7 NEW Barna Trends for Stronger Churches
Here are 7 insights drawn from the data that will help you be a more successful church leader.
1. Pastors have higher life satisfaction than most.
Surprised? Be encouraged.
- 9 in 10 pastors are satisfied with their quality of life.
- Pastors rate their emotional health and spiritual health higher than the general US population does.
- 96% of married pastors are satisfied with their relationships with their spouses.
- 97% rate their relationships with their children as excellent or good.
In the midst of ministry challenges and trials, pastors have personal satisfaction and strength that is higher than among the general US population.
Those statistics are mighty encouraging. Especially if you find yourself standing in the majority.
But what if you’re not satisfied with your life, your emotional and spiritual health, your marriage, or your relationship with your kids? Then what?
Pastors also relate a downside where they rank lower than the general population.
2. Inadequacy, exhaustion and depression harass pastors.
- Pastors are more likely to have feelings of inadequacy in their work (57% vs 30% of employed US adults).
- Pastors are more likely to feel mental or emotional exhaustion (75% vs 55%).
- Nearly half of pastors have struggled with depression.
- 47% struggle finding time to invest in their spiritual health.
But, wait.
How does high life satisfaction go together with feelings of inadequacy and exhaustion?
How can pastors have higher life satisfaction and higher job stress?
Maybe the answer is Jesus.
We love serving Jesus and spending our lives for him. But ministry has big challenges that we can’t fix in our own strength.
So it’s a both/and. Life is satisfying and life is difficult.
We love our calling. Sometimes we hate the work.
If you’re among the pastors who feel inadequate, exhausted, or depressed, you’ll be interested in this next insight from Barna.
3. Personal spiritual disciplines are central to ministry satisfaction and perseverance.
- Pastors who practice their top spiritual discipline (usually prayer) every day or more are also very satisfied with their vocation (75%), their current ministry (73%), and they rate low on spiritual or burnout risk.
- Conversely, those at high spiritual risk (54%) practice their primary spiritual discipline only a few times a month or less.
The Barna team concludes:
“If pastors and those who support them should take anything away from these findings, it’s that consistent spiritual practices matter – to vocational satisfaction and contentedness with one’s own ministry, as well as emotional, spiritual, and relational well-being.”
Your personal spiritual habits make all the difference in your ministry strength.
But you knew that, right? The people who discipled you have been telling you that for years. You say the same thing to the people you disciple. We talk about spiritual disciplines all the time.
But your strength comes in actually sitting down and spending time alone with Jesus.
Are you at risk?
Barna Trends 2018 has a risk metric for pastors. It assesses burnout risk, relational risk, and spiritual risk based on pastors’ answers to questions and their reported well-being.
It becomes a valuable self-assessment to see if you are in danger of relational, spiritual or burnout risk.

The more factors you check in any one section, the higher your risk. Generally you are at low risk if you don’t check any factors; medium risk if you check one or two; and high risk if you check three or more.
If you find yourself at medium or high risk, what steps can you take? Who can you talk with?
See more about it on the Barna website: https://www.barna.com/burnout-breakdown-barnas-risk-metric-pastors/.
Barna identifies one big cultural trend that explains why we struggle with our spiritual practices.
4. Spiritual practices are hindered by the lifestyle of busyness.
In the general US population:
- 1 in 7 US adults sets aside a day a week for Sabbath or rest.
- Only 1 in 5 take any real break from working.
- Just 12% commit to doing activities that recharge them and another 12% to taking a break from electronics.
Pete Scazzero, founder of New Life Fellowship Church in Queens, New York speaks about pastors’ busyness:
“The greatest roadblock [that keeps spiritual leaders from finding time to invest in their own spiritual growth], I believe, is a lack of good models. As evangelical leaders, we have inherited a history of activism that goes back more than 200 years. Our great gift is mission: mobilizing believers and leading people to Christ. But this great gift can also be a liability.”
“Spiritually indispensable concepts like silence, slowness, solitude, and being (instead of doing) are difficult for most of us who are heirs to evangelicalism’s activist impulse.”
No one is judging you, Pastor. It’s difficult to fit regular spiritual practices into your busy life. It’s hard for everyone.
And it’s also hard to fit in other practices that will help you flourish.
5. Growth practices are neglected.
Reading
- Almost half of the US population (45%) read at least 5 books per year. 18% of American didn’t read any books last year.
- One-fifth exceeded 15 books. (Mostly women and students.)
- 18% of men report reading less.
My goal this year is to read 20 books. I used to read 36 books a year. I’m part of the 18% of men who are reading less.
I’ve made a conscious choice to spend a half hour a day reading pertinent pastor-type blogs, like this one.
To focus my book-reading, I’m intentionally targeting my book choices. This year, I’ll read four classics of literature, four books on church growth, at least one theology book, at least one book on history, and ten others of my choice.
What is your reading goal for 2018? How is it going so far?
Conferences
- 3 in 10 pastors never attend a conference.
That’s surprising. I rely on a yearly conference for an infusion of inspiration and a new look at best practices to reach my city for Christ.
Here are some conferences that I recommend:
- Purpose Driven Church Conference – June 26-28, 2018
- The Global Leadership Summit – August 9-10, 2018
- Essential Church Conference – September 25-27, 2018
- Gateway Conference – October 1-2, 2018
- Outreach Summit 2018 – October 3-5, 2018
For more conference options, google “Church Conferences 2018” and you’ll find multiple articles with lists of good conferences.
Make this an action item and get your 2018 conference scheduled this month.
6. A healthy pastor and a healthy leadership team correlate to a growing church.
- Difficult relationships with the church’s board correlate to higher pastor burnout.
- Pastors in large or growing congregations are more likely to report that their relationship with their board is a powerful partnership.
- Pastors who are satisfied with their ministry report a positive relationship with their board.
- Discontented pastors are more likely to report power struggles, feeling under-appreciated, and that the board is one of the worst parts of ministry.
A healthy pastor plus healthy board relationships usually equals a growing church.
If your relationship with your board is difficult, you’ll find a partial solution in this next fact.
7. Prayer among church leaders is infrequent.
- Only one-third (34%) of US Protestant pastors say that their relationship with their elders could be characterized by frequent prayer together.
Could your tension with your board be lessened by regular prayer together?
What if you tried more than an opening and closing prayer, but 20, 30, or even 60 minutes of prayer time with your leaders? Every month.
And see what God does.
How to Pray with Board Members
I learned a long time ago that a group of friends works better together and has higher satisfaction levels than a group of mere colleagues. So our board meetings have friendship and prayer blended into them.
We start our monthly meetings at 7:00 p.m., but we convene an hour ahead of time for the really important stuff.
From 6:00-6:30, we eat dinner together. We rotate who brings the food, and who brings drinks and utensils. Our iron law is “no business talk during dinner.” Our first half hour is spent catching up on one another’s family, business, vacations, and other interests.
Then, we pray together from 6:30 to 7:00. We start with praise, and mix in both personal prayers (which arise from our dinner conversation) and church-related prayers. It’s spiritual, satisfying, and bonding.
On our twice-annual retreats, we pray at length following Bible study at breakfast and dinner, plus we have at least one more hour-long prayer time before returning home after we’ve completed our retreat business.
What’s Next?
How to Turn Information and Analysis into Action
The key question is: how will what you just discovered change what you do? Don’t click away without choosing something to do to become a stronger pastor.
Here are some action points:
- Renew your commitment to practice the spiritual disciplines that keep you close to Jesus.
- Read through the Barna Risk Metrics carefully and talk with someone if you have medium or high risk factors.
- Read Isaiah 58:13-14 and then recommit to taking a weekly Sabbath. Talk with your spouse about what that looks like for your family. If you need further encouragement in this area, read my short little book “I Love Sundays.”
- Set a reading goal and read for a short time every day.
- Schedule a conference for 2018.
- Initiate extended, and regular, prayer with your board.
Тhe Government Decided to Stop Working on the ‘National Strategy For the Child’
 At the request of Prime Minister Boyko Borissov, the work on the National Children’s Strategy project was halted due to negative public reactions, the social ministry said. However, they emphasize that the purpose of the document was never to take children from their families and to oppose the interests of children and their parents. However, the Ministry of Labor and Social Policy takes into account the reactions of the public and the fears that have arisen as a result of speculative interpretations of the measures set out in the draft strategy. The state will not decide instead of the parents or seize their rights. Support and care for the child and parents are linked. The best environment for the child is the family. ,,It is important for all of us to have a common understanding of the development of the next generation of Bulgarians”, said Boyko Borissov.
At the request of Prime Minister Boyko Borissov, the work on the National Children’s Strategy project was halted due to negative public reactions, the social ministry said. However, they emphasize that the purpose of the document was never to take children from their families and to oppose the interests of children and their parents. However, the Ministry of Labor and Social Policy takes into account the reactions of the public and the fears that have arisen as a result of speculative interpretations of the measures set out in the draft strategy. The state will not decide instead of the parents or seize their rights. Support and care for the child and parents are linked. The best environment for the child is the family. ,,It is important for all of us to have a common understanding of the development of the next generation of Bulgarians”, said Boyko Borissov.
Barna Group: The State of the Church (2019)
You are reading a free research sample of State of the Church & Family Report
The Christian church has been a cornerstone of American life for centuries, but much has changed in the last 30 years. Americans are attending church less, and more people are experiencing and practicing their faith outside of its four walls. Millennials in particular are coming of age at a time of great skepticism and cynicism toward institutions—particularly the church. Add to this the broader secularizing trend in American culture, and a growing antagonism toward faith claims, and these are uncertain times for the U.S. church. Based on a large pool of data collected over the course of this year, Barna conducted an analysis on the state of the church, looking closely at affiliation, attendance and practice to determine the overall health of Christ’s Body in America.
