannine Community (JSNTSup 61; Sheffield: JSOT Press, 1991). Toon, P., Justification and Sanctification (Westchester, IL: Crossway Books, 1983). Torrance, T.F., God and Rationality (New York: Oxford University Press, 1971). —The Trinitarian Faith (Edinburgh: T. & T. Clark, 1988). Tugwell, S., G. Every, J.O. Mills and P. Hocken, New Heaven? New Earth? An Encounter with Pentecostalism (London: Darton, Longman, & Todd, 1976). Turner, W.C., Jr, ‘The United Holy Church of America: A Study in Black Holiness Pentecostalism’ (PhD dissertation, Duke University, 1984).
Tuttle, R.G., Mysticism and the Wesleyan Tradition (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1989). Ulanov, A., and B. Ulanov, Primary Speech: A Psychology of Prayer (Atlanta: John Knox, 1982). Vaccaro, G., Identidad Pentecostal (Quito: Consejo Latinoamericano De Iglesias, 1988). Valliere, P., Holy War and Pentecostal Peace (New York: Seabury Press, 1983). Vaughan, J.D., The Silver Trumpet (Lawrenceburg, TN: James D. Vaughan, 1908). Volf, M., ‘Materiality of Salvation: An Investigation in the Soteriologies of Liberation and Pentecostal Theologies’, JES 26.3 (Summer, 1989), pp. 447-67.
—‘On Loving with Hope: Eschatology and Social Responsibility’, Transformation 7.3 (July/September, 1990), pp. 28-31. Wacker, G., ‘Taking Another Look at the Vision of the Disinherited’, RSR 8.1 (January, 1982), pp. 15-22.
—Review of Vision of the Disinherited by R.M. Anderson, Pneuma 4.2 (Fall, 1982), pp. 53-62. —‘The Functions of Faith in Primitive Pentecostalism’, HTR 77 (July/October, 1984), pp. 353-75. Wagner, C.P., Spiritual Power and Church Growth (Altamont Springs, FL: Strang Communicatons, 1986). Wainwright, G., Doxology (New York: Oxford University Press, 1980). Waldner, M.M., ‘Christian Mission in Eschatological Perspective: Promoting the Dynamic of Eschatology for Missionary Motivation (DMiss dissenation, Fuller Theological Seminary, School of World Mission, 1987). Waldrop, R., ‘La teologia de la Liberacion: Enfoque critico’, Pastoralia 7.15 (December, 1985), pp. 31-44. Waldvogel, E.L., ‘The “Overcoming Life”: A Study in the Reformed Evangelical Origins of Pentecostalism’ (PhD dissertation, Harvard University, 1977).
—‘The “Overcoming” Life: A Study in the Reformed Evangelical Contribution to Pentecostalism’, Pneuma 1.1 (Spring, 1979), pp. 7-9. Walvoord, J.F., The Rapture Question (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1979). Ware, K., The Orthodox Way (Crestwood, NY: St Vladimir’s Seminary Press, 1980). Wheelock, D.R., ‘Spirit-Baptism in American Pentecostal Thought’ (PhD dissertation, Emory University, 1983). White, J.F., Protestant Worship: Traditions in Transition (Louisville, KY: Westminster Press/John Knox, 1989). Williams, J.R., The Era of the Spirit (Plainfield, NJ: Logos, 1971).
—The Pentecostal Reality (Plainfield, NJ: Logos, 1972). —‘Pentecostal Spirituality’, One in Christ 10.12 (1974), pp. 180-92. —‘The Holy Spirit and Eschatology’, Pneuma 3.2 (Fall, 1981), pp. 54-58. —Renewal Theology (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1990), II. Willis, W. (ed.), The Kingdom of God in 20th Century Interpretation (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1987). Winsett, R.E. (ed.), Gospel Song Messenger (Memphis, TN: R.E. Winsett, n.d.). —Songs of Pentecostal Power (Dayton, TN: R.E. Winsett, 1908). —Songs of Perennial Glory (Chattanooga, TN: R.E. Winsett, 1916). Wood, L.W., ‘Thoughts upon the Wesleyan Doctrine of Entire Sanctification with Special Reference to some similarities with Roman Catholic Doctrine of Confirmation’, Wesleyan Theological Journal 15.1 (Spring, 1980), pp. 88-99.
—Pentecostal Grace (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1980).
Yoder, J.H., The Politics of Jesus (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1972). Yoder, P.B., Shalom: The Bible’s Word for Salvation, Justice, and Peace (Newton, KS: Faith and Life Press, 1987). Zegwaart, H., ‘Apocalyptic Eschatology and Pentecostalism: The Relevance of John’s Millenium for Today’, Pneuma 10.1 (Spring, 1988), pp. 3-25.
Index of Biblical References Genesis 4.1 68
Proverbs 28.13 121
Isaiah 5.16 122 55.7 121
Jeremiah 1.5 68 22.16 68 31.34 68
Ezekiel 33.15 121
Joel 2.28-32 49
Amos 3.3 75
Jonah 3.8 121
Matthew 3.13-17 81 3.15 121 5.23, 24 121 9.13 121 9.36 142 11.4-6 49, 51
12.31 81, 169 15.32 128 16.24-26 211 16.24 202 21.43 173 24.3 64 24.14 7, 64 25.12 49 28.19 21, 186
Mark 1.14 121 1.15 121 3.21 169 3.29 169 8.34-38 211 13.10 64
Luke 6.45 99 11.20 49, 51 12.10 81, 169 12.32 57 12.45 49 14.26-35 211 14.26 202, 211 14.27 202 14.33 202 15.21 121 18.13 121 19.8 121
John 3.8 51 3.16 128 8.31 202 9.4 6 10.3 155 13 11, 13, 95 13.10 123 14–17 81 14.16 21,51, 155 15 174 15.3 123 15.7-12 29 15.12 128
15.26 155 16.7-14 155 17 169 17.15 123 17.17 123, 151 17.19 151 20.21 123 20.22 123
Acts 1–2 3 2 92 2.9-11 45 2.10 45 2.11 45 2.16 88 2.38 186 2.39 61 3.19 121 5.3, 4 169 7.51 81, 169 10 22 10.42 121 10.43 121 10.46-47 52 11.15-17 29 15 184 15.8 22 15.28 29 17.30 121 17.31 121
Romans 3.25 121 5.5 128 6.6 84, 151 6.7 84 6.18 151 6.22 151 8.13 135 8.24 219 8.26 171 8.28 21 8.31 143 14.17 177
1 Corinthians
1.26 24 2.14-16 51 4.20 177 10.11 92 11 110 12-14 107 12 21 12.4-6 21 12.8-10 150 13 83, 132, 174, 204 14 106 14.16 21, 105 15 108 15.28 21
2 Corinthians 1.23 51 4.7-10 144 7.1 140 7.9 121 7.11 121 13.14 21
Galatians 2.20 202 5.6 136 5.16 202 5.22 85 5.24 135, 202 5.25 176
Ephesians 1.14 51 2.10 136, 174 2.22 51 4.22 108 4.36 81, 169 6.10-20 153 6.10 131
Philippians 2.12 202 2.13 202
Colossians 3.1-3 169
1 Thessalonians 4.3 123 5.19 81, 169 5.23 96, 123
2 Timothy 3.5 22
Hebrews 2.11 85, 123 6.1-12 134 6.1-6 51 6.10 140 9.14 202 10.14 151 10.15 151 10.29 81, 169 12 219 12.14 123, 140, 147, 176
James 4.7 135, 153
1 Peter 1.8 156 2.2 133 2.5 93 4.17 219
1 John 1.6 75, 130 1.7 81, 85 1.9 85 2.15-17 80 2.16 98 3 160 4.18 126
5.4 135
Jude 3 4
Revelation 1-3 96, 219 3.1 96 14.6 7 14.7 7 22.15 130
Index of Names
Ahlstrom, S. 210 Albrecht, D.E. 107 Alexander, D.A. 198 Alexander, D.L. 71 Alexander, P.H. 72 Anderson, E.P. 144 Anderson, R.M. 17, 55, 187, 208 Aquinas, T. 35 Arrington, F.L. 72 Arthur, W. 4 Augustine 44, 71
Bakker, J. 74, 188 Baldree, J.M. 99 Barrett, D.B. 9, 10, 213, Barth, K. 25, 26, 31, 32, 35, 44, 170 Bartlemann, F. 41, 42, 99, 100, 185 Beaman, J. 98, 207 Blumhofer, E. 39 Boer, H.R. 52, 216, 217 Bowman, R. 212 Bowers, J.P. 145 Bridges Johns, C. 11, Brueggemann, W. 60, 122 Bruner, F.D. 12, 36, 54, 71, 188 Bundy, D.D. x, 69, Burgess, S.M. 37, 39,
Calvin, J. 29, 35, Campos, B.L. 35, 36 Cashwell, G.B. 6, 74, Cassidy, M. 207 Castillo, P. x,
Chappell, P.O. 7 Christenson, L. 36 Clapper, O.S. 33, 34 Clayton, A.L. 184 Clemmons, I.C. 210 Comacho, H. 199 Comblin, J. 172, 173, 199 Conyers, A.J. 162 Cooey, P. 130 Copeland, K. 195 Corum, F.T. xvi Crawford, F. 187 Crews, E.M. 13
Dake, F.J. 72 Dayton, D.W. 4, 17, 19, 40, 43, 54, 56, 59, 199, 217, 218 D’Epinay, C.L. 10 Dieter, M. 4, 40, 41, 42, 197, 198 Dorman, D.A. 196 Dowd, M.B. 16 Drayer, J.R. 56 Duffield, G.P. 13 Duggan, M.W. 23, 196 Dunn, J.D.G. 12, 13, 36, 188 Dupree, S.S. 43 Durham, W. 103, 104, 145, 184, 185, 186
Edwards, J. 34, 128, 129, 130, 183, 221 Ellis, V.B. 137, Ervin, H.M. 27, 36
Farah, C., Jr 195 Faupel, D.W. x, 4, 6, 7, 8, 12, 17, 53, 54, 184, 186, 194 Finney, C. 4, 38, 41 Fletcher, J. 193, 197
Gaetan, A. 199 Gaines, M. x, 158 Gammie, J.G. 56 Gause, R.H. xii, 84, 103, 196 Gee, D. 195 Gerlach, L.P. 107, 166 Giron, R. x, 199 Graham, E.M. 82 Gregory of Nyssa 18
Hagin, K. 195 Hawkins, G.S. 212 Haynes, E. 77, 78, 79, 148, 155, 157 Henry, C.F.H. 15, 77 Hill, F.E. 38 Hine, V.H. 107, 166 Hocken, P. 67, 196, 198 Hodge, C. 28 Hollenweger, W.J. x, 1, 14, 15, 16, 17, 24, 37, 38, 42, 43, 107, 207 Holmes, N.J. 58, 186, 208 Howell, J.H. 13 Hunter, H.D. x, 36, 67, 71 Hunter, W. 77
Irwin, B.H. 197
Jackson, R. 195 Joachim of Fiore 193, 197 Jones, C. 14, 30, 107 Jones, C.E. 16, 69, 207 Jones, C.P. 147 Jones, J.W. 29, 37
Käsemann, E. 3, 54, 55 Kierkegaard, S. 35, King, J.H. 58, 160, 186, 198, 199, 208 Knight, H.H. xii, 33, 126, 128, 129 Kydd, R.A.N. 37
Ladd, G.E. 64, 65 Land, S.J. 19, 36, 91 Lang, B. 154 Larkin, C. 193 Lawrence, B.F. 59, 60 Lederle, H.I. 71 Leone, M.P. 166 Lovett, L. x, 13, 14, 43 Luther, M. 7, 29, 114, 200, 222
Macarius the Egyptian 18 MacArthur, J. 36
McClung, L.G. 13 McDonnell, C. 154 McDonnell, K. 14, 23, 27, 71 McGee, G.B. 180, 191 McGinn, B. 197 McLean, M.D. 16, 30 McPherson, A.S. 23, 187, 210 Maddox, R. 33 Mahan, A. 38, 41 Martin, L.G. 147 Martin, R. 162 Marty, M. 189 Mason, C.H. 6, 42, 186, 209, 210 Menzies, R.P. 39, 40, 188 Miller, W. 79, 148 Mills, E. 79, 148 Mills, J.O. 53, 54, 58, 133 Mills, W.E. 16 Moberg, D.O. 178 Moltmann, J. 31, 32, 56, 62, 196, 197, 198, 200, 206 Moody, D.L. 4, 38 Moomean, A. 150 Moore, R.D. xi, 68 Morris, L.N. 77, 140 Muntzer, T. 35 Myland, D.W. 198
Nelson, D.J. 13, 24 Newbigin, L. 21, 22, Nichols, D.R. 27, 28, 32 Niebuhr, H.R. 21, 130, 139, 208
O’Connor, E. 71 Outler, A.C. 45 Ozman, A. 4
Packard, V. 117 Palmer, P. 4, 38, 43, 44, 82, 140, 147, 185, 209, 210 Parham, C.F. 4, 8, 13 Paulk, E. 212, Pearlman, M. 13 Peters, J.L. 131, 185 Pinson, M.M. 186 Pluss, J.D. 13 Poloma, M. 63, 190 Pomerville, P.A. 13, 115
Quebedeaux, R. 188
Ranaghan, K.M. 23, 67, 88, 145, 146 Reed, D.A. 13 Riss, R.M. 43, 185, 187, 194, 210 Robeck, C.M., Jr x, 16, 99, 190, 213, 217 Roberts, O. 74 Roberts, R.C. 129, 130, 134, 140, 162, 166, 174 Rogers, W.J. 60 Rosato, P.J. 167 Runyon, T. xi, 32, 33, 74
