Ministry by Walking Around and the Network of Seven Churches of Revelation
Ministry by Walking Around and the Network of Seven Churches of Revelation
Although the Book of Revelation has been vastly studied and interpreted throughout church history, usually the focus is on one major issue within the text, namely, the role and future of the church. The main reason for this has been the in-depth prophetic and pastoral messages to the Seven Churches.
The value of the messages to the Seven Churches of Revelation is constituted by the fact that they are the last recorded Biblical messages to the Christian Church.[1] The letters to the Seven Churches obviously do not contain all of the usual elements used in the New Testament epistolary form. It is generally accepted that they were written as an application of the Revelation context and not as individual messages to the churches.
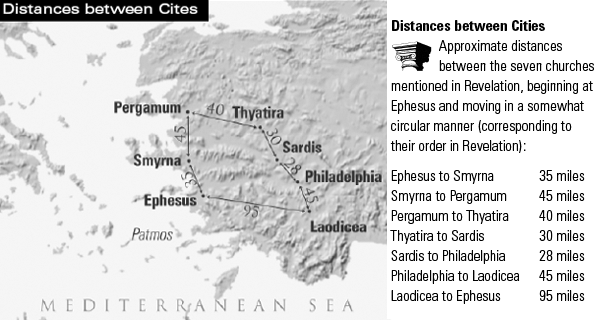
This contextual connection between the seven letters suggests a network of inter-church communication which was established between the seven churches. Several common elements are obvious from the text, the most obvious is their common geographical location as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Distances between the Seven Cities of Revelation
The addressed churches are located clockwise, almost like they are forming a strategic circle of ministry.[2] Most churches are located thirty to forty miles from one another, which perhaps was the possible daily limit for traveling during that time. The shape of the circle of ministry, based on the order in which the churches were addressed, suggests a method of managing known today as Management by Walking Around (MBWA). The example in Revelation not only presupposes such methodology, but purposefully gives its clockwise direction in relation to the location of origin of the letters from the Island of Pathmos.
The purposeful positioning of the churches provided a common network (circle of ministry). It is also obvious from the text that at the time of writing, simplicity and democracy in organization were characteristics of the New Testament church government.[3] In the context of networking, each church maintained its own individuality because it is addressed separately in the text.[4]
Furthermore, the seven churches shared a common context of ministry in the area of Asia Minor which consisted of a great mixture of languages, customs and religions. All of the seven churches were located in cities which were under Roman rule and combined the customs of Roman, Greek, Assyrian, Persian, Babylonian, Egyptian and Jewish cultures as well as the various languages and dialects within them. The commonality in the context of ministry continued with the presence of numerous religious groups, cults, sects and gilds which were closely interwoven with civil affairs. Universal citizenship, universal religion, and a universal church were all ideas for which the Roman Empire was beginning to prepare. In such context, the seven churches shared a common goal of ministry, namely, spreading the Christian message.[5]
The seven letters were inspired by one occasion and one purpose as a tool for inter-church networking.[6] The message was not sporadic or spontaneous but thoughtfully planned and designed for each of the churches, based on an in-depth knowledge of the individual problems, members and solutions for future development.[7] The text demonstrates a common structure within the church illustrated by the common structure shared by each message. The letters reveal that the congregations shared similar practices of worship, ministry and teaching which were accompanied by problems and persecution.
A significant part of the common structure was the leadership because each church had a divinely-appointed messenger,[8] addressed by a common “divinely-charged”[9] network elder, who received a transmitted divine message. Such process shows that the networking was done by means of communication, of which the epistolary form is also proof.[10] The written text was only a formal documentary or a contract of the holistic communication accomplished through various multimedia means including those that relied on audio, visual and other senses. It constructed a mystical, divinely-inspired, supernatural and non-virtual reality which transformed the recipient of the message in the same way it did the messenger. Through this means, the network communication was not a miscommunication, but rather an authentic translation from the divine source to the very members of the congregations.
This form of communication was absolutely necessary for the common context of ministry in which the seven churches operated. This common context was the earth, not heaven,[11] and their common goal was to conquer.[12] Yet, at the same time the text is undisputable in that each church contained people prepared to conquer. This fact makes the victory of the church inevitable. Thus, while the churches are dealing with various problems and persecutions, they are already conquerors.
