The Forgotten Azusa Street Mission: The Place where the First Pentecostals Met
For years, the building on Azusa Street has also been an enigma. Most people are familiar with the same three or four photographs that have been published and republished through the years. They show a rectangular, boxy, wood frame structure that was 40 feet by 60 feet and desperately in need of repair. Seymour began his meetings in the Mission on April 15, 1906. A work crew set up a pulpit made from a wooden box used for shipping shoes from the manufacturer to stores. The pulpit sat in the center of the room. A piece of cotton cloth covered its top. Osterberg built an altar with donated lumber that ran between two chairs. Space was left open for seekers. Bartleman sketched seating as nothing more than a few long planks set on nail kegs and a ragtag collection of old chairs.
What the new sources have revealed about the Mission, however, is fascinating. The people worshiped on the ground level — a dirt floor, on which straw and sawdust were scattered. The walls were never finished, but the people whitewashed the rough-cut lumber. Near the door hung a mailbox into which tithes and offerings were placed since they did not take offerings at the Mission. A sign greeted visitors with vivid green letters. It read “Mene, Mene, Tekel, Upharsin” (Daniel 5:25, kjv), with its Ns written backwards and its Ss upside down. Men hung their hats on exposed overhead rafters where a single row of incandescent lights ran the length of the room.
These sources also reveal that the atmosphere within this crude building — without insulation or air conditioning, and teeming with perspiring bodies — was rank at best. As one writer put it, “It was necessary to stick one’s nose under the benches to get a breath of air.”
Several announced that the meetings were plagued by flies. “Swarms of flies,” wrote one reporter, “attracted by the vitiated atmosphere, buzzed throughout the room, and it was a continual fight for protection.”
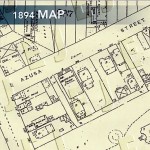
A series of maps drawn by the Sanborn Insurance Company give a clear picture of the neighborhood. The 1888 map discloses that Azusa Street was originally Old Second Street. The street was never more than one block in length. It ended at a street paving company with piles of coal, along with heavy equipment. A small house, marked on the map by a “D” for domicile, sat on the front of the property with the address of 87. (See highlighted section.) A marble works business specializing in tombstones stood on the southeast corner of Azusa Street and San Pedro. Orange and grapefruit orchards surrounded the property. On the right of the map a Southern Pacific railroad spur is clearly visible. The City Directory indicates that the neighborhood was predominantly Jewish, though other names were mixed among them.
A second map of the property was published in 1894. Old Second Street had become Azusa Street, and the address had been changed to 312. The house had been moved further back on the property where it served as a parsonage. The dominant building at 312 Azusa Street was the Stevens African Methodist Episcopal Church. At the front of the building a series of tiny parallel lines on the map mark a staircase that stood at the north end of the building providing entry to the second floor, the original sanctuary.
The only known photograph of the church from this period shows three interesting features. First, it shows the original staircase. Second, and less obvious, the original roofline had a steep pitch. Third, three gothic style windows with tracery lines adorned the front wall.
By 1894, the citrus groves had largely disappeared. On the southern side they were replaced by lawn. The smell of orange blossoms and the serenity of the orchard were rapidly being replaced by the banging of railroad cars and the smell of new lumber. A growing number of boarding houses and small businesses, including canneries and laundries, were moving into the immediate area by this time. The property marked “YARD” on the map is the beginning of the lumberyard that soon came to dominate the area. The City Directory reveals fewer Jewish names, and more racial and ethnic diversity in the neighborhood, including African Americans, Germans, Scandinavians, and Japanese.
Stevens AME Church occupied the building at 312 Azusa Street until February 1904 when the congregation dedicated a new brick facility at the corner of 8th and Towne and changed their name to First AME Church. Before the congregation could decide what to do with the property on Azusa Street, however, an arsonist set the vacant church building on fire. The structure was greatly weakened, and the roof was completely destroyed. The congregation decided to turn the building into a tenement house. They subdivided the former second-floor sanctuary into several rooms separated by a long hallway that ran the length of the building. The stairs were removed from the front of the building and a rear stairwell was constructed, leaving the original entry hanging in space. The lower level was used to house horses and to store building supplies, including lumber and nails.
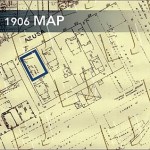
In 1906, a new Sanborn Map was published. (See 1906 map.) The building was marked with the words “Lodgings 2nd, Hall 1st, CHEAP.” The transition of the neighborhood had continued. The marble work still occupied the southeast corner of Azusa Street and San Pedro, but a livery and feed supply store now dominated the northeast corner. A growing lumberyard to the south and east of the property now replaced the once sprawling lawn. A Southern Pacific railroad spur curved through the lumberyard to service this business.