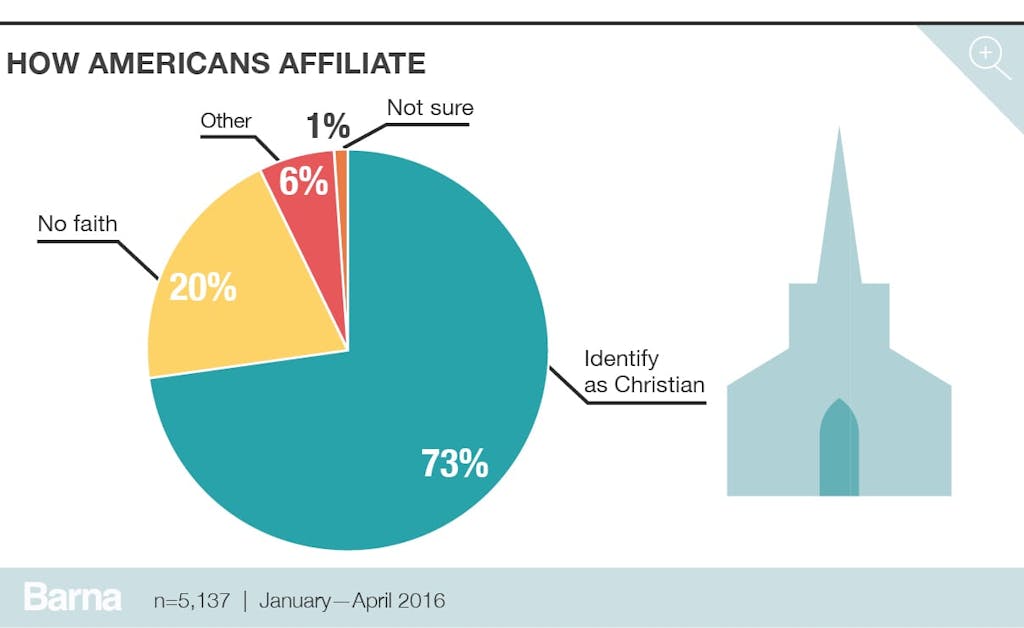
Most Americans Identify as Christian
Debates continue to rage over whether the United States is a “Christian” nation. Some believe the Constitution gives special treatment or preference to Christianity, but others make their claims based on sheer numbers—and they have a point: Most people in this country identify as Christian. Almost three-quarters of Americans (73%) say they are a Christian, while only one-fifth (20%) claim no faith at all (that includes atheists and agnostics). A fraction (6%) identify with faiths like Islam, Buddhism, Judaism or Hinduism, and 1 percent are unsure. Not only do most Americans identify as Christian, but a similar percentage (73%) also agree that religious faith is very important in their life (52% strongly agree + 21% somewhat agree).
Attending Church Is a Good Indicator of Faith Practice
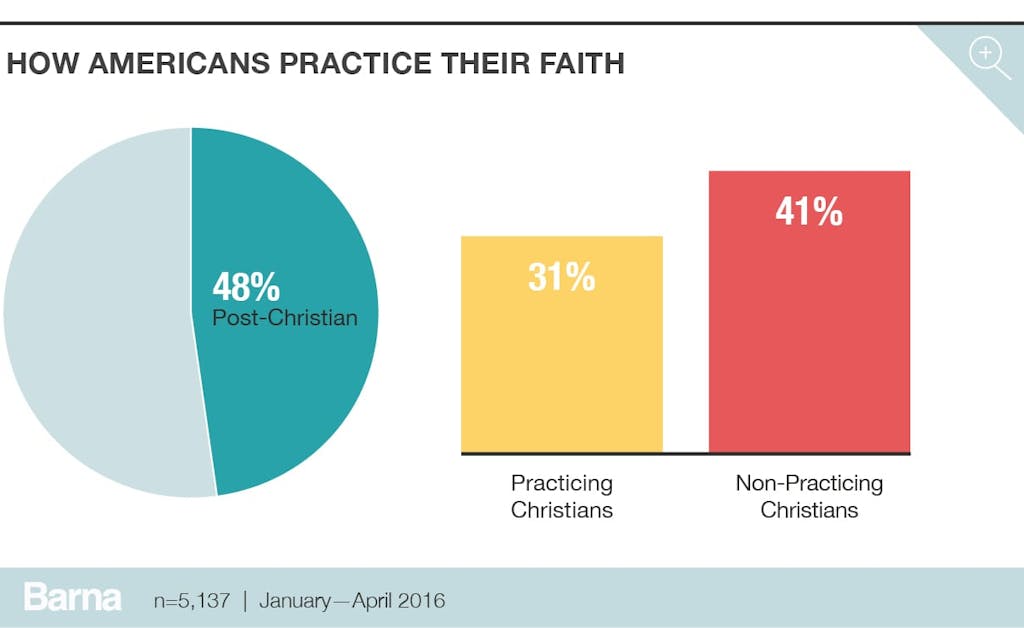
Even though a majority of Americans identify as Christian and say religious faith is very important in their life, these huge proportions belie the much smaller number of Americans who regularly practicetheir faith. When a variable like church attendance is added to the mix, a majority becomes the minority. When a self-identified Christian attends a religious service at least once a month and says their faith is very important in their life, Barna considers that person a “practicing Christian.” After applying this triangulation of affiliation, self-identification and practice, the numbers drop to around one in three U.S. adults (31%) who fall under this classification. Barna researchers argue this represents a more accurate picture of Christian faith in America, one that reflects the reality of a secularizing nation.
Another way Barna measures religious decline is through the “post-Christian” metric. If an individual meets 60 percent or more of a set of factors, which includes things like disbelief in God or identifying as atheist or agnostic, and they do not participate in practices such as Bible reading, prayer and church attendance (full description below), they are considered post-Christian. Based on this metric, almost half of all American adults (48%) are post-Christian.
Most Americans Attend Small to Medium Churches
As far as Barna is concerned, regular church attendance is central to understanding faith practice among American adults. Whether their church is large or small, charismatic or traditional, significant numbers of Americans sit in the pews each Sunday to worship together. Despite the enormous cultural impact of megachurches and megachurch pastors like Joel Osteen and his 40,000+ Lakewood Church, the largest group of American churchgoers attends services in a more intimate context. Almost half (46%) attend a church of 100 or fewer members. More than one-third (37%) attend a midsize church of over 100, but not larger than 499. One in 11 (9%) attends a church with between 500 and 999 attenders, and slightly fewer (8%) attend a very large church of 1,000 or more attendees.

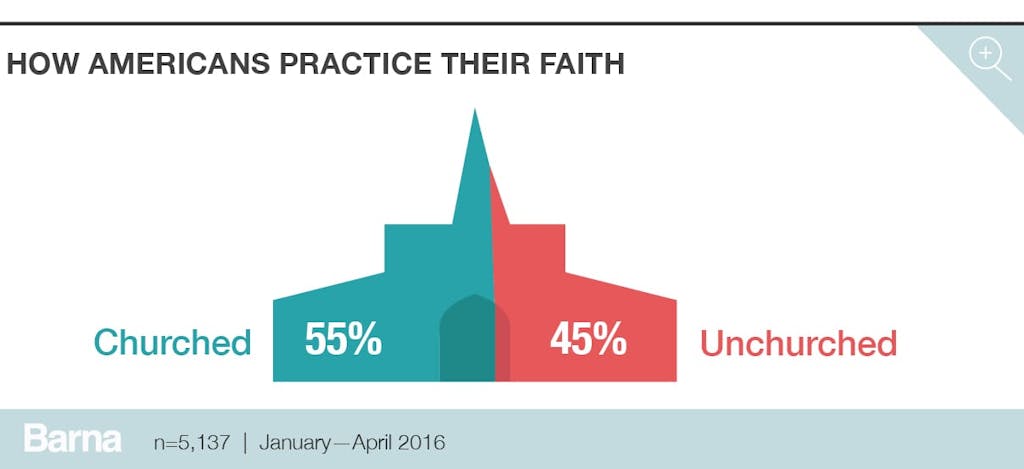
There Are More Churched Than Unchurched Americans
Digging deeper into church attendance, Barna uses another metric to distinguish between two main groups: those who are “churched” versus those who are “unchurched.” Churched adults are active churchgoers who have attended a church service—with varying frequency—within the past six months (not including a special event such as a wedding or a funeral). Unchurched adults, on the other hand, have not attended a service in the past six months. (They may be dechurched, meaning they once attended regularly, or purely unchurched, meaning they have never been involved in a Christian faith community.) Under these definitions, a slight majority of adults (55%) are churched—though the country is almost evenly split, with 45 percent qualifying as unchurched adults.
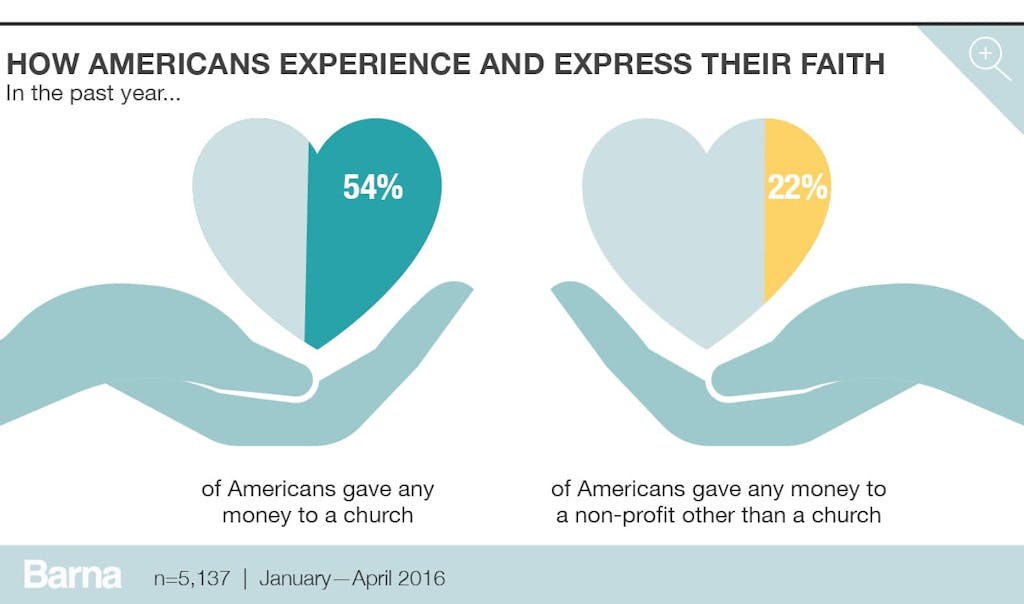
Christians Are More Generous Than Their Secular Peers
In Matthew 6, Jesus lays out three essential components of discipleship: prayer, fasting and almsgiving. The latter of the three, which we might also call justice and personal charity, is one of the pillars of a healthy spiritual life. Though residents in some cities are more generous than others, Americans give to churches more than any nonprofit organization. More than half of Americans (54%) have given money to a church in the past year—half that number have given to a nonprofit other than a church (22%). The remaining one-quarter (24%) have given to neither. Unsurprisingly almost all practicing Christians (94%) have given to a church, compared to one-quarter (23%) of atheists or agnostics. In fact, practicing Christians tend to be more generous overall than their secular counterparts: 96 percent of practicing Christians gave to a church or a nonprofit, compared to 60 percent among atheists and agnostics.