Sailers, D.E. xi, 25, 26, 33, 91, 129, 130, 164 Sandford, F.W. 8, Sandidge, J.L. x, 16, 217 Sauls, N.D. 13 Schleiermacher, F.D.E. ix, 26 Schlesinger, D. 212 Sepúlveda, J. 19, 35, Seymour, W.J. 4, 5, 13, 42, 66, 69, 70, 83, 101, 103, 104, 105, 112, 120, 148, 155, 156, 209, 210 Shedd, C. 10, Shelton, J.B. 188 Sheppard, G.T. 16, 213 Shepperd, J.W. 13 Shopshire, J.M. 13 Showalter, A.J. 156 Smith, H.B. 189 Smith, H.E. 137 Smith, H.W. 38 Smith, T. 63, 178, 208 Snyder, H.A. 174, 199 Spittler, R.P. 14, 15, 71, 213 Spurling, R.G., Jr 101, 186 Stockard, P.D. 212 Stoll, D. 10, 20 Stronstad, R. 49, 188 Swaggart, J. 74, 188 Symeon, St 18, Synan, H.V. x, 36, 40, 53, 159, 187, 198, 199
Taylor, C. 77, 78 Taylor, G.F. 56, Thomas, J.C. xi, 13, 95 Tomlinson, A.J. 6, Torrance, T.F. 21 Tugwell, S. 54, 58
Turner, W.C., Jr 13
Unamuno, M. de 35
Vaccaro, G. 19 Valliere, P. 20, 172, 207 Van Cleave, N.M. 13 Vaughan, J.D. 156 Volf, M. 199, 200
Wacker, G. 16, 55, 59, 189, 208 Wainwright, G. 14, 37, 107 Waldrop, R. x, 199 Waldvogel, E.L. 13 Ward, H. 53, 187 Warfield, B.B. ix, 15, 28, 41, 71, 219 Warner, W.E. 9 Wesley, C. 82 Wesley, J. 7, 15, 22, 23, 24, 31, 32, 34, 38, 44, 45, 46, 82, 86, 100, 114, 128, 131, 132, 140, 177, 183, 185, 197, 200, 202, 207, 212, 221, 222 Wheelock, D.R. 13, 23, 40 White, J.F. 208 Williams, J.R. 14, 15, 36 Williams, T.L. 157 Wilmore, G. 210 Wilson, L.F. 99 Winsett, R.E. 79, 80, 83, 109, 111, 140, 146, 147, 148, 156 Woodworth-Etter, M. 210
Yarnold, E. 14, 37, 107
Zaretsky, I.I. 166
Other Books from CPT Press R. Hollis Gause, Living in the Spirit: The Way of Salvation (2009). ISBN 9780981965109 Kenneth J. Archer, A Pentecostal Hermeneutic: Spirit, Scripture and Community (2009). ISBN 9780981965116 Larry McQueen, Joel and the Spirit: The Cry of a Prophetic Hermeneutic (2009). ISBN 9780981965123 Lee Roy Martin, Introduction to Biblical Hebrew (2009). ISBN 9780981965154 Lee Roy Martin, Answer Key to Introduction to Biblical Hebrew (2009). ISBN 9780981965161 Lee Roy Martin, Workbook for Introduction to Biblical Hebrew (2010). ISBN 9780981965185 Martin William Mittelstadt, Reading Luke–Acts in the Pentecostal Tradition (2010). ISBN 9780981965178 Roger Stronstad, The Prophethood of All Believers (2010). ISBN 9780981965130 Kristen Dayle Welch, ‘Women with the Good News’: The Rhetorical Heritage of Pentecostal Holiness Women Preachers (2010). ISBN 9780981965192
Endnotes 1 (Chapter 1) Acts 1–2. 2 E. Käsemann, New Testament Questions of Today (London: SCM Press, 1969), p. 100. 3 W. Arthur, The Tongue of Fire; or the True Power of Christianity (New York: Harper, 1856), pp. 189-227. 4 M.E. Dieter, The Holiness Revival of the Nineteenth Century (Metuchen, NJ: Scarecrow Press, 1980); D.W. Dayton. The Theological Roots of Pentecostalism (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1987); D.W. Faupel, ‘The Everlasting Gospel: The Significance of Eschatology in the Development of Pentecostal Thought’ (PhD thesis, University of Birmingham, England, 1989). 5 W.J. Seymour, AF 1.1 (1906), p. 1. 6 AF 1.1 (1906), p. 1. 7 AF 1.3 (1906), p. 1. 8 D.W. Faupel, ‘The Function of “Models” in the Interpretation of Pentecostal Thought’, Pneuma 2.1 (Spring, 1980), pp. 47-49. 9 A.J. Tomlinson (ed.), The Evening Light and Church of God Evangel 10 John 9.4. 11 P.G. Chappell, ‘Healing Movements’, DPCM, pp. 353-74. 12 This is a common designation used throughout the early issues of The Apostolic Faith. 13 Faupel, ‘The Function of “Models”’, pp. 87-99. 14 F.W. Sandford, ‘The Everlasting Gospel’, cited in Faupel, ‘Everlasting Gospel’, p. 47. 15 Each issue of The Apostolic Faith carried news from the mission fields and testimonies of those preparing to go ‘into the harvest’. 16 W.E. Warner, ‘Publications’, DPCM, pp. 742-51. 17 All the statistics in this discussion are from D. Barrett, ‘Statistics. Global’, DPCM, pp. 810-30. 18 See David Stoll’s discussion of the current situation in Is Latin America Turning Protestant? (Los Angeles: University of California Press, 1990). 19 Barrett, ‘Statistics, Global’, p. 119. 20 Barrett, ‘Statistics, Global’, p. 119. 21 C.L. D’Epinay, Haven of the Masses (London: Luttetworth Press, 1969). 22 C. Bridges Johns, Pentecostal Formation: A Pedagogy among the Oppressed (JPTSup, 2; Sheffield: Sheffield Academic Press, 1993). 23 The two most able assaults on the Pentecostal doctrine have come from F.D.
Bruner. A Theology of the Holy Spirit: The Pentecostal Experience and the New Testament Witness (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1970) and J.D.G. Dunn, Baptism in the Holy Spirit (Philadelphia: Westminster Press, 1970). Dunn’s work is the most inviting, understanding, and helpful. 24 Faupel, (‘Everlasting Gospel’, pp. 6-13) terms the two approaches the ‘doctrinal’ and the ‘behavioral’. 25 One of the best known and widely used has been M. Pearlman, Knowing the Doctrines of the Bible (Springfield, MO: Gospel Publishing House, 1937). A more recent work, which includes, in addition to all the usual systematic loci, a long chapter on divine healing, is G.P. Duffield and N.M. Van Cleave, Foundations of Pentecostal Theology (Los Angeles: L.I.F.E. Bible College, 1983). A holiness-Pentecostal approach is taken in N.D. Sauls, Pentecostal Doctrines: A Wesleyan Approach (Dunn, NC: The Heritage Press, 1979), p. 1. 26 A theologically and philosophically informed hermeneutical investigation is found in J.D. Pluss, Therapeutic and Prophetic Narratives in Worship: A Hermeneutic Study of Testimony and Visions (Bern: Peter Lang, 1988). 27 Pneuma contains short articles on various historical figures which have been or are about to be the subject of dissertations or theses. W.J. Seymour and Charles Fox Parham, for example, are treated in recent dissertations: See D.J. Nelson, ‘For such a Time as this: The Story of William J. Seymour and the Azusa Street Revival’ (PhD thesis, University of Birmingham, England, 1981). The DPCM contains articles on all the prominent early pioneers. 28 In addition to the standard denominational histories for groups such as the Pentecostal Holiness, Assemblies of God and Church of God, Oneness Pentecostalism has been studied by D.A. Reed (‘Origins and Development of the Theology of Oneness Pentecostalism in the United States’ [PhD dissertation, Boston University, 1978]) and J.H. Howell (‘The People of the Name: Oneness Pentecostalism in the United States’ [PhD dissertation, Florida State University, 1985]). The roots of Black Holiness Pentecostalism are discussed in W.C. Turner Jr, ‘The United Holy Church of America: A Study in Black Holiness Pentecostalism’ (PhD dissertation, Duke University, 1984); L. Lovett, ‘Black Holiness-Pente-costalism: Implications for Ethics and Social Transformation’ (PhD dissertation, Emory University, 1979); and J.M. Shopshire, ‘A SocioHistorical Characterization of the Black Pentecostal Movement in North America’ (PhD dissertation, Northwestern University, 1975). E.L. Waldvogel traced the roots of the ‘baptistic’ Pentecostals in her 1977 Harvard University dissertation, ‘The “Overcoming Life”: A Study in the Reformed Evangelical Origins of Pentecostalism’. E.M. Crews, Jr has looked at the effects of ‘redemption and lift’ (upward social mobility) in his 1988 Harvard University
dissertation, ‘From Back Alleys to Uptown: A History of the Church of God (Cleveland, Tennessee)’. See the article and bibliography in J.W. Shepperd, ‘Worship’, DPCM, pp. 903-905; and J.C. Thomas, Footwashing in John 13 and the Johannine Community (JSNTSup, 61; Sheffield: JSOT Press, 1991). This is a carefully and persuasively argued proposal for the sacramental legitimacy of the footwashing rite in today’s church. Two of the more prominent contemporary Pentecostal missiologists are L.G. McClung (Azusa Street and Beyond: Pentecostal Missions and Church Growth in the Twentieth Century [South Plainfield, NJ: Bridge Publishing, 1986]) and P.A. Pomerville (The Third Force in Mission [Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1985]). 29 Brief, general treatments of Pentecostal spirituality are found in J.R. Williams, The Pentecostal Reality (Plainfield, NJ: Logos, 1972), esp. pp. 57-84; R.P. Spittler, ‘Pentecostal and Charismatic Spirituality’, DPCM, pp. 804-809; and W.J. Hollenweger, ‘Pentecostals and the Charismatic Movement’, in C. Jones, G. Wainwright and E. Yarnold (eds.), The Study of Spirituality (New York: Oxford University Press, 1986), pp. 549-53. See also the excellent brief comments of K. McDonnell in ‘The Distinguishing Characteristics of the Charismatic-Pentecostal Spirituality’, One in Christ 10.2, (1974), pp. 117-28. McDonnell makes much of the categories of ‘presence’ and ‘crisis’ which I also emphasize while seeing the crisis as an important category not only for Pentecostals but also for all Christians (though I do use it in a slightly different way than McDonnell). 30 See W.J. Hollenweger, ‘The Critical Tradition of Pentecostalism’, JPT 1 (1992), pp. 7-17. 31 J.R. William, Renewal Theology 2 (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1990). 32 Two of the more noteworthy recent approaches are M.D. McLean, ‘Toward a Pentecostal Hermeneutic’, Pneuma 6.2 (Fall, 1984), pp. 35-36; and G.T. Sheppard, ‘Pentecostalism and the Hermeneutics of Dispensationalism: Anatomy of an Uneasy Relationship’, Pneuma 6.2 (Fall. 1984), pp. 5-34. 33 See McLean, ‘Pentecostal Hermeneutic’, n. 35 and M.B. Dowd, ‘Contours of a Narrative Pentecostal Theology and Practice’ (paper presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Pentecostal Studies, 1985). 34 G. Wacker, ‘The Functions of Faith in Primitive Pentecostalism’, HTR 77 (July/October, 1984), pp. 353-75. 35 Pneuma 9.1 (Spring, 1987) was devoted to Pentecostals and ecumenical dialogue. J.L. Sandidge and C.M. Robeck, Jr have been especially active in this important work, whereas several Pentecostal churches from the Third World have joined the World Council of Churches. 36 G. Wacker, ‘Bibliography and Historiography of Pentecostalism (U.S.)’,