The Apostolic Faith, the newspaper of the Azusa Street Mission between September 1906 and June 1908, later referred to the nearby Russian community. Many of these recent immigrants were employed in the lumberyard. They were not Russian Orthodox Christians as one might guess; they were Molokans — “Milk drinkers.” This group had been influenced by some of the 16th-century Reformers. They did not accept the dairy fasts of the Orthodox Church. They were Trinitarians who strongly believed in the ongoing guidance of the Holy Spirit. Demos Shakarian, grandfather of the founder of Full Gospel Business Men’s International, was among these immigrants who were led to Los Angeles through a prophetic word given in 1855.
Henry McGowan, later an Assemblies of God pastor in Pasadena, was a member of the Holiness Church at the time. He was employed as a teamster. He timed his arrival at the nearby lumberyard so he could visit the Mission during its afternoon services.
This map suggests why some viewed the Mission as being in a slum. A better description would be an area of developing light industry.
In April 1906, when the people who had been meeting at the house at 214 North Bonnie Brae Street were forced to move, they found the building at 312 Azusa Street was for sale. The photograph below taken about the time that the congregation chose to move into the building shows the “For Sale” sign posted high on the east wall of the building, as well as the rear of the tombstone shop. Seymour, pastor of the Azusa Street Mission, and a few trusted friends met with the pastor of First AME Church and negotiated a lease for $8 a month.
An early photograph reveals what the 1906 version of the map indicates. The pitched roof had not been replaced. The building had a flat roof. The staircase that had stood at the front of the building had been removed.
In a sense, this building suited the Azusa Street faithful. They were not accustomed to luxury. They were willing to meet in the stable portion of the building. The upstairs could be used for prayer rooms, church offices, and a home for Pastor Seymour.
Articles of incorporation were filed with the state of California on March 9, 1907, and amended May 19, 1914. The church negotiated the purchase of the property for $15,000 with $4,000 down. It was given the necessary cash to retire the mortgage in 1908. The sale was recorded by the County of Los Angeles on April 12, 1908.
The Forgotten Azusa Street Mission: The Place where the First Pentecostals Met
For years, the building on Azusa Street has also been an enigma. Most people are familiar with the same three or four photographs that have been published and republished through the years. They show a rectangular, boxy, wood frame structure that was 40 feet by 60 feet and desperately in need of repair. Seymour began his meetings in the Mission on April 15, 1906. A work crew set up a pulpit made from a wooden box used for shipping shoes from the manufacturer to stores. The pulpit sat in the center of the room. A piece of cotton cloth covered its top. Osterberg built an altar with donated lumber that ran between two chairs. Space was left open for seekers. Bartleman sketched seating as nothing more than a few long planks set on nail kegs and a ragtag collection of old chairs.
What the new sources have revealed about the Mission, however, is fascinating. The people worshiped on the ground level — a dirt floor, on which straw and sawdust were scattered. The walls were never finished, but the people whitewashed the rough-cut lumber. Near the door hung a mailbox into which tithes and offerings were placed since they did not take offerings at the Mission. A sign greeted visitors with vivid green letters. It read “Mene, Mene, Tekel, Upharsin” (Daniel 5:25, kjv), with its Ns written backwards and its Ss upside down. Men hung their hats on exposed overhead rafters where a single row of incandescent lights ran the length of the room.
These sources also reveal that the atmosphere within this crude building — without insulation or air conditioning, and teeming with perspiring bodies — was rank at best. As one writer put it, “It was necessary to stick one’s nose under the benches to get a breath of air.”
Several announced that the meetings were plagued by flies. “Swarms of flies,” wrote one reporter, “attracted by the vitiated atmosphere, buzzed throughout the room, and it was a continual fight for protection.”
A series of maps drawn by the Sanborn Insurance Company give a clear picture of the neighborhood. The 1888 map discloses that Azusa Street was originally Old Second Street. The street was never more than one block in length. It ended at a street paving company with piles of coal, along with heavy equipment. A small house, marked on the map by a “D” for domicile, sat on the front of the property with the address of 87. (See highlighted section.) A marble works business specializing in tombstones stood on the southeast corner of Azusa Street and San Pedro. Orange and grapefruit orchards surrounded the property. On the right of the map a Southern Pacific railroad spur is clearly visible. The City Directory indicates that the neighborhood was predominantly Jewish, though other names were mixed among them.
A second map of the property was published in 1894. Old Second Street had become Azusa Street, and the address had been changed to 312. The house had been moved further back on the property where it served as a parsonage. The dominant building at 312 Azusa Street was the Stevens African Methodist Episcopal Church. At the front of the building a series of tiny parallel lines on the map mark a staircase that stood at the north end of the building providing entry to the second floor, the original sanctuary.
The only known photograph of the church from this period shows three interesting features. First, it shows the original staircase. Second, and less obvious, the original roofline had a steep pitch. Third, three gothic style windows with tracery lines adorned the front wall.