Americans Express Their Faith in a Variety of Ways
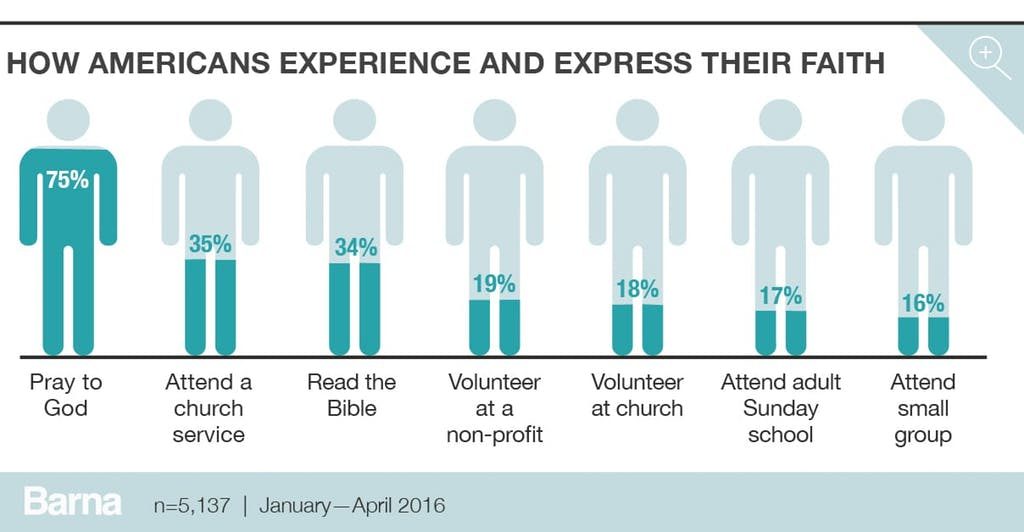
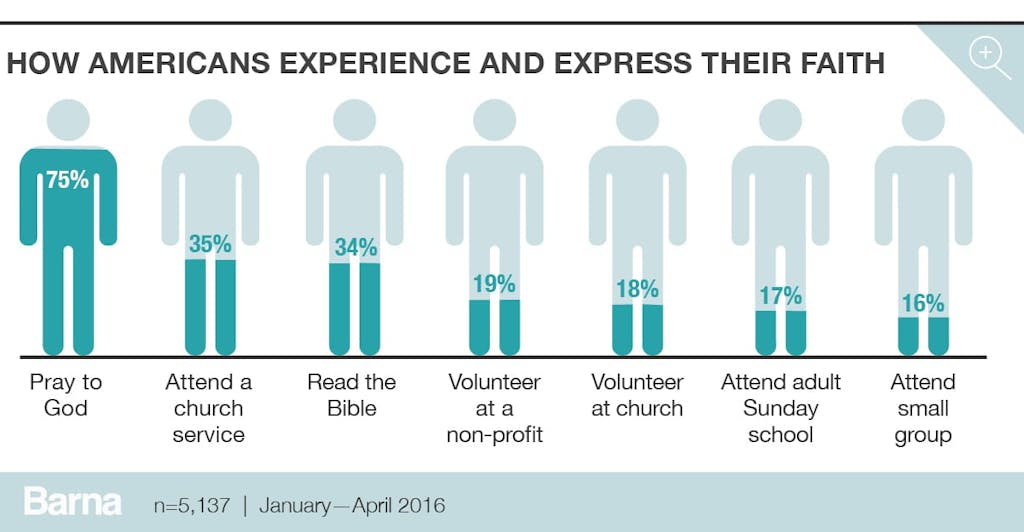
While regular church attendance is a reliable indicator of faithful Christian practice, many Americans choose to experience and express their faith in a variety of other ways, the most common of which is prayer. For instance, three-quarters of Americans (75%) claim to have prayed to God in the last week. This maps fairly well onto the 73 percent who self-identify as Christian. Following prayer, the next most common activity related to faith practice is attending a church service, with more than one-third of adults (35%) having sat in a pew in the last seven days, not including a special event such as a wedding or funeral. About the same proportion (34%) claim to have read the Bible on their own, not including when they were at a church or synagogue. About one in six American adults have either volunteered at a nonprofit (19%) or at church (18%) in the last week. Slightly fewer attended Sunday school (17%) or a small group (16%).
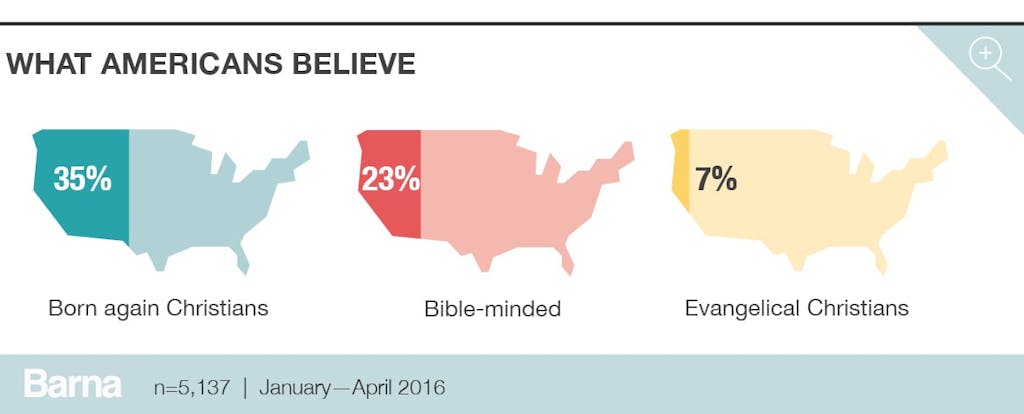
Evangelicals Are a Small but Influential Group
Classifications and metrics are vital to understanding the religious makeup of the United States. Barna uses several of these to identify key faith groups in America, including “born again Christians,” “evangelical Christians” and those who are “Bible-minded.” The largest of these groups are born again Christians, which make up roughly one-third of the population (35%). These individuals have made a personal commitment to Jesus Christ that is still important in their life today and believe that, when they die, they will go to heaven because they have confessed their sins and accepted Jesus Christ as their savior. The next largest group are those considered Bible-minded, who make up about one-quarter of the population (23%). They believe the Bible is accurate in all the principles it teaches and have read the Scriptures within the past week. Finally, the small (7%) but influential group of evangelicals are those who meet the born again criteria plus seven other conditions (detailed below), which are made up of a set of doctrinal views that touch on topics like evangelism, Satan, biblical inerrancy and salvation.
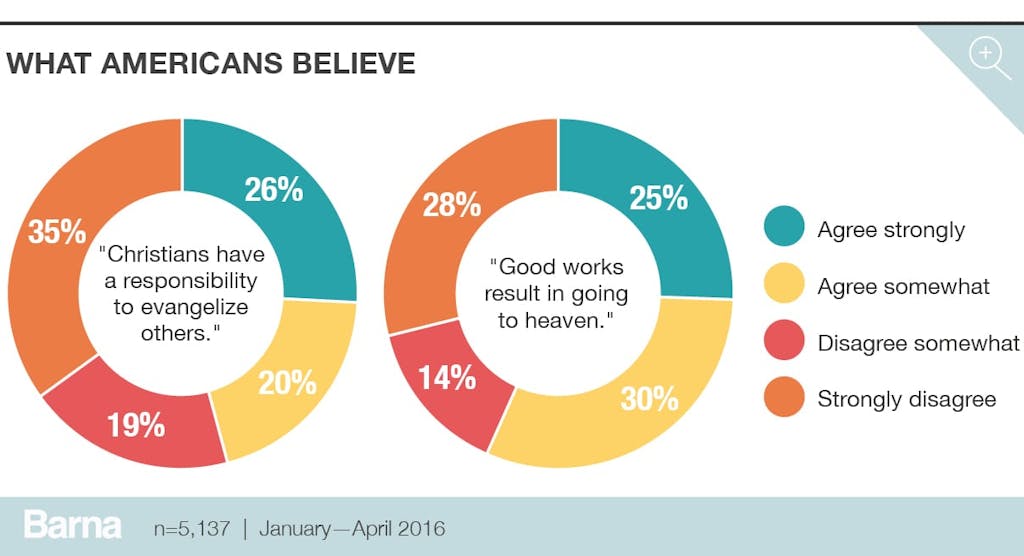
Americans Hold Both Orthodox and Heterodox Views
Religion and politics: two topics best excluded from polite conversation. This old adage appears to have the support of most Americans. When asked whether they, personally, have a responsibility to tell other people their religious beliefs, most people (54%) disagree (46% believe otherwise, very close to an even split). Getting at orthodoxy (or, rather, heterodoxy) among the American population, most (55%) agree that if a person is generally good, or does good enough things for others during their life, they will earn a place in heaven.