DPCM, pp. 65-76. 37 W.J. Hollenweger, ‘After Twenty Years’ Research on Pentecostalism’, International Review of Mission 75.297 (January, 1986), pp. 3-12. 38 Dayton, Theological Roots of Pentecostalism. 39 Faupel, ‘Everlasting Gospel’. 40 R.M. Anderson, Vision of the Disinherited: The Making of American Pentecostalism (New York: Oxford University Press, 1979). 41 Faupel, ‘Everlasting Gospel’, p. 17. 42 D.N. Dayton, ‘Yet Another Layer of the Onion or Opening the Ecumenical Door to Let the Riffraff in’, The Ecumenical Review 40.1 (January, 1988), pp. 87-110. 43 J. Sepúlveda, ‘Reflections on the Pentecostal Contribution to the Mission of the Church in Latin America’, trans. J. Beaty and S.J. Land, JPT 1 (1992), pp. 93-108. G. Vaccaro, ldentidad Pentecostal (Quito: Consejo Latinoamericano de Iglesias, 1988). See also the entire December 1975 issue of Pastoralia 7.15. 44 Stoll, Is Latin America Turning Protestant? 45 See P. Valliere, Holy War and Pentecostal Peace (New York: Seabury Press, 1983), esp. Ch. 1. 46 1 Corinthians 15.28. 47 Romans 8.28. 48 John 14.16. 49 H.R. Niebuhr, ‘Theological Unitarianisms’, TTod 40.2 (July, 1983), pp. 15057. 50 T.F. Torrance, The Trinitarian Faith (Edinburgh: T &T Clark, 1988). 51 L. Newbigin, The Household of God (London: SCM Press, 1953), p. 87. 52 Newbigin. Household of God, p. 87. 53 2 Timothy 3.5 54 Newbigin, Household of God, p. 88. 55 Newbigin, Household of God, p. 88. 56 K. McDonnell, ‘The Experiential and the Social: New Models from the Pentecostal Roman Catholic Dialogue’, One in Christ 9 (1973), pp. 43-58. 57 M.W. Duggan, ‘Implications for Pentecostal-Charismatic Theology’ (paper presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Pentecostal Studies, Gaithersburg, MD, 1985). 58 K.M. Ranaghan, ‘Rites of Initiation in Representative Pentecostal Churches in the United States, 1901-1972’ (PhD dissertation, University of Notre Dame, 1974). 59 D.R. Wheelock, ‘Spirit-Baptism in American Pentecostal Thought’ (PhD dissertation, Emory University, 1983), p. 334. See also Nelson, For such a Time
as this. 60 Walter J. Hollenweger, ‘After Twenty Years’ Research on Pentecostalism’, Theology 87 (November, 1984), p. 404. 61 1 Corinthians 1.26. 62 K. Barth, Prayer (ed. D.E. Saliers; trans. S. Terrien; Philadelphia: Westminster Press, 1985), p. 18. 63 K. Barth, Evangelical Theology: An Introduction (New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 1963), pp. 160-64. 64 Saliers, in Barth, Prayer, pp. 17-19 (emphasis mine). 65 McDonnell, ‘The Experiential’, p. 48. 66 McDonnell, ‘The Experiential’, p. 48. 67 H.M. Ervin, ‘Hermeneutics: A Pentecostal Option’, Pneuma 3.2 (Fall, 1981), p. 22. 68 D.R. Nichols, ‘The Search for a Pentecostal Structure in Systematic Theology’, Pneuma 6.2 (Fall, 1984), pp. 57-76. 69 Nichols, ‘The Search’, pp. 68-75. 70 Nichols, ‘The Search’, pp. 68-69. 71 Nichols, ‘The Search’, p. 73. 72 J.W. Jones, The Spirit and the World (New York: Hawthorn Books, 1975), p. 99. 73 Jones, The Spirit and the World, pp. 98-99. 74 Jones, The Spirit and the World, pp. 100, 106. 75 McLean, ‘Pentecostal Hermeneutic’, p. 50. 76 Jürgen Moltmann, The Trinity and the Kingdom (New York: Harper & Row, 1981). 77 K. Barth, Church Dogmatics (Edinburgh: T. & T. Clark, 1961), IV.3.1, pp. 183-84, cited and discussed in Nichols, ‘The Search’, p. 67. 78 Moltmann, Trinity and the Kingdom, pp. 124-28, 209-22 and The Church in the Power of the Spirit (New York: Harper and Row, 1977), pp. 189-96. 79 T.H. Runyon, ‘The Importance of Experience for Faith’ (Ministers’ Week Address, Emory University, 1988), p. 4; the address is revised and appears in R. Maddox (ed.), Aldersgate Reconsidered (Nashville: Abingdon Press, 1990), pp. 93-108. 80 Runyon, ‘Experience’, p. 16. 81 See D.E. Saliers, The Soul in Paraphrase (New York: Seabury Press, 1980); idem, Worship and Spirituality (Philadelphia: Westminster Press, 1984); H.H. Knight, III, The Presence of God in the Christian Life (Metuchen, NJ: Scarecrow Press, 1992); G.S. Clapper, John Wesley on Religious Affections: His Views on Experience and Emotion and their Role in the Christian Life and Theology
(Metuchen, NJ: Scarecrow Press, 1989). 82 Sepúlveda, ‘Reflections’, p. 1. 83 B.L. Campos, ‘From Experience to Pentecostal Theology’ (trans. J. Beaty and S.J. Land, paper presented to the Encuentro Pentecostal Latinoamericano, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1989), pp. 1, 4, 5. 84 Campos, ‘Experience’, p. 1. 85 Vinson Synan surveys the charismatic movement in the various ‘mainline’ churches in The Twentieth Century Pentecostal Explosion (Altumante Springs, FL: Strang, 1989), esp. pp. 109-20, 159-72. See also the excellent Lutheran charismatic theology of L. Christenson (ed.), Welcome Holy Spirit (Minneapolis: Augsburg, 1988). 86 J. MacArthur, Jr, The Charismatics: A Doctrinal Perspective (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1978) and idem, Speaking in Tongues (Chicago: Moody Press, 1988). 87 Bruner, A Theology of the Holy Spirit; J.D.G. Dunn, Jesus and the Spirit (Philadelphia: Westminster Press, 1970). See the Pentecostal responses in H.M. Ervin, Conversion-Initiation and the Baptism in the Holy Spirit (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1984); idem, Spirit Baptism: A Biblical Investigation (Peabody, Massachusetts: Hendrickson, 1987); and H.D. Hunter, Spirit Baptism: A Pentecostal Alternative (Lanham, MD: University Press of America, 1983); and J.R. Williams, Renewal Theology (3 vols.; Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1993). 88 W.J. Hollenweger, ‘Pentecostals and the Charismatic Movement’, in Jones, Wainwright and Yarnold (eds.), The Study of Spirituality, pp. 549-53. 89 Hollenweger, ‘Pentecostals’, p. 551. 90 For a broader historical perspective consult S.M. Burgess, The Spirit and the Church: Antiquity (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1984); R.A.N. Kydd, Charismatic Gifts in the Early Church: An Exploration into the Gifts of the Spirit during the First Three Centuries of the Christian Church (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson. 1984); S.M. Burgess, ‘The Doctrine of the Holy Spirit: The Ancient Fathers’, DPCM. pp. 417-32; ‘The Doctrine of the Holy Spirit: The Medieval Churches’, DPCM, pp. 432-44. 91 Hollenweger, ‘Twenty Years’ Research’, p. 4. 92 Hollenweger, ‘Twenty Years’ Research’, p. 4. 93 AF 1.4 (1906), p. 2. 94 E. Blumhofer, ‘Purity and Preparation’, in S.M. Burgess (ed.), Reaching Beyond: Chapters in the History of Perfectionism (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1986), p. 275. 95 W.M. Menzies, ‘The Non-Wesleyan Origins of the Pentecostal Movement’, in V. Synan (ed.), Aspects of Pentecostal-Charismatic Origins (Plainfield, NJ:
Logos, 1975), p. 97. 96 V. Synan, The Holiness-Pentecostal Movement in the United States (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1971). 97 Dieter, The Holiness Revival and idem, ‘The Development of Nineteenth Century Holiness Theology’, Wesleyan Theological Journal 20.1 (Spring, 1985), pp. 61-77; and idem, ‘The Wesleyan Holiness and Pentecostal Movements: Commonalities, Confrontation and Dialogue’ (paper presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Pentecostal Studies, Wilmore, KY, 1988). 98 Dayton, Theological Roots of Pentecostalism. 99 Wheelock, ‘Spirit Baptism’, p. 210. 100 Dieter, ‘The Wesleyan-Holiness and Pentecostal Movements’, pp. 2-4. 101 F. Bartleman, Azusa Street (South Plainfield, NJ: Bridge Publishing, 1980), pp. 164, 166. 102 Hollenweger, ‘Twenty Years’ Research’. See also L. Lovett, ‘Black Origins of Pentecostalism’, in Aspects of Pentecostal-Charismatic Origins (Plainfield, NJ: Logos, 1975), pp. 145-58. See also W.J. Hollenweger, ‘The Black Pentecostal Concept: Interpretations and Variations’, Concept 30 (1970), pp. 1617; and S.S. Dupree (ed.), Biographical Dictionary of African-American, Holiness-Pentecostals 1880-1990 (Washington, DC: Middle Atlantic Regional Press, 1989). 103 D.W. Dayton, Discovering an Evangelical Heritage (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1976). 104 R.M. Riss, ‘Role of Women’, DPCM, pp. 893-99. 105 P. Palmer, The Promise of the Father (Boston, MA: H.V. Degen, 1859). 106 Barth, Evangelical Theology, p. 58. 107 J. Wesley, ‘On the Wedding Garment’, in A.C. Outler (ed.), The Works of John Wesley: Sermons IV (Nashville: Abingdon Press, 1987), pp. 139-48. 108 J.M. Kirk, in Church Hymnal (Cleveland, TN: Tennessee Music and Printing Co., 1951), p. 327. 109 (Chapter 2) Joel 2.28-32. See Stronstad, The Charismatic Theology of St Luke. 110 Mt. 11.4-6; Lk. 11.20. 111 The Evening Light and Church of God Evangel 1.1 (March 1, 1910), p. 8. 112 1 Corinthians 2.14-16. 113 John 14.16. 114 Ephesians 2.22. 115 Hebrews 6.1-6. 116 2 Corinthians 1.23; Eph. 1.14. 117 John 3.8.