This observation brings the reader to the final commonality which the seven churches share; namely, that besides the earthly network of ministry there is another greater, divine, heavenly network which is in control. Such a conclusion is obvious from the fact that all of the churches without exception are known to the sender of the messages.[13] Their problems are relevant, criticism and encouragement which are prophetically delivered solutions are divinely provided and conquest of the church over the problems is definite and inevitable. This is undisputable proof that a God-centered New Testament networking of churches is the dependable and enduring model for both ministry networking and church government. Precisely this heavenly network is the supernatural source of the unique approach through which problems of the churches are to be solved. Thus, in addition to a common present reality, the churches share a future earthly applicability of the paradigm of ministry which makes their message relevant today.[14]
[1] Wade H. Horton, Lectures on the Seven Churches (Cleveland: Pentecostal Resource Center, n/a), 6.
[2] Henry M. Morris, The Revelation Recorded (Wheaton: Tyndale House Publishers, 1987), 66. Merril Tenney, Interpreting Revelation (Grand Rapids: Wm. B. Eerdmans Pubslihing Co., 1957), 50. For an in-depth discussion on the geographical location of the Seven Churches, its significance for the circulation of the letters and the leadership organization see William M. Ramsey, The Letters to the Seven Churches (Grand Rapids: Baker book House, 1979), 186.
[3] McDowell, 38.
[4] McDowell, 37.
[5] Ramsey, 120-21.
[6] Ramsey, 40.
[7] Ramsey, 39-40.
[8] Bruce M. Metzger, Breaking the Code (Nashville: Abingdon Press, 1993), 30. Ramsey, 69, 74ff.
[9] Ramsey, 80.
[10] McDowell, 37.
[11] Metzger, 29.
[12] Metzger, 30.
[13] Wade Horton, Seven Golden Candlesticks (Cleveland: Pathway Press, 1974), 72.
[14] Edward A. McDowell, The Meaning and Message of the Book of Revelation (Nashville: Broadman Press, 1951), 35. Clovis G. Chappell, Sermons from Revelation (New York: Abingdon-Cokesbury Press, n/a), 59.
First Day of School in Bulgaria
Bulgarian Churches Protest against new Child Protection Policy
Several of our students who graduated from our chaplaincy program in Bulgaria about a decade ago, are among the lead organizers of a massive international wave of protests against a new package of child protection laws similar to Norway’s Barnevernet concept. The start is given in Sofia, Capital city of Bulgaria, where people are very unhappy about a new ideological concept of child protection policy which infringes upon the rights of the parents and the integrity of natural family. The protest will be organized through the whole month of September 2019 in many cities of Bulgaria and in other cities throughout the world with many parents turned into grassroots pro-family activists.
The new legal provisions in Bulgaria
Thus, according to the new laws, Bulgarian activists say that:
- multidisciplinary teams (police, social workers, psychologists) will be able to enter people’s homes without a court order and remove children even based on anonymous calls saying the child is neglected or abused
- then the child is placed into foster care via administrative procedure until brought to court, which can take months and in some cases years
- from then onwards, under certain conditions of the law and through non-governmental organizations, the removed child can be adopted by people from all over the world
- after international adoption, the biological family will never see that child again (personal data such as personal ID number, certificate of birth will be changed).
Our information is that Romanian law also includes some similar provisions, but there is still little institutional capacity to implement them. NGOs are already involved in social services and even adoptions in Romania, only that this is little known to the public.
The new concept and ideology was heavily promoted in Bulgaria through Norwegian grants and that is why in some cities the protests will be held in the front of Norway’s embassies and consulates.
„We are worried that Norways has heavily invested in Bulgaria. Our politicians are ready to sell our country’s children. We are a small country, we shall never be England or Germany, so we shall never have their standards of living. And yet they are already removing Bulgarian children from their families based on the reason of poverty. And the Social Services Law adopted in March 2019 will be in force starting from January 1st, 2020”, state the organizers.
Protests are taking place in September in Bulgaria, Germany, Poland, Italy, Canada, Austria, Ireland, Serbia, New Zeeland, Denmark, Lithuania, USA and even Norway.