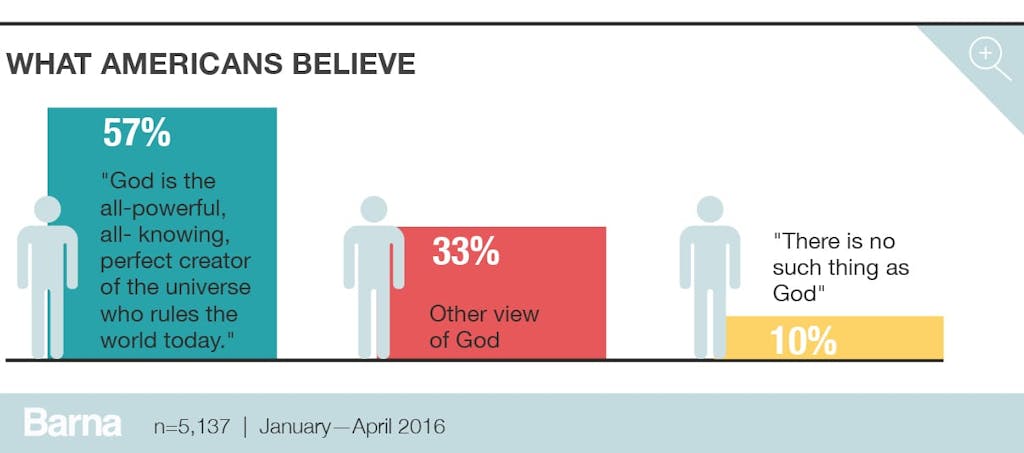
Yet in spite of the popularity of the belief that good works is sufficient for eternal life, from a long list of options for ways to describe God, the majority (57%) choose the most orthodox view: that God is the all-powerful, all-knowing, perfect creator of the universe who rules the world today. Other views of God make up one-third (33%) of the responses, and one in 10 (10%) says there is no such thing as God.
Comment on this research and follow our work:
Twitter: @davidkinnaman | @roxyleestone | @barnagroup
Facebook: Barna Group
About the Research
The study on which these findings are based was conducted via online and telephone surveys conducted in January 2016 and 2016. A total of 5,137 interviews were conducted among a random sample of U.S. adults, ages 18 years of age or older. The sample error is plus or minus one percentage point at 95-percent confidence level.
Born again: Have made a personal commitment to Jesus Christ that is still important in their life today and believe that, when they die, they will go to heaven because they have confessed their sins and accepted Jesus Christ as their savior.
Evangelical Christian: Meet the born again criteria plus seven other conditions. These conditions include saying their faith is very important in their life today; believing they have a personal responsibility to share their religious beliefs about Christ with non-Christians; believing that Satan exists; believing that Jesus Christ lived a sinless life on earth; asserting that the Bible is accurate in all that it teaches; believing that eternal salvation is possible only through grace, not works; and describing God as the all-knowing, all-powerful, perfect deity who created the universe and still rules it today. Being classified as an evangelical is not dependent upon church attendance or the denominational affiliation of the church attended. Respondents were not asked to describe themselves as “evangelical.”
Bible-minded: believe the Bible is accurate in all the principles it teaches and have read the Scriptures within the past week.
Churched: attended church in the past month
Unchurched: have not attended church in the past 6 months
Practicing Christian: Those who attend a religious service at least once a month, who say their faith is very important in their lives and self-identify as a Christian
Non-practicing Christian: Those who self-identify as a Christian but do not qualify as a practicing Christian
Post-Christian: To qualify as “post-Christian,” individuals had to meet 60% or more of the following factors (nine or more). “Highly post-Christian” individuals meet 80% or more of the factors (12 or more of these 15 criteria):
- Do not believe in God
- Identify as atheist or agnostic
- Disagree that faith is important in their lives
- Have not prayed to God (in the last year)
- Have never made a commitment to Jesus
- Disagree the Bible is accurate
- Have not donated money to a church (in the last year)
- Have not attended a Christian church (in the last year)
- Agree that Jesus committed sins
- Do not feel a responsibility to “share their faith”
- Have not read the Bible (in the last week)
- Have not volunteered at church (in the last week)
- Have not attended Sunday school (in the last week)
- Have not attended religious small group (in the last week)
- Do not participate in a house church ( in the last year)
About Barna Group
The Barna Group is a private, non-partisan, for-profit organization under the umbrella of the Issachar Companies. Located in Ventura, California, Barna Group has been conducting and analyzing primary research to understand cultural trends related to values, beliefs, attitudes and behaviors since 1984.
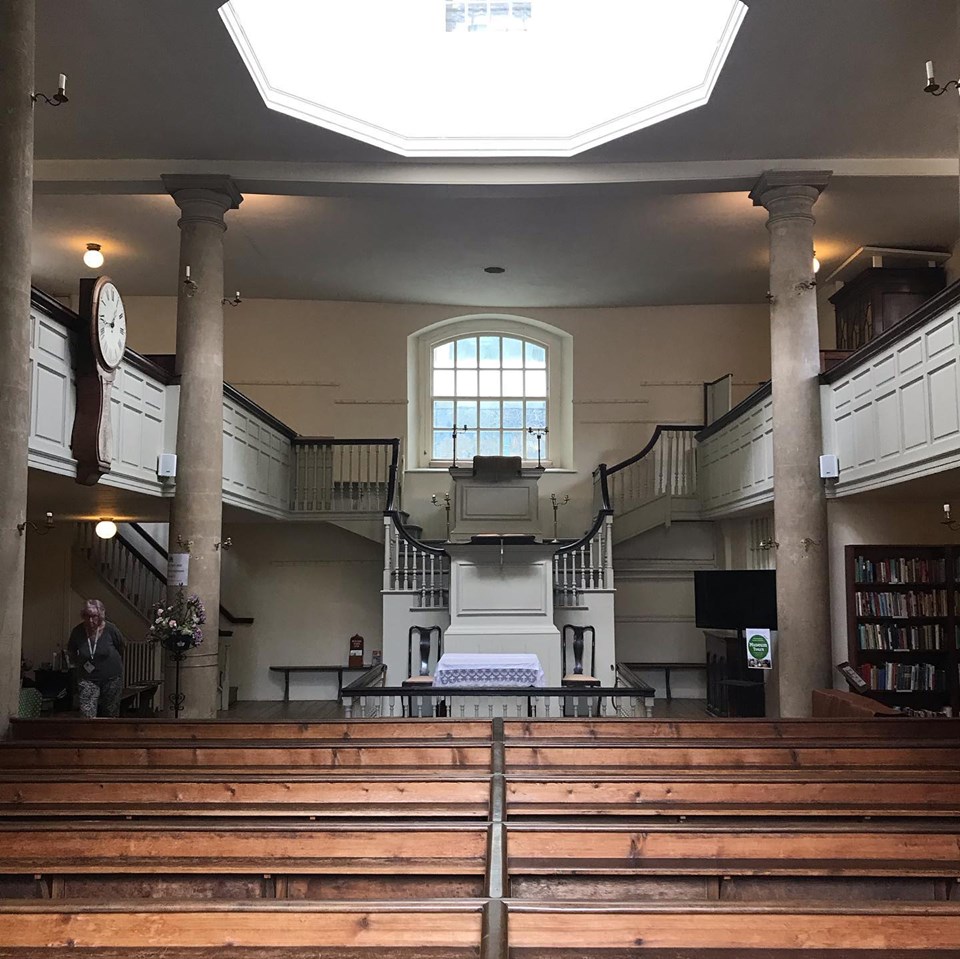
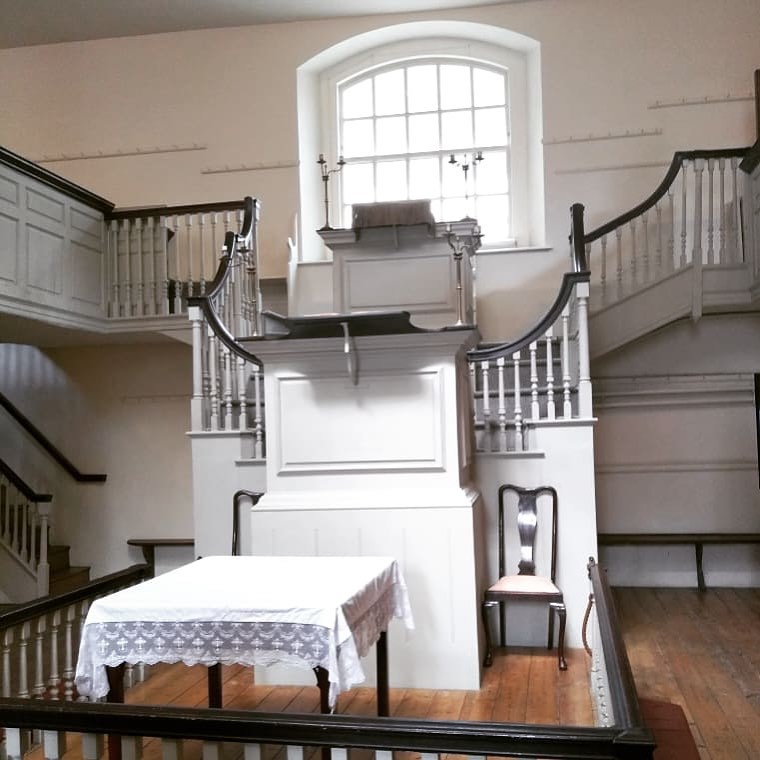
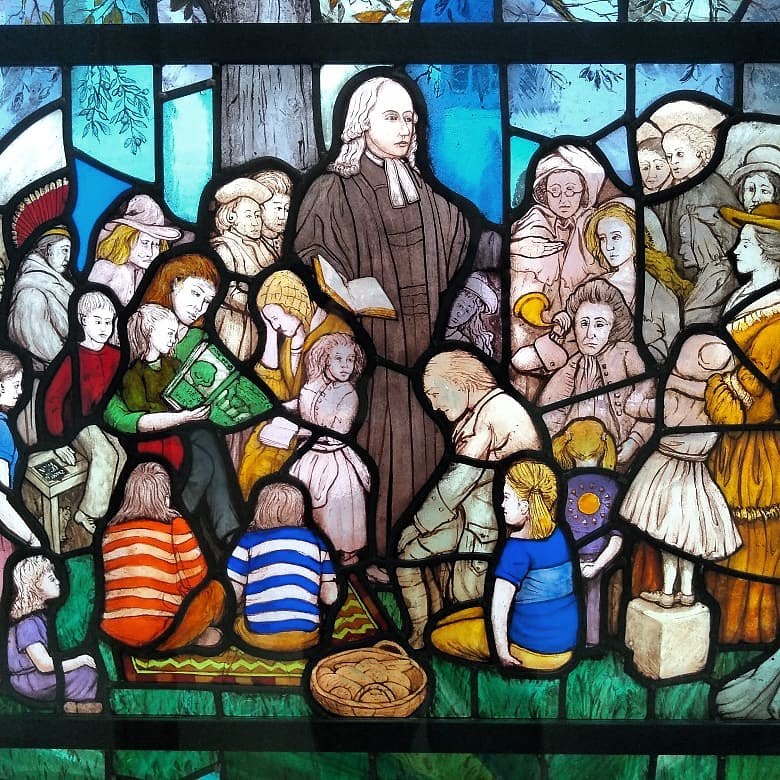
New Wesley Room at Bristol
Here is a bit more about the building from the Methodist Heritage Organization:
George Whitefield invited John Wesley to preach outdoors for the first time to the miners of Bristol in 1739. Within a few weeks’ work started on building the New Room as a meeting place for two of the religious societies in the city, thus creating the world’s first Methodist building.