118 Luke 11.20; Mt. 11.4-6. 119 H.R. Boer, Pentecost and Missions (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1961). 120 Acts 10.46-47. 121 H. Ward, ‘The Anti-Pentecostal Argument’, in Synan (ed.), Aspects of Pentecostal-Charismatic Origins, pp. 99-111. 122 Faupel, ‘Everlasting Gospel’. 123 The first three chapters of the book of Revelation reveal Jesus Christ and the state of the Church as known by him and addressed by the Holy Spirit. Revelation is thus an unveiling of the meaning of history in Jesus Christ by the Holy Spirit and the progressive and particular dealing of God with the Church and world in the light of the end. See J.O. Mills, ‘New Heaven? New Earth?’, in S. Tugwell et al., New Heaven? New Earth? (London: Darton, Longman & Todd, 1976), pp. 69-118. 124 Bruner was the first to use the term ‘pneumatobaptistocentrism’. See his A Theology of the Holy Spirit, esp. p. 337, index entry, ‘Christocentricity’. Bruner fails to see what is everywhere in the early movement—an overwhelming Christocentric emphasis on Jesus as Savior, Sanctifier, Healer, Spirit baptizer, and coming King. Hymns, letters, testimonies, sermons—all the ways in which they ‘did’ theology—testify to Jesus Christ. To be sure, they teach, preach, and experience ‘the baptism in the Holy Ghost’, but they immediately became witnesses to Christ in word and power and demonstration of the Spirit. But then that was true of the New Testament saints as well. See pp. 94, 120, 121 for further development of the ‘distinctiveness’ of the spirituality. 125 Faupel, ‘Everlasting Gospel’, pp. 134-95. 126 Käsemann, New Testament Questions of Today, p. 102. 127 G. Wacker, Review of Vision of the Disinherited by R.M. Anderson, Pneuma 4.2 (Fall, 1982), pp. 53-62. 128 G. Wacker, ‘The Functions of Faith’, pp. 353-75. 129 G.F. Taylor, ‘The Spirit and the Bride’, in D.W. Dayton (ed.), Three Early Pentecostal Tracts (New York: Garland Publishers, repr., 1985), pp. 90-91. 130 J.R. Drayer, ‘The Significance of Apocalypticism in Contemporary British Eschatology’ (ThD dissertation, Southern Baptist Theological Seminary, 1970), p. 242. 131 J. Moltmann, ‘Theology as Eschatology’, in F. Herzog (ed.), The Future of Hope (New York: Herder & Herder, 1970), p. 7. 132 J.G. Gammie, Holiness in Israel (Minneapolis, MN: Fortress, 1989). 133 Luke 12.32. 134 The Church of God, Cleveland Tennessee, for example, no longer has bans on jewelry, movies, etc. Now that more is affordable, it seems that more has
become permissible. The ethical statements are no longer short, blunt prohibitions; now they are principles and propositions with appropriate Scriptures correlated to each. As the story changed so did the ethic. But no new unifying story has emerged to guide ethical behavior, and ‘affordability’ is clearly neither a biblical nor a particularly theologically satisfying ethical stance. 135 J.O. Mills in Tugwell, et al., New Heaven? New Earth?, pp. 69-118. 136 N.J. Holmes and L.S. Holmes, Life Sketches and Sermons: The Story of Pentecostal Pioneer N.J. Holmes (Royston, GA: Press of the Pentecostal Holiness Church, 1920), pp. 139, 140, 143, 144 137 Pentecostal Evangel (March 22, 1924), 6, 7, cited in Wacker, ‘The Functions of Faith’, p. 155. 138 B.F. Lawrence, ‘The Apostolic Faith Restored’, in D.W. Dayton (ed.), Three Early Pentecostal Tracts (New York: Garland Publishers, 1985), p. 12. 139 W. Brueggemann, ‘II Kings 18–19: The Legitimacy of a Sectarian Hermeneutic’, HBT 7 (1985), pp. 1-42. 140 Lawrence, ‘The Apostolic Faith Restored’, p. 13. 141 Acts 2.39. 142 The phrase ‘baptism of the Holy Spirit upon the sanctified life’ recurs frequently in The Apostolic Faith and seems to indicate that the earliest Wesleyan- Pentecostals saw sanctification as a transforming, and Spirit baptism as an empowering, work of grace. 143 A.J. Conyers, God, Hope and History: Jürgen Moltmann and the Christian Concept of History (Macon, GA: Mercer University Press, 1988), p. 77. Conyers is a reliable guide and provides a helpful overview of Moltmann’s discussion on ‘historifying of the world’ and ‘universalizing of history’. See Moltmann’s comment (‘While apocalyptic does conceive its eschatology in cosmological terms, yet there is not the end of eschatology, but the beginning of an eschatological cosmology or an eschatological ontology for which being becomes historic and the cosmos opens itself to the apocalyptic process’) on p. 137 and further discussion in his Theology of Hope (trans. J.W. Leitch; New York: Harper, 1967), pp. 124-38. 144 T. Smith, Revivalism and Social Reform (Gloucester, MA: Peter Smith, 1957). 145 M. Poloma, The Assemblies of God at the Crossroads: Charisma and Institutional Dilemmas (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 1989). 146 The whole context of Acts 1 and 2 is eschatological: it is a salvific fusion of Old Testament prophecies, the life, death, resurrection, and parousia of Jesus, and the outpouring of the Holy Spirit. All these themes found expression in the Pentecostals’ evangelization, eschatological vision, and experience of Spirit-
filling. See G.E. Ladd, The Presence of the Future (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1974), pp. 322, 324, 327: The same God who is now acting in historical events to bring about a fulfillment of the messianic salvation will act out the end of history to bring his kingdom to its consummation … The important point is that these two redemptive acts—the historical and the eschatological—are in fact one redemptive event in two parts … The eschalological consummation of the kingdom is inseparable from and dependent upon what God is doing in the historical person and mission of Jesus … The motif of the apocalypses (IV Ezra 4.25ff.; see also 6.18ff.; 8.63ff.; En. 80.2ff.; 99.lff.; 100.lff.; Jub. 23.16ff.; Sib.Or. 2.199.; Apoc.Bar. 25.1ff.; 48.31ff.; 70.2ff.) is that the evil which has dominated the age will become so intense at the end that complete chaos will reign, both in human social relationships and in the natural order. The motif in the Olivet Discourse (Mt. 24.3ff) is an extension of the conflict motif which characterized both Jesus’ mission and the mission of His disciples in this age. Jesus agreed with the apocalyptists that evil will mark the course of the age; the kingdom of God will abolish evil only in the age to come. But into this evil age something new has come: the good news (Mark 13.10) about the kingdom of God (Mt. 24.14). This message of God’s redemptive acts in history must be proclaimed in all the world before the end comes. Therefore history is not abandoned to evil.
147 The parable of the wise and foolish virgins was a favorite sermon and article topic in early Pentecostal circles. It served as an apologetic and an exhortation for Spirit filling which was equated with ‘oil in the lamp’. 148 Ladd, The Presence of the Future, p. 328. 149 I. Watts and R.E. Hudson, ‘At the Cross,’ in Church Hymnal, p. 264. 150 AF 1.9 (June-September, 1907), p. 2. 151 ‘Christ Abides in Sanctification’, AF 1.9 (June-September, 1907), p. 2. 152 H.D. Hunter, ‘Pentecostal Ordinances’, DPCM, pp. 653-54; P.D. Hocken, ‘Theology of the Church’, DPCM, pp. 211-18. 153 Ranaghan, ‘Rites’, pp. 688-94. 154 R.D. Moore, ‘A Pentecostal Approach to Scripture’, The Seminary Viewpoint 8.1 (1987), pp. 1, 2. 155 R.D. Moore, ‘Canon and Charisma in the Book of Deuteronomy’, JPT 1 (1992), p. 90. 156 See esp. Moore, ‘Canon and Charisma’, pp. 75-92 for an Old Testament theological basis for my use of Spirit-Word in this study. 157 C.E. Jones, ‘Holiness Movement’, DPCM, pp. 406-409; D.D. Bundy, ‘Keswick Higher Life Movement’, DPCM, pp. 518-19. 158 ‘The Church Question’, AF 1.5 (January, 1907), p. 2. 159 R. Spittler, ‘Pentecostal Spirituality’, in D.L. Alexander (ed.), Christian Spirituality: Five Views of Sanctification (Downers Grove, IL: IVP, 1988); E. O’Connor, The Pentecostal Movement in the Catholic Church (Notre Dame: Ave Maria Press, 1971); McDonnell, ‘Distinguishing Characteristics’, pp. 117-28. 160 Lederle and Hunter over against Bruner maintain a second dimension of experience and second charismatic, vocational work of the Spirit, respectively.
See H.I. Lederle, Treasures Old and New: Interpretations of Spirit-Baptism in the Charismatic Renewal Movement (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1988) and Hunter, Spirit Baptism. 161 McDonnell, ‘The Experiential’, pp. 43-58. 162 For a brief overview of dispensationalism and its continued impact on Pentecostalism with some contemporary Pentecostal dissent (Gause, Horton), see F.L. Arrington, ‘Dispensationalism’, DPCM, pp. 247-48, and P.H. Alexander, ‘Finis Jennings Dake’, DPCM, pp. 235-36. 163 A typical version of this testimony from the early years into the 1960s was ‘Praise God! I’m saved, sanctified, filled with the Holy Ghost, a member of the great Church of God, and on my way to heaven; I am determined to hold out to the end’. 164 Perhaps more than any other group in North America today, Pentecostals have developed a special sensitivity for charlatans and the merely exotic. Many traditional or Classical Pentecostals were distrustful of Jimmy Swaggart, embarrassed by Oral Roberts, and in open disagreement with many of the beliefs and practices of the Bakkers long before any of their scandals broke in the news. All Christian groups have scandals—usually not very original: i.e. money, sex, pow-er—but Pentecostals are especially open to criticism because of their ‘high’ claims and expectations. 165 G.B. Cashwell, AF 1.6 (1907), p. 3. 166 1 John 1.6; Amos 3.3. 167 W. Hunter and J.D. Vaughn, in Church Hymnal, p. 133. 168 W.M. Ramsey, ‘The Land of Perfect Day’, in Church Hymnal, p. 22. See also A.E. Brumley, ‘Jesus, Hold My Hand’, p. 52. 169 S.J. Massengale, ‘I Don’t Want to Get Adjusted’, in Church Hymnal, p. 218. 170 ‘Holiness unto the Lord’ by Leila N. Morris appears in Pentecostal hymnals from the earliest days to the present; cf. Henry Date and E.A. Hoffman, Pentecostal Hymns Number Three: A Winnowed Collection for Evangelistic Services, Young People’s Societies and Sunday-Schools (Chicago: Hope Pub. Co., 1894), p. 52. 171 M.S. Lemons and E. Haynes, in E. Haynes and M.S. Lemons (eds.), Church of God Songs: Tears with Joy (Cleveland, TN: Church of God Publishing House, 1920), p. 8. 172 C. Taylor and T. Benton, in Haynes and Lemons, Church of God Songs: Tears with Joy, p. 97. 173 C. Taylor, in Haynes and Lemons, Church of God Songs: Tears with Joy, p. 98. 174 Haynes and Lemons (eds.), Church of God Songs: Tears with Joy, p. 4.
175 Elizabeth Mills and W. Miller, in R.E. Winsett, Songs of Pentecostal Power (Dayton, TN: R.E. Winsett, 1908), p. 179. 176 1 John 2.15-17. 177 J. Oatman, Jr and W.J. Rogers, in Winsett, Songs of Pentecostal Power, p. 60. 178 Ephesians 4.36; Acts 7.51; Heb. 10.29; 1 Thess. 5.19; Mt. 12.31; Lk. 12.10. 179 John 14-17. 180 1 John 1.7. 181 Matthew 3.13-17. 182 F.M. Graham, in Winsett, Songs of Pentecostal Power, p. 213. 183 The Apostolic Faith faith statement, found in almost every issue, held that Spirit baptism was to be upon the sanctified life. 184 1 Corinthians 13. 185 R.H. Gause, in the most significant Pentecostal soteriology to date, deals with the problem of fragmented, episodic, and often seemingly arrested stages or salvation experiences. He makes extensive use of John 17 to show the interrelationship of sanctification, joy, unity, and mission. See R.H. Gause, Living in the Spirit: The Way of Salvation (Cleveland, TN: Pathway Press, 1980). 186 AF 1.11 (October [1907] to January, 1908), p. 2. 187 AF 1.10 (September, 1907), p. 2. 188 AF 1.10 (September, 1907), p. 2. 189 AF 1.10 (September, 1907), p. 2. 190 AF 1.10 (September, 1907), p. 2. 191 See the earliest statement of faith in AF 1.1 (1906), p. 2. 192 AF 1.11 (October [1907] to January, 1908), p. 2. 193 Ranaghan, ‘Rites’, p. 654. 194 Wesley, ‘On the Wedding Garment’ (see p. 54, n. 1). 195 S.J. Land, ‘Pentecostal Spirituality: Living in the Spirit’, in L. Dupre and D. Saliers (eds.), Christian Spirituality: Post-Reformation and Modern (New York: Crossroad, 1989), pp. 484-90. 196 The setting of Acts 2 is the ‘last days’ and early Christians characterized themselves as those upon whom the ends of the ages had come (1 Cor. 10.11). This was also the historical perspective of early Pentecostals. 197 1 Peter 2.5. 198 The Church of God ‘Teachings Made Prominent’, as so many other statements in early Pentecostalism, stood for ‘the whole Bible rightly divided’ as their rule of government, fellowship, and discipline. 199 This is not to deny gullibility, ignorance of the Word, congregational immaturity, charlatans with wrong motives, those mistaking exuberance for
genuine anointing, etc. It is to affirm the usual practice informed by years of experience in ‘testing the spirits’. 200 Thomas, Footwashing in John 13. 201 Revelation 1–3, esp. 3.1. 202 1 Thessalonians 5.23. 203 1 John 2.16. 204 J. Beaman, Pentecostal Pacifism (Hillsboro, KS: Center for Mennonite Brethren Studies, 1989). 205 L.F. Wilson, ‘Bible Institutes, Colleges and Universities’, DPCM, pp. 57-65; J.M. Baldree, ‘Christian Day Schools’, DPCM, pp. 167-69; C.M. Robeck, Jr, ‘Seminaries and Graduate Schools’, DPCM, pp. 772-76; J.M. Baldree, ‘Sunday Schools’, pp. 835-37. 206 Luke 6.45. 207 F. Bartleman, Azusa Street (South Plainfield, NJ: Bridge Publishing, 1980), p. 167. 208 Bartleman, Azusa Street, p. 167. 209 Bartleman, Azusa Street, p. 167. 210 Bartleman, Azusa Street, pp. 168, 169. 211 The Assemblies of God ‘Statement of Fundamental Truths’ and the Church of God (Cleveland, TN) ‘Declaration of Faith’. 212 R.G. Spurling, The Lost Link (Turtletown, TN: Farner Church of God, 1920). 213 AF 1.11 (October [1907] to January, 1908), p. 3. 214 R.H. Gause, ‘The Historical Development of the Doctrines of Holiness in the Church of God’ (unpublished paper delivered to Holiness Study Project, Mt Paran Church of God, Atlanta, GA, 1973). 215 AF 2.13 (May, 1908), p. 2. 216 AF 2.13 (May, 1908), p. 2. 217 AF 2.13 (May, 1908), p. 2. 218 W.J. Hollenweger, ‘Pentecostal and Charismatic’ in Jones, Wainwright, and Yarnold (eds.), The Study of Spirituality, p. 553. 219 Dan Albrecht characterizes Pentecostalism as a revitalization movement in ‘An Investigation of the Sociocultural Characteristics and Dynamics of Wallace’s Revitalization Movements: A Composite Analysis of the Works of Four Social Scientists’ (unpublished paper, Graduate Theological Union and the University of California at Berkeley, 1989). See L.P. Gerlach and V.H. Hine, People, Power, Change: Movements of Social Transformation (New York: The Bobbs-Merrill Co., 1970). 220 1 Corinthians 15 characterizes the resurrection body as a spirit-body.
