As Pentecostals historically…
As Pentecostals historically (and as a movement)
We have been looking for power when we should have been seeking after His presence
We have been looking for gifts and signs and wonders, when we should have been looking for fruits of the Spirit and of character
We have been looking for preachers and prophets to follow, when we should have been looking for God’s presence to abide in
We have been looking for prophetic words and utterance, when we should have been taking more time in personal prayer
We have been growing, when we should have been going
And going when we should have been learning in the Spirit
We have been looking for more ways to build, when we should have been looking for more ways to move and go
We have been looking for ways to influence the world, instead of looking to be uninfluenced by God
And in our desire to be leaders and influencers, we have forgotten how to be led by God
And for a long time as a movement, we have existed at the borderline, at the verge and at the danger of gaining our rightful place in human history, but loosing our royal position in the GLORY of GOD
BUT ONE THING WE DID GET RIGHT: The Baptism with the Holy Ghost (watch the full message)
Read also: Last Days Great REVIVAL
20 recent Pentecostal articles in light of the upcoming Pentecostal Sunday celebration:
- The Forgotten Azusa Street Mission: The Place where the First Pentecostals Met
- Diamonds in the Rough-N-Ready Pentecostal Series (Complete)
- 95th anniversary of the Pentecostal movement in Bulgaria
- Toward a Pentecostal Solution to the Refugee Crises in the European Union
- Historical and Doctrinal Formation of Holiness Teachings and Praxis among Bulgarian Pentecostals
- Pacifism as a Social Stand for Holiness among Early Bulgarian Pentecostals
- The Practice of Corporate Holiness within the Communion Service of Bulgarian Pentecostals
- Sanctification and Personal Holiness among Early Bulgarian Pentecostals
- First Pentecostal Missionaries to Bulgaria (1920)
- Historical and Doctrinal Formation of Holiness Teachings and Praxis among Bulgarian Pentecostals
- The Everlasting Gospel: The Significance of Eschatology in the Development of Pentecostal Thought
- Online Pentecostal Academic Journals
- What made us Pentecostal?
- Pentecostalism and Post-Modern Social Transformation
- Obama, Marxism and Pentecostal Identity
- Why I Decided to Publish Pentecostal Primitivism?
- Historic Pentecostal Revival Tour in Bulgaria Continues
- The Land of Pentecostals
- Pentecostal Theological Seminary Address
- A Truly Pentecostal Water Baptism
As Pentecostals historically…
As Pentecostals historically (and as a movement)
We have been looking for power when we should have been seeking after His presence
We have been looking for gifts and signs and wonders, when we should have been looking for fruits of the Spirit and of character
We have been looking for preachers and prophets to follow, when we should have been looking for God’s presence to abide in
We have been looking for prophetic words and utterance, when we should have been taking more time in personal prayer
We have been growing, when we should have been going
And going when we should have been learning in the Spirit
We have been looking for more ways to build, when we should have been looking for more ways to move and go
We have been looking for ways to influence the world, instead of looking to be uninfluenced by God
And in our desire to be leaders and influencers, we have forgotten how to be led by God
And for a long time as a movement, we have existed at the borderline, at the verge and at the danger of gaining our rightful place in human history, but loosing our royal position in the GLORY of GOD
BUT ONE THING WE DID GET RIGHT: The Baptism with the Holy Ghost (watch the full message)
Read also: Last Days Great REVIVAL
20 recent Pentecostal articles in light of the upcoming Pentecostal Sunday celebration:
- The Forgotten Azusa Street Mission: The Place where the First Pentecostals Met
- Diamonds in the Rough-N-Ready Pentecostal Series (Complete)
- 95th anniversary of the Pentecostal movement in Bulgaria
- Toward a Pentecostal Solution to the Refugee Crises in the European Union
- Historical and Doctrinal Formation of Holiness Teachings and Praxis among Bulgarian Pentecostals
- Pacifism as a Social Stand for Holiness among Early Bulgarian Pentecostals
- The Practice of Corporate Holiness within the Communion Service of Bulgarian Pentecostals
- Sanctification and Personal Holiness among Early Bulgarian Pentecostals
- First Pentecostal Missionaries to Bulgaria (1920)
- Historical and Doctrinal Formation of Holiness Teachings and Praxis among Bulgarian Pentecostals
- The Everlasting Gospel: The Significance of Eschatology in the Development of Pentecostal Thought
- Online Pentecostal Academic Journals
- What made us Pentecostal?