The current building dates from 1748 when the New Room was doubled in size. Its lower floor became known as John Wesley’s Chapel. It is still in regular use for worship as well as being used for cultural and educational activities and exhibitions. Upstairs John Wesley created twelve rooms around a beautiful central octagonal window. These provided accommodation for himself and any visiting preachers assigned to the Bristol circuit. They now contain a highly interactive Museum devoted to telling the story of John and Charles Wesley and the relevance of their work today.
Being well placed in the heart of the city, the New Room became a center for the Wesleys’ work in Bristol. It was where John’s strong sense of social justice was first expressed. The New Room became a base for running a school for the poor, for providing food and clothes to the needy, for offering free medical care to the sick, and for helping those in the nearby prison. It was also the first place to use John Wesley’s ‘class’ system, where members were divided into sub-groups for mutual support and development. The New Room has been described as ‘the cradle of Methodism’.
The New Room was one of John Wesley’s three key centers. Many of the annual conferences were held there, including the one that first created Methodist circuits. Bristol’s trading links encouraged the growth of American Methodism. Thomas Webb, Francis Asbury, and others committed themselves to working there and sailed from nearby.
Bulgarian Orthodox Church deletes controversial opinion on National Strategy for the Child from website
A controversial opinion purported to be from the Bulgarian Orthodox Church’s Holy Synod urging a ban on terminations of pregnancy, for religion to be a compulsory subject in schools, no sex education, and opposing the full ban on corporal punishment in schools, has been deleted from the church’s official website.
The opinion, posted in response to the Bulgarian government’s draft National Strategy for the Child 2019-2030, had not been voted by the Holy Synod, nor approved by the church’s Patriarch Neofit, nor signed by the Metropolitans, Bulgarian National Television (BNT) reported.
It had been sent for posting on the website by Gavriil, the Metropolitan of Lovech, BNT said.
After it appeared on the website on February 8, the opinion – widely covered in the Bulgarian media – caused extensive negative reaction on social networks.
Specialist church news website Dveri said that the opinion had not been considered and approved by the Bulgarian Orthodox Church’s governing body, but was an initiative of the Synod’s cultural and educational department headed by Metropolitan Gavriil.
Dveri quoted a statement by Naum, the Metropolitan of Rousse, who said that the document had not been officially discussed by the Holy Synod.
“The ‘opinion’ binding the Bulgarian Orthodox Church Holy Synod as an institution was a project personally created by Ms Dessislava Panayotova, an associate of the cultural and education department of the Synodal office…that does not mean that the Holy Synod will accept it unhesitatingly and unambiguously,” Naum said.
“The Bulgarian Orthodox Church, as a nutritionist of Bulgarians and moral values in the Bulgarian family, always will promote ethical norms in education, but will not tolerate in any way violence against children, in whatever form, especially if it is linked to so-called ‘religious education and training’,” he said.
Issues related to termination of pregnancy and children at risk are issues for future profound reflection in Bulgarian society “addressing appropriate reflections on God’s will, the dignity of the mother, as well as the significance of each specific case, related to domestic violence and violence specifically against women,” Naum’s statement said.
“All other topics concerning the education and upbringing of Bulgarian children should be discussed by relevant educators and specialists, who also have the view of theological science, thus defining the most accurate and correct approach for future recommendations on the issues raised,” the statement said.
HOW Americans experience FAITH?
New Research on the State of Discipleship in AMERICA Today
OVER 2,000 years ago, Jesus approached twelve seemingly unsuspecting Galileans and bid them: “Come, follow me.” For the next three years, they walked alongside him as he discipled them. Toward the end of his earthly ministry, Jesus commissioned his disciples to go and do the same—to take the Gospel message to the world and make disciples in all the nations.
The Great Commission is an audacious undertaking, all the more so given the fast and sweeping changes taking place in the broader culture. People are lonelier, more distracted and more tethered to their screens, and searching for meaningful lives. As Christians bring the unchanging message of the Gospel to the world, effective approaches to discipleship become more important, especially in a world that is increasingly polarized around spiritual issues.
So what is the current state of discipleship in the U.S.? Is the church effective in its efforts? Are churchgoers involved in discipleship activities, and if so, which models do they prefer? And perhaps most importantly, do investments in discipleship actually affect spiritual growth? To answer these questions, Barna Group, commissioned by The Navigators and NavPress, conducted a comprehensive, multi-phase research study among Christian adults, church leaders, exemplar discipleship ministries and Christian educators. Here’s what the research uncovered.
What We Mean When We Say…
The research examined the language and terminology surrounding discipleship. We asked a random sample of Christians—including practicing and non-practicing Christians—what words or phrases they use to describe “the process of growing spiritually.” The most preferred term was “becoming more Christ-like” (selected by 43% of respondents), followed by “spiritual growth” (31%), and “spiritual journey” (28%).
The term “discipleship” ranked fourth on the list and was only selected by fewer than one in five Christians (18%). “Spiritual maturation” was next (16%). “Sanctification” (9%) and “spiritual formation” (5%) were relatively unused phrases among the general population of Christians.
Interestingly, the more active the person in spiritual activities, the more likely he or she is to use the phrase “becoming Christlike.” In contrast, the “spiritual journey” language is most preferred among non-practicing Christians.
Among those who did not select the term “discipleship,” we asked if the word still has relevance to their Christian experience. Surprisingly, only one-quarter of these respondents said “discipleship” is very relevant. The implication is that while spiritual growth is very important to tens of millions, the language and terminology surrounding discipleship seems to be undergoing a change, with other phrases coming to be used more frequently than the term “discipleship” itself.
Effective Discipleship?
Christian adults believe their churches are doing well when it comes to discipleship: 52 percent of those who have attended church in the past six months say their church “definitely does a good job helping people grow spiritually” and another 40 percent say it “probably” does so. Additionally, two-thirds of Christians who have attended church in the past six months and consider spiritual growth important say their church places “a lot” of emphasis on spiritual growth (67%); another 27 percent say their church gives “some” emphasis.
Church leaders, conversely, tend to believe the opposite is true. Only 1 percent say “today’s churches are doing very well at discipling new and young believers.” A sizable majority—six in 10—feels that churches are discipling “not too well” (60%). Looking at their own church, only 8 percent say they are doing “very well” and 56 percent “somewhat well at discipling new and young believers.” Thus, pastors give their own church higher marks than churches overall, but few believe churches—their own or in general—are excelling in discipleship.
Not surprisingly, emphasis on discipleship is correlated with higher faith engagement. Three-quarters of practicing Christians, who have attended church in the past month and consider their faith very important, say their church places “a lot” of emphasis on spiritual growth (73%), while only 40 percent of non-practicing Christians say the same.