221 Ephesians 4.22. 222 H.H. Heimar and L.L. Pickett, ‘The Healing Waters’, in Winsett, Songs of Pentecostal Power, p. 135. 223 Matthew 3.15. 224 Most immerse, but the Pentecostal Holiness Church gives their members a choice of modes and ages (infant, child, youth, or adult). 225 The Elim Pentecostal Churches of Great Britain celebrate the Lord’s Supper each week. 226 1 Corinthians 11. 227 Winsett, Songs of Pentecostal Power, p. 110. 228 Seymour, ‘The Ordinances Taught by our Lord’, AF 1.10 (September, 1907), p. 2. 229 Matthew 3.8. 230 Pomerville, The Third Force. 231 C.F. Weigele, in Church Hymnal, p. 303. 232 (Chapter 3) L.V. Packard, The Status Seekers (New York: D. McKay Co.; 1959). 233 AF 1.10 (September, 1907), p. 2. 234 AF 1.10 (September, 1907), p. 2. 235 AF 1.10 (September, 1907), p. 2. 236 AF 1.10 (September, 1907), p. 2. 237 W. Brueggemann, Hope Within History (Atlanta: John Knox, 1987), p. 35. 238 Brueggeman, Hope Within History, p. 35. 239 Brueggeman, Hope Within History, p. 33. 240 Brueggeman. Hope Within History, p. 36. 241 AF 1.3 (1906), p. 2. 242 AF 1.3 (1906), p. 2. 243 ‘Bible Salvation’, ‘Sanctification and Power’, ‘The Character of Love’, AF 1.3 (1906), p. 4 (emphasis mine). 244 AF 1.3 (1906), p. 2. 245 AF 1.3 (1906), p. 2. 246 ‘River of Living Water’, AF 1.3 (1906), p. 2 (emphasis mine). 247 H.H. Knight, ‘The Relationship of Narrative to the Christian Affections’ (unpublished paper, Emory University, 1987). 248 John 15.12. 249 Romans 5.5; Mt. 15.32. 250 Knight, ‘Relationship’, p. 6. 251 See D.E. Saliers, The Soul in Paraphrase (New York: Seabury Press, 1980); idem, Worship and Spirituality (Philadelphia: Westminster Press, 1984); R.C.
Roberts, Spirituality and Human Emotion (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1982); idem, The Strengths of a Christian (Philadelphia: Westminster Press, 1984), and H.H. Knight, III, The Presence of God in the Christian Life (Metuchen, NJ: Scarecrow Press, 1992). 252 Saliers, The Soul in Paraphrase, p. 10. 253 J. Edwards, Treatise Concerning Religious Affections (ed. J. Smith; New Haven: Yale University Press, 1959), p. 120. 254 1 John 1.6; Rev. 22.15. 255 H.R. Niebuhr, ‘Coale Lectures’ (Andover Library, Cambridge. MA: Manuscript) cited in P.M. Cooey, Jonathan Edwards on Nature and Destiny (Lewiston, NY: Edwin Mellen, 1985), p. 1. 256 Saliers, The Soul in Paraphrase, p. 11. 257 Roberts, The Strengths of a Christian, p. 22. 258 Ephesians 6.10. 259 J.L. Peters, Christian Perfection and American Methodism (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1985), pp. 187-88. 260 Peters, Christian Perfection and American Methodism, pp. 187-88. 261 John Wesley’s Notes on the New Testament. 262 1 Corinthians 13. 263 1 Peter 2.2. 264 Mills, ‘New Heaven? New Earth?’, pp. 98-100. 265 Hebrews 6.1-12. 266 Roberts, The Strengths of a Christian, p. 23. 267 Ephesians 2.10. 268 Galatians 5.6. 269 AF 1.6 (February-March, 1907), p. 2. 270 Pentecostal Holiness ministers baptize infants but still admonish the parents to nurture the child and, at the appropriate age, call for repentance and expect a regeneration by profession of faith. 271 AF 1.6 (February-March, 1907), p. 1. 272 J. Rowe and H.E. Smith, ‘Love Lifted Me’, in Church Hymnal, p. 265. 273 V.B. Ellis, ‘I’m in a New World’, in Church Hymnal, pp. 94-95. 274 AF 1.6 (February-March, 1907), p. 1. 275 AF 1.6 (February-March, 1907), p. 1. 276 AF 1.5 (January, 1907), p. 1. 277 H.R. Niebuhr, Christ and Culture (New York: Harper & Row, 1951). 278 Roberts, The Strengths of a Christian, p. 26. 279 Hebrews 6.10. Most Pentecostals are, broadly speaking, Arminians. 280 Hebrews 12.14. Leila N. Morris, ‘Holiness unto the Lord’, in Henry Date
and E.A. Hoffman, Pentecostal Hymns Number Three: A Winnowed Collection for Evan-gelistic Services, Young People’s Societies and Sunday-Schools (Chicago: Hope Pub. Co., 1894), p. 52. 281 Phoebe Palmer and Mrs. J.F. Knape, ‘The Cleansing Wave’, in Winsett, Songs of Pentecostal Power, p. 180. 282 2 Corinthians 7.1. 283 AF 1.3 (1906), p. 2. 284 AF 1.3 (1906), p. 2. 285 AF 1.3 (1906), p. 2. 286 AF 1.2 (1906), p. 4. 287 AF 1.3 (1906), p. 4. 288 AF 1.3 (1906), p. 4. 289 Matthew 9.36. 290 As God is ‘for us’ (Rom. 8.31). 291 Fanny J. Crosby and W.H. Doane, ‘Rescue the Perishing’, in Church Hymnal, p. 145. 292 2 Corinthians 4.7-10. 293 E.P. Anderson (ed.), Melodies of Praise (Springfield, MO: Gospel Pub. House, 1957). These hymns are chosen because the Assemblies of God are supposedly the ‘baptistic’ or two-blessing wing of the movement (saved, filled with the Spirit). Though the theologies of the ‘baptistic’ and ‘Wesleyan’ Pentecostals may differ over what does or does not, can or cannot happen in sanctification, yet the concern for holiness, purity, and consecration is still evident in the following hymns. This is true throughout the movement, and was even more obvious in and characteristic of the early Pentecostals. Though rejecting an ‘eradicationist’ view of sanctification, the Assemblies of God, nevertheless, did adopt a statement on ‘entire sanctification’ in their earliest Statement of Fundamental Truths. This was no doubt an attempt to hold the various Wesleyan Pentecostals who had not yet embraced Durham’s finished work doctrine. James Bowers has chronicled an account of how the threeblessing paradigm began to weaken and then almost fade away in the North American constituency of the Church of God. See his ‘Sanctification in the Church of God: A Shift From the Three Blessing Paradigm’ (unpublished paper, Southern Baptist Theological Seminary, 1985). 294 Cited in Ranaghan, ‘Rites’, p. 736 as a ‘Conversion’ song, but is also illustrative of consecration and cleansing. 295 Ranaghan, ‘Rites’, pp. 738, 734. 296 Ranaghan, ‘Rites’, p. 739. 297 Ranaghan, ‘Rites’, p. 741.
298 Ranaghan, ‘Rites’, p. 746. 299 J. Oatman, Jr, and C.H. Gabriel, in Winsett, Songs of Pentecostal Power, p. 130. 300 Sanctification is not the static, terminal stage which, when reached, spells the end of this longing. It is the abiding in wholehearted, longing expectation. It is characterized by the joy of union and wounded longing. 301 C.P. Jones, ‘Deeper, Deeper’, in Church Hymnal, p. 230. 302 The following are all in Winsett, Songs of Pentecostal Power: E.A. Hoffman, ‘Is Your All on the Altar?’, p. 212; T. Monod and R.E. Winsett, ‘None of Self and All of Thee’, p. 174; C.S. Nusbaum, ‘His Way with Thee’, p. 261; Palmer and Knape, ‘The Cleansing Wave’, p. 180; and Oatman and Gabriel ‘Higher Ground’, p. 120. 303 R.E. Winsett, ‘Longing for the Dawning’, in Winsett, Songs of Pentecostal Power, p. 164. 304 L.G. Martin, ‘The Meeting in the Air’, in Winsett, Songs of Pentecostal Power, p. 257. 305 R.H. Cornelius, ‘O, I Want to See Him’, in Church Hymnal, p. 279. 306 G.T. Haywood, in E. Haynes and M.S. Lemons (eds.), Church of God Songs No. 3 (Cleveland, TN: Church of God Publishing House, n.d.), p. 148. 307 Mary Brown and Carrie E. Rounsefell, ‘I’ll Go Where You Want Me to Go’, in Church Hymnal, p. 213. 308 Anon., ‘Sitting at the Feet of Jesus’, in Winsett, Songs of Pentecostal Power, p. 203; and Mills and Miller, ‘We’ll Work till [sic] Jesus Comes’, in Winsett, Songs of Pentecostal Power, p. 179. 309 AF 1.1 (1906), p. 2. 310 Heimar and Pickett, in Winsett, Songs of Pentecostal Power, p. 135. 311 AF 1.11 (October [1907] to January, 1908), p. 3: ‘We ought to claim perfect health in the atonement of Jesus’. 312 AF 1.11 (October [1907] to January, 1908), p. 3. 313 The Greek words ἐξουσία (exousia) and δύναμις (dunamis) mean authority and force, respectively; both words are frequently translated as ‘power’. 314 Ephesians 6.10-20; Jas 4.7. 315 In Heaven: A History the authors divide the views of ultimate destiny into two major camps: the theocentric or more individualistic, contemplative, and the anthropocentric, more social vision of a great reunion. Pentecostals hold something of both views in terms of ultimate destiny and in light of their penultimate eschatological worship. See C. McDonnell and B. Lang, Heaven: A History (New Haven: Yale University Press, 1988). 316 1 Corinthians 15.28.
317 Haynes and Lemons, Songs No. 3, p. 111. 318 Seymour, ‘The Holy Spirit, Bishop of the Church’, AF 1.9 (June-September, 1907), p. 3. Subsequent quotations throughout this paragraph are drawn from this article. 319 Seymour, ‘The Holy Spirit, Bishop of the Church’, p. 3. 320 J.D. Vaughan, The Silver Trumpet (Lawrenceburg. TN: James D. Vaughan, 1908), pp. 43, 59. 321 R.E. Winsett, ‘Waiting for a Blessing’, in Winsett, Songs of Pentecostal Power, p. 2; A.J. Showalter, The Best Gospel Songs and their Composers (Dalton, GA: A.J. Showalter, 1904), p. 158. 322 J.M. Black, ‘When the Roll Is Called Up Yonder’, in Church Hymnal, p. 240. 323 1 Peter 1.8. 324 T.L. Williams, et al., Haynes and Lemons, Songs No. 3, p. 165. 325 Interview with the family of Pedro Pablo Costillo (Managua, Nicaragua, October, 1989). 326 ‘Arrested for Jesus’ Sake’, AF 1.1 (September, 1906), p. 4. 327 ‘Back to Pentecost’, AF 1.2 (October, 1906), p. 3. 328 AF 1.3 (November, 1906), p. 4. 329 AF 1.3 (November, 1906), p. 4. For example, Margaret Gaines, a Church of God Missionary, left Alabama in the 1950s to live among the Arabs in Palestine as a teacher, pastor, and church planter. 330 AF 1.4 (December, 1906), p. 4. 331 ‘Demons Cast Out’, AF 1.6 (February-March, 1907), p. 3. 332 H. Ward, ‘The Early Anti-Pentecostal Argument’, in Synan, Aspects, pp. 99122. 333 J.H. King (ed.), The Apostolic Evangel 1.4, p. 1 (emphasis mine). Cf. King’s very influential, From Passover to Pentecost (Memphis, TN: H.W. Dixon Printing Co., 1914). 334 King, Apostolic Evangel 1.4, p. 1. 335 ‘Marks of Fanaticism’, AF 1.2 (October, 1906), p. 2. 336 AF 1.3 (November, 1906), p. 2. 337 AF 1.12 (January, 1908), p. 3. 338 AF 1.5 (January, 1907), p. 1; 1.6 (February-March, 1907), p. 1; 1.12 (January, 1908), p. 3. 339 AF 1.12 (January, 1908), p. 3. 340 AF 1.12 (January, 1908), p. 3. 341 AF 1.12 (January, 1908), p. 3. 342 Roberts, The Strengths of a Christian, pp. 18, 19.