- Pentecostalism and Post-Modern Social Transformation
- Obama, Marxism and Pentecostal Identity
- Why I Decided to Publish Pentecostal Primitivism?
- Historic Pentecostal Revival Tour in Bulgaria Continues
- The Land of Pentecostals
- Pentecostal Theological Seminary Address
- A Truly Pentecostal Water Baptism
The Forgotten Azusa Street Mission: The Place where the First Pentecostals Met
For years, the building on Azusa Street has also been an enigma. Most people are familiar with the same three or four photographs that have been published and republished through the years. They show a rectangular, boxy, wood frame structure that was 40 feet by 60 feet and desperately in need of repair. Seymour began his meetings in the Mission on April 15, 1906. A work crew set up a pulpit made from a wooden box used for shipping shoes from the manufacturer to stores. The pulpit sat in the center of the room. A piece of cotton cloth covered its top. Osterberg built an altar with donated lumber that ran between two chairs. Space was left open for seekers. Bartleman sketched seating as nothing more than a few long planks set on nail kegs and a ragtag collection of old chairs.
What the new sources have revealed about the Mission, however, is fascinating. The people worshiped on the ground level — a dirt floor, on which straw and sawdust were scattered. The walls were never finished, but the people whitewashed the rough-cut lumber. Near the door hung a mailbox into which tithes and offerings were placed since they did not take offerings at the Mission. A sign greeted visitors with vivid green letters. It read “Mene, Mene, Tekel, Upharsin” (Daniel 5:25, kjv), with its Ns written backwards and its Ss upside down. Men hung their hats on exposed overhead rafters where a single row of incandescent lights ran the length of the room.
These sources also reveal that the atmosphere within this crude building — without insulation or air conditioning, and teeming with perspiring bodies — was rank at best. As one writer put it, “It was necessary to stick one’s nose under the benches to get a breath of air.”
Several announced that the meetings were plagued by flies. “Swarms of flies,” wrote one reporter, “attracted by the vitiated atmosphere, buzzed throughout the room, and it was a continual fight for protection.”
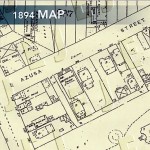
A series of maps drawn by the Sanborn Insurance Company give a clear picture of the neighborhood. The 1888 map discloses that Azusa Street was originally Old Second Street. The street was never more than one block in length. It ended at a street paving company with piles of coal, along with heavy equipment. A small house, marked on the map by a “D” for domicile, sat on the front of the property with the address of 87. (See highlighted section.) A marble works business specializing in tombstones stood on the southeast corner of Azusa Street and San Pedro. Orange and grapefruit orchards surrounded the property. On the right of the map a Southern Pacific railroad spur is clearly visible. The City Directory indicates that the neighborhood was predominantly Jewish, though other names were mixed among them.
A second map of the property was published in 1894. Old Second Street had become Azusa Street, and the address had been changed to 312. The house had been moved further back on the property where it served as a parsonage. The dominant building at 312 Azusa Street was the Stevens African Methodist Episcopal Church. At the front of the building a series of tiny parallel lines on the map mark a staircase that stood at the north end of the building providing entry to the second floor, the original sanctuary.
The only known photograph of the church from this period shows three interesting features. First, it shows the original staircase. Second, and less obvious, the original roofline had a steep pitch. Third, three gothic style windows with tracery lines adorned the front wall.
By 1894, the citrus groves had largely disappeared. On the southern side they were replaced by lawn. The smell of orange blossoms and the serenity of the orchard were rapidly being replaced by the banging of railroad cars and the smell of new lumber. A growing number of boarding houses and small businesses, including canneries and laundries, were moving into the immediate area by this time. The property marked “YARD” on the map is the beginning of the lumberyard that soon came to dominate the area. The City Directory reveals fewer Jewish names, and more racial and ethnic diversity in the neighborhood, including African Americans, Germans, Scandinavians, and Japanese.