Breaking Down Discipleship
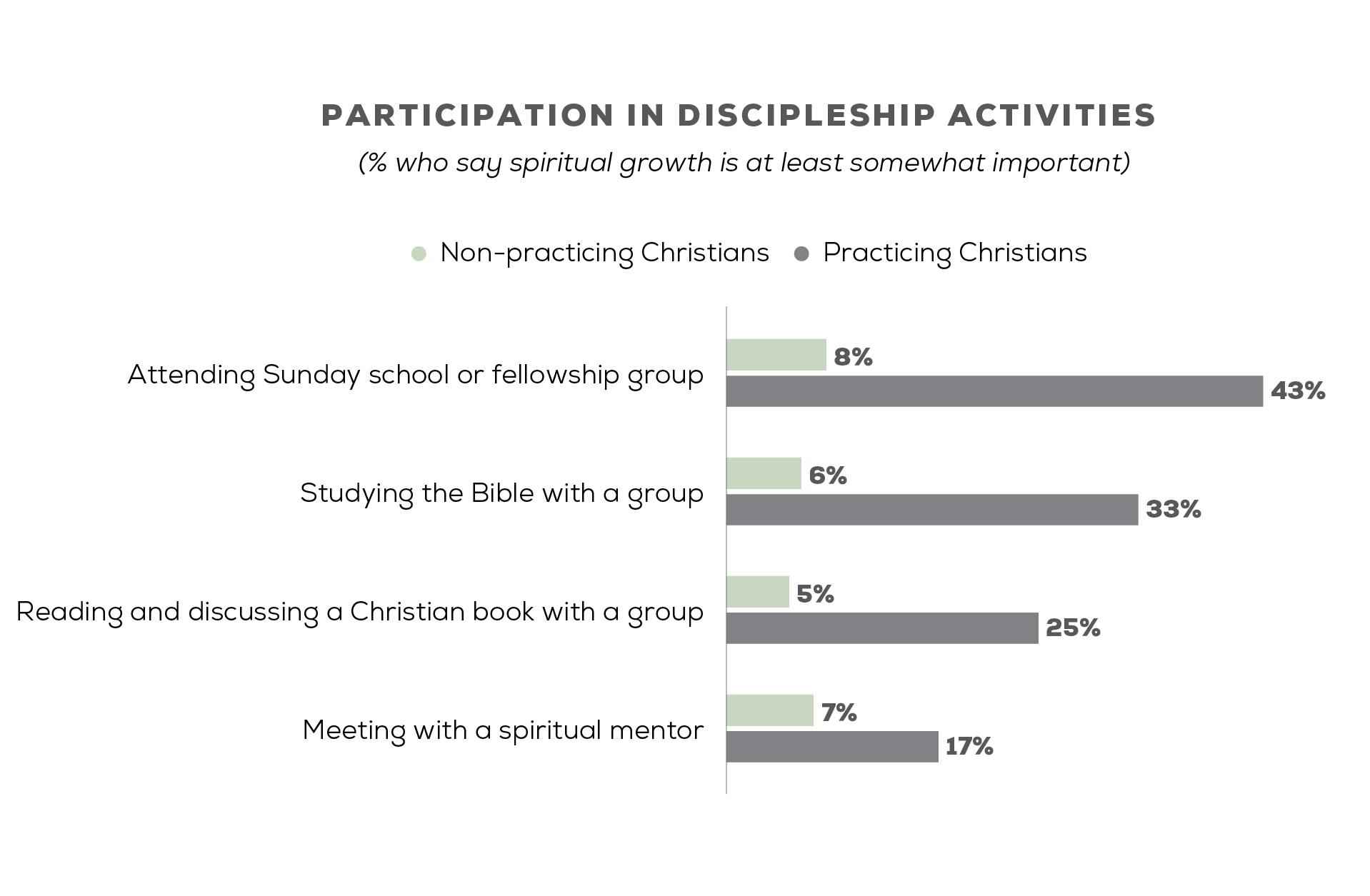
Despite believing their church emphasizes spiritual growth, engagement with the practices associated with discipleship leave much to be desired. For example, only 20 percent of Christian adults are involved in some sort of discipleship activity—and this includes a wide range of activities such as attending Sunday school or fellowship group, meeting with a spiritual mentor, studying the Bible with a group, or reading and discussing a Christian book with a group.
Practicing Christians are more likely to be involved in a variety of spiritual growth activities than are non-practicing Christians. (You can read a definition of practicing Christians below.) Yet, even among practicing Christians, fewer than half are engaged in these four types of spiritual development. Only 17 percent say they meet with a spiritual mentor as part of their discipleship efforts.
To Grow or Not to Grow?
It is difficult for researchers to analyze accurately the degree to which people are changing spiritually. From the point of view of self-perception, most people perceive they are growing and say they want to develop spiritually. Yet, self-perceptions also show that Christians tend to be quite satisfied in their spirituality, perhaps edging toward complacency. Most Christians express satisfaction with their spiritual lives: Thirty-eight percent of Christian adults say they are “happy with where they are in their spiritual life” and another 36 percent are “almost to where they want to be.”
Some good news is that people firmly assert that they want to grow spiritually. This is not the case inother contexts, and represents a continued bright spot within U.S. spirituality. Indeed, three-quarters of practicing Christians (77%) believe it is “very important to see growth in their spiritual life.” Even among non-practicing Christians—people who rarely or ever attend church and who are mostly inactive spiritually—37 percent say it is very important to grow spiritually.
Yet, the research reveals little correlation between activity and perceived growth, further revealing the disconnect between how people think about their spirituality and what’s actually happening in their lives. For example, most practicing Christians feel they have made “a lot” (40%) or “some” (51%) progress in their personal spiritual growth in the past year. However, among respondents who are currently involved in at least one discipleship activity, their self-reported growth was not much higher than these levels. Even among non-practicing Christians, a majority believes they have made spiritual progress in the last year.
One of the implications of these findings is that church leaders must be diligent in finding tools that help people examine the reality of their spiritual growth, not merely how they perceive it.

Motivations for Discipleship
Even though people may not be fully in touch with their level of growth, what motivates people to grow in a spiritual manner? Practicing and non-practicing Christians report different motivations for seeking spiritual growth. Practicing Christians see discipleship as intimately tied with their faith, saying they are most motivated by “a general desire to know Jesus, or God, more” (46%); “a general desire to be more like Jesus” (41%); and because “the Bible instructs us to be more like Jesus” (34%).
Non-practicing Christians, on the other hand, see discipleship as a part of a broader bid for self-improvement, saying they “think it is important to be improving or growing in all things” (51%); “have been through a lot, and growing spiritually will help me” (41%); and “have a general desire to know Jesus, or God, more” (36%).
The research examines differences between various demographic segments, and many differences emerged based upon generation. For instance, when it came to motivations, Millennial Christians are more likely than average to be motivated to grow spiritually because “I have been through a lot and growing spiritually will help me” and “I am inspired by others and want to be more like them.” Younger believers are also more likely than average to say they grow in peer groups and when reading the Bible with others. Millennial Christians are less likely to say they “my church encourages spiritual growth.”
One of the implications of the research, then, is for churches to rethink what is working in connecting with today’s younger Christians, particularly when it comes to relational and mentoring forms of spiritual development.
Discipleship as a Solo Activity?
Christian adults are split on their preferences when it comes to models of discipleship: small group, one-on-one or individual (solitary) format.
Among Christians who say spiritual growth is important, more than one-third say they prefer to pursue spiritual growth on their own (37%). Similarly, two in five of all Christian adults consider their spiritual life to be “entirely private” (41%). This is a greater proportion—though only slightly—than Christians who believe their faith, rather than being private, has an impact on relatives (37%), friends (36%) and their community (33%). In other words, one of the problems revealed by this research is that millions of Christians believe that discipleship is a solo affair, with only personal and private implications.
Even when it comes to what Christians are experiencing in the churches they attend, there does not seem to be much emphasis conveyed about the communal, relational nature of spiritual growth. Just one-third of Christian adults report that their church recommends meeting with a spiritual mentor; half of their churches publically endorse studying the Bible with a group; and half recommend studying the Bible independently.
Among Christian adults, one-quarter prefers a small-group setting for discipleship (25%). Another one in five prefers a combination of group and one-on-one discipleship (21%) and 16 percent prefer one-on-one only. Thus, in total, about one-third of those pursuing spiritual growth are including some element of one-on-one, person-to-person discipleship.

However, not all of those who prefer discipleship “pairs” are currently involved in a one-on-one discipleship relationship: less than one-quarter of Christians adults (23%) are currently being discipled by someone (29% of practicing vs. 12% of non-practicing Christians), and 19 percent are discipling someone else (25% of practicing vs. 9% of non-practicing Christians).
One-on-one discipleship relationships are established in various ways: Of those currently being discipled by another person, one-quarter say that person invited them (27%); one in five invited their mentor (20%); and about one-quarter were paired by the church (23%)—but the largest proportion, 28 percent, were matched “some other way.”
The View from the Pulpit
The study shows how pastors and church leaders are thinking about discipleship. When asked to choose the single method of discipleship they believe is most effective, church leaders tend to select small group formats (52%) nearly two-to-one over discipleship pairs (29%). For good or bad, small groups are the disciple-making format preferred by most of today’s church leaders.
Do church leaders engage in discipleship themselves? Somewhat. Fully 94 percent are currently discipling at least one other Christian. However, only six in 10 are being discipled themselves. Discipleship pastors (72%) are somewhat more likely than senior pastors (59%) to have a spiritual mentor.
One of the compelling findings of the study is that developmental relationships are more common in larger churches: Eight out of 10 church leaders of 500+ member churches report being currently discipled by someone else (78%), compared with 64 percent of those with 100 to 499 members and 55 percent of those who lead in churches with fewer than 100 members.
According to pastors, the most critical elements of discipleship are matters of the heart rather than of structure. Aside from prayer and time with God, the top three spiritual disciplines pastors believe are essential to discipleship are “personal commitment to grow in Christlikeness” (94%), “attending a local church” (91%) and “a deep love for God” (90%). Having “a comprehensive discipleship curriculum” is by far the least-important element of effective discipleship according to pastors, 44 percent of whom select it as essential.
When asked how they want to improve in their discipleship programs, a plurality of church leaders says they would “develop a more clearly articulated plan or approach to discipleship” (27%). Additionally, churches need to develop assessment criteria to track the effectiveness of their dis- cipleship efforts. Less than 1 percent of leaders report using a survey or other evaluation instrument to assess the results of their programs. This underscores one of the previous conclusions, that church leaders and congregants need better methods of thinking about and evaluating their discipleship efforts.

Comment on this research and follow our work:
Twitter: @davidkinnaman | @roxyleestone | @barnagroup
Facebook: Barna Group
About the Research
The data contained in this research report and in the full State of Discipleship monograph originated through a series of research studies conducted by Barna Group. The study was commissioned byNavPress for The Navigators. You can also explore the State of Discipleship case study on our website.
The full project was completed in multiple stages. To begin, 36 educators from Protestant and Catholic seminaries and Bible colleges completed an online survey of open-ended questions during December 2014 and January 2015. These findings were used to revise and conduct an open-ended survey with exemplar churches and ministries.
Leaders of 30 churches and seven parachurch ministries that exemplify excellence in discipleship completed an open-ended, online survey February 3 to March 4, 2015. Respondents were recruited from a list developed by Navigators’ staff as well as nominated by Protestant pastors from Barna’s Pastor Panel.