By 1894, the citrus groves had largely disappeared. On the southern side they were replaced by lawn. The smell of orange blossoms and the serenity of the orchard were rapidly being replaced by the banging of railroad cars and the smell of new lumber. A growing number of boarding houses and small businesses, including canneries and laundries, were moving into the immediate area by this time. The property marked “YARD” on the map is the beginning of the lumberyard that soon came to dominate the area. The City Directory reveals fewer Jewish names, and more racial and ethnic diversity in the neighborhood, including African Americans, Germans, Scandinavians, and Japanese.
Stevens AME Church occupied the building at 312 Azusa Street until February 1904 when the congregation dedicated a new brick facility at the corner of 8th and Towne and changed their name to First AME Church. Before the congregation could decide what to do with the property on Azusa Street, however, an arsonist set the vacant church building on fire. The structure was greatly weakened, and the roof was completely destroyed. The congregation decided to turn the building into a tenement house. They subdivided the former second-floor sanctuary into several rooms separated by a long hallway that ran the length of the building. The stairs were removed from the front of the building and a rear stairwell was constructed, leaving the original entry hanging in space. The lower level was used to house horses and to store building supplies, including lumber and nails.
In 1906, a new Sanborn Map was published. (See 1906 map.) The building was marked with the words “Lodgings 2nd, Hall 1st, CHEAP.” The transition of the neighborhood had continued. The marble work still occupied the southeast corner of Azusa Street and San Pedro, but a livery and feed supply store now dominated the northeast corner. A growing lumberyard to the south and east of the property now replaced the once sprawling lawn. A Southern Pacific railroad spur curved through the lumberyard to service this business.
The Apostolic Faith, the newspaper of the Azusa Street Mission between September 1906 and June 1908, later referred to the nearby Russian community. Many of these recent immigrants were employed in the lumberyard. They were not Russian Orthodox Christians as one might guess; they were Molokans — “Milk drinkers.” This group had been influenced by some of the 16th-century Reformers. They did not accept the dairy fasts of the Orthodox Church. They were Trinitarians who strongly believed in the ongoing guidance of the Holy Spirit. Demos Shakarian, grandfather of the founder of Full Gospel Business Men’s International, was among these immigrants who were led to Los Angeles through a prophetic word given in 1855.
Henry McGowan, later an Assemblies of God pastor in Pasadena, was a member of the Holiness Church at the time. He was employed as a teamster. He timed his arrival at the nearby lumberyard so he could visit the Mission during its afternoon services.
This map suggests why some viewed the Mission as being in a slum. A better description would be an area of developing light industry.
In April 1906, when the people who had been meeting at the house at 214 North Bonnie Brae Street were forced to move, they found the building at 312 Azusa Street was for sale. The photograph below taken about the time that the congregation chose to move into the building shows the “For Sale” sign posted high on the east wall of the building, as well as the rear of the tombstone shop. Seymour, pastor of the Azusa Street Mission, and a few trusted friends met with the pastor of First AME Church and negotiated a lease for $8 a month.
An early photograph reveals what the 1906 version of the map indicates. The pitched roof had not been replaced. The building had a flat roof. The staircase that had stood at the front of the building had been removed.
In a sense, this building suited the Azusa Street faithful. They were not accustomed to luxury. They were willing to meet in the stable portion of the building. The upstairs could be used for prayer rooms, church offices, and a home for Pastor Seymour.
Articles of incorporation were filed with the state of California on March 9, 1907, and amended May 19, 1914. The church negotiated the purchase of the property for $15,000 with $4,000 down. It was given the necessary cash to retire the mortgage in 1908. The sale was recorded by the County of Los Angeles on April 12, 1908.
When East Met West
 Fear not: for I am with thee: I will bring thy seed from the east, and gather thee from the west. (Isaiah 43:5, KJV)
Fear not: for I am with thee: I will bring thy seed from the east, and gather thee from the west. (Isaiah 43:5, KJV)
And I say unto you, that many shall come from the east and west, and shall sit down with Abraham, and Isaac, and Jacob, in the kingdom of heaven. (Matthew 8:11, KJV)
God promised to gather His people from the East and the West in the last days. With the world’s present fragmentation, this prophecy can be fulfilled only through divine intervention. The miraculous initiation of God’s plan began with the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989.
With the collapse of the Berlin Wall, the Old Continent was introduced to a new set of opportunities and obstacles as the vision of a unified Europe quickly materialized. The clashing of two sociopolitical extremes, kept apart for half a century created a host of pressing dilemmas. In the midst of economical, political, social, cultural and simply human diversities, religion played a central role throughout the process that culminated in the emergence of the European Union. The religious reformative processes within Europe were not foreign to Bulgaria, a small post-Communist country located in the corner of Europe, the place where the East and the West, Europe and the Orient, Christianity and Islam have met for centuries.