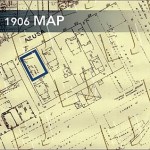
Stevens AME Church occupied the building at 312 Azusa Street until February 1904 when the congregation dedicated a new brick facility at the corner of 8th and Towne and changed their name to First AME Church. Before the congregation could decide what to do with the property on Azusa Street, however, an arsonist set the vacant church building on fire. The structure was greatly weakened, and the roof was completely destroyed. The congregation decided to turn the building into a tenement house. They subdivided the former second-floor sanctuary into several rooms separated by a long hallway that ran the length of the building. The stairs were removed from the front of the building and a rear stairwell was constructed, leaving the original entry hanging in space. The lower level was used to house horses and to store building supplies, including lumber and nails.
In 1906, a new Sanborn Map was published. (See 1906 map.) The building was marked with the words “Lodgings 2nd, Hall 1st, CHEAP.” The transition of the neighborhood had continued. The marble work still occupied the southeast corner of Azusa Street and San Pedro, but a livery and feed supply store now dominated the northeast corner. A growing lumberyard to the south and east of the property now replaced the once sprawling lawn. A Southern Pacific railroad spur curved through the lumberyard to service this business.
The Apostolic Faith, the newspaper of the Azusa Street Mission between September 1906 and June 1908, later referred to the nearby Russian community. Many of these recent immigrants were employed in the lumberyard. They were not Russian Orthodox Christians as one might guess; they were Molokans — “Milk drinkers.” This group had been influenced by some of the 16th-century Reformers. They did not accept the dairy fasts of the Orthodox Church. They were Trinitarians who strongly believed in the ongoing guidance of the Holy Spirit. Demos Shakarian, grandfather of the founder of Full Gospel Business Men’s International, was among these immigrants who were led to Los Angeles through a prophetic word given in 1855.
Henry McGowan, later an Assemblies of God pastor in Pasadena, was a member of the Holiness Church at the time. He was employed as a teamster. He timed his arrival at the nearby lumberyard so he could visit the Mission during its afternoon services.
This map suggests why some viewed the Mission as being in a slum. A better description would be an area of developing light industry.
In April 1906, when the people who had been meeting at the house at 214 North Bonnie Brae Street were forced to move, they found the building at 312 Azusa Street was for sale. The photograph below taken about the time that the congregation chose to move into the building shows the “For Sale” sign posted high on the east wall of the building, as well as the rear of the tombstone shop. Seymour, pastor of the Azusa Street Mission, and a few trusted friends met with the pastor of First AME Church and negotiated a lease for $8 a month.
An early photograph reveals what the 1906 version of the map indicates. The pitched roof had not been replaced. The building had a flat roof. The staircase that had stood at the front of the building had been removed.
In a sense, this building suited the Azusa Street faithful. They were not accustomed to luxury. They were willing to meet in the stable portion of the building. The upstairs could be used for prayer rooms, church offices, and a home for Pastor Seymour.
Articles of incorporation were filed with the state of California on March 9, 1907, and amended May 19, 1914. The church negotiated the purchase of the property for $15,000 with $4,000 down. It was given the necessary cash to retire the mortgage in 1908. The sale was recorded by the County of Los Angeles on April 12, 1908.
Historical and Doctrinal Formation of Holiness Teachings and Praxis among Bulgarian Pentecostals
 Research presentation prepared for the Society of Pentecostal Studies, Seattle, 2013 – Lakeland, 2015, thesis in partial fulfillment of the degree of D. Phil., Trinity College
Research presentation prepared for the Society of Pentecostal Studies, Seattle, 2013 – Lakeland, 2015, thesis in partial fulfillment of the degree of D. Phil., Trinity College
In conclusion, it must be noted that like many other places around the world, Bulgarian Pentecostalism began and continues to be in the periphery of both social and religious life. The movement has been persecuted as new, extreme, outcast and even satanic, but in the end Pentecostalism prevailed from the periphery. The only problem with holding strong in the periphery of society is that you spend all your money, all your time, all your motivation, everything you have to change the center – to change reality itself. It demands an extreme internal passion to continue and to become a movement of social influence. For the external observer this makes no sense. The time and resources spent could be so much helpful somewhere else. Perhaps, in an environment that is more suitable for the center – more controlled by the center. And an environment that does not make the center look bad.