It all started with a Child Strategy
In 2018, in Bulgaria, 152 NGOs were non-transparently financed outside the country to propose “The National Strategy for the Child 2019-2030”, under the slogan “All rights for all children”. It was forwarded to policy makers and decisional factors.
The strategy was based on the following presuppositions:
- all parents are incompetent and incapable and are potential abusers for their children (mentally and physically)
- only the state and NGOs have the right to decide regarding children and children will appropriately develop and thrive only under their expert care.
The strategy has the following characteristics:
- comprehensiveness of object (it targets all children at conception, no matter whether they are in a need, abandoned or injured, “the strategy targets the three stages of childhood, as a period of the entire human life cycle” – pregnancy and early childhood; childhood; teenage years).
- conflicts with the Bulgarian Constitution (Article 47): the “raising and upbringing of children“ is the “right and obligation of their parents,“ and the state’s role in this process is to assist them, not replace them.
- adopts the child-centered model (from the third protocol of the UN Convention, which has NOT been ratified by Bulgaria) – authorizing the child, regardless of the age and maturity, to make decisions and receive social services and counseling without PARENTAL CONSENT.
- defines the child as a separate entity, with separate rights, which is contrary to Bulgarian law, ignoring terms such as: minor, juvenile, parent, guardian/custodian, etc.
After a national protest in 30 Bulgarian cities, on May 11, 2019, Bulgaria’s Prime Minister stated: “There will be no Strategy, I will order the Minister of Labor and Social Policy to reiterate in the morning, lunchtime and evening at the briefing that there is no Strategy for the Children”.
Despite his words, the ideas embedded in the supposedly annulled Strategy are being passed as laws and regulations, changes and amendments that are even contrary to the Bulgarian Supreme Law and also contradict AIN principles enshrined in the European Convention on Human Rights. The ideas in the spirit of the Strategy were pushed into changes in 28 laws (starting with the Child Protection Act) and a passing of a whole new law – the Social Services Act.
Working for the benefit of various non-governmental organizations that promote gender ideology and sexual education, the Law on Social Services was adopted in March 2019 effective January 1, 2020.
„With this law, we have the complete abdication of the state, which openly admits that it is incapable of fulfilling its purpose. The social functions of the state are transferred to private organizations, often international ones (and there is no clear requirement for them to be licensed in Bulgaria). Moreover, every child is their target, not just children in need… The law is working for the benefit of various non-governmental organizations promoting gender ideologies as well as early sexual education.”
Bulgarian activists have now reached over 175,000 concerned citizens, both Bulgarians and foreigners living in Bulgaria. There have been numerous information campaigns and protests in over 30 cities across the nation, which have, unfortunately, been widely ignored by the media and politicians alike.
The Strategy and the new approach to Social and Child Services are based on the Norwegian Model and heavily funded by Norway and its grant mechanism. In the name of “the rights of the child,” politicians, lawmakers and NGOs are busy working to undermine what Bulgarians hold dear: the traditional family and the role of the parents.
Toward a Pentecostal Strategy for the City
Toward a Pentecostal Strategy for the City
One of the questions that seems to come up in this course discussion is how to change the world around us with a more positive and effective approach toward using the Gospel of Salvation. In this particular module, the difficulty addressed is ethnocentricity. The particularity of our search then arrives at the more detailed question, how can we change the culture (respectively subcultures) of our church congregations? This is a drastic move from a closed circle toward an outreach community that many congregations are unable to accomplish. How do we then empower such congregations to be transformed into cultural reach-outs to a single ethnos or multiple ethnic groups?
Problem
The problem in the first quarter of the 21st century has been incongruity of our church strategy with the times we live in and the mindset they occupy. We’ve been preparing the church for the multicultural battle, all and while we should have been equipping the saints how to rebuild the walls since the battle has been lost.
We’ve been equipping leaders for the ministry while the church ship has been sinking only to end up with well trained captains of a sunken fleet. And in a doomed attempt to reconcile the reality of the ministry with their training, they have turned to wave walkers who briefly surface for breaths of fresh air during Sunday worship only to return to the deep blue walk of their daily ministry never finding their lost piece of eight.
