How a Small Ocoee Flower Shares a Big Story
by Kathryn DONEV
With VBS season upon us, we are always looking for inventive ways of sharing the Gospel with our little ones. We are internally motivated by the Biblical mandate of Proverbs 22:6. When we start children off on the way they should go, even when they are old they will not turn from it. So this summer let us shift focus from the Corona Virus to the Corona Filaments of a small plant that tells a big story.
When Spanish Christian missionaries arrived in the jungle of Brazil in the 16th century, they discovered a plant with such beauty and distinctiveness unlike any they had seen before. These explores were encouraged feeling it was a good sign for their mission. After closely observing the structure of the plant’s bloom, they called it the passion flower because to them it symbolized the passion or death of Christ.
This exotic flower (Passiflora Incarnata) grows wild in South America and the southern United States as well. Beginning around June is when you first see the vine emerge from the grown after laying dominate all winter. It is the official state wildflower of Tennessee and is sometimes know as the maypop (term given by the Powhatan Indians), wild apricot, Holy Trinity flower and the ocoee. The Cherokee were the ones to referred to the passion vine as “u-wa-go-hi” or “ocoee”. The root “oco” refers to the plant and “ee” describes location. The word “ocoee” literally means the apricot vine place. The passion flower was considered to be the most beautiful of all flowers among the Cherokee and to this day it is a revered piece of their heritage.
Here’s how a small flower turned to be the center stage of the story of Christ’s ultimate sacrifice.
The passion flower is a strong plant that is resistant to pulling and bending as was Christ who endured the horrific pain of a crucifixion. The radial corona filaments of the flower represent the woven crown of thorns which mocked Christ’s claim of authority. This corona rests upon a cup-shaped structure that reminds of the cup of suffering and the Last Supper. The spiraled tendons of the plant are symbols of the lashes Christ endured and the flower’s trailing tendrils are like the whips. The central flower column receptacle is symbolic of the pillar of Christ’s scourging. The three stigmas are symbols of the nails used in the crucifixion as well as the Holy Trinity. The five anthers remind us of the five piercing wounds Christ suffered. Together the five petals and five sepals refer to the ten disciples who did not betray or deny Jesus. The palmate leaves depict the hands of His persecutors or the Holy lance that pierced Christ’s side. The fragrance of the flower helps us recall the spices used in the burial cloth for the body of Christ. The purple color is symbolic of royalty, the white is for purity. The shape of its fruit is symbolic of the world that Christ saved through his suffering. Finally, because the passion flower is a vine it points to Heaven and will compete with surrounding trees to see the light.
How a Small Ocoee Flower Shares a Big Story
by Kathryn DONEV
With VBS season upon us, we are always looking for inventive ways of sharing the Gospel with our little ones. We are internally motivated by the Biblical mandate of Proverbs 22:6. When we start children off on the way they should go, even when they are old they will not turn from it. So this summer let us shift focus from the Corona Virus to the Corona Filaments of a small plant that tells a big story.
When Spanish Christian missionaries arrived in the jungle of Brazil in the 16th century, they discovered a plant with such beauty and distinctiveness unlike any they had seen before. These explores were encouraged feeling it was a good sign for their mission. After closely observing the structure of the plant’s bloom, they called it the passion flower because to them it symbolized the passion or death of Christ.
This exotic flower (Passiflora Incarnata) grows wild in South America and the southern United States as well. Beginning around June is when you first see the vine emerge from the grown after laying dominate all winter. It is the official state wildflower of Tennessee and is sometimes know as the maypop (term given by the Powhatan Indians), wild apricot, Holy Trinity flower and the ocoee. The Cherokee were the ones to referred to the passion vine as “u-wa-go-hi” or “ocoee”. The root “oco” refers to the plant and “ee” describes location. The word “ocoee” literally means the apricot vine place. The passion flower was considered to be the most beautiful of all flowers among the Cherokee and to this day it is a revered piece of their heritage.
Here’s how a small flower turned to be the center stage of the story of Christ’s ultimate sacrifice.
The passion flower is a strong plant that is resistant to pulling and bending as was Christ who endured the horrific pain of a crucifixion. The radial corona filaments of the flower represent the woven crown of thorns which mocked Christ’s claim of authority. This corona rests upon a cup-shaped structure that reminds of the cup of suffering and the Last Supper. The spiraled tendons of the plant are symbols of the lashes Christ endured and the flower’s trailing tendrils are like the whips. The central flower column receptacle is symbolic of the pillar of Christ’s scourging. The three stigmas are symbols of the nails used in the crucifixion as well as the Holy Trinity. The five anthers remind us of the five piercing wounds Christ suffered. Together the five petals and five sepals refer to the ten disciples who did not betray or deny Jesus. The palmate leaves depict the hands of His persecutors or the Holy lance that pierced Christ’s side. The fragrance of the flower helps us recall the spices used in the burial cloth for the body of Christ. The purple color is symbolic of royalty, the white is for purity. The shape of its fruit is symbolic of the world that Christ saved through his suffering. Finally, because the passion flower is a vine it points to Heaven and will compete with surrounding trees to see the light.