But when this environment is not the center itself, then the periphery becomes a public enemy to the centralized society and is discarded as crazy, obscene and even inhumane. To the point that after giving it all, you start to feel like it was all spent for nothing.
Then you get back to the mission that is more important than our feelings or emotions and convince yourself with all you have left, that the end result is worthy. And then one day you wake up in the center of reality. Even more, you become the center of reality.
And the question remaining is how to balance the center with the periphery. If we were always in the center of culture, religion and economics, we would have never heard the voice of the God of the periphery. The God of the enslaved, oppressed, persecuted, poor, sick and suffering – God of the miraculous…
Pacifism as a Social Stand for Holiness among Early Bulgarian Pentecostals
 Historical and Doctrinal Formation of Holiness Teachings and Praxis among Bulgarian Pentecostals (Research presentation prepared for the Society of Pentecostal Studies, Seattle, 2013 – Lakeland, 2015, thesis in partial fulfillment of the degree of D. Phil., Trinity College)
Historical and Doctrinal Formation of Holiness Teachings and Praxis among Bulgarian Pentecostals (Research presentation prepared for the Society of Pentecostal Studies, Seattle, 2013 – Lakeland, 2015, thesis in partial fulfillment of the degree of D. Phil., Trinity College)
When Pentecostalism began to spread rapidly in Bulgaria in the 1920s, it was viewed hostile as by both Protestant and Orthodox traditions. Not fasting during lent and not sacrificing for the dead, not honoring Mary or the saints was all detrimental in the formation of the identity of Pentecostal churches in Bulgaria. Even insignificant things like not wearing a cross, or not making the sign of the cross and not lighting candles and incense were noticed and severely criticized by the surrounding culture. And of course not drinking alcohol in Bulgaria and the Pentecostal abstinence was met with enormous opposition from other religious groups. Along with that any benevolence, social involvement, spiritual upbringing of minors (including sport actives) was all condemned as harmful protestant propaganda.
But one specific evangelical stand could never be forgiven – the protestant pacifism in the form of conscientious objection against carrying arms. For the newly re-born Balkan state, in a place where war has been ongoing for centuries, to refusal to go to war was essentially to refuse to be a Bulgarian.
The pacifism of Bulgaria’s evangelicals was silent but powerful against both Hitler’s fascism and the militant atheism of the coming Communist Regime. Their deep Christian conviction simply did not allow them to kill, carry a weapon, imprison another human being, swear allegiance to the communist state or take orders from another authority but God. And for their stand, many ministers and believers paid a heavy price. About 40 ministers and members of the Bulgarian Church of God alone were sentenced to hard prison labor for noncompliance with the mandatory military service. Hundreds more known and unknown believers from other evangelical churches followed.
The Practice of Corporate Holiness within the Communion Service of Bulgarian Pentecostals
by Dony K. Donev, D.Min.
Historical and Doctrinal Formation of Holiness Teachings and Praxis among Bulgarian Pentecostals (Research presentation prepared for the Society of Pentecostal Studies, Seattle, 2013 – Lakeland, 2015, thesis in partial fulfillment of the degree of D. Phil., Trinity College)
Pentecostal identity was corporately practiced and celebrated within the fellowship of believers through the partaking of Holy Communion. We have otherwise extensively described the Communion service among Bulgaria’s conservatives in Theology of the Persecuted Church (Part 1: Lord’s Supper https://cupandcross.com/theology-of-the-persecuted-church/). Therefore, here we offer just a brief overview of its main characteristics.