343 R. Martin, ‘Discernment of Spirits’, DPCM, pp. 244-47. 344 Saliers, Soul, pp. 72, 73. 345 Central American Pentecostal practice is no doubt influenced by Roman Catholic usage, but also emphasizes ‘watching’ and ‘waiting’ in prayer in order to be more sensitive to the leading and discipline of the Lord. 346 Roberts, The Strengths of a Christian, pp. 24, 25. 347 Gerlach and Hine (People, Power, Change) analyze Pentecostalism and the Black Power movements and characterize both as potentially revolutionary. For their more recent consideration of this issue as well as a critique of the deprivation reductionist model for analyzing and understanding religious movements, see L.P. Gerlach, ‘Pentecostalism: Revolution or CounterRevolution?’, and V.H. Hine, ‘The Deprivation and Disorganization Theories of Social Movements’, both in U. Zaretsky and M.P. Leone (eds.), Religious Movements in Contemporary America (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1974), pp. 669-99, 646-54. 348 P.J. Rosato, The Spirit as Lord: The Pneumatology of Karl Barth (Edinburgh: T. & T. Clark, 1981); Prologue, p. v., pp. 47-52. 349 Colossians 3.1.3. 350 John 17. The Spirit brings the Son and the Father, who by the Spirit makes a habitation in the midst of and within humanity. 351 Barth, Evangelical Theology, p. 58. 352 Romans 8.26. 353 See Valliere, Holy War and Pentecostal Peace, esp. ch. 1 where the social, moral, and cosmic dimensions of Pentecost are delineated along with a call to the church to become a house of prayer for the healing of all nations. Valliere’s peace message is timely and carefully argued; Pentecostals would do well to consider it carefully. 354 J. Comblin, The Holy Spirit and Liberation (Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books. 1989), p. 184. See also his discussion on pp. 2-3. 355 Roberts, The Strengths of a Christian, p. 24. 356 See John 15 for the fate of the ‘fruitless’ and 1 Corinthians 13 for the ‘profit margin’ of those who express gifts, make offerings, sacrifice themselves, and so forth but lack love. The important point is participation in the divine life and mission of God. Salvation is participation—abiding, fruitful love. 357 H.A. Snyder, The Community of the King (Downers Grove, IL: IVP, 1977). 358 Ephesians 2.10. 359 Those at Azusa emphasized the necessity of the blood every moment. One should trust God, and not the arm of flesh, at all times. Sanctification, then was no static condition of presumption or self-help.
360 Hebrews 12.14. 361 Galatians 5.25. 362 J. Wesley, Explanatory Notes on The New Testament (London: Epworth Press, 1976 [1754]), pp. 575, 598. 363 T. Smith. Revivalism and Social Reform (Gloucester. MA: Peter Smith, 1957); D. Moberg, The Great Reversal: Evangelism versus Social Concern (Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1972). Smith chronicles the wide-ranging and deep social involvement of the early holiness movement, while Moberg charts the great evangelical reversal or turn to the individual. This reversal occurred because of the crushing effects of the Civil War on all optimistic plans to build a utopia. But it also developed among evangelicals with a holiness heritage because of the association of social reform with liberalism and evolutionary progress by the turn of the century. Pentecostals, isolated at first, gradually became more and more associated with the more conservative, individualistic evangelicals. The really strict fundamentalists never did and do not now embrace Pentecostals. 364 G.B. McGee, ‘Apostolic Power for End-Times Evangelism: A HistoricaI Review of Pentecostal Mission Theology’ (unpublished paper presented to the International Roman Catholic and Classical Pentecostal Dialogue in Emmetten, Switzerland, 1990). 365 (Chapter 4) Faupel, ‘Everlasting Gospel’, pp. 265, 332, 333-393; A.L. Clayton, ‘The Significance of William H. Durham for Pentecostal Historiography’, Pneuma (Fall, 1979), pp. 27-42; Reed, ‘Origins and Development’; R.M. Riss, ‘Finished Work Controversy’, DPCM, pp. 306-309; idem, ‘Latter Rain Movement’, DPCM, pp. 532-34. 366 Peters, Christian Perfection, p. 187. 367 J.H. King, From Passover to Pentecost (Memphis, TN: H.W. Dixon, 1914), p. 106. 368 Faupel, ‘Everlasting Gospel’, pp. 33-393. 369 R.M. Riss, ‘The Role of Women’, DPCM, pp. 893-89. 370 Anderson, Vision of the Disinherited, pp. 153-94. 371 H. Ward, ‘The Anti-Pentecostal Argument’, in Synan (ed.), Aspects of Pentecostal-Charismatic Origins, pp. 99-122. 372 For the most vigorous anti-Pentecostal arguments (though Dunn is supportive of part of the argument Pentecostals make), see Bruner, A Theology of the Holy Spirit; and Dunn, Baptism in the Spirit. For strong Pentecostal replies see Ervin, Conversion-Initiation; idem, Spirit Baptism; Stronstad, Charismatic Theology of St. Luke; J.B. Shelton, Mighty in Word and Deed (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, 1991); R.P. Menzies, The Development of Early Christian
Pneumatology (JSNTSup, 54; Sheffield: JSOT Press, 1991). 373 The New Charismatics: The Origins, Development and Significance of NewPentecostalism (Garden City, New York: Doubleday, 1976). 374 Richard Quebedeaux, The New Charismatics II (New York: Harper & Row, 1983), pp. 190-92. 375 G. Wacker, ‘Wild Theories and Mad Excitement’, in H.B. Smith (ed.), Pentecostals from the Inside Out (Wheaton, IL: Scripture Press), p. 27. 376 Wacker, ‘Wild Theories’, p. 28. 377 C.M. Robeck, Jr, ‘Where Do we Go from here?’, Pneuma 7.1 (Spring, 1985), pp. 1-4. 378 Poloma, The Assemblies of God, pp. 232-41. 379 Poloma, The Assemblies of God, pp. 242, 243. 380 McGee, ‘Apostolic Power’. McGee highlights the importance of eschatology for Pentecostal missiology, then worries about the declining power and urgency of the North American Pentecostal eschatological vision. 381 AF 1.1 (September, 1906), p. 2. 382 AF 1.1 (September, 1906), p. 2. 383 The books of Clarence Larkin, famous dispensational illustrator, are still being sold in Pentecostal ‘camp meetings’ and bookstores. C. Larkin, Dispensational Truth or God’s Plan and Purpose in the Ages (Philadelphia: Rev. Clarence Larkin Est., 1920). 384 R.M. Riss, ‘Latter Rain Movement’, DPCM, pp. 532-34; Faupel, ‘Everlasting Gospel’, pp. 394-518. 385 For reviews and critiques of prosperity or ‘faith’ theology, see C. Farah. From the Pinnacle of the Temple: Faith versus Presumption (Plainfield. NJ: Logos. n.d.); idem, ‘A Critical Analysis: The “Roots and Fruit” of Faith-Formula Theology’, Pneuma 3.1 (Spring, 1981), pp. 3-21; D. Gee, Trophimus I Left Sick: Our Problems of Divine Healing (London: Elim Publishing, 1952). For an overview followed by a brief bibliography of prosperity and non-prosperity sources, see R. Jackson, ‘Prosperity Theology and the Faith Movement’, Themelios 15.1 (October, 1989), pp. 16-24. Pentecostals developed pastoral responses to these ‘hyper-faith’ views early in the century. To critics who charge that they encourage such extremes they would reply that it is better to err on the side of what God can and may do than to say what he cannot and will not do—at least with regard to miracles, signs, and wonders. But it would seem that both positions need each other in a way analogous to the way faith needs works, fruit needs gifts, and all need patient, humble love if magical techniques and ‘creeping naturalism’ are both to be avoided and the mission of the church advanced in the modern world.
386 The trinitarian perspective of this chapter emerged during the last ten years of teaching with my colleague R.H. Gause in the Church of God School of Theology (now Pentecostal Theological Seminary) in Cleveland, Tennessee. It has been deepened and extended by the following: J. Moltmann, ‘The Fellowship of the Holy Spirit—A Trinitarian Pneumatology’, SIT 37 (1984), pp. 287-300; P. Hocken, ‘The Meaning and Purpose of “Baptism in the Spirit’’’, Pneuma 7.2 (Fall, 1985), pp. 125-34; D.A. Dorman, ‘The Purpose of Empowerment in the Christian Life’, Pneuma (Fall, 1985), pp. 147-65; M. Duggan, ‘The Cross and the Holy Spirit in Paul: Implications for Baptism in the Holy Spirit’, Pneuma 7.2 (Fall, 1985), pp. 135-46. 387 For accessible primary source reading in Joachim of Fiore, see B. McGinn (ed.), Apocalyptic Spirituality (New York: Paulist Press, 1979), Joachim has proven suggestive to Jürgen Moltmann and his ‘constantly present interacting strata’ approach to the Trinitarian dispensations: Melvin Dieter relates Moltmann and Joachim to John Fletcher, ‘Wesley’s early systematizer’, and Fletcher’s dispensational development of sanctification as baptism in the Holy Spirit. See Dieter’s excellent article, ‘The Development of Nineteenth Century Holiness Theology’. Dieter goes to the heart of the theological predispositions and hermeneutics separating the more Reformed understandings of history and pneumatology from that of Holiness and Pentecostal approaches. 388 Dieter, ‘Holiness Theology’. 389 Critics are quick to point out Irwin’s theological eccentricities and later moral failure (‘open and gross sin’), but his creativity and early leadership led eventually to the formation of the Pentecostal Holiness Church under his assistant, J.H. King. See B.H. Irwin, ‘Pyrophobia’, The Way of Faith (28 October 1896), p. 2; and H.V. Synan, ‘Benjamin Hardin Irwin’, DPCM, pp. 471-72. 390 D.W. Myland, ‘The Latter Rain Covenant and Pentecostal Power’, in Three Early Pentecostal Tracts (The Higher Life Series; New York: Garland Publishing, 1985) is cited in Hocken, “‘Baptism in the Holy Spirit’’’. 391 D.A. Alexander, ‘Bishop J.H. King and the Emergence of Holiness Pentecostalism’, Pneuma 8.2 (Fall, 1986), pp. 159-83. More work needs to be done on King’s integration. My work represents a step in that direction. See also H.V. Synan, ‘Joseph Hillery King’, DPCM, pp. 520-21. H.A. Snyder, The Divided Flame (Grand Rapids: Zondervan, 1986), is coming at the HolinessPentecostal construction from the Holiness side. In my opinion, we are not that far apart. Snyder’s work is all the more important, since he too seeks to correlate soteriology with ecclesiology and missiology. Our only difference may be in the nuancing of eschatology. 392 Comblin, The Holy Spirit and Liberation, p. 184. Comblin’s work is the
most creative recent Roman Catholic appreciation of the positive theological and pastoral benefits of Pentecostalism. Although there will still be differences over the Marian and ecclesiological views, there is much agreement on the importance of pneumatology, spirituality, and experience for the life and mission of the church. For creative, interactions from the Pentecostal side with liberation perspectives see Pastoralia 7.15 (December, 1985), pp. 55-68, articles resulting from a consultation held in Puerto Rico in 1984. See especially the articles by Hector Comacho, Aida Gaetan, Rudolfo Giron, and Ricardo Waldrop. The conclusions are preserved in this issue of Pastoralia in the ‘Declaracion de la consulta de lideres educacionales de la iglesia de Dios: Dessarrollo de un modelo pastoral pentecostal frente a la teologia de la liberacion’, pp. 99-106. See also the brief suggestive analysis by D.W. Dayton in ‘Pentecostal/Charismatic Renewal and Social Change: A Western Perspective’, Transformation 5.4 (October/December, 1988), pp. 7-13. Miroslav Volf has compared Pentecostal and Liberation approaches to salvation to find some surprising commonalities as points for further development in ‘Materiality of Salvation: An Investigation in the Soteriologies of Liberation and Pentecostal Theologies’, JES 26.3 (Summer, 1989), pp. 447-67. 393 See Moltmann, Trinity and Kingdom, p. 208. 394 M. Volf in ‘On Loving with Hope: Eschatology and Social Responsibility’, Transformation 7.3 (July-September, 1990), pp. 28-31, urges Pentecostals to keep the hope in love by remembering that creation is to be transformed, not annihilated, by the Spirit. His article shows how works are significant in the kingdom without sacrificing the sovereignty of God. 395 See Mt. 16.24; Lk. 14.26, 27, 33; Jn 8.31; Phil. 2.12, 13; Gal. 2.20; 5.16, 24. 396 Hebrews 9.14. 397 1 Corinthians 13, cited frequently in this study, is the model of integration for spirituality. Beliefs and practices express, shape, strengthen, and are rooted in the love which is the integrating core of Christian spirituality. Entire satisfaction as wholeheartedness is the only appropriate response to one who has and does so love. 398 See Moltmann, ‘The Fellowship of the Holy Spirit’. 399 Pentecostalism represents a major new approach in Christianity which is both supplementary and complementary. It is an indigenized folk religion which overwhelmingly has a black and brown majority in its constituency. Although there are theological, ethical, and political differences I have argued that there is a core; a spiritual fundament present in the first part of the century with roots in the nineteenth and eighteenth centuries and, through Wesley, all the way back through eastern and western sources to the early church. This is an important
point which an exclusive focus on phenomenological or external similarities may obscure. It is also important for the theological revisioning and cooperative praxis—a simultaneous operation—of the future. See Walter Hollenweger’s fore-word to C.E. Jones, A Guide to the Study of the Pentecostal Movement (2 vols; Meruchen. NJ: Scarecrow Press, 1983), I, pp. vii, viii. See Valliere, Holy War; J. Moltmann, The Church in the Power of the Spirit (New York: Harper & Row, 1977), pp. 289-336. 400 Note R.J. Cassidy, Society and Politics in the Acts of the Apostles (Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books, 1988). It is this countercultural, potentially transformative, leavening influence that Pentecostals and others are just beginning to see and work out in terms of political and missionary implications. 401 Valliere, Holy War, pp. 46-86. 402 Jay Beaman traces the early pacifist stance of several Pentecostal bodies; this was all but abandoned as the twentieth century progressed into more and more horrible global and regional conflicts and Pentecostals moved more into the mainstream of North American culture. They still represent a ‘third way’ of peace in many Third World countries, as in Guatemala, for example, where they are often killed by the right and the left. But Pentecostals are also now fielding candidates in Chile, Brazil, South Africa, and parts of Asia. 403 H.R. Niebuhr, The Social Sources of Denominationalism (New York: World Publishing, 1929); Anderson, Vision of the Disinherited. See the perceptive critique of Anderson by Grant Wacker and Timothy Smith (Religious Studies Review 8.1 [January, 1982], pp. 15-28) from Pentecostal and Holiness perspectives, respectively. 404 J.F. White, Protestant Worship: Traditions in Transition (Louisville, KY: Westminster/John Knox, 1989). 405 I.C. Clemmons, ‘Charles Harrison Mason’, DPCM, pp. 585-88. Clemmons cites Gayraud Wilmore and Sidney Ahlstrom in support of his claim of the place of honor and significance for Seymour and Mason in particular and Blacks in general in Pentecostal origins. R.M. Riss, ‘The Role of Women’, DPCM, pp. 893-94. See also the entries in DPCM for Phoebe Palmer, Pandiu Ramabai, Aimee Semple McPherson, Maria Woodworth-Etter, et al. 406 P.D. Stockard, ‘Modern Kingdom Theology: A Brief Review and Critique of the Book, Held in the Heavens Until God’s Strategy for Planet Earth by Earl Paulk’ (Term Paper, Church of God School of Theology, 1989). Stockard conducted interviews and reviewed the essential primary and secondary materials. See also the more stinging critique of Robert Bowman, Gary S. Hawkins, and Dan Schlesinger,‘The Gospel According to Paulk: A Critique of “Kingdom Now Theology”’, Christian Research Journal 10.3 (Winter/Spring