Ocoee Church of God Celebrates 40 Years
 Historical Significance of the Tennessee/Georgia Old Federal Road in the Trail of Tears and its Connection to the Church of God
Historical Significance of the Tennessee/Georgia Old Federal Road in the Trail of Tears and its Connection to the Church of God
New Echota, Georgia was the capital of the Cherokee Nation from 1825 to 1838. This is the location where the Treaty of New Echota or the Treaty of 1835 was signed on December 29, 1835 by U.S. government officials and representatives of a minority Cherokee political faction called “The Treaty Party” or “Ridge Party”. This treaty was not approved by the Cherokee National Council nor signed by Principal Chief John Ross. Regardless, it established terms under which the Cherokee Nation were to receive a sum not exceeding five millions dollars for surrendering their lands and possessions east of the Mississippi river to the U.S. Government and agreeing to move to the Indian Territory west of the Mississippi River, which later became part of Oklahoma.
The Red Clay State Historic Park, located 17 miles southwest of the Church of God Headquarter in Cleveland, Tennessee, marks the last location of the Cherokee councils where Chief John Ross and nearly 15,000 Cherokees rejected the proposed Treaty of 1835. Despite the questionable legitimacy of this Treaty, in March 1838, it was amended and ratified by the U.S. Senate and became the legal basis for the forcible removal of the Cherokee Nation known as the Trail of Tears. The name came from the Cherokees who called the removal “Nunna-da-ul-tsun-yi,” which means “the place where they cried.” The last pieces of land controlled by the Cherokee Nation at that time were North Georgia, Northern Alabama and parts of Tennessee and North Carolina. The forced journey was through three major land routes. Each route could have taken some 1,000 miles and over four months to walk. The removal of the Cherokees and other tribes from their homelands in the Southeast began May 16, 1838.
The Georgia Road or present day Federal Road was a route of the Trail of Tears that the Cherokee people walked during their forced removal from their homelands. The route was built from 1803 to 1805 through the newly formed Cherokee Nation on a land concession secured with the 1805 Treaty of Tellico with the agreement that the U.S. Government would pay the Cherokee Nation $1,600.00. The Treaty was signed on October 25, 1805 at The Tellico Blockhouse (1794 – 1807) – an early American outpost located along the Little Tennessee River in Vonore, Monroe County, Tennessee that functioned as the location of official liaisons between the United States government and the Cherokee. The route was originally purposed to be a mail route because of the great need to link the expanding settlements during the westward expansion of the U.S. colonies. It was in 1819 after improvements to the road that it was called “the Federal Road”.
The Tellico Blockhouse was the starting point for the Old Federal Road, which connected Knoxville to Cherokee settlements in Georgia. The route ran from Niles Ferry on the Little Tennessee River near the present day U.S. Highway 411 Bridge, southward into Georgia. Starting from the Niles Ferry Crossing of the Little Tennessee River, near the U.S. Highway 411 bridge, the road went straight to a point about two miles east of the present town of Madisonville, Tennessee. This location is 20 some miles north of the Tellico Plains area that marks the site of the beginning of the Church Cleveland, Tennessee. The road continued southward via the Federal Trail connecting to the North Old Tellico Highway past the present site of Coltharp School, intersected Tennessee Highway 68 for a short distance and passed the site of the Nonaberg Church. East of Englewood, Tennessee it continued on the east side of McMinn Central High School and crossed Highway 411 near the railroad overpass. Along the west side of Etowah, the road continued near Cog Hill and the Hiwassee River near the mouth of Conasauga Creek where there was a ferry near the site of the John Hildebrand Mill. From the ferry on the Hiwassee River the road ran through the site of the present Benton, Tennessee courthouse. It continued on Welcome Valley Road and then crossed the Ocoee River at the Hildebrand Landing. From this point the road ran south and crossed U.S. Highway 64 where there is now the River Hills Church of God formerly the Ocoee Church of God. Continuing south near Old Fort, the route crossed U.S. Highway 411 and came to the Conasauga River at McNair Landing. Near the south end of the village of Tennga, Georgia is an historic marker alongside of Highway 411m which states the Old Federal Road was close to its path for the next twenty-five miles southward. It would have been at this point in Tennga that the Trail of Tears would have taken a turn onto GA-2 passing the Praters Mill near Dalton Georgia to connect in Chattanooga, Tennessee.