- It was done in a time and place directed by the Holy Spirit
- If some did not have water baptism they were taken to a close by river to be baptized while the rest of the church prayed
- Upon returning, if some did not have yet the baptism with the Holy Spirit, the church would pray until all were baptized
- It began with each participant audibly asking all members for forgiveness
- they would also audible respond with the words: WE FORGIVE YOU and may GOD also forgive you
- The communion bread was prepared on the spot baked by women whose names were also reveled in prayer
- All drank from one cup, which strangely for their strict practice of abstinence from alcohol, was filled with alcoholic wine
- Communion was served only to those who had the fullness of the Spirit, and had just requested and were given forgiveness
- The presbyter would quote Jude 20 to each partaking believer thus directing them to audibly speak in tongues before they could participate in communion
- Interpretation often followed to confirm the spiritual stand of the believer
- If there were any leftovers, the Communion elements were served again until all was used
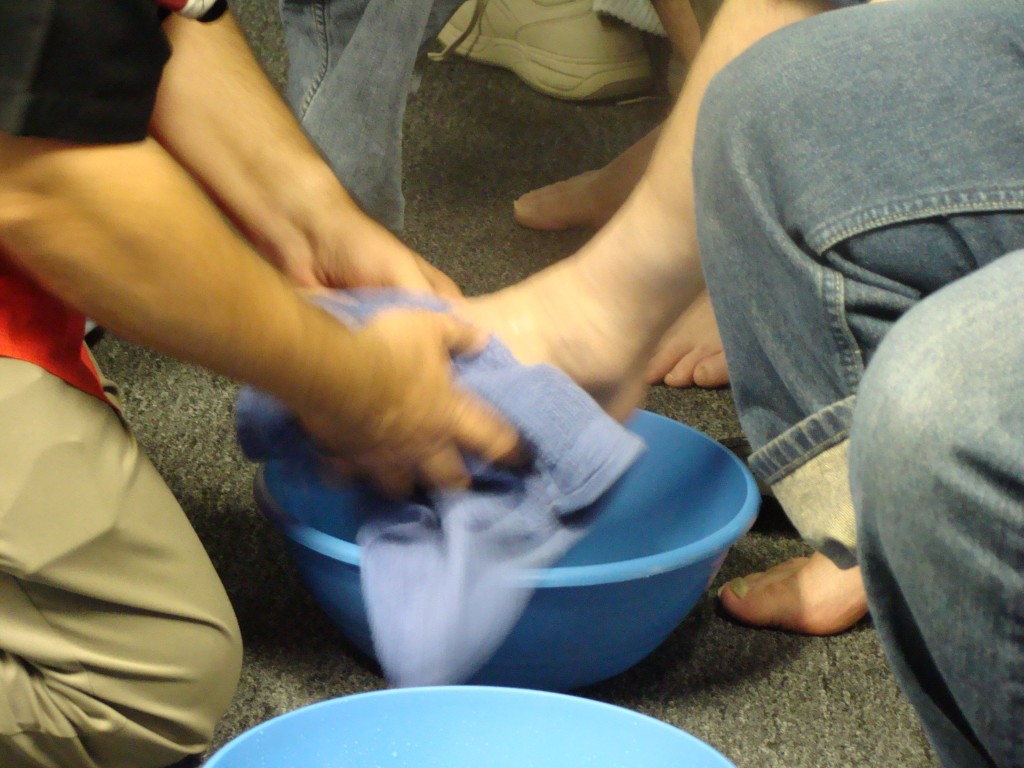
- Communion was incomplete without foot washing as a seal that the whole sacrament was fulfilled.
Sanctification and Personal Holiness among Early Bulgarian Pentecostals
Historical and Doctrinal Formation of Holiness Teachings and Praxis among Bulgarian Pentecostals (Research presentation prepared for the Society of Pentecostal Studies, Seattle, 2013 – Lakeland, 2015, thesis in partial fulfillment of the degree of D. Phil., Trinity College)
With all said about the importance of Spirit baptism and the importance of the Trinity in the Pentecostal experience of the believer, it comes as a great surprise that sanctification was never mentioned as a specific doctrine among early Bulgarian Pentecostals. Voronaev’s teaching included: (1) salvation through new birth, (2) baptism with the Holy Spirit, (3) healing and (4) the second return of Christ. Sanctification was never specifically mentioned as a separate doctrine.
To this day, sanctification is not an official doctrine for the Evangelical Methodist Episcopal Church of Bulgaria. In 1928, Bulgaria’s Pentecostal Union also included holiness as number ten in their first bylaws. Sanctification was not defined as a second work of grace, but as a “continuous life of holiness”. With the enormous theological Methodist influence, it is astounding that the doctrine of sanctification was never taught as a separate work of grace. Even when after Pentecostalism spread in Bulgaria, it was not included in the tri-fold formula for “spiritual fullness” of the believer.