For the battle was lost long ago before the present generation of ministers ever came to existence. They know not the battle. They’ve only seen the ruins that were left within the broken walls of the church. And they have been struggling to reconcile the incomputable of what church eldership has been teaching them to battle against with the Nehemiah calling for restoration, which God has placed upon them. For the answer has never been in building a New Jerusalem for a fresh start, but restoring the old Jerusalem and its former glory to a new state that reclaims our history and heritage.
Context
Recent analysis of migrant churches in the United States reveals that the predominant majority of them are located in cities which have a high influxation and concentration of immigrants. Such localities are called “gateway cities”. Immigrants typically enter the United States through one of these cities and settle there. These areas contain over half of the foreign-born population in the United States as follows:
- New York, NY – Foreign born population 18.7%
- Los Angeles, CA – Foreign born population 27.1%
- Houston, TX – Foreign born population 12.3%
- Washington, DC – Foreign born population 8.6%
- Miami, FL – Foreign born population 33.6%
- Chicago, IL – Foreign born population 11.1%
- San Francisco, CA – Foreign born population 20.0%
Strategy
Asking the right questions is important, but the answers cannot be generic for all ethnic groups or cultural settings. There is a strong need to be flexible and observe changes in culture, but not to change the message of the Gospel or compromise our witness. Several common things are noted in any cultural setting where our ministry is involved:
First and foremost, people of all cultures prefer to be personal with a purpose, rather than being project driven. No one longs to be part of someone else’s project. Yet, our very existence demands personal purpose, which could serve as a great cultural catalyst in a church ministry.
Secondly, cross cultural ministry is not done merely on relationships, but on being real in the relationships. The greatest halt of ministry work is when people realize the relationship with the church has not been a real one, but merely a part of a program or a paradigm.
Finally, our cross cultural model for ministry should not be just salvation oriented, but soul oriented. There is a great difference between writing down the number of saved every Sunday and actually caring for the eternal well-being of the saved souls. In fact, this is so fundamentally determinative that it should be the goal in mind of every new church plant.
The ORIGINAL Barney Creek Stones of Spurling
Even though not intending to form a new church or denomination, their rejection of Landmarkist values placed them in conflict with traditional churches in that area. Within a short period of time it became clear that they would not be allowed to remain as members of their churches. On August 19, 1886, after being barred from his local Baptist church, he and eight others organized the Christian Union at the Barney Creek Meeting House in Monroe County, Tennessee. They agreed to free themselves from man-made creeds and unite upon the principles of the New Testament. Between 1889 and 1895, Spurling organized three other congregations, all with the name Christian Union and functioning independently under Baptist polity. While this group would later disband and its members return to their original churches, the Church of God traces its origins to this 1886 meeting.
THE COMMITMENT to follow a biblical pattern of Church government has shaped the Church of God from our founding in 1886. R.G. Spurling called for Christian Union members to “take the New Testament, or law of Christ, as your only rule of faith and practice.” His invitation was to give “each other equal rights and privilege to read and interpret for yourselves as your conscience may dictate” and to sit “together as the Church of God to transact business [as] the same…” (Tomlinson, Last Great Conflict, pp. 185-86).
Birchland Ocoee Farms Offers Hub for Local Economy
Birchland Ocoee Farms, home of popular River Maze is located at 1371 US-64 in Benton, TN on the banks of the Ocoee, “where the river flows, and memories grow!” It is a family farm of four generations that is owned and operated by Joe and Dianne Fetzer. Opening day is September 21st when the Farm will host the annual Dinner by the River, a community event that showcases food that is produced by local farmers and businesses.
Among those that will participate in Dinner by the River this year are Appalachian Bee owned by Diane Raven in Ocoee, Apple Valley Orchard operated by Chuck McSpadden in Cleveland, Trew Organic Farms, owned by Bill Trew of Ocoee, Sandy Hood’s Pick-Your-Own Blueberry Patch of Benton, Blackberry Hills Bakery owned by Barbara Leonard of Old Fort, Lamon Farms owned by Randall Lamon of Cleveland, Hoe Hop Valley Farm operated by Walter and Candyce Bates of Parksville, Cookson Creek Farm in Ocoee operated by Clarence and Debbie Hair, The Rafting Goat owned by Mack Haynes of Old Fort, Sannie Mae’s Heirloom Foods of Benton, Rowe Family Farms, and Birchland Ocoee Farms. The dessert makers and event planners are Elois Ledford and Kayla Green from Bakery on Main of Benton. The chefs are Kevin and Dana Caylor of The Crepe Outdoors. Inspired by Olivia Weatherford, a portion of the proceeds go to St. Jude’s Research on Neuroblastoma and there will be a silent auction to benefit, “LIV – In The Journey”.