Out of the 15,000 Cherokee who endured the forced migration west after the Treaty of 1835, it is estimated that several thousand died along the way or in internment holding camps. This Old Federal route is where some of Cherokee holding camps would have been located. The Fort Marr or Fort Marrow military post constructed around 1814 under the 1803 Treaty, is the last visible remains of these camps. The original fort was built on the Old Federal Road near the Tennessee/Georgia state line near the Conasauga River. It was relocated in 1965 beside U.S. Hwy. 411 in Benton and then to it’s current location in the Cherokee National Forest on the grounds of the Hiwassee/Ocoee State Park Ranger Station at Gee Creek Campground in Delano, Tennessee. This location provides access to popular Church of God water baptismal sites. In June 4, 1838 Captain Marrow reported having 256 Cherokees at his fort ready for emigration.
The Native Americans were forcefully removed from their homes, plantations and farms all because of greed. Thousands of people lost their lives including the wife of Chief John Ross. Parts of the Old Federal Road have been washed away with floods of tears, but there are parts that still remain. The Church of God, having its roots in the same territory of the Cherokee, Chickamauga, Muskogee Creek, Choctaw and Chickasaw people, plays a vital role in the process of reconciliation among the descendants of the Trail of Tears. And the historical buildings and markers along the Trail or Tears must be preserved. The churches along the route even though they were not actual structures during the time period are a historical beacon of hope which still crying out for those lost on this tragic journey.
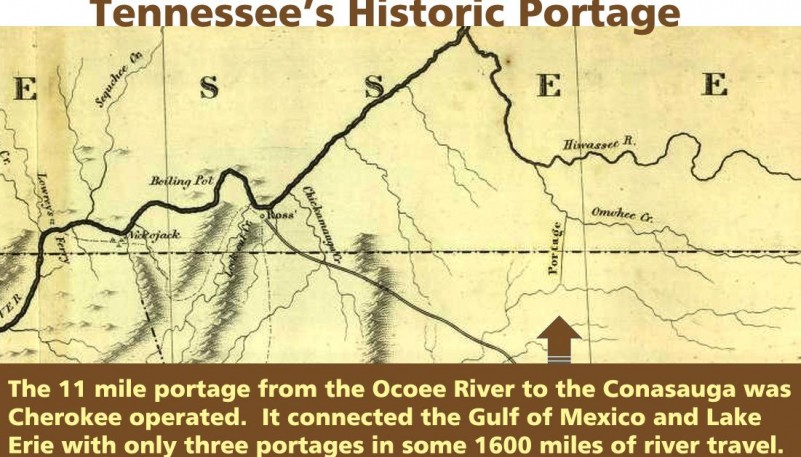
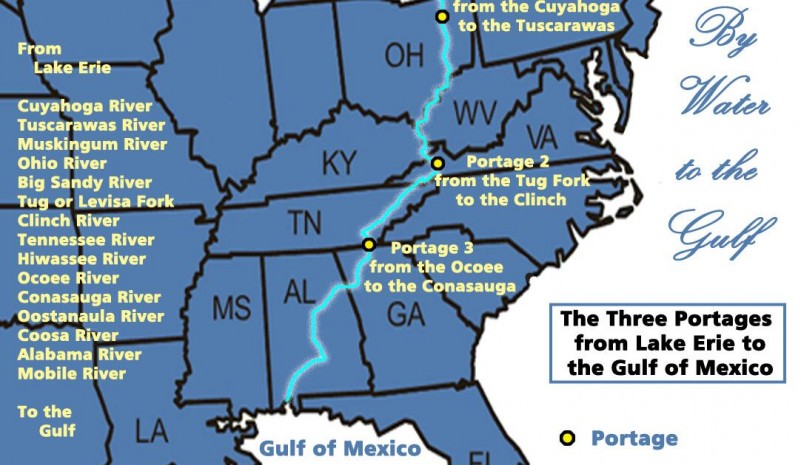
Famous boatyards near Benton, Tennessee and nearby Spring Place, Georgia were operated by the Cherokee Hildebrand and McNair families respectively. These were opposite ends of a portage of very long importance in eastern North America. The eleven mile canoe portage or, latter, a wagon transport portage, between the upper reaches of the Ocoee River in Tennessee and the Conasauga River in Georgia, provided one of the most significant “shortcuts” in the East.