Nevertheless, the search for a deeper spirituality was always there. When liberal theology entered Bulgaria in the beginning of the 20th century, the more conservative believers were forced to separate from the larger city congregations into home services and cottage meetings.
These small communities were enclosed, but easily identified by their extreme personal asceticism. There was no use of instruments in worship, no denominational structure and a distinct social disengagement from the world. Men shaved their heads completely and grew long mustaches. They wore no dress ties, because they pointed downward toward hell. Women wore head coverings as a sign for the angels both within and outside church services. Even the mother of Bulgaria’s Pentecostalism, Olga Zaplishny, who was college educated and spent years in the United States wore a head cover and enforced all ladies to follow her example.
Doctrine of the Trinity among Early Bulgarian Pentecostals
Historical and Doctrinal Formation of Holiness Teachings and Praxis among Bulgarian Pentecostals (Research presentation prepared for the Society of Pentecostal Studies, Seattle, 2013 – Lakeland, 2015, thesis in partial fulfillment of the degree of D. Phil., Trinity College)
The Doctrine of the Trinity was not foreign for the Eastern Orthodox mindset of the first Bulgarian Pentecostals. They grew in a spiritual context where eastern pneumotology historically promoted the graduate process of theism development, with the Spirit being involved in both original creation of the world and the new-birth of the believer. For them, God’s work did not end there, but continued throughout a process of personal sanctification of the believer. This gradual process would have the same triune characteristics as of the triune God, providing the believer an experience with each person of the Trinity.
The historically inherited value of the Trinity is evident in the Bylaws of the Pentecostal Union where it was listed second only to the verbal inspiration of the Bible. As ordained Assemblies of God ministers, both Zaplishny and Voronaev subscribed to the 1916 Statement of Fundamental Truths, which resolved the “oneness controversy” and because of that were unquestionably Trinitarian. All documents from the time period prove that the movement they started in Eastern Europe followed their theological teachings.
Water Baptism among early Bulgarian Pentecostals
Historical and Doctrinal Formation of Holiness Teachings and Praxis among Bulgarian Pentecostals (Research presentation prepared for the Society of Pentecostal Studies, Seattle, 2013 – Lakeland, 2015, thesis in partial fulfillment of the degree of D. Phil., Trinity College)
The sacrament of water baptism was not new for Bulgarian believers. But Pentecostals did NOT accept infant baptism. Converts who were baptized as babies or any other Eastern Orthodox ritual were re-baptized before being received in the church. Among early Bulgarian Pentecostals, baptism was always done outside in “running water.” It was also considered mandatory for salvation as Bulgaria’s early Pentecostals insisted on spiritual fullness including: (1) salvation, (2) water baptism and (3) baptism with the Spirit. This formula of spiritual experience satisfied the witness of blood, water and Spirit (1 Jn. 5:8) on earth and corresponded with the triune God in heaven (1 Jn. 5:7), from whom the believer’s spiritual experience originated.
Historical and Doctrinal Formation of Holiness Teachings and Praxis among Bulgarian Pentecostals
by Dony K. Donev, D.Min.
Historical and Doctrinal Formation of Holiness Teachings and Praxis among Bulgarian Pentecostals (Research presentation prepared for the Society of Pentecostal Studies, Seattle, 2013 – Lakeland, 2015, thesis in partial fulfillment of the degree of D. Phil., Trinity College)
Protestant work in Bulgaria began in 1815 when agents of British and Foreign Bible Society, Robert Pinkerton (1780-1859) and Benjamin Barker (d.1859), initiated a search for Bible translators in the spoken Bulgarian vernacular. As a result a new translation of the New Testament in Bulgaria was published in 1840 and the whole Bible in 1871.
By the liberation of Bulgaria from Turkish Yoke in 1878 Protestantism was well established in Bulgaria. Graduates from Protestant Robert’s College became prominent politicians in the new Bulgarian state. When the first Pentecostal missionaries arrived in 1920, they found a century old protestant tradition in Bulgaria.


![51DUWeyraBL._SY344_PJlook-inside-v2,TopRight,1,0_SH20_BO1,204,203,200_[1]](https://cupandcross.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/51DUWeyraBL._SY344_PJlook-inside-v2TopRight10_SH20_BO1204203200_1.jpg)