1988), pp. 9-13, and 11.1 (Summer/Fall, 1988), pp. 15-20. 407 D. Barrett, ‘Global Statistics’, DPCM, pp. 810-29. See also J.W. Sheppard, ‘Sociology of Pentecostalism’, DPCM, pp. 794-99; especially intriguing is Sheppard’s comments on p. 799 that ‘the assumption that Pentecostals are likely to be politically conservative has left another segment of the population— namely politically liberal or radical Pentecostals whose concern is with social justice and with liberation—under researched’. 408 See R.P. Spittler, ‘Society for Pentecostal Studies’, DPCM, pp. 793-94, and Robeck, ‘Seminaries and Graduate Schools’, pp. 722-26. 409 Boer, Pentecost and Missions, pp. 215-17. 410 Jerry Sandidge, a long-time participant in and careful researcher of Pentecostal ecumenical endeavors, has provided a concise, useful summary of the ‘Roman Catholic/Classical Pentecostal Dialogue’ in DPCM, pp. 240-44. 411 See J.L. Sandidge, ‘World Council of Churches’, DPCM, pp. 901-903. 412 See C.M. Robeck, Jr, ‘Pentecostal World Conference’, DPCM, pp. 707-10. 413 See C.M. Robeck, Jr, ‘National Association of Evangelicals’, DPCM, pp. 634-36. Along with Donald Dayton, I question the taxonomy (a narrow understanding of ‘evangelical’) and historiography (a one-dimensional, dichotomized understanding of ‘reason’ and ‘emotion’—‘reason’, standing for the evangelical establishment in North America and ‘emotion’, for the Holiness Pentecostal and ethnic faith communities) of modern, North American evangelical writers. When this approach is taken, what Dayton has called the ‘presbyterian paradigm’ takes the field as the only player. See, for example, Dayton’s ‘Yet Another Layer of the Onion’, pp. 87-110. Dayton’s historiographical and theological work should encourage Pentecostals to begin to overcome their theological ‘inferiority complex’, but in ways faithful to their folk, narrative traditions, and essential spirituality. The evangelicalization of Pentecostalism could become the pentecostalization of evangelicalism thus moving both to consider alternatives to the Princeton theology of Warfield et al. and its common sense philosophical underpinnings. 414 1 Peter 4.17; Rev. 1–3; Heb. 12. 415 Romans 8.24.
Pentecostal Theology of Freedom for the Postcommunist Era
“Stand fast therefore in the liberty wherewith
Christ hath made us free” for “if the Son therefore
shall make you free, ye shall be free indeed”
This paper is intended as a part of larger research entitled Theology of the Persecuted Church. It focuses on they way freedom is understood by the underground church and its successor, the postcommunist church after the fall of the Communist regime. In this sense, the research presents the theological view of freedom from the time of postmodern transition in Eastern Europe in retrospect with the times of underground worship and in dialogue with the major modern theologians. The main purpose is to construct an authentic view of freedom in the major areas of the life and ministry of the postcommunist Pentecostal church.
Postcommunist Europe
On his first official visit to West Germany in May 1989, Mikhail Gorbachev informed Chancellor Kohl that the Brezhnev doctrine had been abandoned and Moscow was no longer willing to use force to prevent democratic transformation of its satellite states. At 6:53 p.m. on November 9, 1989, a member of the new East German government gave a press conference to inform that the new East German travel law would be implemented immediately. At the East Berlin Bornholmer Strasse, the people demanded to open the border. At 10:30 p.m. the border was opened.[1] That meant the fall of the Berlin Wall and the end of the Cold War.
The unification of one Germany brought the clash of two political extremes within one nation. It brought together two Europes kept apart for half-a-century, a dynamic which introduced the continent to a new set of opportunities among which was the vision for a unified Europe and its realization.
A new set of dilemmas was introduced as well. Among all economical, political, social, cultural and simply human points of diversity, religion remained central for the process through which the European Union was emerging. The official “United in Diversity” (reminding of the American E Pluribus Unum) claimed unification, without mentioning God. The new European constitution announced that Europe draws “inspiration from the cultural, religious and humanist inheritance of Europe.”[2]
For us who lived in the last days of Communist Bulgarian, the fall of the wall was a miracle which the world witnessed. Coming out from the severe Communist persecution and surrounded by the Balkan religious wars, suddenly the country of Bulgaria experienced a time of liberation which gave the start of spiritual revival mobilizing Bulgarian Protestants. In the midst of extreme poverty, due to prolonged economical crisis, this revival became an answer for many. It also provided a sense of liberation, but not in the Western political understanding of democracy and freedom, but rather liberation toward the realization of the Kingdom, a world much higher, much better and in way more realistic than any human ideality. The liberation from sin then turns not only into a social movement, but as a theological conception it provides an alternative to the existing culture thus becoming a reaction against the surrounding context and proposing a new theological model and a new paradigm for life itself based on substantive faith and belief.
Freedom of Will
Even when approached theologically, in the Eastern European postcommunist context today, the term freedom of will carries a strong political nuance. For many Eastern European Protestants, freedom characterizes the struggle against the communism regime and the divine motivation to endure it as a calling of faith for the individual and the community.
The years before communist era were characterized with opposition against the historical monopoly of the Eastern Orthodox Church. In this context, the protestant movement in Bulgaria also struggled against spiritual dominion defending the cause of religious freedom and the right of each individual and community to believe and express beliefs.
The hundred years of Bulgarian Protestantism have been accompanied with constant struggle against oppression of conscience and will thus creating a general acceptance of free human will. This has coincided with the theology of the largest and fastest growing Evangelical movements in Bulgaria. In this context, even evangelical churches, like the Baptists, have grown to accept and practice the doctrine of free will.
Based on the political, socioeconomic and purely ecclesial factors, in postcommunist Eastern Europe, the Calvinistic paradigm of predestination and election as practiced in a Western sense are not successful. This is based partially on their new doctrinal presence within the Bulgarian reality and their untested effectiveness through under persecution. It is also natural that they are often qualified in parallel with political and religious oppression, and therefore rejected as divine attributes or actions. If human regimes are oppressive through limiting freedom and consciences, how is God to identify with such regimes and practice the same type of “horrible decree?” On the contrary, in Eastern European Protestant theology, God is seen as a Liberator of human consciences and a desire for freedom.
By no means, is this tension to be confused with a denial of the total authority of God. God remains the electing God in Jesus Christ, but how?[3] Is it through a “horrible decree” or through a personal life-changing experience defined by the Bible? Is it through an oppressive act of lawful but unconditional predetermination which God by His nature is omnipotent to implement, or through an act of supernatural transformation of humanity through divine self-sacrifice? And does this election barricade every possible human choice? No, as it is obvious in the denial of Peter; but also as seen in his restoration, that every choice of human will is answered by God through unconditional divine love.
Therefore, we experience “the secret of predestination to blessedness,” not in a cause and effect paradigm as Augustine and the Reformers, but rather through preserving its significance by experiencing the love of God.[4] Thus, the human will is freed by the love of God to receive salvation for eternity. The human freedom then is not ignored or oppressed, but on the contrary it is “placed in the context of cosmic drama” where the real bondage is not the one by God, but the one by sin which oppresses the human will and distances it to death. The Gospel, however, proclaims the victory of Christ over these oppressors thus liberating human will to its initial creation state as a gift from God.[5] This theology comes from a concrete experience of God in real life, and the quest to serve and follow God. As theology shows that the truth about God and the truth about ourselves always go together, the experience of God is a constant tension and a dynamic process, rather than blind servanthood to rigid principles that can never fully encompass the divine will. And through this experience of liberation of the human will in order that one may be free to choose salvation through Christ, God establishes His “testament of freedom.”[6]
Freedom from Oppression
As God liberates humanity from sin, He liberates it from sin’s moral and social consequences. Thus, forgiveness of sin presupposes not only the quest for sanctification and perfection after the image of God, but also the struggle against oppression and establishment of social balance. As the above shows, the postcommunist revival in Eastern Europe cannot be explored apart from the contextual political and socioeconomic dynamics. The reason for this is that the Spirit with value before God is a social spirit that makes the expression of the divine liberation the very purpose of the existence of the church.[7] The practice of this expression challenges the relationship between theology and practice as it questions theology’s epistemological and praxis relationship to the oppressed with whom Christ is crucified.[8]
As in such context, theology is challenged to identify with action, the church must choose between contextualizing and enforcing theology. To choose contextualization is to attempt to relate it to the existing culture thus creating a state of relativism. Such approach is observed in some Asian and Black theology. The danger is to go beyond the boundary pass which theology ceases being theology in action and becomes simply a nominal religious culture. In Eastern Europe, such approach has been long-practiced by the Eastern Orthodox and has unquestionably resulted in nominal religion. The nominality of its expression has been a factor preventing the experience of God, thus denouncing the very reason for the church’s existence. Attempts to restore the Eastern Orthodox “symphony” between church and state have altered the existence of the independent synods which claim the succession of the same historical religious institution.
The second direction, to move toward enforcement of theology after the paradigm proposed by Liberation theology, is quiet a dangerous approach often resulting in armed conflicts. Keeping in mind the historical tension on the Balkans and Bulgaria’s success in undergoing the postcommunist transition without an armed civil conflict, this approach is virtually inapplicable. Therefore, an alternative must be proposed before history itself become oppression.
In this context, a move toward a theology of freedom seems most reasonable. It must purpose to prevent political and socioeconomic oppressions which are already present in various legal and illegal forms in Bulgaria. Such paradigm must also be concerned with intrachurch oppressive tensions which are present both among and within religious denominations, striving especially against such oppressive modes that come from the desire of an oppressed mentality to oppress others.
Such working model of social transformation is presented in Paul’s Epistle to Philemon. An older interpretation of the book explains that Onesimus, a runaway slave, meets Paul in prison, becomes a Christian and is sent by Paul back to his master. A more cotemporary interpretation claims that Onesimus is a slave sent by Philemon to help care for Paul in prison where he converts to Christianity and desires to stay with Paul as a missionary associate.
Regardless of the interpretation of the story plot, the epistle carefully presents a more in-depth set of problems that deal with persecution, imperialism, slavery, mastership, classes, ownership, imprisonment and above all justice. It further makes a more aggressive mood and places the church, represented in the text not merely by masses, but by the very divine appointment of apostolic authority.
The theme of imprisonment as a direct result of persecution is clearly present through the epistle’s plot and more specifically verses 1, 9, 13 where Paul uses the expression “prisoner of Christ” to describe his present status. The expression “prisoner of Christ” carries a sense of belongingness making the phrase different than the sometimes rendered “prisoner for Christ.” While the latter wrong rendering moves the focus toward the purpose of Paul’s imprisonment, the Greek genitive in the phrase “prisoner of Christ” denotes ownership. Although imprisoned in a Roman prison and kept by a Roman guard, Paul denies the Roman Empire ownership of himself, thus claming that he is owned by Christ alone. This is also a denial of the Roman citizenship that has led to this oppressive state of persecution and the recognition of a citizenship in the divine reality of liberation.