Opening day for Birchland Ocoee Farms’ Corn Maze is set for September 28th when J103 will be onsite. This year marks their 15th Annual Corn Maze with the theme “Trek Thru Truth in Tennessee,” the theme of their first maze in 2005. The 2019 Soybean Maze will feature Ott, the hardworking little tractor based on a story written by Jack Higgins, a member of the Polk County Hall of Fame. Other farm activities at The River Maze include: Pumpkin Patch, Hayrides, Cow Train, Corn Cannons, “Spookey Maze”, “Farm Chores Frenzy,” Barnyard Basketball and Football, Flume Zoom and Team Building activities.
Music on The River, a fundraiser to benefit all Polk County Public Libraries will also be held at Birchland Ocoee Farms. This event will take place October 3rd at 6:00 pm. It will feature dinner, live music from local musicians and silent auction. Tickets can be purchased at West Polk Public Library in Benton. On Sunday October 13th Savannah Renfro Photography will be having a Pumpkin Patch Mini Photo Shoot Sessions. You can contact Savannah to reserve your spot today at (423) 715-9983.
For more information about hours of operation and special events that Birchland Ocoee Farms offers, you may text or call us at (423) 650-0710 or 423-650-7224. You may also email them: [email protected] or [email protected]. This Fall, let’s all show our support of the local economy.
VBS for Adults
For reasons obvious to most of our readers, I was able to attend no less than 10 (ten) VBS/Kids crusades this summer. Seven Baptist, several Pentecostals and a Methodist one.
The themes ranged from jungle journey and the Lion King to giddy up cowboys and cowgirls and world/planet/time travelling. All cool themes with lots of props and much careful preparation all in the name of bringing the Good News to the little ones. A noble cause truly worthy of any expense and labor for any church out there.
Time and length ranged from one whole day or one evening service to three nights and even several week long ones. For most of it, the ones held in most Baptist churches were designed by LifeWay and were well structured with kids constantly moving from station to station. The rest were somewhat free style, but still designed with the expectation of lots of children attending. In between each module there was candy, snacks or even a full blown supper.
The location of each VBS and the way it was designed for the crowd flow made the initial impression important. Signs welcoming and directing newcomers were grate, but the friendliness of the people made up for less signage and more human touch. Registration was a must and parents’ preferences were not taken lightly. The decorations of each room helped the children adjust to the new setting and work through the set curriculum. And yes, lots of kids made lots of mess so cleanness in class rooms, play areas and bathrooms were tended to. Some churches had a designated team that made sure the facilities were clean for the next group. And where cleanness was not intentional, it was observed that many parents did not return with their children.
Most VBS programs were designed around age groups. Some included even classes for toddlers and several had adult classes too. The ones that did not, included a family night toward the end of the week for parents to attend. A family night was a great feature for parents who did not attend but dropped their kids every night and picked them up afterwards. They were addressed with materials and opportunities for a spiritual renewal.
The thematic VBSs progressed with learning daily and build up on the previous day. The groups of children toggled between Bible lesson, crafts, games and lots of music. Kids were greatly encouraged to participate and learn the songs and dancing, recite Bible verses and answer questions from the covered material. Some parents participated too.
Prayer was made a central focal point for most of the VBSs observed. The Baptists ones, especially, had pledges of allegiance at the start of the service and assembly with prayer toward the end. A memorable experience for all children who enjoy social setting, making new friends and learn the Bible.
Here are several take ways to observe for a VBS in your church:
- Prepare for lots of children – if you have it they will come
- Train your workers. Form teams for each task. Assign measurable goals to ensure smooth moving through the program
- Self designed VBS programs work as good as the paid ones, as long as designed with the children and families in mind
- Chose the length of the event carefully with regard of your constitutions. For the most of it, less is really more.
- Do not underestimate friendliness, cleanness and the safety of the children.