After the exodus from Communism, the Bulgarian church quickly found itself unprepared for the role of religious frontier. The Orthodox majority, historically striving for symphony between church and state, remained insecure and drained from its symbiotic half-century existence with the Communist Regime. This condition quickly resulted in ongoing series of internal struggles and splits.
At the same time, the Protestant movement retained strength in some of its most powerful communities through the existence of underground churches. As freedom presented opportunity, Protestantism quickly spread. Pentecostal wings, represented by main stream denominations like the Church of God, the Assemblies of God and some newly found independent charismatic formations were primarily responsible for the rapid growth. While Orthodoxy remained a significant majority fide nomine tenus and the Catholic Church retained membership of 70,000, the Pentecostal revival which swept Bulgaria from 1989 to 1995 claimed over 100,000 new believers.
Unfortunately, the first steps toward freedom were sporadic and unplanned. The rapid growth could not compensate the lack of training and leadership, which the Protestant communities experienced under Communism. Global fast-paced change swept Eastern Europe, catching the Bulgarian church unprepared. The Protestant movement was unable to become a direct beneficiary of the freedom which it had long prophesied and fervently expected. The incapacity of the Protestant movement contributed to a preposterous preponderance of apathy in every area of church life:
1. Leadership: During the Communist Regime, the Protestant churches were constantly bombarded with direct denial of their independent existence as free religious communities. Insufficient leadership training created numerous deficiencies including inadequate knowledge of church governing procedures, low levels of personal and corporate accountability and ignorance of the church’s political and social roles. After the fall of the Wall, these crises in leadership quickly produced congregational splits and added to the confusion generated by the socio-economical struggles in the young Bulgarian democracy.
2. Religious freedom: State control and direct interference in church business continued even after 1989 through a government agency called Directorate of Religious Affairs. The agency could not provide the intended balance between church and state due to its default state ties. Its bureaucratic management style and lack of experts on all of the represented religious groups facilitated the legislation of regulations and actions which have led to continuous tensions between the various religious groups. Many Bulgarian and international observers have noted that the present situation may have been orchestrated by the state to control the religious life in Bulgaria by creating a complete dependence on the Directorate of Religious Affairs.
3. Communication: During the regime, the underground church discouraged official administration and communication due to fear of persecution. In the era of freedom, this practice continued, limiting contact between church leadership and local congregation. Lack of communication resulted in the failure to relate reverence of protestant tradition to the younger generation.
4. Postmodernism: Due to a focus on political and economical issues, the church in Bulgaria and the Bulgarian culture never realized the speed with which the emerging postmodernism entered 21st Century Bulgaria. The introduced secularism maintained the atheistic trend used as social foundation by the Communist Regime. Within the church, postmodern supporters quickly produced complete denial of historical and theological progress, demoralization and discontinuity with Biblical holiness.
5. Theology: The unification of Europe opened doors for travel and immigration, which initiated a theological exchange for which the Bulgarian church was unprepared. Subconsciously and inescapably, foreign theology flooded the Bulgarian church without the test of time and experience.
Perhaps the above list may not seem that much different than the multitude of issues currently faced by Protestantism around the globe. However, the situation associated with the meeting of the East and West in Bulgaria is defined by a distinguishing feature – the mentality of the people. It is there that the political, economical and, not lastly, theological transformations must take place. Without such transformations, even liberated, the Bulgarian church remains underground in reality.
The meeting of East and West facilitated the unification campaign occurring in Europe. The push towards a unified Europe shaped the formation of religious freedom in Bulgaria as Bulgarian politicians quickly implemented a new law of religions to replace the 1945 Confessions Act composed and used by the Communist Regime. The new legal definition was an unsuccessful attempt to impose a governmental solution to the crises experienced by the Orthodox Church and other religious communities in Bulgaria. The results were disastrous. On July 21, 2004, in a preplanned action upon the Chief Prosecutor’s order, the police stormed through 250 churches, detaining clergies in controversial raid to restore proprietorship of the official Bulgarian Orthodox Church.
What has become obvious thus far is the fact that state, law or government are unable and should not attempt to dictate the existence or actions of the church which as a divinely established institution holds a predominate place above them. Neither constitution, nor human law, but the Bible alone must be the source for transformation and reconstruction of the Bulgarian Church. The Bulgarian Christians must reclaim their past as a persecuted church which knows from experience how to go through persecutions and survive. At the same time, the persecuted church must continue to ask the question, how is it possible for a church to preserve its Biblical identity without going through persecutions? It is from this quest for Biblical identity in postcommunist and postmodern context, that a theology of freedom will emerge to respond to the needs and demands of the Christian community in Eastern Europe.