Paul’s negation goes a step further, proposing that while the Roman Empire may be authoritative in the temporal context, by no means it is authoritative in the spiritual eternal reality. Having established the temporality of Rome and the eternity of God, Paul denies to the Roman Empire the right to pronounce judgment over social injustice and to establish social status or world order, proposing that no one but the Christian church is the agent divinely designed and supernaturally equipped for these functions. The social injustice of persecution and wrongful imprisonment, the social tensions between classes, the problems within the church and every dilemma presented in the epistle are to be judged by no one but God through his elect. The reality of the situation is that the church is experiencing severe persecuting because the Roman Empire is denying the church social space. Paul, however, denies the reality of such oppressive human system and claims that the church is the one that must deny social space for oppressive structures as the Roman Empire.
The text calls for revolution; not merely, a revolution in the physical violent sense, but a revolution of the mind where human existence and mentality are liberated through Biblical paradigm combined with divine supernatural power to participate in a new spiritual social reality where justice is set by the standard of God. Such a move calls for a new paradigm and for a theology of freedom which creates an anti-culture and an alternative culture to the existing oppressive system. Such idea challenges the church with the claim that Christianity is and should be a scandal and an offence to the world, and not merely a religion but the belief that “Jesus is the most hazardous of all hazards.”[9]
Feast of Freedom or the Bulgarian Easter
Amidst political and socioeconomic crises since the fall of the Berlin Wall, Bulgaria has experienced a rebirth of Bulgarian spirituality. Many observers have referred to this restoration process as the rebirth of the Bulgarian Easter, and even which historically has been connected with the unity and power of the Bulgarian nation.
Bulgaria accepted a Christian country in 864 AD under the reign of Kniaz Boris I. A millennium later, in the middle of the 19th century, Bulgaria found itself occupied by the Ottoman Empire and religiously restricted by the Greek Orthodox Patriarchy which dictated the religious expression of the Bulgarian church.
On April 3, 1860, during Easter Sunday service in Constantinople, the Bulgarian bishop Illarion of Makriopol expressed the will of the Bulgarian people by solemnly proclaiming the separation of the Bulgarian church from the patriarchal in Constantinople. The day commemorating the Resurrection of Jesus Christ coincided with the resuscitation of the Bulgarian people. Although, the struggle continued for another decade, under the influence of Russia, Turkey was forced to legally recognize the independence of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church. In 1870 a firman of the sultan decreed the establishment of an autonomous Bulgarian church institution.
The connection between the historical Bulgarian Easter and the contemporary rebirth of Bulgarian spirituality has been used in many aspects of the Bulgarian politics and culture at the beginning of the 21st century. As part of the Eastern Church, Bulgarian orthodox theology pays much more attention to the resurrection rather than to the birth of Christ thus placing its eschatological hope in a future experience rather then a past one. Such dynamic is natural, as the acceptance of Christianity in Bulgaria purposes to bring hope in national politics and communal life. Thus, in an almost historical tradition, the Bulgarian Easter represents the Bulgarian eschatological hope for a supernatural national revival. It also communicates with the sense of liberation from political, economical and religious oppression and a longing for the freedom to live life.
The Bulgarian Easter then provides an alternative to the present moment of tension and straggle in the crucifixion. Similar to Moltmann’s view of the resurrection of Christ, the Bulgarian hope foresees the resurrection of the Bulgarian nation as a divine act of protest against oppression and injustice and as recognition of God’s passion for life.[10] Thus, the resurrection is an alternative not only to the present world, but also to the reality of eternal death.
Death is therefore seen not only as an agent of eternity, but also as an agent of fear, suffering and oppression in the present reality which affects life in all its economical, political, social and even religious aspects. As death diminishes the value of life, the liberating power from Easter often remains ignored. But in order for the church to continue being a church, it must speak as a witness of the resurrection which is impossible without participating in God’s divine liberation which recreates the word to its original state of creation. Thus, the hope of Easter means rebirth of the living hope.
The resurrection hope is an influential factor which directs the life dynamics of the church beyond its walls. Being liberated from sin, the believer desires the liberation of others and claims the right to serve. But true Biblical servanthood cannot exist and therefore does not tolerate oppression, thus becoming a social transformation factor in the midst of oppressive cultures. The resurrected church rebels against the destruction of life and the denial of the right of very human to live. But different than other human systems, the church does not feed off its resistance against oppression. Its source of power is the eschatological hope for the full restoration of life and its eternal continuation in eternity.
A final question must be raised about the pessimistic character of such hope, as traditional evangelical eschatology in Bulgaria has been premillennial and due to its Pentecostal majority clearly pretribulation. Such eschatological views, at large, have been considered to be pessimistic and escapist in nature due to their strong focus on the future. Yet, such determinative presupposition seems inaccurate and much limited in its observation when applied within the postcommunist context where Protestant churches have been greatly involved in the struggle against oppressive regimes and constraining politics even to the point of martyrdom.
It is then natural, that in the underground context of persecution it is unthinkable for the church to identify with the regime in anyway. Actually, such identification is vied by the believers as spiritual treason and cooperation with authority is viewed as backsliding. By no means, however, is such a premillennial eschatological view in this context pessimistic for the church. Neither does the church remain unconcerned with the present reality. On the contrary, through its very act of negation of the right of an oppressive system to dictate reality, the church establishes an alternative culture which is the Kingdom of God. Thus in the midst of persecution and oppression, the church remains in its Biblical boundaries as an agent of the Kingdom of God by providing eschatological hope.
Yes, this eschatological view is escapist, as it promotes eternal separation from the oppressive reality. What other alternative can a persecuted and underground church find to survive and relate to the Biblical image of the ecclesia and at the same time it is clearly concerned with the transformation of the present world as shown above? For while its pessimism concerns the oppressive system of the world, its optimism declares the church as an already-reality in which freedom of sin, death and oppression and eternity with God is celebrated. Therefore, the church itself remains an optimistic reality and optimistic eschatological hope. For, without this hope the tension of life toward future and even life it self will vanish.[11] Without hope for the beyond, we remain in the now for eternity.
Epilogue
Due to its relational and reactional role to historical process, Eastern European postcommunist theology is a new historical and theological event. Yet, as theology of freedom, it relates to other theological approaches internationally. This similarity is enforced by the approaching postmodern era which the Bulgarian nation seems unprepared to understand. In such context, the church and its theology become the agents providing answers to social tensions.
Postcommunist theology provides a point of departure from the oppressive system of the communist regime toward a new social and ecclesial alternative. Such dynamic is by no means new to the Protestant movement in Bulgaria, which has dealt successfully with these same issues even in more severe context of underground existence and persecution. Therefore, the church has proved its commitment to identify with the oppressed through addressing and engaging its experience through the experience of God and its adequate and substantive theological interpretation. Such approach provides an alternative to oppressive system and structures, unquestionably critiques their tools and methods, and rebukes the agents who represent and practice them, thus denying them place in history.
A further concern for developing strategies for social transformation is also strongly present including education, law, politics and economics. These dynamics employ Christians in a common task and motivate the church for further development and implementation in order to connect theology with practice and thus to fulfill the divine calling for church’s role in the processes of restoration of justice and social transformation, both now and eschatologically.
Bibliography
Anderson, David E. “European Union Debate on Religion in Constitution Continues”
May 26, 2004.
Barth, Karl (tr. E.C. Hoskyns), The Epistle to the Romans (Oxford: Oxford University
Press: n/a).
Ford, David F. ed., The Modern Theologians (Malden: Blackwell Publishers, 1997).
Geffrey B. Kelly & F. Burton Nelson, A Testament to Freedom: The Essential Writings
of Dietrich Bonhoeffer (San Francisco: Harper Publishing House, 1995).
Green, Clifford. Karl Barth: Theologian of Freedom (Minneapolis: Fortress Press, 1989).
Grentz, Stanley J. Theology for the Community of God (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans
Publishing Company, 1994).
Johnson, Ed. Associated Press, June 19, 2004.
Moltmann, Jürgen. The Power of the Powerless, (Norwich: SCM Press Ltd., 1983).
Taylor, Mark K. Paul Tillich: Theologian of the Boundaries (London: Collins, 1987).
[1] The Fall of the Berlin Wall, http://www.dailysoft.com/berlinwall/history/fall-of-berlinwall.htm June 29, 2004; also Jeremy Isaacs and Taylor Downing, The Cold War, Thomas Fleming, The Berlin Wall and Wolfgang Schneider, Leipziger Demotagebuch.
[2] Ed Johnson, Associated Press, June 19, 2004 and David E. Anderson, “European Union Debate on Religion in Constitution Continues” May 26, 2004.
[3] Clifford Green, Karl Barth: Theologian of Freedom (Minneapolis: Fortress Press, 1989), 184.
[4] Karl Barth, (tr. E.C. Hoskyns), The Epistle to the Romans (Oxford: Oxford University Press: n/a), 324.
[5] Stanley J. Grentz, Theology for the Community of God (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans Publishing Company, 1994), 437.
[6] Geffrey B. Kelly & F. Burton Nelson, A Testament to Freedom: The Essential Writings of Dietrich Bonhoeffer (San Francisco: Harper Publishing House, 1995).
[7] Green, 106.
[8] David F. Ford, ed., The Modern Theologians (Malden: Blackwell Publishers, 1997), 369.
[9] Barth, 99.
[10] Jürgen Moltmann, The Power of the Powerless, (Norwich: SCM Press Ltd., 1983).
[11] Mark K. Taylor, Paul Tillich: Theologian of the Boundaries (London: Collins, 1987), 325.
13 Titles and Resources at Flower Pentecostal Heritage Center
April 30, 2023 by Cup&Cross
Filed under Featured, News, Publication, Research

Pentecostal Seminary Address
Toward a Pentecostal Strategy for the City
Toward a Pentecostal Strategy for the City
One of the questions that seems to come up in this course discussion is how to change the world around us with a more positive and effective approach toward using the Gospel of Salvation. In this particular module, the difficulty addressed is ethnocentricity. The particularity of our search then arrives at the more detailed question, how can we change the culture (respectively subcultures) of our church congregations? This is a drastic move from a closed circle toward an outreach community that many congregations are unable to accomplish. How do we then empower such congregations to be transformed into cultural reach-outs to a single ethnos or multiple ethnic groups?
Problem
The problem in the first quarter of the 21st century has been incongruity of our church strategy with the times we live in and the mindset they occupy. We’ve been preparing the church for the multicultural battle, all and while we should have been equipping the saints how to rebuild the walls since the battle has been lost.
We’ve been equipping leaders for the ministry while the church ship has been sinking only to end up with well trained captains of a sunken fleet. And in a doomed attempt to reconcile the reality of the ministry with their training, they have turned to wave walkers who briefly surface for breaths of fresh air during Sunday worship only to return to the deep blue walk of their daily ministry never finding their lost piece of eight.
For the battle was lost long ago before the present generation of ministers ever came to existence. They know not the battle. They’ve only seen the ruins that were left within the broken walls of the church. And they have been struggling to reconcile the incomputable of what church eldership has been teaching them to battle against with the Nehemiah calling for restoration, which God has placed upon them. For the answer has never been in building a New Jerusalem for a fresh start, but restoring the old Jerusalem and its former glory to a new state that reclaims our history and heritage.
Context
Recent analysis of migrant churches in the United States reveals that the predominant majority of them are located in cities which have a high influxation and concentration of immigrants. Such localities are called “gateway cities”. Immigrants typically enter the United States through one of these cities and settle there. These areas contain over half of the foreign-born population in the United States as follows:
- New York, NY – Foreign born population 18.7%
- Los Angeles, CA – Foreign born population 27.1%
- Houston, TX – Foreign born population 12.3%
- Washington, DC – Foreign born population 8.6%
- Miami, FL – Foreign born population 33.6%
- Chicago, IL – Foreign born population 11.1%
- San Francisco, CA – Foreign born population 20.0%
Strategy
Asking the right questions is important, but the answers cannot be generic for all ethnic groups or cultural settings. There is a strong need to be flexible and observe changes in culture, but not to change the message of the Gospel or compromise our witness. Several common things are noted in any cultural setting where our ministry is involved:
First and foremost, people of all cultures prefer to be personal with a purpose, rather than being project driven. No one longs to be part of someone else’s project. Yet, our very existence demands personal purpose, which could serve as a great cultural catalyst in a church ministry.
Secondly, cross cultural ministry is not done merely on relationships, but on being real in the relationships. The greatest halt of ministry work is when people realize the relationship with the church has not been a real one, but merely a part of a program or a paradigm.
Finally, our cross cultural model for ministry should not be just salvation oriented, but soul oriented. There is a great difference between writing down the number of saved every Sunday and actually caring for the eternal well-being of the saved souls. In fact, this is so fundamentally determinative that it should be the goal in mind of every new church plant.