- Don’t miss a family day. Everyone likes hot dogs and water slides on a hot summer day.
This goes without saying, but focus on God – it is easy to lose track and purposes in the larger design of such events.
Bulgarian Orthodox Church deletes controversial opinion on National Strategy for the Child from website
A controversial opinion purported to be from the Bulgarian Orthodox Church’s Holy Synod urging a ban on terminations of pregnancy, for religion to be a compulsory subject in schools, no sex education, and opposing the full ban on corporal punishment in schools, has been deleted from the church’s official website.
The opinion, posted in response to the Bulgarian government’s draft National Strategy for the Child 2019-2030, had not been voted by the Holy Synod, nor approved by the church’s Patriarch Neofit, nor signed by the Metropolitans, Bulgarian National Television (BNT) reported.
It had been sent for posting on the website by Gavriil, the Metropolitan of Lovech, BNT said.
After it appeared on the website on February 8, the opinion – widely covered in the Bulgarian media – caused extensive negative reaction on social networks.
Specialist church news website Dveri said that the opinion had not been considered and approved by the Bulgarian Orthodox Church’s governing body, but was an initiative of the Synod’s cultural and educational department headed by Metropolitan Gavriil.
Dveri quoted a statement by Naum, the Metropolitan of Rousse, who said that the document had not been officially discussed by the Holy Synod.
“The ‘opinion’ binding the Bulgarian Orthodox Church Holy Synod as an institution was a project personally created by Ms Dessislava Panayotova, an associate of the cultural and education department of the Synodal office…that does not mean that the Holy Synod will accept it unhesitatingly and unambiguously,” Naum said.
“The Bulgarian Orthodox Church, as a nutritionist of Bulgarians and moral values in the Bulgarian family, always will promote ethical norms in education, but will not tolerate in any way violence against children, in whatever form, especially if it is linked to so-called ‘religious education and training’,” he said.
Issues related to termination of pregnancy and children at risk are issues for future profound reflection in Bulgarian society “addressing appropriate reflections on God’s will, the dignity of the mother, as well as the significance of each specific case, related to domestic violence and violence specifically against women,” Naum’s statement said.
“All other topics concerning the education and upbringing of Bulgarian children should be discussed by relevant educators and specialists, who also have the view of theological science, thus defining the most accurate and correct approach for future recommendations on the issues raised,” the statement said.
Global Network of Bulgarian Evangelical Churches outside of Bulgaria (2019 Report)
 Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in the European Union (2019)
Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in the European Union (2019)
- Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in Germany
- Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in Spain
- Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in England
- Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in France
- Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in Belgium
- Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in Italy
- Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in Cyprus
- Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in Crete
Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in America (2019 Report)
- Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in Chicago (2019 Report)
- Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in Texas (2019 Report)
- Bulgarian Evangelical Churches – West Coast (2019 Report)
- Atlanta (active since 1996)
- Los Angeles (occasional/outreach of the Foursquare Church – Mission Hills, CA)
- Las Vegas (outreach of the Foursquare Church – http://lasvegaschurch.tv)
- San Francisco (occasional/inactive since 2012, Berkeley University/Concord, CA)
Bulgarian Evangelical Churches in Canada (2019 Report)
- Toronto (inactive since 2007)
- Toronto/Slavic (active since 2009)
- Montreal (occasional/inactive since 2012)
CURRENTLY INACTIVE CHURCHES/CONGREGATIONS:
- New York, NY (currently inactive)
- Buffalo, NY (occasional/inactive)
- Jacksonville, FL (occasional/inactive since 2014)
- Ft. Lauderdale / Miami (currently inactive)
- Washington State, Seattle area (currently inactive)
- Minneapolis, MN (occasional/inactive since 2015)
READ MORE:
- First Bulgarian Church in Chicago Opened in 1907
- Gateway Cities for Bulgarian Evangelical Churches
- How to Start a Bulgarian Church in America from A-to-Z
- Unrealized Spiritual Harvest as a Paradigm for Cross-Cultural Ministries among Migrant and Disfranchised Ethnic Groups in America Today
Bulgarian Pentecostal riddle…
Five kings with five crowns
Four bishops and castle in the middle
Who will blow the whistle
and who will play the fiddle?
A Bulgarian Pentecostal riddle…