Following these two qualitative studies, an online and telephone survey was conducted among 615 Protestant senior pastors and 218 discipleship pastors. Churches were contacted from a random list of U.S. Protestant churches, with approximately 543 interviews conducted by phone and 290 online. The interviews were conducted between April 7 and May 30, 2015.
At the same time, a nationwide study of Christian adults ages 18 and older was conducted using an online panel and phone interviews (with a mix of 60% landline and 40% cell phone). Surveys for this portion of the research study were completed between March 26 and April 15, 2015. A total of 2,013 surveys were complet- ed: 1,300 online and 703 via phone. The sample error on this survey is plus or minus 3.1 percent points at the 95-percent confidence level. Data were weighted by age, gender, etc., to be representative of all U.S. Christians ages 18 and older.
Survey calls were made at various times during the day (for churches) and evenings (for adults), so that every individual selected for inclusion was contacted up to five separate days, at different times of the day, to maximize the possibility of contact. This is a quality control procedure to ensure that individuals in the sampling frame have an equivalent probability of inclusion within the survey, thereby increasing the survey reliability. All of the interviews were conducted by experienced, trained interviewers who were supervised at all times; every interviewer was monitored during their performance on the project. The survey was conducted through the use of a CATI (Computer Assisted Telephone Interviewing) system. This system ensures that question skip patterns are properly administered by interviewers and that survey data are recorded accurately.
The online portion of the study was conducted among a representative random sample of adults and churches using a web-enabled consumer panel.
*Definitions
Practicing Christians are self-identified Christians who say their faith is very important to their lives and who have attended a worship service, other than for a special occasion, one or more times during the past month.
Non-practicing Christians are self-identified Christians who do not qualify as “practicing” under the criteria above.
About Barna Group
Barna Group (which includes its research division, Barna Research Group) is a private, non-partisan, for-profit organization under the umbrella of the Issachar Companies. Located in Ventura, California, Barna Group has been conducting and analyzing primary research to understand cultural trends related to values, beliefs, attitudes and behaviors since 1984. If you would like to receive free e-mail notification of the release of each update on the latest research findings from Barna Group, you may subscribe to this free service at the Barna website
PENTECOSTAL BABEL
PENTECOSTAL BABEL
As we reflect upon Pentecost Sunday, I submit here my recently published article in the preaching journal of Columbia Theological Seminary. I was pleased that this piece was made the lead article in the Pentecost edition of the Journal for Preachers (just ahead of Walter Brueggemann’s contribution, which made me feel pretty good!). The article is also a smattering of one of the chapters of my upcoming theological memoir, which is presently being copy-edited by Cascade Books. I welcome your comments and criticisms!
“NOW, DO NOT GO FROM THIS MEETING AND TALK ABOUT TONGUES, BUT TRY TO GET PEOPLE SAVED!”
WILLIAM SEYMOUR, THE AZUSA STREET MISSION
One of the reasons that I voraciously enjoy the Journal for Preachers is that I am a Pentecostal. I find myself terrifically motivated by the perspectives of this community of mainline Protestant preachers, who seem to so effortlessly move exegetical and theological dirt around the jobsite to uncover treasures I would never otherwise discover. In this collegial spirit, I thought our readers might enjoy a Pentecostal perspective on the Day of Pentecost, particularly the phenomenon that pushes the entire story off the ground: the gift of tongues. In circles where the emphasis of Acts 2 is typically placed on the birthday of the Church, perhaps moving the dirt around the tongue talking, the early morning racket, and the accusations of drunkenness will reveal some hidden gems.
The Sign of Tongues in the Pentecostal Tradition
It is safe to say that the average man on the street, if he has heard of a Pentecostal, associates us with one of our odder habits: what is typically called “speaking in tongues.” We take this phrase from the King James translation of the book of Acts in the New Testament, a translation that was hammered out during Shakespearean times. You might also call the habit, more contemporarily, “speaking in languages.”
Speaking in tongues is what Pentecostals became known for early on, especially at the Azusa Street Revival at the beginning of the twentieth century. Its leader, William Seymour, tried his best to focus people’s attention not toward the phenomenon of tongues, but toward the lifestyle such Spirit-empowerment produced. “If you get angry, or speak evil or backbite, I care not how many tongues you may have, you have not the baptism with the Holy Spirit,” the illiterate Seymour preached.[i] Still, it is hard not to focus on a group of people who spontaneously burst into shouting a bunch of syllables that sound like gibberish.
“We believe in speaking with other tongues as the Spirit gives utterance,” my denomination’s faith statement reads, “and that it is the initial evidence of the baptism in the Holy Ghost.” As if speaking in tongues were not aberrant enough, this statement seriously upped the ante. If you don’t speak in tongues, you haven’t really had a full experience of the Holy Spirit, we declared. The gift of tongues is the entrance requirement into Spirit baptism and the complete Christian life. If you don’t do it, according to our particular tradition, you’re not a bona fide Pentecostal.
Our motives in this effort to encourage the gift of tongues have always been pure, but slapping a bunch of strictures around the activity of the Holy Spirit is tricky business at best, like trying to tame the wind. At worst, we can dress up to play the part of God. Certainly God “does not change like the shifting shadows,” James 1:17 says, but neither is God beholden to formulas. In erring to the latter side, I have seen and heard all kinds of personal stories about well-meaning Pentecostals trying to “help” others receive the gift of tongues, and the stories range from the horrific to the hokey.
Growing up, there were plenty of altar calls to receive the Holy Spirit by way of the “sign” of speaking in tongues (signage is the language for the gift used in Mark 16:17). People often testified of “seeking” the gift for many months (One new convert of our congregation who was in seeking mode remarked, “The Holy Ghost sure is an elusive thing, ain’t He?”). Seekers would crowd the altar, and holy huddles would form around them, swaying back and forth, everyone praying out loud, eight, ten, twelve hands on the seeker’s shoulders and head. At some point after the seeker had been thoroughly leaned on by the group, someone would take the lead. The leader would stand face to face with the seeker, and the oral exam would begin. “Speak out!” “Speak anything that comes to mind!” I have seen people pat the chin of the speaker with the back of their hand up and down, over and over. Judge us if you must, but the Catholics believe that the communion wine transubstantiates into real blood. Are we Pentecostals not also allowed some hocus-pocus?
If there were Holy Ghost blockages that the prayer huddles could not break through, individual attention was warranted. The pros were called in with tactical stents. One friend of mine was taken to a room and given practice words. “You can do it!” he recalls the pro’s encouragement. In my mind the scene looks like an interrogation room in an episode of Law and Order, a hanging light bulb over a metal desk, the pro with a walkie-talkie strapped to his belt to relay any breakthrough. Even with such serious help, my friend never did speak in tongues.
In fact, I know all kinds of people who identify with Pentecostalism but never crossed the tongues threshold. My denomination is still trying to figure out what to do with them. Jesus told Nicodemus in John 3:8 that “the Spirit blows wherever it pleases.” “The Holy Ghost sure is an elusive thing, ain’t he?”
Glossolalia and the Repair of Language
There are all kinds of smart studies on the phenomenon of speaking in tongues, typically called glossolalia in academic circles (from the Greek words glossa – language – and laleo – to speak). The experience of tongues is not particular to Pentecostals, or even to Christians, but there does seem to be a common thread uniting those who participate: Glossolalia is the language of the underclass. In the words of Randall Balmer at Barnard University: “It provides a voice to people who feel they have no voice.”[ii]
I fear that such a definition might be interpreted as Marxist escapism, tongues as an opiate for the poor. I have never thought about tongues as some Christian version ofthe Exorcist, eyes rolling back into the head for a few moments of ecstasy, like a drug hit. Tongues are not the result of some kind of divine possession, which seems to be Paul’s point in 1 Corinthians 14:32 — “The spirits of prophets are subject to the control of prophets.” Instead, at the most elemental level, tongues are about…tongues. Tongues are about language, about words. They beg the question, “Where does language come from and what does it mean to do?”
Even the most secular among us would readily acknowledge that the project of human language is in deep disrepair. The Quaker spiritualist, Richard Foster, contends:
The tongue is our most powerful weapon of manipulation. A frantic stream of words flows from us because we are in a constant process of adjusting our public image. We fear so deeply what we think other people see in us that we talk in order to straighten out their understanding.[iii]
Is not such evidence of the seductive and devalued power of language all around us? Just listen to the droll of the cable news wars, in which language is weaponized to the point where logic and objectivity are chess pieces to be played, ninjas stars to be thrown. And hasn’t the larger church lost the battle of fighting devalued words with more devalued words that are theological in nature? “Christian language needs to be redeemed,” Marcus Borg argues.[iv] The Church has not been able to save us from the word vomit soup we now swim in. We are all growing increasingly illiterate, shouting words back and forth that have little meaning and less value. All that matters is how sharply we can carve out the edges of our words.
Historically, Christian thought has been on the forefront of deconstructing the power of words to their constituent elements. There is plenty in the Bible about the potency of language (my mother was fond of quoting James 1:19 in our home, “Be quick to listen and slow to speak”) and this tradition has grown throughout the centuries. From the first monk, Anthony the Great in the third century, Christian monks attacked word vomit with the powerful weapon of silence. Thomas Merton, the famous trappist monk of the last century, renowned for his vows of silence, considered words to be the building blocks of the “false self” that we project onto others for our own perceived good.[v] His corrective: create silence. Soren Kierkegaard, a Danish theologian, wrote well over a century ago, ““If I were a doctor and could prescribe just one remedy for all the ills of the modern world, I would prescribe silence.”[vi] Scores of similarly beautiful quotations on the power of silence from a thousand Christian mystics fill the literature of church history.
Pentecostals are a part of this Christian trajectory, but have attacked the same problem of word vomit from a dramatically different angle. You might say that the monastic tradition fought word inflation by raising the interest rates on language. The fewer words in play, the better their value. We Pentecostals did not follow this approach. As an underclass people, perhaps we saw silence as, in the words of Wendell Berry, “the distinguishing characteristic of absolute despair.”[vii] So we just decided to receive a whole new language altogether, and by doing so, to transcend despair.
The Post-Babel Language of God
In Acts 2, the followers of Jesus are waiting for the fulfillment of the promise of 1:5: “For John baptized with water but in a few days you will be baptized with the Holy Spirit.” And then, like a sandstorm, it hit. “All of them were filled with the Holy Spirit and began to speak in other tongues as the Spirit enabled them” (2:4). But that is only where the true story begins. It is the response of the onlookers to the phenomenon of speaking in tongues that constitutes the real meat of the narrative of Acts 2.
Now there were staying in Jerusalem God-fearing Jews from every nation under heaven. When they heard this sound, a crowd came together in bewilderment, because each one heard their own language being spoken. Utterly amazed, they asked: “Aren’t all these who are speaking Galileans? Then how is it that each of us hears them in our native language? Parthians, Medes and Elamites; residents of Mesopotamia, Judea and Cappadocia, Pontus and Asia, Phrygia and Pamphylia, Egypt and the parts of Libya near Cyrene; visitors from Rome (both Jews and converts to Judaism); Cretans and Arabs—we hear them declaring the wonders of God in our own tongues!” Amazed and perplexed, they asked one another, “What does this mean?” (2:5-12)
Languages old and new, spewing forth from the poor white trash of Galilee, now suddenly linguists. Indeed, what does such an event mean?
It is hard to doubt that a very specific Old Testament text stands behind Acts 2, backlighting its meaning. It was way back in Genesis 11 where the nations highlighted in Acts 2 first endured their birth. There, the story of the Tower of Babel adds two great brush strokes to the burgeoning picture of YHWH in the early days of humanity, a God who is ferociously particular. Those two new particularities painted in Genesis 11 are simply that (1) God doesn’t care much for urban living and (2) really disdains dictatorial regimes with their forced homogeneity. “Come, let us build ourselves a city, with a tower that reaches to the heavens, so that we may make a name for ourselves,” the whiz kids of the Mesopotamian valley devised in Genesis 11:4. Armed with their Apple computers, their new brick-making technology and cool, horn-rimmed eyeglasses, they sought to remake history.
But God is not enthused.
“Come, let us go down and confuse their language so they will not understand each other,” God decides after convening a council of Himself. “That is why it was called Babel – because there the Lord confused the language of the whole world,” scattering them “across the face of the whole earth.” In the Old Testament tradition, God’s response to Babel is where languages (other than Hebrew?) began. The project of multiple languages/tongues was meant to prevent human oppression at the Tower of Babel.
Of course, humanity found a way to derail that project of multiple languages as well. The Egyptian Empire would soon rise, forcing everything it could force on those who did not speak Egyptian. The Babylonians would give way to the Persians would give way to Alexander the Great would give way to the Romans. One Tower of Babel was replaced with thousands more ethnically specific. By the time of Acts 2, there are too many towers to count; thousands of ethnic groups, attempting to build bigger towers, to control the “foreigners” around them. And then the Holy Ghost descends, and in one fell swoop, there are no more foreigners. A bunch of tongue-talking, illiterate Galileans turned all the towers of Babel to rubble.
At the Day of Pentecost, the crisis whereby human languages separated the peoples of the earth, keeping them at odds with one another, is suddenly eradicated. Oppression gives way to the birth pangs of unity. “We hear them declaring the wonders of God in our own tongues!” the astonished nations of the world gather to proclaim. Languages that were once unintelligible are rendered intelligible. Confusion gives way to understanding. “What does this mean?”
Every Christian tradition has to answer this question for themselves, of course. There were some in the Jerusalem crowd that simply assumed the disciples had been binging on bloody maries and mimosas, what with all their round-the-clock celebration of Jesus’ supposed resurrection. We tongue-talkers are still considered imbalanced, if not loony.
But for Pentecostals, the answer to the question of the crowds still rings out. “What does this mean?” It means in part that God has visited us to change lives and to change history, to forge new creation from the old. This new creation, wrought by the Holy Spirit, requires not silence, but declaration. This new creation requires wonder and bewilderment. Most of all, this new creation requires new tongues — the only intelligible language in God’s new world. Ralph Waldo Emerson said that language is the archive of history.[viii] God’s new history operates on new words. Tongues are God’s grand finale of holiness; the final sanctification of language itself so that all things might be made new.
T.S. Eliot wrote about his frustration of “Trying to learn to use words, and every attempt is a wholly new start, and a different kind of failure.”[ix] If part of the meaning of the Tower of Babel is that no particular group of people has the corner on the word market, I am certainly not insinuating that Pentecostals have a corner on the tongues market. Such a claim would be transforming tongues to propaganda. I am sure there are abuses and forgeries. Rainer Maria Rilke told a young poet, “Even the best err in words when they are meant to mean most delicate and almost inexpressible things.”[x]
Even so, what I mean to say is that rather than capitulating to word vomit or silence, there is something beautiful about offering the very elements of language as worship unto the God of all language. Our babble somehow levels the towers of Babel all over again. Each Sunday, is this not what we preachers do?
[i] Aaron T. Friesen, Norming the Abnormal: The Development and Function of the Doctrine of Initial Evidence in Classical Pentecostalism (Eugene, OR: Pickwick, 2013), pg. 58.
[ii] Miller, “BeliefWatch: Spirit Filled.” http://www.newsweek.com/beliefwatch-spirit-filled-107031, para. 4.
[iii] Richard Foster, Celebration of Discipline: The Path to Spiritual Growth (New York: Harper Collins, 1988), pg. 101.
[iv] Marcus J. Borg, Speaking Christian: Why Christian Words Have Lost Their Meaning and Power – and How they can be Restored (New York: Harper One, 2011), pg. 2.
[v] Fred Herron, No Abiding Place: Thomas Merton and the Search for God (Lanham, NY: University Press of America, 2005), pg. 55.
[vi] Rabindra N. Kanungo and Manual Mendonca, Ethical Dimensions of Leadership(Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1996), pg. 101.
[vii] Wendell Berry, What Are People For?: Essays (Berkeley, CA: Counterpoint, 2010), pg. 59.
[viii] Ralph Waldo Emerson, The Essays of Ralph Waldo Emerson (Cambridge: Harvard, 1997), pg. 13.
[ix] T.S. Elliot, Four Quartets (Orlando: Harcourt, 1943), pg. 30.
[x] Rainer Maria Rilke, Letters to a Young Poet (New York: W.W. Norton, 1934), pg. 26.
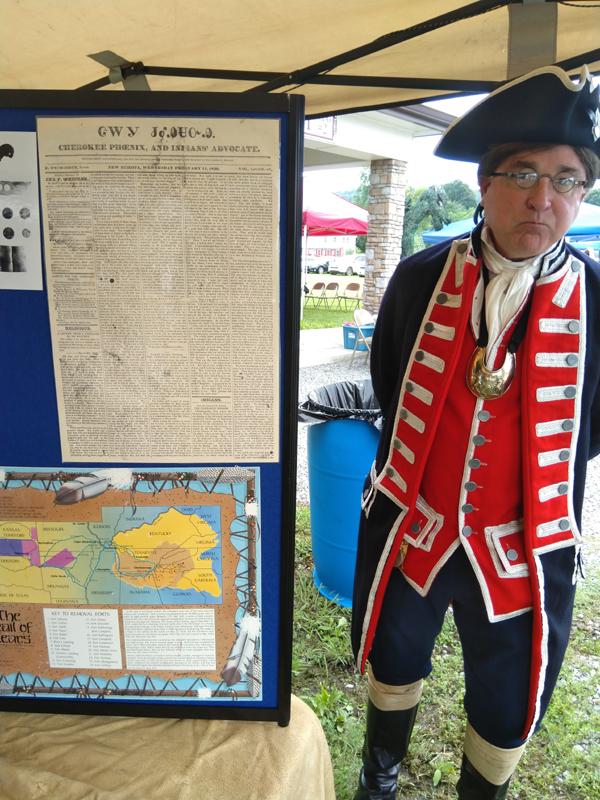
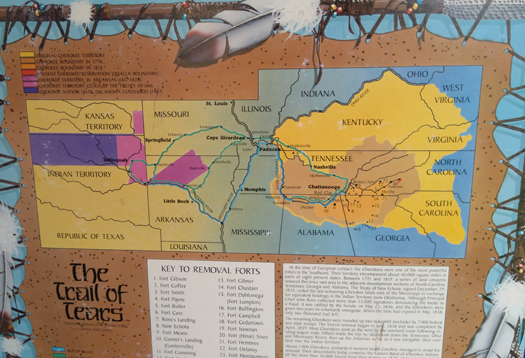
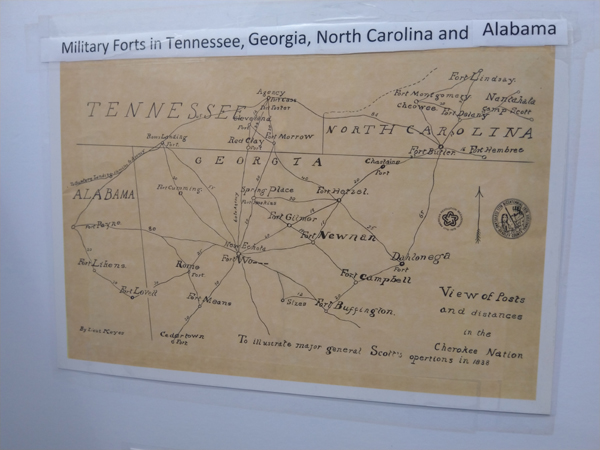
Tellico Plains: Trail of Tears Remembrance Walk
Cup & Cross featured in the Introduction to Anabaptist History
 This book will serve as a tool for the serious student of Anabaptist history, as well as an in-depth introduction for those who are relatively new to the history of the church. It covers the doctrines of Anabaptism
This book will serve as a tool for the serious student of Anabaptist history, as well as an in-depth introduction for those who are relatively new to the history of the church. It covers the doctrines of Anabaptism